
인도 도로 화물 운송 시장 규모는 2026년 1,675억 1,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2025년 1,539억 달러에서 성장할 전망입니다. 2031년 2,559억 2,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2026-2031년 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 8.84%로 확대될 전망입니다.

이 두드러진 성장은 제조업의 강력한 회복, 급성장하는 전자상거래 부문, 고속도로 및 멀티모달 회랑에 대한 공공 부문의 단호한 추진으로 인도가 세계에서 가장 빠르게 성장하는 주요 경제국으로서의 지위를 반영합니다. 146,145킬로미터에 이르는 국도망의 정비, FASTag 요금 징수 시스템 보급, 전용 화물 회랑(Dedicated Freight Corridors)의 조기 도입 등 인프라 확충에 의해 운송 시간이 단축되어 트럭 가동률이 향상되어 운송 능력 부족이 완화되고 있습니다. GST(물품 서비스세), 전자 운송 증명서(e-way bill), 고객측 서비스 레벨 계약(SLA)의 도입으로, 화물주가 컴플라이언스 대응 및 기술 장비가 완비된 제공업체를 선택하게 되어, 조직화된 물류 서비스의 침투가 진행되고 있습니다. 한편 디지털 결제 및 지방도시(Tier 3·4)의 전자상거래 수요에 힘입어 인도의 지방 소비 확대는 배송 경로를 재구축하고 중단거리 운송의 화물량 전망을 강화하고 있습니다.
온라인 소매의 3급 및 4급 도시권에 대한 침투는 인도의 도로 화물 운송 시장에 안정적인 화물량 증가를 가져오고 있습니다. 인도의 전자상거래 부문은 지역 스마트폰 보급률 및 UPI 결제의 급속한 확대에 따라 2025-2030년 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 22%로 추이할 전망입니다. 퀵 커머스 사업자는 10분 배송을 실현하기 위해 지방 도시에 마이크로 풀필먼트 거점을 구축하고 있어, LTL(소구화물)의 집하 및 크로스 도킹 수요를 환기하고 있습니다. Delhivery가 18,700개 이상의 우편번호 지역을 다루는 것은 새로운 시대의 물류망 확산을 보여줍니다. 주경 검사, 축중 제한, 옥트로이 대체 조치의 협상이 가능한 지역 운송업자는 기존에는 비공식 네트워크에 머물렀던 화물 획득의 우위성을 가지고 있습니다. 디지털 결제 기반은 대금 상환의 마찰을 해소해, 소구 화물의 투명성 및 추적 가능한 청구서 발행을 지지하고 있습니다.
2024년에는 고속도로의 1일당 건설 거리가 40km에 달했고, 34,800km의 목표를 내세우는 바라트말라 계획의 기세를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 가티 샤쿠티 계획에 의한 통합적인 계획 책정에 의해 용지 취득의 승인 기간이 수년 단위로부터 수개월 단위로 단축되어, 도로, 철도 및 유틸리티 회랑의 제휴가 진행되고 있습니다. 항구에서 공장으로의 연결 개선으로 아흐메다바드와 뭄바이 간 및 델리와 칸푸르 간 간선 도로에서 트럭의 평균 속도가 이미 15-20% 향상되었습니다. 마스크사가 항만 주변에 50억 달러의 투자를 약속한 것은 회랑의 성능 향상에 대한 다국적 기업의 신뢰를 나타내는 것입니다. 건설 붐 자체가 시멘트, 철강, 기계류의 화물 수요를 창출하고, 기본적인 제조업의 물류를 강화하는 추가적인 화물량을 가져오고 있습니다.
바쁜 기간에 운전자 부족으로 인한 차량의 유휴는 델리와 뭄바이 사이와 방갈로르와 첸나이 사이에서 가동률을 최대 20% 저하시켜 간선 운송 요금 상승 및 리드 타임 장기화를 초래하고 있습니다. 청년 근로자들은 며칠 간의 주간 운송보다 EC 허브에서 예측 가능한 이동 근무를 선호하는 경향이 있으며 장거리 트럭 운송에서 경험이 풍부한 인재 유출을 초래하고 있습니다. 국영 훈련 센터는 고립되어 운영되고 있기 때문에 기술 인정의 불균일이나 안전 기준의 편차가 발생하고 있습니다. 대형 차량 운전자의 임금 상승률은 전년 대비 12-15%로 추정되며, 이 비용 전가가 화주에 대한 운임에 가중되고 있습니다. 안전 기술 지원은 효과적이지만 인적 자본의 제약이 여전히 인도 도로 화물 운송 시장의 운송력 확대의 발판이 되고 있습니다.
국내 제조업이 생산 연동형 장려금 제도와 연계하고 있기 때문에 전자기기, 자동차부품, 의약품의 설비 투자가 유치되어 수출 화물량 증가로 이어지고 있습니다. 2026-2031년 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 10.05%로 추이하는 제조업은 인도의 도로 화물 운송 시장에서 최대 증가량을 차지하고 있습니다. 도매 및 소매업은 소비 주도의 FMCG(일용소비재) 및 내구 소비재의 역류 운송에 지지되어 30.21%로 최대의 점유율을 유지하고 있습니다. 농업, 어업 및 임업은 안정된 기반을 유지하는 한편, 산업 화물 운송 증가에 따라 점유율은 미세 감소 경향에 있습니다.
생산 연동형 보조금(PLI) 대상 공장은 항만 주변과 서부 전용 화물 회랑(WDCC)의 결절점에 집적되어 있으며, 구자라트주-마하라슈트라주-델리 간 운송 밀도를 밀어 올리고 있습니다. 정책의 안정 지속 및 외국 직접투자(FDI)의 지속을 전제로 하면 2031년까지 제조업 화물의 인도 도로 화물 운송 시장 규모는 542억 달러를 넘을 전망입니다. 콜드체인의 격차가 축소되는 가운데, 농업 분야의 점유율은 10%대 전반에서 안정될 전망입니다. 전용 화물 회랑이 철도를 고부가가치 분야로 인도하는 한편, 화주가 도어 투 도어의 유연성을 중시하는 경향은 도로 운송 사업자를 운송 모드의 유출로부터 지키고 있습니다.
국내 운송망은 2025년 시점에서 63.02%의 점유율을 차지했으며, 현재도 우세하지만, 장래의 성장은 국경을 넘은 운송망으로 시프트하고 있으며, 2026-2031년 CAGR 10.23%를 기록할 전망입니다. 단기 성장 요인으로는 인도 방글라데시 회랑의 종이없는 통관과 서행 화물의 멀티 모달 운송 비용 절감을 약속하는 IMEC 파이프라인 계획이 있습니다. 마스크사에 의한 내륙부 중시의 항만 투자는 2030년까지 수출용 컨테이너 취급 능력을 두배로 하는 것을 목표로 하고 있으며, 인도의 도로 화물 운송 시장에서 국제 운송 비율을 높일 전망입니다.
세관 체류 시간은 평균 85시간으로 아시아 주요 허브에 비해 여전히 병목 현상이 되고 있습니다. 디지털 통관 및 블록체인 대응 선하 증권으로 인해 이 수치가 크게 줄어들고 더 많은 수출업체가 트럭 및 철도를 결합한 컨테이너 운송 루프를 선택할 것으로 예측됩니다. 지방 소비가 증가함에 따라 국내 운송 거리는 여전히 증가하지만, 세계 공급망의 재편은 인도가 중국을 대체하는 옵션으로 자리매김하고, 신흥 육해 회랑을 경유한 GCC(만안 협력 이사회) 국가와 유럽으로의 양국간 운송 경로를 촉진합니다.
2025년 시점에서는 광물, 강재 코일 및 포장이 끝난 FMCG를 운송하는 풀 트랙 적재(FTL)가 80.12%의 점유율을 유지했습니다. 그러나 2026-2031년 소구화물(LTL)의 CAGR 9.89%는 인도 도로 화물 운송 시장 전체를 웃도는 성장을 나타내고 있습니다. 나그푸르, 인돌, 하이데라바드에 설치된 허브 앤 스포크 방식의 디포가 신속한 픽업을 지원하여 도시간 페어의 90%에서 배송 시간을 48시간 미만으로 단축합니다. 알고리즘이 혼합 화물을 팔레트화 컨테이너에 할당하면 적재율이 향상되고 킬로당 비용이 절감됩니다.
자산 경량형 제3자물류는 최종 마일리지 배송에 소유자 운영자의 마이크로 플릿을 활용하여 자본 투자를 최소화하면서 서비스 영역을 확대합니다. 화물 플랫폼은 동적 대시보드를 제공하고 슬롯 시간을 보장하여 예측 가능한 서비스에 대한 프리미엄 가격을 제공합니다. 벌크 상품에서의 FTL(풀 트랙 로드)의 중요성은 흔들리지 않지만, 소구화가 진행됨에 따라 그 점유율은 약간 저하될 것으로 예측됩니다.
India road freight transport market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 167.51 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 153.9 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 255.92 billion, growing at 8.84% CAGR over 2026-2031.
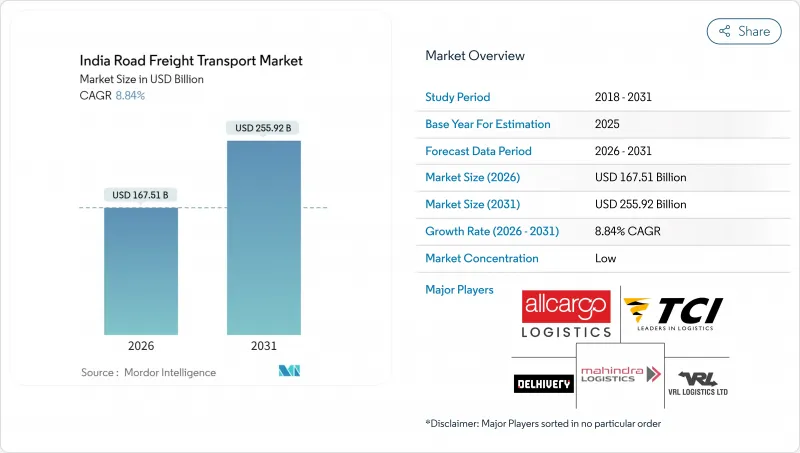
The headline growth mirrors India's position as the world's fastest-growing major economy, with a robust manufacturing revival, a booming e-commerce sector, and a decisive public-sector push on highways and multimodal corridors. Infrastructure additions such as the 146,145 km national highway network, widespread FASTag tolling, and the early roll-out of Dedicated Freight Corridors are shrinking transit times, lifting truck utilization, and easing capacity shortages. Organized logistics penetration is rising as GST, e-way bills, and customer-side service-level agreements push shippers toward compliant, technology-equipped providers. Meanwhile, India's rural consumption story, backed by digital payments and tier-3 and tier-4 e-commerce demand, is redrawing delivery routes and fortifying volume prospects for small and mid-distance hauls.
Penetration of online retail into tier-3 and tier-4 catchments is propelling steady incremental volumes for the India road freight transport market. India's e-commerce sector is tracking a 22% CAGR between 2025-2030 as rural smartphone ownership and UPI payments scale rapidly. Quick-commerce players are building micro-fulfilment hubs in secondary towns to meet ten-minute delivery pledges, raising demand for LTL consolidation and cross-docking. Delhivery now covers 18,700+ pin codes, signaling the breadth of new-age distribution lanes. Regional carriers that can negotiate state-level border checks, axle-load limits, and octroi substitutes are positioned to win loads that once stayed within informal networks. The digital payment backbone removes cash-on-delivery friction and supports transparent, trackable invoicing for small consignments.
Daily highway construction hit 40 km in 2024, underscoring the momentum behind Bharatmala's 34,800 km mandate. Integrated planning under PM Gati Shakti has compressed right-of-way approvals from multiple years to months and is aligning road, rail, and utility corridors. Improved port-to-factory links are already nudging average truck speeds upward by 15-20% on the Ahmedabad-Mumbai and Delhi-Kanpur arteries. Maersk's USD 5 billion port-side investment commitment underlines multinational confidence in corridor performance gains. The construction boom itself churns freight for cement, steel, and machinery, adding volume layers that reinforce basal manufacturing flows.
Peak-season fleet idling due to driver gaps has clipped utilization by up to 20% on Delhi-Mumbai and Bangalore-Chennai sectors, inflating line-haul rates and stretching lead times. Young workers favor predictable shifts in e-commerce hubs over week-long interstate runs, causing an experience drain in long-haul trucking. State-run training centers work in silos, leaving skills certification uneven and safety standards patchy. Wage inflation, estimated at 12-15% year-on-year for heavy-vehicle operators, compounds cost-pass-through into shipper tariffs. Safety-tech aids help, yet human capital constraints remain a drag on capacity expansion in the India road freight transport market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Domestic manufacturing's link to Production Linked Incentive schemes is attracting electronics, auto-component, and pharmaceutical cap-ex, translating to elevated outbound tonnage. With a 10.05% CAGR between 2026-2031, manufacturing contributes the highest incremental volume to the India road freight transport market. Wholesale and Retail Trade remains the single-largest shareholder at 30.21%, powered by consumption-led FMCG and consumer durables backflows. Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry retains a steady base, though its share inches down as industrial freight climbs.
PLI-linked factories are clustering near ports and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor junctions, prompting higher load density on Gujarat-Maharashtra-Delhi stretches. The Indian road freight transport market size for manufacturing consignments is likely to exceed USD 54.2 billion by 2031, assuming stable policy continuity and sustained foreign direct investment. Agriculture's share may steady around the low-teens as cold-chain gaps narrow, all else equal. Shipper preference for door-to-door flexibility continues to shield road carriers from modal leakage, even as Dedicated Freight Corridors bring rail into higher-value brackets.
The domestic lattice dominates today with a 63.02% share in 2025, yet future growth tilts toward cross-border links, which are clocking a 10.23% CAGR between 2026-2031. Near-term catalysts include paperless customs on the India-Bangladesh corridor and IMEC's pipeline, which promises multimodal savings on westbound cargo. Maersk's hinterland-driven port investments aim to double export-bound container capacity by 2030, lifting the international slice of the India road freight transport market.
Customs dwell time, averaging 85 hours, remains a bottleneck compared with leading Asian hubs. Digital customs and blockchain-enabled bills of lading are expected to chop that figure materially, pulling more exporters toward truck-plus-rail containerized loops. Domestic mileage will still swell as rural consumption rises, but global supply-chain realignments position India as a China-plus-one alternative, spurring bilateral lanes into GCC and Europe via emerging land-sea corridors.
Full-Truck-Load kept 80.12% share in 2025, serving minerals, steel coils, and packaged FMCG. Yet LTL's 9.89% CAGR between 2026-2031 outpaces the overall India road freight transport market. Hub-and-spoke depots in Nagpur, Indore, and Hyderabad feed rapid trans-shipment, cutting delivery promises to under 48 hours for 90% of urban pairs. Algorithms allocate mixed orders into palletized pods, lifting fill factors and shrinking per-kilo costs.
Asset-light third-party logistics use owner-operator micro fleets for last-mile links, minimizing cap-ex and accelerating coverage. Freight platforms supply dynamic dashboards that guarantee slot times, unlocking premium pricing for predictable service. FTL will remain irreplaceable for bulk commodities, yet its share ratio is projected to erode marginally as parcelization broadens.
The India Road Freight Transport Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Manufacturing, and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Truckload Specification (FTL and LTL), Distance (Long Haul and Short Haul), Goods Configuration (Fluid Goods and Solid Goods), Temperature Control (Non-Temperature and Temperature Controlled), and by Containerization. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).