
인도의 전동 릭샤 시장의 규모는 2025년에 14억 2,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 14.30%로, 2030년에는 27억 7,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

이 급성장은 정부 인센티브, 국가 수준의 적극적인 정책, 전자상거래 수요 증가, 도시 지역의 대기질 목표 증가를 반영합니다. 여객 운송 회사의 우위성, 납축전지의 강력한 재활용 경제성, 전자상거래 물류의 전기화물에 대한 빠른 전환이 모멘터를 지속하고 있습니다. 배터리의 화학적 성질, 모듈러 파이낸스 모델, 파워트레인의 효율도 병행하여 진보하고 있으며, Tier-I의 도시에서 Tier-II나 Tier-III의 마을까지, 대응 가능한 저변이 확대되고 있습니다. 경쟁업체 간의 적대관계는 레거시 OEM, 혁신적 신흥기업, 세계 자동차 업체들이 다음 성장의 물결을 파악하기 위해 자본과 엔지니어링 능력을 투입함에 따라 치열해지고 있습니다.
FAME-II 프로그램의 연장과 Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme 2024 간의 연방 정부의 연속성으로 인해 1대당 보조금은 그대로 유지되고 주요 도시 이외의 운전자의 구매 비용 장벽이 낮아졌습니다. 마하라슈트라주, 카르나타카주, 델리주에서는 구매 시 리베이트에서 도로세 면제에 이르기까지 주에 의한 추가 조치가 더욱 절약 효과를 높여 전동 릭샤는 판매 시점에서 ICE 모델과 가격 경쟁력을 가지고 있습니다. 보조금의 밀도는 등록대수와 강한 상관관계가 있으며, 주 보조금의 강도가 표준편차로 상승할 때마다 판매대수는 46.16% 상승합니다. 현지 금융기관은 투자 회수 기간의 단축을 보고하면서 보다 광범위한 신용 참여를 촉진하고 있습니다. 이러한 재정 지원책을 결합하여 인도의 전동 릭샤 시장은 비공식적인 환승 수요가 급증하고 있는 비용에 민감한 Tier-II 클러스터로 더욱 밀어 올릴 수 있습니다.
확대하는 인도의 중규모 도시 네트워크는 대중 교통의 퍼스트 마일과 라스트 마일의 틈을 메우기 위해 오토 릭샤에 크게 의존합니다. 전기자동차는 가솔린 차량과 CNG 차량이 1km당 3-4루피인 반면, 1km당 0.50-0.70루피의 운영 비용을 절감할 수 있으므로, 오너 드라이버는 곧 수익을 올릴 수 있습니다. 우버(Uber)와 라피도(Rapido)와 같은 공유 모빌리티 애그리게이터는 지방 정부의 대기 정화 의무와 라이더의 가격 민감도를 충족시키기 위해 E 릭샤를 도입했습니다. 일일 이용률이 높으면 연료비의 재정이 증폭되어 고액의 선행투자에 대한 투자회수가 가속됩니다. 원활한 디지털 예약은 자산 생산성을 높이고 운영자의 경제성을 더욱 강화하며 인도의 전동 릭샤 시장 전체적으로 채용을 뒷받침합니다.
대규모 대출 파이프라인이 없기 때문에 실효 금리가 높고 대출 비율이 낮으며 일일 운임 수입에 생계를 의존하는 독립 운전자의 도입에 물을 공급하고 있습니다. 기술적 위험에 대한 인식에서 많은 금융기관들은 전기자동차를 비표준 자산으로 취급하며, 운영 비용이 낮음에도 불구하고 대출 범위를 좁히고 있습니다. 비정규 대금업자가 이 격차를 메우지만 매우 높은 금리를 요구하기 때문에 총소유비용의 장점이 손상됩니다. 개발 금융 기관은 개인 대출의 위험을 줄이기 위해 혼합 파이낸스 풀을 형성하고 있지만 주요 도시 외에는 아직 도입이 늦어지고 있습니다. 주류은행이 전동 릭샤의 인수를 정상화할 때까지 선행투자하기 쉬운 가격대에 가장 민감한 부문에서는 잠재성장률 이하를 달성할 것으로 예상됩니다.
인도의 전동 릭샤 시장 점유율은 현재 여객 운송차 부문이 독점하고 있으며, 2024년 판매 대수의 83.92%를 차지해 도시 내 공유 모빌리티의 핵심 역할을 확고히 하고 있습니다. 밀집한 도시 루트와 종일 이용에 의해 드라이버는 킬로당 1엔의 에너지 비용을 활용할 수 있기 때문에 부문의 회복력이 강화되고 있습니다. 그러나 온라인 소매가 활성화하고 배기가스가 없는 라스트 원 마일 배송 수요를 뒷받침하고 있기 때문에 물품 운송업체는 CAGR 가장 빠른 29.44%로 성장을 지속하고 있습니다. 아마존 인디아, 플립 카트, 퀵 커머스 기업은 기존 OEM과의 조달 파이프라인을 공식화하여 예측 가능한 수량 성장을 보장합니다. 냉장차와 같은 시장 세분화는 식품 유통 및 의약품에서 대응 가능한 시장을 확대합니다. 적재량 증가와 텔레매틱스의 통합으로 화물용 E 릭샤는 미래의 도시 물류의 청사진에 필수적입니다.
절대적인 수량면에서는 승용형이 계속 인도의 전동 릭샤 시장을 독점할 것이지만, 프리미엄 사양의 조합에 의해 화물용 유닛의 금액 기여는 꾸준히 증가할 것으로 보입니다. 상용차에 대한 세제우대조치와 Tier-II 도시의 마이크로풀필먼트 전용 허브가 화물의 누적 보급률을 높일 것으로 보입니다. 도시의 혼잡 요금이 엄격해짐에 따라, 화물 운송업체는 경형 트럭보다 전동 릭샤를 선호하게 되어, 이 부문의 장기적인 상승 경향이 강해질 것으로 보입니다.
인도의 전동 릭샤의 출력별 시장 점유율은 2024년 총 수요의 54.35%를 차지하는 1-1.5kW 모터 부문이 견인했습니다. 이 출력 대역은 배터리 수명을 절약하면서 정차가 잦은 시가지 주행에 충분한 토크를 제공하며 전형적인 여객 운행에 이상적입니다. 사업자는 저렴한 초기 비용과 실용적인 항속 거리의 균형 잡힌 제안을 평가하고 있으며, 특히 사용 빈도가 높은 도시 지역의 듀티 사이클에서는 그 점을 높이 평가했습니다.
한편 인도의 전동 릭샤 시장에서는 1.5kW 이상의 파워트레인이 가장 급성장하고 있어 적재량과 경사로 대응에 대한 요구가 높아짐에 따라 CAGR 32.12%로 확대되고 있습니다. 이 부문은 통합 모터 컨트롤러 및 IP 표준 인클로저와 같은 e-axle 기술의 진보를 통해 인도의 격렬한 몬순 조건 하에서의 내구성을 높이고 신뢰를 높입니다.
고출력 브래킷은 냉장화물, 가파른 경로, 빠른 소요 시간을 요구하는 프리미엄 라이드 헤일링 레이어를 지원합니다. 부품 공급업체는 자석과 고정자의 국산화를 진행하고 수입품을 줄이고 가격대를 안정화시킵니다. 단위당 경제성이 향상됨에 따라 인도의 1.5kW 이상급 전동 릭샤 시장의 규모는 수익 점유율을 확대하고 비용뿐만 아니라 성능에 초점을 맞춘 새로운 경쟁력층의 도래를 알리는 것으로 예측됩니다.
The Indian electric rickshaw market size is estimated at USD 1.42 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.77 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 14.30% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
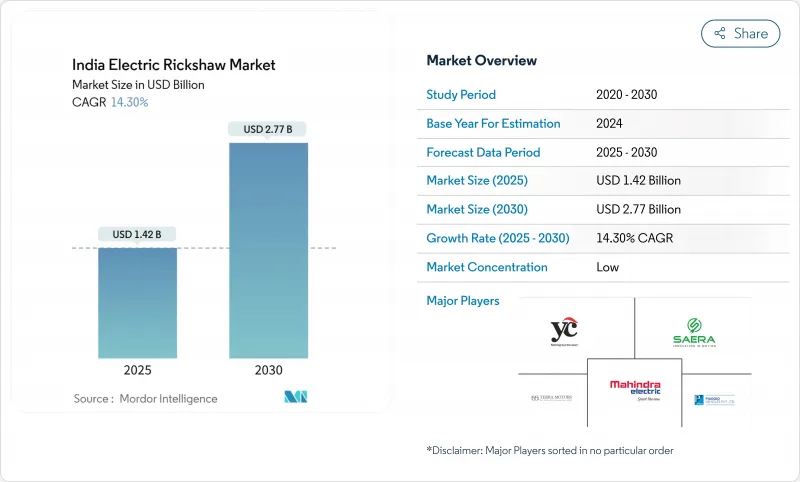
This rapid expansion reflects government incentives, aggressive state-level policies, growing e-commerce demand, and heightened urban air-quality goals. Passenger carrier dominance, strong recycling economics for lead-acid batteries, and the swift pivot of e-commerce logistics toward electric cargo variants are sustaining volume momentum. Parallel advances in battery chemistry, modular finance models, and power-train efficiency are widening the total addressable base beyond Tier-I metros into Tier-II and Tier-III towns. Competitive rivalry intensifies as legacy OEMs, innovative start-ups, and global automakers commit capital and engineering talent to capture the next wave of growth.
Federal continuity between the extended FAME-II program and the Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme 2024 keeps per-vehicle subsidies intact, lowering acquisition cost barriers for drivers outside major metros. State top-ups-ranging from purchase rebates to road-tax waivers in Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Delhi-stack further savings, making electric three-wheelers price-competitive with ICE models at the point of sale. Subsidy density correlates strongly with registrations; assessments reveal a 46.16% sales uplift for each standard-deviation rise in state support intensity. Local financiers report shorter payback periods, encouraging broader credit participation. Combined, these fiscal levers push the Indian electric three-wheeler market deeper into cost-sensitive Tier-II clusters where informal transit demand is surging.
India's expanding network of mid-sized cities relies heavily on auto-rickshaws to bridge first- and last-mile gaps in public transit. Electric variants cut running expenses to INR 0.50-0.70/km against INR 3-4/km for petrol or CNG, creating immediate earnings upside for owner-drivers. Shared-mobility aggregators such as Uber and Rapido are onboarding e-rickshaws to meet municipal clean-air mandates and rider price sensitivity. High daily utilization amplifies fuel-cost arbitrage, accelerating payback on the higher upfront purchase. Seamless digital booking elevates asset productivity, further reinforcing operator economics and boosting adoption across the Indian electric three-wheeler market.
The lack of scale credit pipelines keeps effective interest rates high and loan-to-value ratios low, dampening uptake among independent drivers whose livelihood depends on daily fare receipts. Technology-risk perceptions lead many lenders to treat electric variants as non-standard assets, constricting credit lines despite lower running costs. Informal money-lenders bridge the gap but charge punitive rates, eroding total cost of ownership benefits. Development-finance institutions advocate blended-finance pools to de-risk retail lending, yet implementation remains slow outside major cities. Until mainstream banks normalize underwriting for electric three-wheelers, growth will undershoot potential in segments most sensitive to up-front affordability.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
India electric rickshaw market share is currently dominated by the passenger carrier segment, which accounted for 83.92% of unit sales in 2024, cementing its role as the backbone of intra-city shared mobility. Dense urban routes and all-day utilization let drivers exploit penny-per-kilometer energy costs, reinforcing segment resilience. Goods carriers, however, are registering the fastest 29.44% CAGR as online retail pushes demand for nimble, emissions-free last-mile delivery. Amazon India, Flipkart, and quick-commerce players are formalizing procurement pipelines with established OEMs, ensuring predictable volume growth. Segment-specific designs such as refrigerated bodies widen addressable markets in food distribution and pharmaceuticals. Higher payload ratings and telematics integration make cargo e-rickshaws an essential piece of future city-logistics blueprints.
In absolute volume terms, passenger variants will continue to dominate the Indian electric three-wheeler market, yet the value contribution from cargo units will rise steadily through premium specification mixes. Tax breaks for commercial vehicles and dedicated micro-fulfillment hubs in Tier-II cities will push cumulative cargo penetration higher. As urban congestion charges tighten, freight operators will prefer electric three-wheelers over light trucks, cementing the segment's long-term upside.
India electric rickshaw market share by power output was led by the 1-1.5 kW motor segment, which accounted for 54.35% of total demand in 2024. This power band delivers sufficient torque for frequent stop-start city driving while conserving battery life, making it ideal for typical passenger operations. Operators value its balanced offering-affordable upfront cost with practical range-especially in high-usage urban duty cycles.
In contrast, powertrains rated above 1.5 kW are witnessing the fastest growth in the India electric rickshaw market, expanding at a 32.12% CAGR as payload demands and gradient-handling requirements rise. The segment is benefiting from advancements in e-axle technologies, including integrated motor controllers and IP-rated enclosures, which enhance durability during India's heavy monsoon conditions and boost fleet confidence.
The higher-powered bracket supports refrigerated cargo, steep-gradient hill-stations, and premium ride-hailing tiers that demand faster trip times. Component suppliers are localizing magnets and stators, cutting imported content and stabilizing price points. As unit economics improve, the Indian electric three-wheeler market size for the above-1.5 kW class is projected to widen its revenue share, ushering in a new competitiveness layer focused on performance rather than solely cost.
The India Electric Rickshaw Market Report is Segmented by Vehicle Type (Passenger Carriers and More), Power Output ( Up To 1 KW and More), Battery Type (Lead-Acid and More), Battery Capacity (Up To 3 KWh and More), Charging Mode (Plug-In Charging and More), Ownership Model (Individual Owner-Drivers and More), and States (Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).