
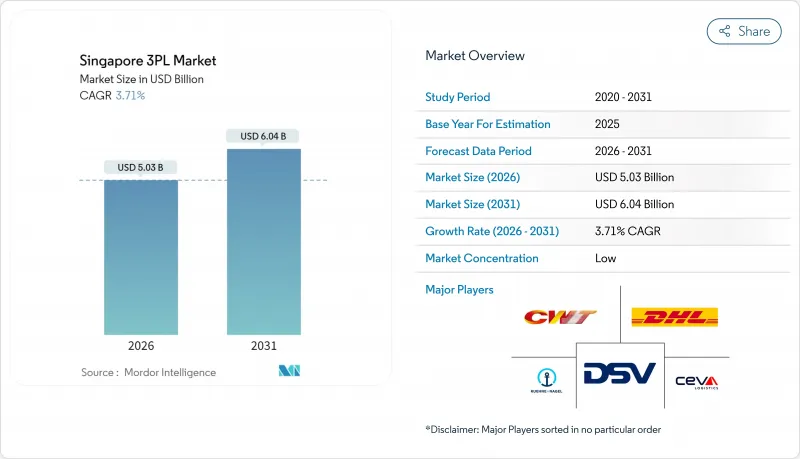
싱가포르의 제3자 물류(3PL) 시장은 2025년 48억 5,000만 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 50억 3,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 60억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
예측기간(2026-2031년)의 CAGR은 3.71%로 전망되고 있습니다.

이 꾸준한 확장은 싱가포르가 자랑하는 타의 추종을 불허하는 멀티모달 연결성, 65개의 자유무역협정 네트워크, 그리고 인프라 메가 프로젝트의 파이프라인에 기인하고 있으며, 이들 전체가 결합되어 동 도시 국가의 동남아시아 주요 중계 및 유통 허브로서의 역할을 강화하고 있습니다. 급속한 전자상거래의 보급은 생명과학 생산에서 발생하는 콜드체인 수요를 가속화하고 창고 자동화의 도입 확대는 아웃소싱 물류의 대상 기반을 확대하고 있습니다. 한편, 하이브리드 자산 모델은 서비스 혁신에 대한 진입 장벽을 낮추고 있습니다. 한편, 토지 및 인건비의 급등, 심각한 항만 혼잡, 새로운 탄소 배출 보고 의무 등 구조적인 비용 압력이 증대하고 있으며, 이들은 규모, 자동화 및 강력한 규제 대응 능력을 가지는 사업자에게 유리하게 작용합니다. 세계적인 물류 대기업에 의한 전략적 인수는 아시아태평양의 엔드 투 엔드 공급망 구축에서 싱가포르 우량 거점의 소유가 필수적이 되고 있음을 보여줍니다.
동남아시아 온라인 소매의 급성장은 융통성 속도, 역물류 서비스 및 라스트마일 배송 효율에 대한 수요 구조를 변화시키고 있습니다. 싱가포르는 소매업체의 재고 집중으로 6억 8,000만 명의 지역 소비자에게 2-3일 내 배송을 실현하기 위한 방대한 취급량을 차지하고 있습니다. 물류 사업자는 소포 분류 라인의 확장과 통관 API의 통합을 진행해, SKU의 복잡화나 반품 플로에 대한 대응을 강화하고 있습니다. 싱가포르 우편공사는 2,220만 달러를 투자한 설비 갱신으로 지역 전자상거래 물류허브의 처리능력을 하루 40만개로 4배 확대했습니다. 이는 대응책의 자본 집약성을 여실히 보여줍니다. 소셜 커머스 판매자와 대형 상품 카테고리는 타사 전문업체의 수익 기반을 더욱 확대하고 있습니다. 한편, ASEAN 영역 내의 규제 조화가 진행됨으로써 크로스보더 마찰이 감소하고, 싱가포르 경유 게이트웨이로 처리되는 화물량이 증가하고 있습니다.
총 공사비 200억 달러 규모의 투아스 메가포트는 2040년까지 연간 6,500만 TEU의 처리 능력으로 완공을 예상하고 있으며, 완전 자동화 안벽 크레인, 무인 운전 차량, AI에 의한 버스 스케줄링을 도입할 예정입니다. 이를 통해 선박의 턴어라운드 시간을 단축해 물류 이용자의 운영 코스트 절감을 실현합니다. 창이 공항의 화물 인프라 확충(제2 항공화물 물류파크 포함)과 병행하여 연간 취급 능력은 300만 톤에서 540만 톤으로 확대될 전망입니다. 또한 자유무역지구 모델을 도입하여 적재 사이클의 신속화를 도모합니다. 이러한 장기 프로젝트는 지정학적 혼란으로 인한 공급망 우회 수요와 함께 인근 게이트웨이가 토지 및 고도 제약에 직면하는 가운데 싱가포르로 우회화물을 유도하는 선구적 이점을 제공합니다.
토지 부족을 배경으로 2025년에는 공업용 임대료가 월 평방미터당 11.8-31.1달러까지 상승했습니다. 한편 명목임금은 GDP 성장이 둔화되는 가운데 5.2% 상승하고 있습니다. 경비원은 현재 단계적 임금 모델(Progressive Wage Model)에 근거하여 월 최소 1,961달러를 벌고 있으며, 임시직 경제를 구성하는 택배 배달원에 대한 강제적인 연금 기여는 급여 총액의 17-20%에 해당하는 부담을 추가하고 있습니다. 이러한 구조적 비용 상승 요인은 노동 집약적인 창고 업무와 라스트마일 배송 차량에 의존하는 사업자의 이익률을 압박하여 자동화의 급속한 도입과 비필수 업무의 선택적인 오프쇼어링을 촉진하고 있습니다.
2025년 시점에서 국내 운송 관리는 싱가포르의 제3자 물류(3PL) 시장에서 32.65%를 차지하였습니다. 이는 멀티모달 운송망에 의해 지원되는 인구 밀집도로 인해 라스트마일 경로 조정이 복잡하다는 것을 반영합니다. 소매업체가 더 엄격한 배송 시간과 실시간 시각화를 요구하는 가운데, 이 부문은 지속적인 성장을 계속하고 있습니다. 부가가치형 창고 및 유통 서비스는 수익 기반은 작지만, 사업자가 키트 조립, 라벨 부착 및 반품 관리를 외부로 위탁해 운전 자금을 절감하는 움직임으로 인해, 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 7.02%를 나타낼 것으로 전망됩니다. 높은 수익성과 계약의 연속성이 신규 참가자를 끌어들이고 있지만, 메자닌 자동화에 필요한 설비 투자가 기존 사업자의 우위성을 유지하고 있습니다.
엣지 컴퓨팅 센서와 AI 탑재 선반 분할 소프트웨어는 피킹에서 출하까지의 사이클을 20% 단축시켜 고객의 기대를 높이고 있습니다. 이를 통해 운송, 창고 보관 및 통관을 단일 SLA로 통합하는 오케스트레이션 플랫폼에 대한 수요가 확대되고 있습니다. 또한, 싱가포르와 말레이시아, 태국을 연결하는 크로스보더 트럭 운송 경로가 추가되어 국제 운송 관리 제공업체에게 유리한 경로 밀도가 향상되었습니다. 하이브리드 전기 트럭의 보급이 진행되고 있는 가운데, 저장소 네트워크 내에 배터리 교환 거점을 통합하는 기업은 추가적인 고객 점유율을 획득하여 싱가포르의 제3자 물류(3PL) 시장에서 순수한 운송에서 통합형 물류 솔루션으로의 구조적 전환을 강화하고 있습니다.
The Singapore 3PL Market was valued at USD 4.85 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 5.03 billion in 2026 to reach USD 6.04 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 3.71% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
The steady expansion stems from Singapore's unrivaled multimodal connectivity, its network of 65 free-trade agreements, and a pipeline of infrastructure megaprojects that collectively deepen the city-state's role as Southeast Asia's principal transshipment and distribution hub. Rapid e-commerce penetration accelerated cold-chain demand from life-sciences production, and rising adoption of warehouse automation increases the addressable base for outsourced logistics, while hybrid asset models lower entry barriers for service innovation. At the same time, escalating land and labor costs, acute port congestion, and new carbon-reporting mandates add structural cost pressure that rewards operators with scale, automation, and strong regulatory compliance capabilities. Strategic acquisitions by global logistics majors highlight how ownership of premium Singapore footprints is becoming essential for end-to-end Asia-Pacific supply-chain orchestration.
Southeast Asia's online retail boom is transforming demand profiles for fulfillment speed, reverse-logistics services, and last-mile routing efficiency. Singapore captures outsized volumes because merchants consolidate inventory in the republic to reach 680 million regional consumers in two-to-three-day delivery windows. Logistics providers are scaling parcel-sortation lines and integrating customs-clearance APIs to handle higher SKU complexity and return flows. Singapore Post quadrupled processing capacity to 400,000 parcels daily at its Regional eCommerce Logistics Hub after a USD 22.2 million upgrade, illustrating the capital intensity of this response. Social-commerce sellers and bulky-item categories further broaden the revenue pool for third-party specialists, while regulatory harmonization across ASEAN lowers cross-border friction and boosts volumes handled through Singapore gateways.
The USD 20 billion Tuas Mega-Port, slated for full completion by 2040 with 65 million TEU annual capacity, introduces fully automated quay cranes, driverless vehicles, and AI-driven berth scheduling that together compress vessel turnaround times and trim operating costs for logistics users. Parallel expansion of Changi Airport's cargo infrastructure, including a second air-freight logistics park, will lift capacity from 3 million to 5.4 million tons yearly and embed a free-trade zone model that accelerates transshipment cycle times. These long-horizon projects dovetail with supply-chain rerouting caused by geopolitical disruptions, giving Singapore a first-mover advantage in capturing diverted traffic as neighboring gateways confront land and depth constraints.
Industrial rents climbed to USD 11.8-31.1 per m2 monthly in 2025 amid land scarcity, while nominal wages advanced 5.2% even as GDP growth lagged. Security officers now earn at least USD 1,961 per month under the Progressive Wage Model, and compulsory pension contributions for gig couriers add a 17-20% payroll burden. These structural cost inflators compress margins for providers relying on labor-intensive warehousing and last-mile fleets, prompting accelerated automation rollouts and selective offshoring of non-core activities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Domestic Transportation Management accounted for 32.65% of the Singapore third-party logistics market in 2025, reflecting the complexity of orchestrating final-mile routes across a densely populated island supported by multimodal links. The segment continues to grow steadily as retailers push tighter cut-off times and real-time visibility expectations. Value-Added Warehousing & Distribution, while representing a smaller revenue base, is forecast to deliver a 7.02% CAGR through 2031 as merchants outsource kitting, labeling, and returns management to trim working capital. Higher margin profiles and sticky contracts attract new entrants, but the capital spend required for mezzanine-floor automation preserves an edge for incumbents.
Edge-computing sensors and AI-powered slot-assignment software have cut pick-to-ship cycles by 20%, heightening customer expectations and boosting demand for orchestration platforms that bundle transport, warehousing, and customs clearance into a single SLA. Cross-border trucking lanes linking Singapore to Malaysia and Thailand add route density that benefits international transportation management providers. As hybrid electric trucks gain mileage, firms integrating battery-swap nodes within their depot networks stand to capture incremental wallet share, reinforcing the structural shift from pure haulage toward integrated logistics solutions within the Singapore third-party logistics market.
The Singapore Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market Report is Segmented by Service (Domestic Transportation Management, International Transportation Management, and More), by End User (Automotive, Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing, Life Sciences & Healthcare, Technology & Electronics, E-Commerce, and More), and by Logistics Model (Asset-Light, Asset-Heavy, Hybrid). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).