
화물 운송 시장의 2025년 시장 규모는 5,722억 5,000만 달러로 예상되며, 2030년에는 7,408억 5,000만 달러에 이르고, CAGR 5.3%로 확대될 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
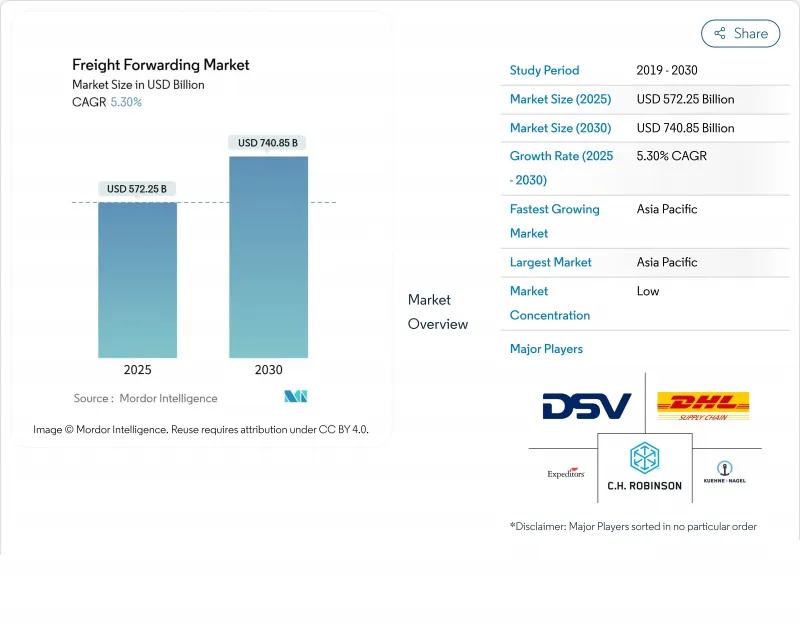
지정학적 긴장과 수차례의 공급망 충격에도 불구하고 상승 기조가 계속되는 것은 디지털 플랫폼, 탄력성이 있는 복합 일관 수송 네트워크, 지속적인 전자상거래 흐름이 수요를 유지하고 있기 때문입니다. 소포 사이즈의 크로스보더 화물에 대한 수요 증가, 정온 수송 능력에 대한 꾸준한 투자, 니어 쇼어링을 향한 구조적 전환은 모든 주요 무역 레인의 화물량을 증가시키고 있습니다. 2차적인 효과로는 기술 도입의 가속화, 실시간 시인성을 축으로 한 새로운 프리미엄 서비스 층, 규모의 우위성을 추구하는 포워더에 의한 통합 등을 들 수 있습니다. 2025년에 DSV가 159억 달러로 DB Shanker를 인수한 것을 필두로 하는 M&A 활동은 화물 수송 시장에서의 경쟁적 포지셔닝이 어떻게 규모와 데이터 밀도에 의해 지지되고 있는지를 시사하고 있습니다.
아시아에서의 기록적인 온라인 소비는 북미 소비자를 향한 소량 소포의 흐름을 촉진하고 있습니다. 운송주선인은 기존 시설을 소포 분류 허브에 재사용하고 통관 사전 절차를 통합하고 구매 시 마찰을 없애기 위해 예측 관세 계산 도구를 이용합니다. 현재는 단순한 비용보다 서비스 속도가 라우팅 결정을 좌우하게 되어, 운송 회사는 태평양 횡단 익스프레스 레인의 주 1편의 운항을 확대하고 있습니다. 동위원소의 소포 수준 가시성 및 브랜드 반품과 같은 부가가치 기능은 기존 사업자가 순수한 소포 인테그레이터에 대항하여 점유율을 보호하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
멕시코, 폴란드, 튀르키예의 근접 제조업은 화물량을 장거리 해상 운송에서 보다 단거리의 복합 일관 운송으로 옮겨가고 있습니다. 미국과 멕시코 사이의 국경을 넘어서는 트럭 운송 수요는 2024년에 두 자릿수의 성장을 보였으며 합리화된 국경 통관 소프트웨어와 보세 내륙 항구에 대한 투자를 자극합니다. 통관에 익숙한 포워더는 복잡한 관세 제도를 수익화하고, 철도와 트럭의 통합 솔루션은 해상 운송의 대체 수단에 비해 도어 투 도어 소요 시간을 35% 단축합니다.
정박지 대기 행렬의 장기화, 장비 부족 및 예측 불가능한 운항 스케줄로 인해 운송 시간의 편차가 증가하고 있습니다. 주요 아시아 항구의 평균 체류 시간은 2023년에 비해 2배 이상 증가하고 있으며, 장비 재배치에는 현재 여러 주요 항로에서 18일의 추가 일수가 소요됩니다. 포워더는 수주 전부터 컨테이너 슬롯을 사전 예약하고, 우선 게이트 창구를 협상하고, 정체하는 허브를 우회하기 위해 보조 피더를 전세하고 있습니다. 아시아 유럽 항로의 스팟 운임은 2025년 초에 255%나 급등하였고, 화주는 조달처를 재검토하거나 비용 상승을 흡수할 필요에 이르렀습니다.
해상화물은 대양을 횡단하는 대량화물의 TEU당 운송비용이 가장 낮기 때문에 2024년 화물 운송 시장 점유율 62%를 유지했습니다. 이 부문은 슬롯 비용을 낮게 억제하는 대형 선박의 배치, 자동화된 터미널, 확장된 메인 라인 피더 네트워크의 혜택을 받고 있습니다. 그 규모의 크기에도 불구하고 해상 운송 서비스는 조임목에 직면하여 일정의 무결성이 손상되면 화주가 철도와 항공 우편을 추가하는 동기 부여가 됩니다. 따라서 포워더가 해상, 철도, 육상을 번들해 아시아 유럽항로의 리드타임을 2-4일 단축하는 복합운송 솔루션의 CAGR은 6.4%를 기록했습니다. 유라시아 대륙의 회랑에서의 철도 수송량은 2024년에 10.7% 증가하여 계속해서 라우팅 리스크의 분산을 도모하고 있습니다. 항공 운송은 여전히 중요도가 높은 제약, 일렉트로닉스, 패션 드롭을 계속 지배하고 있으며, 그 용량은 네트워크가 재건됨에 따라 회복되고 있습니다. 육상 운송은 지역 배송과 라스트 원 마일의 완성을 보장하지만, 연료 충전 및 운전자 부족이 라인 운송 요금을 증가시키기 때문에 여전히 비용에 민감합니다. 모드에 관계없이 라우팅을 구성하는 포워더는 모든 화물 운송 시장 지역에서 더 높은 월렛 점유율과 더 깊은 고객층을 확보할 수 있습니다.
멀티모달 서비스 화물 운송 시장의 규모는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 6.4%로 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다. 통합 제어 타워 플랫폼, 통합 견적 엔진, 블록 트레인 차터는 운영 민첩성과 마진 유지성을 향상시킵니다. 순수한 해상 운송 및 항공 운송 전문가는 현재 인터모달 철도 사업자와 제휴하여 고객이 사업자를 변경하지 않도록 붙잡습니다. 통관 인도를 디지털화하고 컨테이너 장비를 자동으로 할당하며 단일 대시보드로 도착 알림을 출시하는 기술이 핵심 역할을 합니다. 시장 리더 보고서에 따르면 종단 간 복합 일관 운송 계약은 고객 유지율을 22% 향상시켜 화물 운송 시장에서 오케스트레이션된 서비스 번들의 끈끈함을 돋보이게 합니다.
대기업은 2024년 화물 운송 시장 규모의 70%를 차지하였으며 5만 TEU 이상의 연간 입찰량을 활용해 지수연동형 해상 및 항공계약을 체결하고 있습니다. 대기업의 조달 부서는 통합된 세계 KPI와 탄소 회계를 요구하고 있으며, 포워더는 운영 데이터 위에 분석 계층을 구축하도록 촉구하고 있습니다. 소규모 수출업체는 지금까지 협상력이 부족했지만, 현재는 디지털 마켓플레이스가 중소기업 수요를 집약하고, 매일 스팟 임베디드로 운송 회사에 경매를 실시해, 운임 지출을 12% 삭감하고 있습니다. 이 역동적인 움직임으로 화물 운송 시장의 중소기업의 CAGR은 6.6%에 달할 전망입니다. 운임 플랫폼은 중소기업의 현금 흐름주기에 맞추어 즉각적인 견적, 이정표 경보, 통합 무역 금융 모듈을 제공합니다.
초보 화주는 화물의 신고를 제대로 하지 못해서 벌금이 부과될 수 있기 때문에 중소기업의 참여는 컴플라이언스 요구도 날카롭게 합니다. 디지털 서류 작성 위저드는 제한된 자재에 플래그를 지정하고 표준 서식을 사전에 입력하여 세관 보류를 19% 줄입니다. 포워더는 보험, 관세 환급 신고, 전자 인보이싱을 구독 계층에 번들하여 수익을 다양화하고 있습니다. 대기업 산업 고객은 고중량 프로젝트 화물과 공장 이전 작업을 여전히 독점하고 있지만, 전자상거래 보충품과 틈새 완제품을 출하하는 중소기업에 의한 성장세가 더욱 높습니다. 따라서 화물 운송 시장은 자원에 제약이 있는 수출 기업 수요가 가속화됨에 따라 점차 균형잡힌 고객 포트폴리오를 보여줄 것으로 예상됩니다.
아시아태평양은 2024년 수익 점유율 36%로 화물 운송 시장을 선도하였고 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)은 7.8%로 확대될 전망입니다. 베트남, 인도네시아, 인도는 제조업의 다각화가 브랜드에 의한 조달 리스크 헤지로 작용해 지역별 판매량을 높입니다. 상하이, 심천, 싱가포르의 주요 항구는 트럭의 턴어라운드 시간을 단축하는 자동 크레인과 스마트 게이트 기술에 많은 투자를 하고 있지만 정박지 이용률은 여전히 과거 최고 수준에 가깝습니다. DP월드는 아시아태평양 항만이 2027년까지 총 연간 20만 TEU를 취급할 것으로 예상하고 있으며, 이 지역이 세계 공급 체인에서 중요한 역할을 하고 있음을 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
북미는 화물 운송 시장에서 2위를 차지하고 있으며, 미국의 왕성한 소비자 수요와 2024년 미국과 멕시코의 국경을 넘은 운송량을 10% 끌어올리는 니어쇼어링의 진행에 의해 지지되고 있습니다. 텍사스 주와 애리조나 주에 걸친 더블 스택 회랑에 대한 철도 투자는 장거리 트럭에서 인터모달로의 모달 이동을 가속화하여 운전자의 용량 병목 현상을 완화합니다. 밴쿠버와 프린스 루퍼트에 위치한 캐나다 게이트웨이는 혼잡한 미국 서해안 터미널에서 아시아 화물을 흡수하여 철도 적재 능력을 확대합니다.
유럽 네트워크는 운전자 부족, 엄격한 배기 가스 규제, 패치워크 국경 규제 등 복합적인 과제에 직면하고 있습니다. 그러나 부가가치 서비스 가운데 특히 제약 및 첨단기술에 대한 수요가 지속됨에 따라 수익이 유지되고 있습니다. 로테르담, 함부르크, 앤트워프의 주요 허브는 Fit-for-55의 목표를 준수하기 위해 세관을 디지털화하고 육상 전원 솔루션을 도입했습니다. 남미는 2027년 완성 예정으로 메르코스르 지역 내 운송 비용을 최대 40% 절감할 수 있는 카프리콘 BI 해상 회랑을 배경으로 급성장할 전망입니다. 중동은 제벨 알리 항과 킹 압둘라 항을 확장하여 동서 무역의 가교가 됩니다.
The freight forwarding market is valued at USD 572.25 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 740.85 billion by 2030, expanding at a 5.3% CAGR.
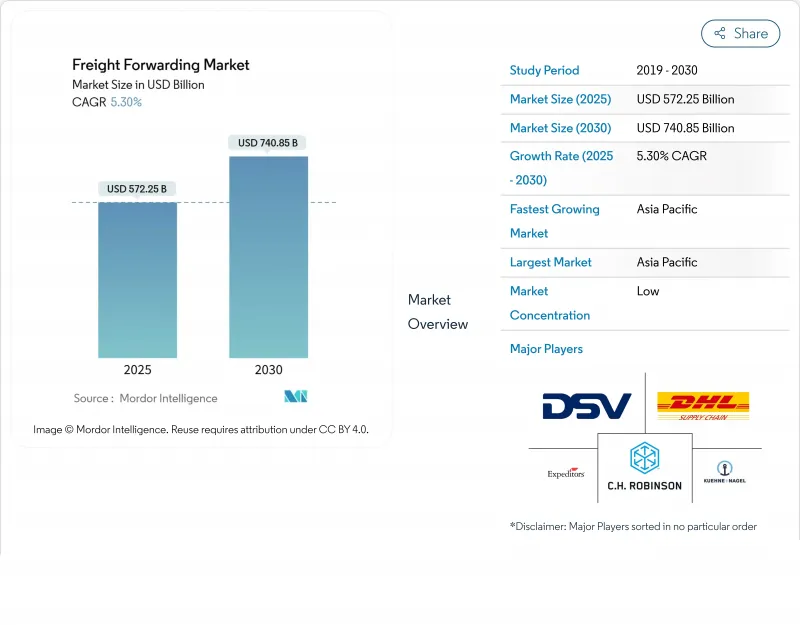
The upward trajectory continues despite geopolitical tensions and repeated supply-chain shocks because digital platforms, resilient multimodal networks, and sustained e-commerce flows keep volumes intact. Heightened demand for parcel-sized cross-border shipments, steady investment in temperature-controlled capacity, and a structural pivot toward near-shoring all lift volumes in every major trade lane. Second-order effects include faster technology adoption, new premium service tiers built around real-time visibility, and an observed tilt toward consolidation as forwarders strive for scale advantages. M&A activity, spearheaded by DSV's USD 15.9 billion takeover of DB Schenker in 2025, illustrates how scale and data density now underpin competitive positioning in the freight forwarding market.
Record online spending in Asia continues to drive small-parcel flows toward North American consumers. Freight forwarders are repurposing existing facilities into parcel sortation hubs, integrating customs pre-clearance, and layering predictive duty-tax calculators to remove purchase friction. Service speed rather than simple cost now determines routing decisions, encouraging carriers to expand weekly sailings on trans-Pacific express lanes. Value-added features, such as isotopic parcel-level visibility and branded returns, help incumbents defend share against pure-play parcel integrators.
Proximity manufacturing in Mexico, Poland, and Turkiye pulls freight volumes from long-haul ocean to shorter multimodal corridors. Cross-border truckload demand on the US-Mexico lane grew double digits in 2024, stimulating investments in streamlined border-clearance software and bonded inland ports. Forwarders with customs brokerage depth monetize complex tariff regimes, while integrated rail-truck solutions shorten door-to-door time by 35% compared with ocean alternatives.
Extended berth queues, equipment shortages, and unpredictable sailing schedules inflate transit variability. Average dwell time at major Asian ports more than doubled versus 2023, and equipment repositioning now adds an 18-day buffer on several head-haul trades. Forwarders pre-book container slots weeks ahead, negotiate priority gate windows, and charter supplemental feeders to bypass gridlocked hubs. Spot rates on Asia-Europe lanes spiked 255% in early 2025, forcing shippers to rebalance sourcing or absorb cost surges.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Ocean freight retained a 62% freight forwarding market share in 2024 because it offers the lowest cost per TEU for high-volume goods moving across oceans. The segment benefits from megavessel deployments, automated terminals, and expanded mainline-feeder networks that keep slot costs low. Despite its scale, ocean services face chokepoints, motivating shippers to add rail or air legs when schedule integrity falters. Multimodal solutions therefore log a 6.4% CAGR, as forwarders bundle ocean, rail, and road to shave lead times by two to four days on Asia-Europe lanes. Rail volumes on the Eurasian corridor climbed 10.7% in 2024 and continue to diversify routing risk. Air forwarding still dominates time-critical pharma, electronics, and fashion drops, with capacity rebounding as belly-hold networks rebuild. Road forwarding secures regional distribution and last-mile fulfilment but remains cost-sensitive because fuel surcharges and driver scarcity inflate line-haul rates. Forwarders that orchestrate mode-agnostic routing enjoy higher wallet share and deeper client lock-in across every freight forwarding market region.
The freight forwarding market size for multimodal services is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 6.4% by 2030. Integrated control-tower platforms, unified quoting engines, and block-train charters enhance operational agility and margin retention. Pure ocean or air specialists now partner with intermodal rail operators to keep customers from switching providers. Technology that digitises customs hand-offs, auto-allocates container equipment, and releases arrival notifications in a single dashboard plays a central role. Market leaders report that end-to-end multimodal contracts lift client retention by 22%, highlighting the stickiness of an orchestrated service bundle in the freight forwarding market.
Large enterprises captured 70% of the freight forwarding market size in 2024, leveraging yearly tender volumes above 50,000 TEUs to lock in index-linked ocean and air contracts. Their procurement departments demand unified global KPIs and carbon accounting, driving forwarders to build analytics layers atop operational data. Smaller exporters historically lacked negotiating power, but digital marketplaces now aggregate SME demand and auction it to carriers in daily spot buys, cutting freight spends by 12%. This dynamic pushes the SME slice of the freight forwarding market to a 6.6% CAGR. Freight platforms offer instant quotes, milestone alerts, and integrated trade-finance modules that align with SME cash-flow cycles.
SME participation also sharpens compliance needs because novice shippers may misdeclare cargo, inviting fines. Digital documentation wizards flag restricted commodities and pre-populate standard forms, reducing customs holds by 19%. Forwarders diversify revenue by bundling insurance, duty-drawback filing, and e-invoicing into subscription tiers. Large industrial clients still dominate heavyweight project cargo and plant relocation work, but the incremental growth momentum lies with SMEs shipping e-commerce replenishment and niche finished goods. The freight forwarding market will therefore exhibit a progressively balanced customer portfolio as demand from resource-constrained exporters accelerates.
The Freight Forwarding Market Report is Segmented by Mode of Transport (Air Freight Forwarding, Ocean Freight Forwarding, and More), by Enterprise Size (Small & Medium Enterprises, and More), by Forwarder Model (Traditional Asset-Light Forwarders, and More), by End-User Industry (Industrial and Manufacturing, and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Asia-Pacific led the freight forwarding market with a 36% revenue share in 2024 while expanding at a 7.8% CAGR through 2030. Manufacturing diversification into Vietnam, Indonesia, and India spikes regional volumes as brands hedge sourcing risk. Major ports in Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Singapore invest heavily in automated cranes and smart-gate technology that shortens truck turnaround times, yet berth utilizations still hover near record highs. DP World expects Asia-Pacific ports collectively to handle 200,000 TEUs annually by 2027, affirming the region's anchoring role in global supply chains.
North America ranks second in the freight forwarding market, bolstered by the United States' strong consumer demand and ongoing near-shoring that boosts US-Mexico cross-border traffic by 10% in 2024. Railroad investments in double-stack corridors across Texas and Arizona accelerate modal shift from long-haul truck to intermodal, easing driver-capacity bottlenecks. Canadian gateways in Vancouver and Prince Rupert expand rail-mount capacity to redirect Asia cargo away from crowded US West Coast terminals.
Europe's network faces compounded challenges from driver shortages, stringent emissions mandates, and patchwork border regulations. However, sustained demand for value-added services, especially in pharma and high-tech machinery, preserves revenue. Leading hubs in Rotterdam, Hamburg, and Antwerp digitize customs and deploy shore-power solutions to comply with the Fit-for-55 goals. Beyond the tri-continent core, South America grows rapidly on the back of the Capricorn BI oceanic Corridor, which promises to cut intra-Mercosur transit costs by up to 40% once completed in 2027. The Middle East expands Jebel Ali and King Abdullah Port to position itself as a bridging node between East-West trade, while African corridors benefit from Chinese-financed rail revamps that unlock inland commodity flows.