
말레이시아의 사이버 보안 시장은 2025년 61억 5,000만 달러에서 2026년에는 65억 9,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 보입니다. 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 7.16%로 성장을 지속하여, 2031년까지 93억 2,000만 달러에 이를 전망입니다.

이 낮은 두 자릿수 성장률은 말레이시아의 사이버 보안 시장을 해당국 광범위한 ICT 생태계 내에서도 빠르게 성장하는 디지털 인프라 부문 중 하나로 자리매김하게 합니다. 클라우드 우선 정책, 2024년 사이버 보안법에 따른 엄격한 라이선싱, 데이터 유출 사고의 금전적 비용 등이 각각 지속적인 수요를 주도하고 있습니다. 대기업들은 기존 통제 체계를 제로 트러스트 프로그램으로 확대하고 있으며, 중소기업들은 초기 비용을 낮추는 구독 서비스를 통해 처음으로 보안 솔루션을 도입하기 시작했습니다. 5G 엣지 네트워크, 하이퍼스케일 데이터 센터, 운영 기술 현대화에 대한 병행 투자는 말레이시아의 사이버 보안 시장의 장기적 성장 가능성을 더욱 공고히 하고 있습니다.
말레이시아의 가속화된 클라우드 우선 전략은 정부 지출을 클라우드 액세스 보안 브로커(CASB) 및 워크로드 보호 플랫폼과 같은 클라우드 네이티브 방위 체계로 전환시키고 있습니다. 각 부처는 이제 모든 애플리케이션 마이그레이션 계획에 분류, 암호화, 지속적 모니터링을 통합하여 자문 및 관리 서비스에 대한 기본 수요를 높이고 있습니다. 공공 부문의 초기 성공 사례에 대한 가시성은 금융 기관과 통신 사업자들이 유사한 아키텍처를 채택하도록 장려하여 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장 전반에 걸쳐 증폭 효과를 창출하고 있습니다. 시스템 통합업체들은 공유 책임 모델을 중심으로 포트폴리오를 재설계하여 컨설팅, 배포, 관리형 탐지 서비스를 단일 계약으로 묶어 제공하고 있습니다. 이러한 변화들은 종합적으로 일회성 급증이 아닌 구조적인 지출 증가로 이어지고 있습니다.
2024년 사이버 보안법은 침투 테스트, 보안 운영 및 기타 핵심 서비스에 대한 의무적 라이선싱을 시행하며, 핵심 인프라 운영자는 분야별 실무 규정을 준수해야 합니다. 기업들은 이 법에 대응하여 준수를 이사회 차원의 최우선 과제로 격상시키고, 새로운 법적 기준에 맞춰 통제 체계를 조정하기 위해 외부 감사인을 고용하고 있습니다. 조기 라이선스를 확보한 공급업체들은 기업들이 규제 위반을 피하기 위해 사전 자격을 갖춘 파트너를 선호함에 따라 가시적인 판매 우위를 점했습니다. 이 법안은 또한 사고 보고 시한을 공식화하여 실시간 탐지 도구 및 위협 인텔리전스 통합 수요를 촉진했습니다. 이러한 변화들은 반복적인 규정 준수 의무를 IT 예산에 반영시켜 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장 규모에 지속적인 성장 동력을 제공하고 있습니다.
경험 많은 설계자 부족으로 복잡한 클라우드 마이그레이션이 지연되며 프로젝트 기간이 37% 연장되고 인건비가 25% 이상 증가합니다. 이 부족 현상은 대규모 전환 계약 입찰가를 부풀려 기업 예산을 압박하고 주요 마일스톤을 지연시킵니다. 기업들은 MSSP에 아키텍처를 아웃소싱하거나 지역 허브에서 전문성을 도입해 대응하지만, 비자 발급 지연으로 단기적 해결은 제한적입니다. 공급업체 로드맵에는 설계 시간을 단축하는 로우코드 정책 엔진과 참조 아키텍처가 포함되지만, 규제 대상 워크로드에 대한 실무 감독은 여전히 필수적입니다. 따라서 인재 부족은 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장 연평균 성장률(CAGR)에 지속적인 억제요인으로 작용합니다.
솔루션은 2025년 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장에서 52.20% 점유율을 유지했으며, 하이브리드 환경을 보호하는 네트워크 및 클라우드 보안 제품군이 주도했습니다. 그러나 기업들이 상시 가동되는 전문성을 추구함에 따라 서비스 부문이 2031년까지 연평균 7.42% 성장률로 솔루션을 추월할 것으로 전망됩니다. 높은 탐지 정확도, 24시간 모니터링, 내장형 규정 준수 대시보드는 MSSP(관리형 보안 서비스 제공업체)를 전술적 공급업체가 아닌 전략적 파트너로 포지셔닝합니다. 월간 활성 자산 기반 가격 모델은 중견 기업의 진입 장벽을 낮춥니다. 현지 공급업체들은 규제에 대한 친숙함을 활용해 사이버 보안법과 연계된 계약을 확보하는 반면, 세계의 공급업체들은 포인트 도구 전반에 걸친 경보를 통합하는 오케스트레이션 플랫폼을 패키지화합니다. 자문, 배포, MDR 서비스의 융합은 기술 재판매를 넘어선 가치 제안을 제공하며, 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장에서 서비스 주도 성장을 공고히 합니다.
그럼에도 엄격한 데이터 거주 규정을 가진 조직에게는 솔루션 포트폴리오가 여전히 중요합니다. BFSI(금융 서비스) 및 유틸리티 분야의 어플라이언스 교체 주기는 방화벽, 침입 방지, 보안 이메일 게이트웨이의 수익을 유지합니다. 차세대 SIEM 플랫폼은 행동 분석 및 자동화를 통합해 인재 부족을 상쇄하며, 제품 혁신을 국가적 기술 개발 목표와 연계합니다. 공급업체들은 영구 라이선스와 클라우드 기반 분석을 번들로 제공해 온프레미스 제어와 SaaS 가시성을 연결합니다. 현지 통합업체와의 공동 제공은 가치 실현 시간을 단축하며, 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장의 협력적 특성을 반영합니다.
2025년 말레이시아의 사이버 보안 시장 규모에서 온프레미스 시스템이 52.85%를 차지했는데, 이는 은행 및 공공 서비스 분야에서 레거시 워크로드와 데이터 주권 규정이 여전히 지배적이기 때문입니다. 해당 분야의 하드웨어 교체는 어플라이언스 공급업체에게 안정적인 기반을 제공합니다. 그러나 클라우드 배포는 2031년까지 연평균 8.05% 성장률로 확장되며 온프레미스 업그레이드를 추월할 전망입니다. 사용량 기반 가격 정책, 지속적인 기능 출시, AI 기반 분석은 디지털 우선 전략을 추구하는 기관에 클라우드 제어 기능을 매력적으로 만든다. 공유 책임 프레임워크는 기업이 유지보수를 전문 공급업체에 위탁하도록 유도하여 말레이시아 사이버 보안 시장의 장기적 채택을 지원합니다.
공급업체 로드맵에는 규제 대상 고객을 안심시키기 위한 말레이시아 내 데이터 현지화 노드가 포함됩니다. 시간이 지남에 따라 주권 클라우드 플랫폼의 개선으로 잔여 저항이 약화될 수 있으나, 산업 제어 네트워크와 연계된 하드웨어 교체는 온프레미스 장비에 대한 지속적인 시장을 보장합니다.
The Malaysia cybersecurity market is expected to grow from USD 6.15 billion in 2025 to USD 6.59 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 9.32 billion by 2031 at 7.16% CAGR over 2026-2031.
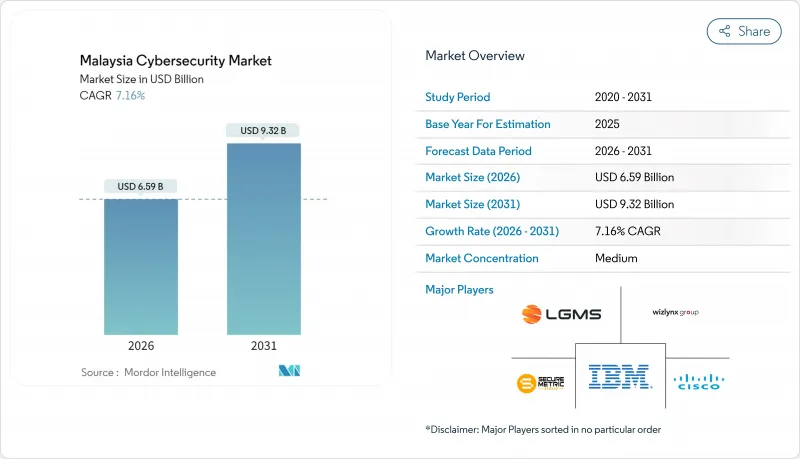
This low-double-digit trajectory positions the Malaysia cybersecurity market among the faster-growing digital-infrastructure segments within the country's wider ICT ecosystem. Cloud-first mandates, strict licensing under the Cyber Security Act 2024, and the monetized cost of data breaches are each propelling sustained demand. Large enterprises are broadening existing controls into zero-trust programs, while small and medium enterprises are starting first-time deployments through subscription services that lower upfront costs. Parallel investments in 5G edge networks, hyperscale data centers, and operational-technology modernization further anchor a long runway for the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
Malaysia's accelerated cloud-first strategy is redirecting government spending toward cloud-native defenses such as cloud access security brokers and workload-protection platforms. Ministries now integrate classification, encryption, and continuous monitoring into every application-migration plan, lifting baseline demand for advisory and managed services. Public-sector visibility into early success stories is encouraging financial institutions and telecom carriers to adopt similar architectures, creating a multiplier effect across the Malaysia cybersecurity market. System integrators have redesigned portfolios around shared-responsibility models, bundling consulting, deployment, and managed detection under single contracts. Collectively, these changes translate to a structural uplift in addressable spending rather than a one-time spike.
The Cyber Security Act 2024 enforces mandatory licensing for penetration testing, security-operations, and other core services, while critical-infrastructure operators must observe sector-specific codes of practice. Organizations have responded by elevating compliance to board-level priority and retaining external auditors to align controls with the new legal baseline. Providers that secured early licences gained a measurable sales advantage because enterprises prefer pre-qualified partners to avoid regulatory missteps. The act also formalized incident-reporting timelines, spurring demand for real-time detection tools and threat-intelligence integrations. Together, these shifts embed recurring compliance obligations into IT budgets, sustaining momentum in the Malaysia cybersecurity market size.
Complex cloud migrations stall because experienced architects remain scarce, extending project timelines by 37% and boosting labor costs by more than one-quarter . The scarcity inflates bids for large transformation contracts, squeezing corporate budgets and delaying key milestones. Organizations counter by outsourcing architecture to MSSPs or importing expertise from regional hubs, but long visa lead times cap near-term relief. Vendor roadmaps now include low-code policy engines and reference architectures that cut design hours, yet hands-on oversight remains indispensable for regulated workloads. Talent constraints therefore act as a persistent drag on the Malaysia cybersecurity market CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Solutions maintained 52.20% share of the Malaysia cybersecurity market in 2025, led by network and cloud-security suites that protect hybrid environments. However, services are forecast to outpace solutions at a 7.42% CAGR through 2031 as enterprises look for always-on expertise. Higher detection accuracy, round-the-clock monitoring, and built-in compliance dashboards position MSSPs as strategic partners rather than tactical suppliers. Pricing models based on monthly active assets lower entry barriers for mid-tier firms. Local providers leverage regulatory familiarity to capture contracts tied to the Cyber Security Act, while global vendors package orchestration platforms that unify alerts across point tools. Convergence of advisory, deployment, and MDR services brings value propositions beyond technology resale, solidifying service-led growth in the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
The solutions portfolio nevertheless remains critical for organizations with strict data-residency rules. Appliance refresh cycles in BFSI and utilities sustain revenue for firewall, intrusion-prevention, and secure-email gateways. New-generation SIEM platforms incorporate behavioral analytics and automation to offset talent scarcity, aligning product innovation with national skills-development goals. Vendors bundle perpetual licenses with cloud-delivered analytics to bridge on-premise controls and SaaS visibility. Co-delivery with local integrators accelerates time to value, reflecting the collaborative nature of the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
On-premise systems accounted for 52.85% of the Malaysia cybersecurity market size in 2025 because legacy workloads and data-sovereignty mandates still dominate in banking and public service. Hardware refreshes in these sectors provide a stable base for appliance vendors. Yet cloud deployments are expanding at an 8.05% CAGR through 2031, outstripping on-premise upgrades. Consumption-based pricing, continuous feature releases, and AI-driven analytics make cloud controls appealing for institutions pursuing digital-first strategies. Shared-responsibility frameworks encourage enterprises to off-load maintenance to specialized providers, supporting long-term adoption in the Malaysia cybersecurity market.
Vendor roadmaps include data-localization nodes within Malaysia to reassure regulated customers. Over time, improvements in sovereign-cloud platforms may erode the remaining resistance, but hardware refreshes tied to industrial-control networks ensure a continuing market for on-premise gear.
The Malaysia Cybersecurity Market Report is Segmented by Offering (Solutions [Application Security, Cloud Security, and More], Services [Professional Services, and More]), Deployment Mode (Cloud, On-Premise), End-User Industry (BFSI, Healthcare, IT and Telecom, Industrial and Defense, Retail and E-Commerce, and More), End-User Enterprise Size (Large Enterprises, Smes). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).