
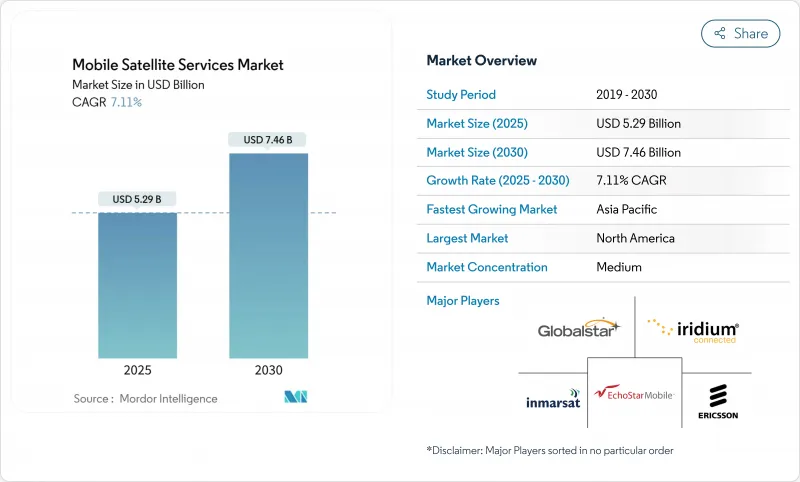
모바일 위성 서비스 시장은 2025년에 52억 9,000만 달러에 이르고, 2030년에는 74억 6,000만 달러로 확대되며, CAGR 7.12%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다.

음성 중심 링크에서 광대역 및 장치 간 직접 연결로의 급속한 전환은 지상파 백홀에 대한 의존도를 낮추면서 수요 패턴을 재구성하고 있습니다. 3GPP를 통한 비지상 네트워크 표준의 상업화, 저궤도(LEO) 별자리 발사 비용 급락, 지역 및 해역의 지속적인 연결 격차가 모바일 위성 서비스 시장 기회를 확대하고 있습니다. 정부 조달 주기가 가속화되고 있는 이유는 보안 소부린 링크가 재량 지출에서 전략적인프라로 이동하기 때문이며, 기업의 디지털화 프로그램은 광섬유 및 휴대전화 정전에 대한 표준 보험으로 위성 통신 용량을 예산화하고 있습니다. 또한 수직 통합형 LEO 사업자와의 경쟁 격화는 레거시 정지 위성의 기존 사업자에게 플릿 기술의 근대화, 소프트웨어 정의 페이로드의 채용, 멀티 궤도 용량의 이용 기반 계약에 번들화를 강요하고 있습니다.
일부 지정학적 충돌로 인해 해외 사업자에 대한 의존성이 드러난 후 소블린 연결에 대한 요구가 급증했습니다. 유럽 위원회는 기관, 구급대, 중요 인프라에 암호화 광대역을 제공하는 다궤도 IRIS2 계획에 106억 유로(113억 달러)를 승인했습니다. 미국, 일본, 인도에서도 비슷한 조달 계획이 있으며 양자 내성 암호화와 다중 궤도 중복성이 지정되었습니다. SES는 2025년 초에 31억 달러를 투자하여 Intelsat 인수를 완료하고, 정부 기관 포트폴리오를 강화하고, 단일 목구멍 계약으로 GEO-MEO-LEO의 레이어 용량을 제공합니다. 따라서 이익률이 높은 정부 기관과의 계약은 함대 업그레이드를 지원하고 모바일 위성 서비스 시장의 도달 가능한 수익 풀을 확장합니다.
L-밴드, S-밴드 및 Ku-밴드 게이트웨이가 상호 운용할 수 없기 때문에 대륙 횡단 플릿을 보유한 기업은 여전히 여러 단말기를 구분하고 있습니다. 모바일 위성 서비스 협회는 2024년 로밍 표준을 지지하기 위해 결성되었지만, 칩셋의 단편화는 여전히 계속되고 있으며, 많은 실적를 가로지르는 화물주 및 항공사의 총소유비용을 높이고 있습니다. 원활한 로밍이 없으면 모바일 위성 서비스 시장의 인지 가치는 단일 SIM으로 세계에 액세스할 수있는 지상파 휴대폰보다 낮습니다. 멀티모드 단말기는 출현하고 있지만, 인증, 안테나 설계의 타협, 한정된 생산 규모가 채용을 늦추고 있습니다.
데이터 연결은 2024년 매출의 63.4%를 차지하며 모바일 위성 서비스 시장에서 광대역과 스트리밍이 고객의 예산의 중심이 되는 방법을 보여주었습니다. 기업은 비디오 감시, 승무원의 복리 후생 액세스, 원격 소프트웨어 업데이트 등 일반적으로 불가능한 백홀을 위해 높은 처리량 회선을 예약합니다. 음성은 해상 조난과 조종석의 안전 확보라는 틈새 분야를 유지하고 있지만, 대역폭을 중시한 계약은 분 단위의 과금을 능가하고 있습니다. IoT/M2M 계약은 가장 빠르게 성장하고 있으며, 농업, 광업, 유틸리티이 원격 센서 그룹을 확대함에 따라 2030년까지의 CAGR은 12.4%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 새로운 센서 모듈이 늘어날 때마다 위성의 운영 비용은 매우 적으며 수익이 증가합니다. 따라서 IoT 엔드포인트의 모바일 위성 서비스 시장 규모는 기기당 평균 수익이 낮음에도 불구하고 크게 증가할 전망입니다.
비디오 및 데이터 증가는 트래픽을 온보드로 처리하고 지상 병목 현상을 줄일 수 있도록 운영자가 재생 페이로드를 채택하는 것을 뒷받침합니다. 744TOPS를 실행하는 12개의 AI 강화 LEO 위성을 발사한 중국은 스펙트럼 효율 향상으로 여분의 주파수 할당 없이 추가 처리량을 자유롭게 판매할 수 있는 궤도 엣지 컴퓨팅을 소개했습니다. 유연한 소프트웨어 정의 허브는 용량을 계절적 해상 레인에서 허리케인의 부흥 구역까지 몇 분 안에 재배치할 수 있어 활용도를 향상시킵니다. 또한 Capacity As-A-Service 계약으로의 전환은 클라우드 컴퓨팅에서 도입된 모델인 최선형 링크가 아닌 성능 보증을 제공하는 인센티브를 운영자에게 제공합니다. 이러한 변화는 총체적으로 데이터의 우위성을 강화하고 2030년까지 모바일 위성 서비스 시장의 60%를 데이터가 차지한다는 예상을 뒷받침하는 것입니다.
모바일 위성 서비스 시장 보고서는 서비스별(음성, 데이터, 광대역 등), 주파수별(L-band, S-band 등), 최종사용자 산업별(해상, 항공, 정부 및 방위 등)로 분류됩니다.
북미는 2024년에 모바일 위성 서비스 시장에서 38.1%의 점유율을 유지했는데, 이는 국방부와의 대규모 계약, 확립된 규제 경로, 조기 기기에 대한 직접 연결 시험 때문입니다. 미국은 에너지 파이프라인과 구급대 네트워크에서의 플릿 방송에 힘입어 지역별 수익의 대부분을 차지했습니다. 캐나다는 북방 영토의 유니버설 서비스 의무화를 통해 수요를 확대했으며, 멕시코는 공유 위성 용량을 활용하여 산악 지역의 커뮤니티를 연결했습니다. 지역적인 C대역의 재공급으로 다운링크 대역폭이 추가되어, 사업자는 새로운 우주선을 발사하지 않고 소비자용 광대역의 제공을 확대할 수 있게 되었습니다.
아시아태평양은 정부가 디지털 주권을 추구하고 민간 콩그로말리트가 물류 체인을 디지털화하기 때문에 전 지역 중 가장 빠른 CAGR 10.2%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 발사율은 여전히 활황을 보이고 있으며, KDDI와 같은 지역의 기업은 일본의 산 경향이 있는 지형 전체에서 표준 스마트폰에 메시지를 전달하는 'au 스타링크 직접'를 상업화했습니다. 중국은 '일대일로'의 항로에 대응하는 높은 처리량의 Ka 밴드 위성을 추가하여 국가의 통신 용량을 확대하고 인도는 농촌 지역의 광대역을 확대하기 위해 Bharti Airtel과 SpaceX의 합의를 환영했습니다. 동남아시아 열도는 재난 구조, 어업 감시 및 학교 연결을 위한 용량을 단일 주권 계약으로 번들링하는 조달 틀에 서명했습니다.
유럽에서는 IRIS2 안보 프로그램에 의해 지원되는 강력한 제도적 수요가 발생했습니다. 유럽 GNSS 청은 양자 안전 업링크 연구를 위한 보조금을 급격히 추진하고, SpaceRISE 컨소시엄은 GEO, MEO, LEO 부문을 결합한 다중 궤도 네트워크를 구축하기 시작했습니다. 중동 통신 사업자는 유럽의 선단 소유자와 협력하여 홍해의 새로운 항로에서 해상 통신을 제공하고, 아프리카 통신 사업자는 유럽 공급자로부터 Ka 밴드 대역의 통신 용량을 조달하고 국내 광섬유의 격차를 메웠습니다. 라틴아메리카는 허리케인 지역에서 재해에 강한 위성 오버레이를 추구하고, 안데스 국가는 마이크로파 링크가 불가능한 지형에서의 긴급 대응에 L 밴드 핸드 헬드 위성 전화를 채택했습니다.
The mobile satellite services market reached USD 5.29 billion in 2025 and is forecast to rise to USD 7.46 billion by 2030, advancing at a 7.12% CAGR.
Rapid migration from voice-centric links to broadband and direct-to-device connectivity is reshaping demand patterns while lowering reliance on terrestrial backhaul. Commercialisation of 3GPP non-terrestrial network standards, the sharp drop in launch costs for Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO) constellations, and persistent connectivity gaps across rural and maritime zones are expanding the mobile satellite services market opportunity. Government procurement cycles are accelerating because secure sovereign links have moved from discretionary spend to strategic infrastructure, and enterprise digitalisation programmes now budget satellite capacity as standard insurance against fibre or cellular outages. Intensifying competition from vertically integrated LEO operators is also pressuring legacy geostationary incumbents to modernise fleet technologies, adopt software-defined payloads and bundle multi-orbit capacity into usage-based contracts.
Sovereign connectivity requirements surged after several geopolitical flashpoints exposed reliance on foreign operators. The European Commission approved EUR 10.6 billion (USD 11.3 billion) for the multi-orbit IRIS2 programme that will furnish encrypted broadband to institutions, first responders, and critical infrastructure.Similar procurement tracks in the United States, Japan, and India specify quantum-resistant encryption and multi-orbit redundancy. SES completed its USD 3.1 billion acquisition of Intelsat in early 2025 to strengthen its government portfolio and offer layered GEO-MEO-LEO capacity under single-throat contracts. High-margin government deals therefore underpin fleet upgrades and expand the reachable revenue pool for the mobile satellite services market.
Enterprises with transcontinental fleets still juggle multiple terminals because L-Band, S-Band, and Ku-Band gateways do not interoperate. The Mobile Satellite Services Association formed in 2024 to champion roaming standards, yet chipset fragmentation persists and drives higher total cost of ownership for shippers and airlines that traverse many footprints. Without seamless roaming, the perceived value of the mobile satellite services market remains lower than terrestrial cellular, where a single SIM offers worldwide access. Multimode terminals are emerging, but certification, antenna design compromises, and limited production scale have slowed adoption.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Data connectivity accounted for 63.4% of 2024 revenue, underscoring how broadband and streaming now anchor customer budgets in the mobile satellite services market. Enterprises book high-throughput circuits to backhaul video surveillance, crew welfare access, and remote software updates that would otherwise be impossible. Voice retains a niche in maritime distress and cockpit safety, yet bandwidth-driven contracts are eclipsing per-minute billing. IoT/M2M subscriptions grew fastest and are forecast to post 12.4% CAGR to 2030 as agriculture, mining, and utilities scale remote sensor fleets. Each new sensor module adds incremental revenue at negligible satellite operating cost, making the segment strategically significant for margin expansion. The mobile satellite services market size for IoT endpoints is therefore poised to rise meaningfully despite lower average revenue per device.
Video and data growth pushes operators to adopt regenerative payloads so traffic can be processed onboard, reducing ground bottlenecks. China's launch of 12 AI-enhanced LEO satellites that execute 744 TOPS showcases orbital edge computing, where spectral efficiency gains free additional throughput for sale without extra spectrum allocation. Flexible software-defined hubs let capacity be redeployed from seasonal maritime lanes to hurricane recovery zones within minutes, improving utilisation. The transition to capacity-as-a-service contracts also incentivises operators to provide performance guarantees rather than best-effort links, a model imported from cloud computing. These shifts collectively reinforce data's primacy and validate the expectation that data will still exceed 60% of the mobile satellite services market by 2030.
The Mobile Satellite Services Market Report is Segmented by Service (Voice, Data, Broadband, and More), Frequency (L-Band, S-Band, and More), End-User Industry (Maritime, Aviation, Government and Defense, and More),
North America retained 38.1% share of the mobile satellite services market in 2024 because of large Department of Defense contracts, well-established regulatory pathways, and early direct-to-device pilots. The United States accounted for most regional revenue, buoyed by fleet broadcasts across energy pipelines and first-responder networks. Canada increased demand through universal service mandates in its northern territories, and Mexico leveraged shared satellite capacity to connect mountainous communities. Regional C-band refarming provided additional downlink bandwidth, allowing operators to widen consumer broadband offers without launching new spacecraft.
Asia Pacific is set to post a 10.2% CAGR, the fastest among all regions, as governments pursue digital sovereignty and private conglomerates digitise logistics chains. Launch rates remain brisk, and regional players such as KDDI commercialised "au Starlink Direct" to bring messaging to standard smartphones across Japan's mountainous topography. China expanded national capacity by adding high-throughput Ka-Band satellites that will serve Belt and Road shipping routes, while India welcomed agreements between Bharti Airtel and SpaceX to widen rural broadband. Southeast Asian archipelagos signed procurement frameworks that bundle capacity for disaster-relief, fisheries monitoring, and school connectivity into a single sovereign contract.
Europe experienced robust institutional demand anchored by the IRIS2 security programme. The European GNSS Agency fast-tracked grants for quantum-safe uplink research, and the SpaceRISE consortium began constructing a multi-orbit network with combined GEO, MEO, and LEO segments. Middle East operators collaborated with European fleet owners to provide maritime coverage along new Red Sea shipping lanes, and African telcos sourced Ka-Band capacity from European providers to bridge national fibre gaps. Latin America pursued disaster-resilient satellite overlays in hurricane zones, and Andean nations adopted L-Band handheld satellite phones for emergency response in terrain where microwave links are infeasible.