
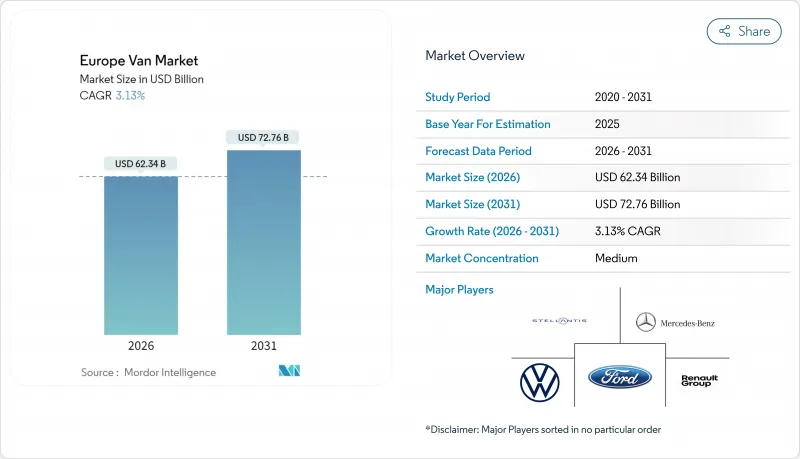
유럽의 밴 시장 규모는 2026년에 623억 4,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2025년 604억 5,000만 달러에서 2031년까지는 727억 6,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 보이며, 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR3.13%로 성장할 전망입니다.

전기차 시장의 성장 동력은 EU 배출가스 기준 강화, 전자상거래 물류 붐, 배터리 가격 급락에서 비롯되지만, 장거리 운송 능력은 여전히 디젤 파워트레인이 주도하고 있습니다. 시장 주도권은 대규모 구매 주문과 자체 충전 인프라 투자를 결합할 수 있는 규모를 갖춘 독일 차량 업체들이 계속 유지하고 있습니다. 동시에 스텔란티스와 메르세데스-벤츠의 플랫폼 전략, 그리고 가격 경쟁력을 앞세운 신규 진입사인 BYD와 SAIC 맥서스가 통합 충전, 소프트웨어, 금융 서비스가 모든 거래의 일부가 되면서 경쟁 구도를 재정의하고 있습니다. 반도체 병목 현상과 차고지 급속 충전 인프라 부족으로 단기 생산량은 제한되지만, 총소유비용(TCO) 균형점 도달과 대체 연료 규제가 맞물리며 유럽의 밴 시장은 전기화 차량으로의 돌이킬 수 없는 전환점을 맞이하고 있습니다.
전기 밴 구매는 정책 준수에서 비용 중심 결정으로 전환하고 있습니다. EU27시장 중 21시장에서 총소유비용이 디젤차를 상회했기 때문입니다. DHL에 의한 포드 E-트랜짓 2,400대 계약은 일괄 발주와 급여 날인 제도가 규모 확대를 가속하는 실례를 보여줍니다. 또한 B면허의 적용 범위가 4.25톤까지 확대됨으로써 라이선싱 제한이 해소되었습니다. 예측에 의하면, 2026년까지 소형 상용 BEV(배터리식 전기자동차)의 가격이 디젤차와 동등해, 장기적인 수요가 고정화될 전망입니다. 플리트 관리자도, 정숙한 주행 성능과 순간의 토크 응답성에 의한 도시에서의 생산성 향상을 평가하고 있어, 충전 네트워크가 미정비인 지역에 있어서도 도입의 기세를 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
급성장하는 전자상거래로 밴 운행 밀도가 높아지고 배송 경로가 단축되면서, 조용하고 무공해인 BEV가 도시 거점에 이상적인 솔루션으로 부상하고 있습니다. 바르셀로나의 마이크로 허브 프로그램은 밴 주행 거리를 30% 단축했으며, 즉각적인 토크와 낮은 소음으로 도시 진입 제한을 받지 않는 소형 BEV를 선호합니다. 다크 스토어와 구독형 배송 모델은 수요를 계절적 피크를 넘어 확산시켜 연중 활용도를 보장합니다. 경로 최적화 소프트웨어는 교통 시스템과 연동되어 배송률을 높이고 에너지 사용을 줄입니다. 이러한 운영상의 이점은 무제한 도시 진입과 결합되어 전기 밴을 서유럽의 전역의 라스트마일 차량군에 선호되는 주력 차량으로 만듭니다.
전기 밴의 초기 구매 가격은 디젤 대비 40-60% 높은 수준이며, 대형 사이트의 경우 차고 충전기로 인해 투자 비용이 100만 유로(약 117만 달러)를 초과할 수 있어 운영 비용은 낮아도 소규모 운송업체의 현금 흐름에 부담을 줍니다. 리스 업체가 잔존 가치 데이터를 확보하지 못해 자금 조달 장벽이 높아지고, 회수 기간이 일반 예산 주기를 초과하여 연장됩니다. 금리 상승은 자본 부담을 가중시키며, 국가별 공공 보조금 차이가 커 계획 수립에 불확실성을 초래합니다. 이러한 비용 장벽으로 지역 운영사 및 중소기업의 도입 속도가 둔화되고 있으며, 이들은 종종 중고 BEV 공급이 개선되거나 초기 비용을 흡수하는 완비형 ‘서비스형 트럭(Truck-as-a-Service)’ 패키지가 등장할 때까지 전기화를 연기합니다.
N1 클래스 I 밴은 2025년 유럽의 밴 시장 점유율의 48.76%를 차지하고 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 3.52%로 확대될 것으로 전망됩니다. 이는 B 면허 적용 범위가 4.25톤까지 확대되어 제로 방출 차량의 운전 면허 요건이 완화된 것을 반영합니다. 컴팩트한 차체는 저배출 구역, 좁은 도매장, 신속한 도로 어깨 배송에 적합하며, 실제 주행 250-300km의 배터리 항속 거리는 근무 중 충전 없이 도시 지역의 전체 업무 사이클을 커버합니다.
클래스 II 및 III 모델은 냉장 식품 운송, 건설 기계 및 지역 배송에 여전히 필수적이지만 포드의 89kWh E-Transit 업데이트 버전과 같은 고밀도 충전기와 400km 주행 가능한 배터리의 출현을 기다리고 있습니다. 플릿 관리자는 kW 시간당 적재 효율(Kg/kWh)을 비교하고 추가 배터리 중량이 생산성을 저하시키지 않도록 주시하고 있습니다. 차세대 인산철 리튬 전지 팩에 의한 경량화 및 저비용화가 진행되는 가운데, 중량급 클래스도 조기 도입의 파를 타는 태세를 정돈해, 경상용 차 부문이 전동화의 교두보로서의 역할을 강화하고 있습니다.
5m³ 초과 밴이 유럽 밴 시장을 주도하며 2025년 점유율 62.78%를 기록할 전망입니다. 이는 높은 적재 공간 활용도로 수익성 킬로미터를 극대화하는 도매 유통업체들이 주도합니다. OEM들은 르노 마스터의 11-22m³ 구성과 같은 모듈식 플랫폼으로 이 핵심 시장을 공략합니다. 해당 플랫폼은 높은 지붕, 다양한 휠기반, 2톤 적재량 상한을 결합합니다.
그러나 5m³ 이하 모델은 4.67%의 연평균 성장률(CAGR)로 증가 중입니다. 골목길 기동성, 편리한 주차, 가격 부담을 줄이는 낮은 배터리 용량을 중시하는 식료품 퀵커머스 및 약국 배송 업체들이 이를 뒷받침합니다. 소형 BEV는 50kWh 미만 배터리 팩이 구매 비용과 충전 시간을 단축시켜 총소유비용(TCO) 손익분기점에 더 빨리 도달합니다. 이러한 양극화는 OEM들에게 두 가지 로드맵을 추진하게 합니다 : 팔레트화 화물에 최적화된 고적재량 변종과, 유휴 시간 및 진입료로 인해 디젤 경제성이 약화되는 고밀도 도시 순환로를 위해 설계된 소형 소프트웨어 기반 마이크로밴입니다.
The European van market market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 62.34 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 60.45 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 72.76 billion, growing at 3.13% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Momentum stems from tightening EU emission limits, the boom in e-commerce logistics, and fast-falling battery prices, while diesel powertrains still underpin long-haul capacity. Market leadership continues to rest with German fleets that have the scale to combine large procurement orders and in-house charging investments. At the same time, platform strategies from Stellantis and Mercedes-Benz, along with price-focused entrants BYD and SAIC Maxus, are redefining competitive dynamics as integrated charging, software, and financing services become part of every deal. Although semiconductor bottlenecks and depot fast-charging gaps curb near-term output, the convergence of total cost of ownership (TCO) parity and alternative-fuels rules indicates the European van market is approaching an irreversible switch toward electrified fleets.
Electric-van purchases are moving from policy compliance to cost-driven decisions as the total cost of ownership now beats diesel in 21 of 27 EU markets. DHL's 2,400-unit Ford E-Transit deal shows how bulk orders and salary-sacrifice programs accelerate scale, while B-permit extensions up to 4.25 t erase licensing limits. Projections indicate price parity for light commercial BEVs by 2026, locking in long-term demand. Fleet managers also value silent operation and instant torque that improve urban productivity, reinforcing momentum even where charging networks remain incomplete.
Rapid e-commerce growth drives higher van density and shorter delivery routes, making quiet, zero-emission BEVs ideal for city nodes. Barcelona's micro-hub program trimmed van miles 30%, favoring compact BEVs with instant torque and low noise that face no urban access bans . Dark stores and subscription delivery models spread demand beyond seasonal peaks, ensuring year-round utilization. Route-optimization software integrates with traffic systems, boosting drop rates while lowering energy use. These operational gains combine with unrestricted urban access to make electric vans the preferred workhorse for last-mile fleets across Western Europe.
Up-front prices for electric vans remain 40-60% above diesel, while depot chargers can push investment above EUR 1 million (~USD 1.17 million) for large sites, straining the cash flow of small haulers despite lower running costs . Financing hurdles grow as leasing firms lack residual-value data, lengthening payback periods beyond typical budget cycles. Rising interest rates add to capital pressure, and public subsidies vary widely by country, creating planning uncertainty. These cost barriers slow adoption among regional operators and SMEs, who often defer electrification until second-hand BEV supply improves or turnkey Truck-as-a-Service packages absorb initial outlays.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
N1 Class I vans claimed 48.76% of the European van market share in 2025 and will expand at a 3.52% CAGR through 2031, reflecting how B-permit extensions up to 4.25 t remove driver-license barriers for zero-emission vehicles. Their compact footprints suit low-emission zones, narrow loading bays, and quick curbside drop-offs, while real-world battery ranges of 250-300 km now cover full urban duty cycles without mid-shift charging.
Class II and III models remain indispensable for refrigerated food, construction tools, and regional parcel runs but await denser chargers and 400 km batteries such as Ford's 89 kWh E-Transit update. Fleet managers compare kilograms delivered per kilowatt-hour payload efficiency to ensure that added battery mass never dilutes productivity. As next-generation lithium-iron-phosphate packs cut weight and cost, heavier classes are positioned to join the early adoption curve, reinforcing the light-duty segment's role as an electrification beachhead.
Vans above 5 m3 dominated the European van market, with 62.78% of the share in 2025, powered by wholesale distributors that maximize revenue kilometers via higher cube utilization. OEMs serve this core with modular platforms such as the Renault Master's 11-22 m3 configurations, which blend tall roofs, multiple wheelbases, and two-tonne payload ceilings.
Yet, less than/equal to 5 m3 models are rising at a 4.67% CAGR, underpinned by grocery quick-commerce and pharmacy delivery firms that prize alley maneuverability, easy parking, and lower battery capacities that keep sticker prices in check. Compact BEVs reach total cost-of-ownership breakeven faster because sub-50 kWh packs trim purchase costs and charge times. The bifurcation pushes OEMs toward dual roadmaps: high-cube variants optimized for palletized freight and smaller, software-enabled micro-vans engineered for dense urban loops where idle time and access fees erode diesel economics.
The Europe Van Market Report is Segmented by Gross Vehicle Weight (N1 Class I, N1 Class II, and N1 Class III), Cargo Space (Less Than/Equals 5 M3 and Above 5 M3), End User (Commercial Fleets, Government and Municipal, and More), Drive Type (IC Engine - Petrol, IC Engine - Diesel, and More), Sales Channel (Direct OEM Fleet Sales, and More), and Country. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).