
미국의 공장 자동화 및 산업 제어 시장은 2025년 492억 2,000만 달러에 이르고, 2030년에는 807억 1,000만 달러에 이르고, CAGR 10.40%를 보일 것으로 예측됩니다.

이 성장 예측은 노동력 부족을 보완하고, 보다 엄격한 안전규칙을 준수하며, CHIPS법과 인플레이션 저감법을 통해 제공되는 리쇼어링 인센티브를 도입하는 스마트한 생산 라인에 제조업의 축족을 반영하고 있습니다. 반도체 공장, 배터리 공장, 청정 에너지 부품 제조업체가 새로운 설비 투자를 선도하는 반면, 브라운필드는 실시간 최적화를 위해 프로그래머블 로직 컨트롤러(PLC), 머신 비전 시스템, 산업용 IoT 센서의 개수를 꾀하고 있습니다. 하드웨어가 계속 지출의 대부분을 차지하고 있지만, 제조업체가 성과 기반의 계약을 추구하는 가운데, 사이버 보안, 예지 보전, 성능 보증을 번들한 서비스 주도의 계약이 기세를 늘리고 있습니다. 사이버 리스크 증가와 관세 불확실성은 여전히 장애물로 남아 있지만 전반적인 투자 테제는 국내 디지털 대응 생산에 보상하는 주 및 연방 정부의 정책 조정에 의해 강화되고 있습니다.
CHIPS와 과학법은 애리조나, 텍사스, 오하이오의 수십억 달러 규모의 공장이 울트라 클린 로봇, 나노미터 정밀도의 모션 시스템, 입자 오염을 최소화하는 자동 자재관리를 지정함으로써 과거 최대의 국내 반도체 투자 파동을 일으켰습니다. 칩 제조에 할당된 각 10억 달러는 일반적으로 고속 웨이퍼 반송 로봇, 머신러닝 구동 프로세스 제어 및 안전 통합 PLC 플랫폼에 대한 수요를 확대하여 자동화 지출의 2-3억 달러를 끌어올립니다. 국가 수준의 감면 조치는 또한 대규모 프로젝트를 남부와 서부의 산간부로 이동시킵니다. 거기에서는 목적을 가지고 건설된 그린필드 사이트가 첫날부터 완전히 디지털화된 무등화 제조 셀을 채용할 수 있습니다. 공장 주인이 인증주기를 단축하고 기밀을 보호하는 턴키 솔루션을 요구하는 가운데 하드웨어, MES 소프트웨어, 라이프사이클 서비스를 번들하는 공급업체가 경쟁력을 획득하고 있습니다.
제조업의 급여는 현재 75만명분의 부족에 직면하고 있으며, 2030년에는 210만명분의 미충족 직무가 발생하는 위험성이 있기 때문에 경영진은 단조로 반복이 많은 작업을 담당하는 협동 로봇(cobot)을 도입하는 한편, 직원을 품질, 유지관리, 데이터 분석 등의 스킬을 강화시켜 재배치해야하는 압박을 받고 있습니다. 조사에 따르면 57%의 공장이 로봇은 인간의 일을 없애는 것이 아니라 오히려 확장한다고 응답하고 있으며 노동조합이 있는 시설에서도 도입이 진행되고 있습니다. 자동차 조립 제조업체가 선진을 끊고 있지만, 플러그 앤 플레이의 코봇이 저가격화해, 코드 불필요한 프로그래밍 인터페이스를 획득함에 따라, 중소의 작업 현장도 이것에 추종하고 있습니다. 연방 정부 및 주 교육 보조금은 로봇의 운영과 안전에 관한 인증 프로그램의 수업료를 부담하여 노동과 기술의 융합을 가속화하고 이러한 동향을 증폭시키고 있습니다.
일부 산업 혁명에 걸쳐 건설된 공장에서는 독자적인 프로토콜 패치워크가 실행되고 있어 원활한 데이터 흐름을 어렵게 만듭니다. 통합자는 네이티브 이더넷 인터페이스가 없는 Y2K 이전에 설치된 PLC에 종종 직면하여 프로젝트 비용과 위험을 증가시키는 맞춤형 드라이버를 강요합니다. TSN 상의 OPC UA와 같은 오픈 아키텍처의 움직임은 연결성의 표준화를 목표로 하고 있지만, 다운타임의 윈도우가 좁아져 자본 예산이 늘어나고 있어 소프트웨어 벤더의 예측보다 진전이 늦어지고 있습니다. 자동화 업체 및 부품 공급업체가 참여하는 공동 이니셔티브는 사전 인증된 상호 운용성 번들을 출시하기 시작했지만 많은 소규모 기업은 투자 대 효과가 명확해질 때까지 프로젝트를 늦추고 있습니다.
2024년 지출은 하드웨어가 72%를 차지하고 제조업은 생산 라인의 디지털화를 위해 로봇, 드라이브, 센서, HMI를 구입했습니다. 하드웨어의 미국 공장 자동화 및 산업 제어 시장 규모는 한 자리 대 중반의 성장이 예측되는 반면, 서비스는 구독 기반 지원, 원격 상태 모니터링, 성능 보증으로의 전환을 시사하고 보다 빠르게 확장합니다. 주요 공급업체는 소프트웨어 라이선스, 사이버 보안 관리, 인재 교육을 다년간 계약에 번들어 수익을 안정시키고 인센티브를 고객의 생산량에 맞춥니다. 소프트웨어 플랫폼은 현장 데이터를 MES 및 클라우드 분석에 연결하여 스크랩 및 에너지 강도를 줄이는 폐쇄 루프 최적화를 가능하게 합니다. 따라서 하드웨어 계층은 여전히 필수적이지만 가치 획득은 디바이스, 데이터 및 전문 지식을 측정 가능한 결과에 연결하는 통합자 및 OEM으로 전환하고 있습니다.
서비스 부문의 CAGR 12.8%는 제조업체가 선행 투자보다 예측 가능한 영업 지출을 선호한다는 것을 반영합니다. 서비스형 로봇 용접 셀, 서비스형 비전 검사, 서비스형 보안 패키지는 기술의 진부화를 헤지하려고 하는 일류 자동차 제조업체와 소비재 제조업체에 지지되고 있습니다. 원격 운영 센터를 갖춘 벤더는 24시간 365일 지원 및 실시간 통찰력을 제공하여 인력을 늘리지 않고 평균 수리 시간을 단축하고 지속적인 개선 주기를 추진합니다. 이러한 모델은 새로운 마진 풀을 만들어 혼잡한 하드웨어 시장에서 공급자를 차별화합니다.
The United States factory automation and industrial controls market reached USD 49.22 billion in 2025 and is forecast to climb to USD 80.71 billion by 2030, advancing at a 10.40% CAGR.
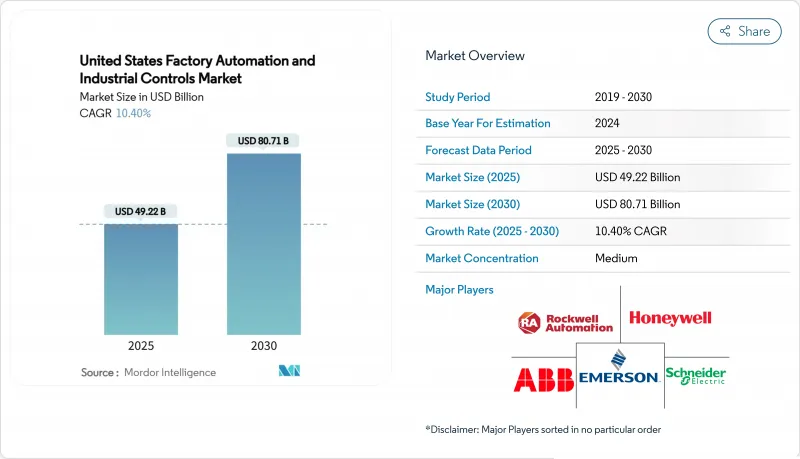
The projected growth reflects a manufacturing pivot toward smart production lines that offset labor shortages, comply with stricter safety rules, and capture reshoring incentives delivered through the CHIPS Act and Inflation Reduction Act. Semiconductor fabs, battery plants, and clean-energy component makers lead new capital expenditure, while brownfield sites race to retrofit programmable logic controllers (PLCs), machine-vision systems, and industrial IoT sensors for real-time optimization. Hardware continues to dominate spending, yet service-led contracts that bundle cybersecurity, predictive maintenance, and performance guarantees are gaining momentum as manufacturers pursue outcome-based agreements. Heightened cyber-risk and tariff uncertainty remain hurdles, but the overall investment thesis is reinforced by state and federal policy alignment that rewards domestic, digitally enabled production.
The CHIPS and Science Act has triggered the largest wave of domestic semiconductor investment on record, with multibillion-dollar fabs in Arizona, Texas, and Ohio specifying ultra-clean robotics, nanometer-precision motion systems, and automated material handling that minimize particle contamination. Every USD 1 billion allocated to chip fabrication typically pulls USD 200-300 million of automation spend, magnifying demand for high-speed wafer transfer robots, machine-learning-driven process control, and safety-integrated PLC platforms. State-level abatements further shift large projects toward the South and Mountain West, where purpose-built greenfield sites can adopt fully digital, lights-out manufacturing cells from day one. Suppliers that bundle hardware, MES software, and lifecycle services gain a competitive edge as fab owners seek turnkey solutions that shorten qualification cycles and protect sensitive.
Manufacturing payrolls face a 750,000-person gap today and risk 2.1 million unfilled roles by 2030, pressing management teams to deploy collaborative robots (cobots) that assume monotonous, high-repetition tasks while up-skilling employees into quality, maintenance, and data-analytics positions. Surveys show 57% of plants report that robots augment rather than eliminate human jobs, reinforcing adoption even in unionized facilities. Automotive assemblers are first movers, but small and midsize job shops follow suit as plug-and-play cobots drop in price and gain no-code programming interfaces. Federal and state training grants amplify the trend by covering tuition for certificate programs in robot operation and safety, accelerating labor-technology convergence.
Plants built across several industrial revolutions run a patchwork of proprietary protocols, making seamless data flow difficult. Integrators often confront PLCs installed before Y2K with no native Ethernet interface, forcing custom drivers that inflate project cost and risk. Open-architecture movements such as OPC UA over TSN aim to standardize connectivity, but progress is slower than software vendors predict because downtime windows remain narrow and capital budgets are stretched. Collaborative initiatives involving automation majors and component suppliers have begun to release pre-certified interoperability bundles, yet many small firms still delay projects until clearer return on investment emerges
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Hardware accounted for 72% spending in 2024 as manufacturers purchased robots, drives, sensors, and HMIs to digitalize production lines. The United States factory automation and industrial controls market size for hardware is projected to post mid-single-digit growth while services expand faster, signaling a transition toward subscription-based support, remote condition monitoring, and performance guarantees. Leading suppliers bundle software licenses, cybersecurity management, and workforce training into multi-year agreements that stabilize revenue and align incentives with customer output. Software platforms bridge field data to MES and cloud analytics, enabling closed-loop optimization that lowers scrap and energy intensity. The hardware layer thus remains indispensable, yet value capture is migrating to integrators and OEMs that orchestrate devices, data, and domain expertise into measurable outcomes.
The services segment's 12.8% CAGR reflects manufacturer preference for predictable operating expenditure over upfront capital outlay. As-a-service robotic welding cells, vision-as-a-service inspection, and security-as-a-service packages resonate with tier-one automotive and consumer packaged goods firms seeking to hedge technology obsolescence. Vendors that co-locate remote operations centers provide 24/7 support and real-time insight, shortening mean time to repair and driving continuous improvement cycles without inflating headcount. Such models unlock new margin pools and differentiate suppliers in a crowded hardware market.
United States Factory Automation and Industrial Controls Market Report is Segmented by Component (Hardware, Software, and More), Type (Industrial Control Systems and Field Devices), and End-User Industry (Oil and Gas, Metals and Mining, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).