
필리핀의 화물 및 물류 시장 규모는 2025년에 152억 6,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 204억 1,000만 달러로 확대될 것으로 예측되며, CAGR(2025-2030년) 5.99%로 성장할 전망입니다.

8조 8,000억 PHP(1,581억 9,000만 달러)의 'Build, Better, More' 프로그램, 외국인 소유권의 자유화, 전자상거래 수요 증가가 이 확대에 박차를 가하고 있습니다. 도로 화물이 네트워크의 핵심임에 변함이 없지만 항만 자동화 및 항공 화물 업그레이드로 모달 의사결정이 재구성되고 있습니다. 외국인 투자자들은 세계 전문 지식과 지역 도달 범위를 결합한 합작 투자를 통해 진입하여 창고 관리, 화물 운송 및 마지막 마일 딜리버리에서 기술 도입을 가속화하고 있습니다. 세계 은행이 7억 5,000만 달러의 대출을 포함한 정부 주도의 디지털 연결 정책은 물리적 인프라를 보완하고 소규모 사업자가 플랫폼 및 비즈니스 모델을 채택할 수 있도록 합니다.
8조 8,000억 PHP(1,581억 9,000만 달러)의 플래그쉽 파이프라인은 11,945km의 도로 프로젝트를 완료하고, 추가로 15,769km를 건설 중이며, 루손 섬의 소요 시간을 최대 50% 단축하고, 바탕가스, 마닐라, 클라크, 수빅을 통일했습니다. 도로, 항만, 철도의 조화로운 업그레이드는 운송 시간 단축, 공급망 스케줄링 엄격화, 트럭 회전 속도 향상을 약속합니다. 투자자들은 선행자 이익을 보장하기 위해 새로운 고속도로 부근의 물류 허브 건설을 급격히 진행하고 있습니다. 계약 물류 공급자는 고속도로 맵을 따라 네트워크 설계를 수행하여 후방 운송의 공차 거리를 줄입니다. 복합 일관 운송 노드가 출현함에 따라 트럭 운송과 내항 해운을 통합하는 사업자는 단일 운송 라이벌보다 비용면에서 우위를 차지하고 있습니다.
마닐라 인터내셔널 컨테이너 터미널(MICT)은 N4 3.4 운영 체제와 150억 PHP(2억 6,964만 달러) 상당의 야드 개수를 실시해, 버스 시간을 35% 단축하고, 마닐라의 2023년의 처리 능력을 506만 TEU로 끌어올렸습니다. 신속한 통관은 하차 비용을 줄이고 화물의 재고 버퍼를 줄입니다. 포워더는 예약 도구에 실시간 항만 데이터를 통합하여 수출업체가 혼잡을 최소화한 항로를 선택할 수 있도록 합니다. 설비의 자동화에 의해 게이트의 개문 시간이 연장되고, 야간의 드레이지 운송을 서포트해, 낮의 교통을 완화하는 것으로, 엄격한 납기를 해내는 라스트 원마일 플리트에도 장점이 있습니다.
1,354억 필리핀 페소(24억 3,000만 달러)의 운수 예산에도 불구하고, 화물 철도는 여전히 매우 적으며, 그 중 2024년 철도 운송에 충당되고 있는 것은 불과 11억 7,000만 필리핀 페소(2,103만 달러)입니다. 중공업은 벌크화물을 트럭으로 옮겨야 하기 때문에 규모의 이점을 잃게 됩니다. 세계은행은 물류 비용은 동지역의 동업 타사보다 20-30% 높다고 지적하고 있습니다. 민간 컨소시엄은 경제 구역과 항구를 연결하는 화물 전용 철도를 평가하고 있지만 토지 취득 장애물은 여전히 높습니다. 도로 철도 컨테이너 실험을 실시하는 사업자는 코리도가 착공하면 선행자 이익을 얻을 수 있습니다.
도매 및 소매업은 2024년 매출액의 30.79%를 차지하였고, CAGR(2025-2030년) 6.59%로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다. 제조업은 반도체 후공정 공장, 퍼스널케어 제조, 예측 가능한 원료 유입에 의존하는 음료 라인의 확대와 관련이 있습니다. 건설업은 인프라 정비를 흡수하여 조골재, 철강, 시멘트 수요를 밀어 올렸습니다. 농업, 어업, 임업은 콜드체인 업그레이드로 유통 기한이 연장되고, 농부의 수익이 향상되며, 성장이 기대됩니다.
소매업체와 공장 모두 실시간 재고 스냅샷과 조정된 보충을 요구하며 물류 파트너는 IoT 센서와 API 게이트웨이를 통합합니다. CREATE MORE 세제 혜택에 근거한 마스크의 완성 센터에 대한 투자는 해상에서 창고까지의 통합 서비스가 다국적 제조업체들에게 지지되는 방법을 보여줍니다. 석유 및 가스, 광업은 특수한 대형 리그와 위험물 컴플라이언스를 필요로 하며, 급성장하고 있는 '기타'의 대역, 헬스케어, 교육, 리버스 로지스틱스는 필리핀의 화물 및 물류 시장 내 고부가가치, 고서비스 틈새에 익숙한 오퍼레이터에게 기회를 창출합니다.
화물 운송은 2024년 총 매출의 63.34%를 차지했으며, 필리핀 화물 및 물류 시장의 핵심 역할을 강조합니다. 트럭 운송, 내항 해운, 항공화물 및 파이프라인은 7,600개가 넘는 섬에 있는 국가 공급망의 연속성을 지원합니다. 택배, 익스프레스 및 소포(CEP) 분야는 소셜 커머스 판매업자나 마켓플레이스 대기업이 전국에 익일 배송을 약속하고 있기 때문에 현재는 축소하고 있는 반면, 2025-2030년 6.89%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 기록할 전망입니다. 창고 및 보관 부문과 화물 운송 부문은 업스트림의 생산 및 강하의 소매를 동기시키는 중요한 링크를 형성하고 있습니다.
CEP 내부의 기세는 경쟁 경계를 되돌리고 있습니다. 순수한 소포 회사는 디지털 지갑을 통합하고 전통적인 3PL은 점유율을 보호하기 위해 크라우드 소싱 라이더 모델을 채택합니다. 창고업체는 로봇을 도입하고 의약품 및 농산물 임차인을 유치하기 위해 다온도 구역을 건설합니다. 포워더는 항만의 자동화나 외자와의 제휴를 활용해, 통관 중개에 키팅이나 리버스 및 로지스틱스 등의 부가가치 서비스를 번들합니다. 이러한 변화를 종합하면 필리핀 화물 및 물류 시장에서 생태계가 사일로화된 실행이 아닌 엔드 투 엔드 오케스트레이션으로 향하고 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
The Philippines freight and logistics market size stands at USD 15.26 billion in 2025 and is projected to advance to USD 20.41 billion by 2030, reflecting a 5.99% CAGR (2025-2030).
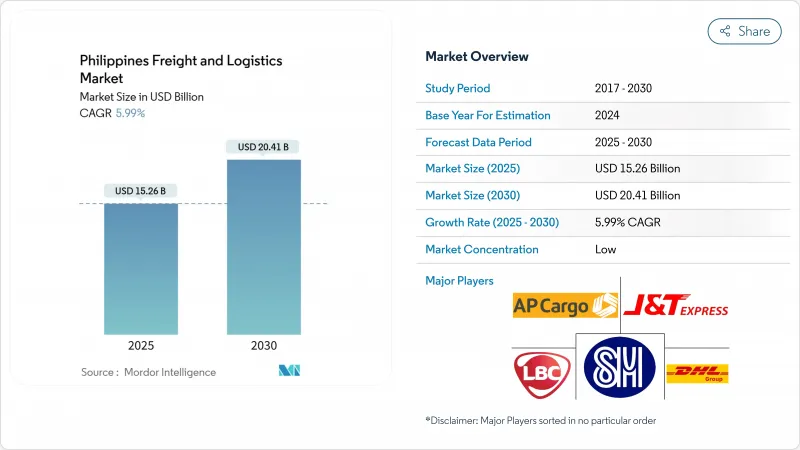
The expansion gains momentum from the PHP 8.8 trillion (USD 158.19 billion) "Build, Better, More" program, liberalized foreign-ownership rules, and increased e-commerce demand. Road freight remains the backbone of the network, yet port automation and air-cargo upgrades are reshaping modal decisions. Foreign investors are entering through joint ventures that pair global expertise with local reach, accelerating technology adoption across warehousing, freight forwarding, and last-mile delivery. Government-led digital connectivity policies, including a USD 750 million World Bank loan, complement physical infrastructure and allow smaller operators to adopt platform business models.
The PHP 8.8 trillion (USD 158.19 billion) flagship pipeline has completed 11,945 km of road projects and is constructing 15,769 km more, slashing Luzon travel times by up to 50% and linking Batangas, Manila, Clark, and Subic into a unified corridor. Harmonized road, port, and rail upgrades promise lower transit times, tighter supply-chain scheduling, and higher truck turns. Investors are fast-tracking distribution hubs near the new expressways to secure first-mover advantages. Contract logistics providers are aligning network designs with the expressway map to cut empty back-haul miles. As multimodal nodes emerge, operators that integrate trucking with coastal shipping gain cost leverage over single-mode rivals.
Manila International Container Terminal (MICT) applied an N4 3.4 operating system and yard upgrades worth PHP 15 billion (USD 269.64 million), slicing berth time by 35% and raising Manila's 2023 throughput to 5.06 million TEUs. Quicker clearances reduce demurrage penalties and lower inventory buffers for shippers. Forwarders embed real-time port data in booking tools, letting exporters choose sailings with minimal congestion. Equipment automation unlocks longer gate hours, which supports night-time drayage and eases daytime traffic, benefiting last-mile fleets working tight delivery windows.
Freight rail remains negligible despite a PHP 135.4 billion (USD 2.43 billion) transport budget, of which only PHP 1.17 billion (USD 21.03 million) targets rail transport in 2024. Heavy industries lose scale benefits when bulk cargo must shift to trucks. Logistics costs run 20-30% higher than regional peers, the World Bank notes. Private consortia are evaluating dedicated cargo spurs between economic zones and ports, but land-acquisition hurdles persist. Operators experimenting with road-rail containers position themselves for first-mover gains once corridors break ground.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Wholesale and retail trade represented 30.79% of 2024 revenue with a projected CAGR (2025-2030) of 6.59%, mirroring the nation's consumption-driven economy. Manufacturing is linked to the expansion of semiconductor back-end plants, personal-care production, and beverage lines that depend on predictable inbound raw-material streams. Construction absorbed the infrastructure push, buoyed demand for bulk aggregates, steel, and cement. Agriculture, fishing, and forestry are expected to grow with cold chain upgrades, facilitating longer shelf life and better farm-gate revenue.
Retailers and factories alike now seek real-time inventory snapshots and coordinated replenishment, prompting logistics partners to embed IoT sensors and API gateways. Maersk's fulfilment-center investments under CREATE MORE tax incentives illustrate how integrated ocean-to-warehouse services resonate with multinational manufacturers. Oil, gas, and mining require specialized heavy-haul rigs and hazardous-cargo compliance, while the fast-growing "others" band, healthcare, education, and reverse logistics, creates opportunities for operators proficient in high-value, high-service niches within the Philippines freight and logistics market.
Freight transport generated 63.34% of the 2024 total revenue, underscoring its role as the backbone of the Philippines freight and logistics market. Trucking, coastal shipping, air cargo, and pipelines underpin national supply-chain continuity across more than 7,600 islands. Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) segment, though a smaller slice today, is clocking a 6.89% CAGR between 2025-2030 as social-commerce sellers and marketplace giants promise next-day delivery nationwide. The warehousing and storage segment and freight forwarding form critical links that synchronize upstream production with downstream retail intake.
Momentum inside CEP is redrawing competitive boundaries: pure-play parcel firms are integrating digital wallets, while traditional 3PLs adopt crowdsourced rider models to protect share. Warehouse operators deploy robotics and construct multi-temperature zones to attract pharmaceutical and agrifood tenants. Forwarders leverage port automation and foreign-capital partnerships to bundle customs brokerage with value-added services such as kitting and reverse logistics. Collectively, these shifts confirm an ecosystem moving toward end-to-end orchestration rather than siloed execution in the Philippines freight and logistics market.
The Philippines Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and More) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).