
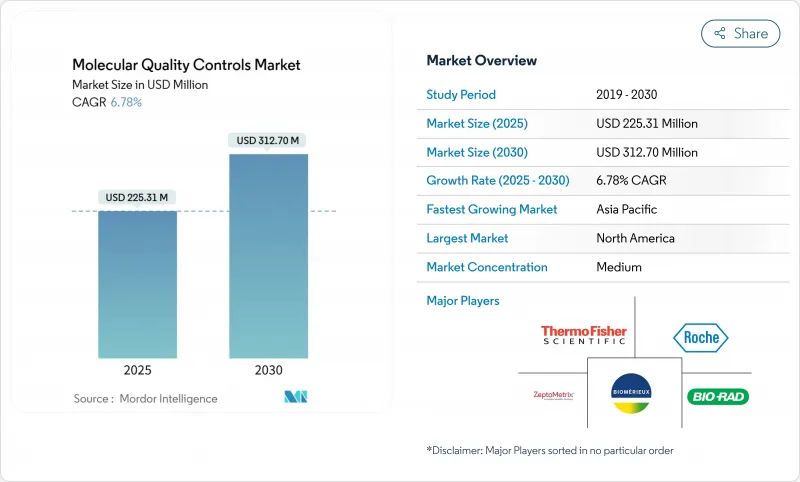
분자 품질 관리 시장 규모는 2025년에 2억 2,531만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) CAGR 6.78%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 3억 1,270만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

미국 식품의약국(FDA)의 임상 검사(LDT) 최종 규칙, ISO 15189:2022 인증의 세계 추진, 단일 분석에서 멀티플렉스 및 차세대 시퀀싱(NGS) 검사에 대한 검사 시설의 급속한 이동입니다. 독립적인 제3자 기관에 의한 관리는 분석 정확도를 입증하기 위한 기본적인 도구이지만, 실험실이 자동화와 미들웨어를 통합함에 따라 장비별 관리가 늘어나고 있습니다. 종합적인 유전체 프로파일링에 대한 종양학의 필요성 확대, 외부 품질 평가(EQA)의 의무화 증가, 집중적인 품질 기준을 충족해야 하는 포인트 오브 케어 분자 플랫폼으로의 임상적 전환으로 수요가 강화되고 있습니다. 반대로, 런 당 높은 관리 비용, 희소 병원체 표준 물질 공급 병목, 규제 경로의 중복 등이 당면 지출을 억제하고 있습니다.
COVID-19 공중 보건 응급 상황에서 진단 실험실은 전례 없는 양을 처리했고 FDA는 291개의 분자 분석을 승인하고 높은 처리량 플랫폼의 확장성을 입증했습니다. 팬데믹 후에도 실험실이 분자 검사를 약리 유전체학, 항균제 내성 감시, 유전성 암 패널로 확대했기 때문에 처리량은 증가한 채로 있습니다. 각 멀티플렉스 타겟에는 검증 계층이 추가되어 실험실은 분석 드리프트를 피하기 위해 견고한 타사 컨트롤에 의존하지 않을 수 있습니다. 실험실 정보 시스템과 통합된 디지털 QC 대시보드는 수작업 검증 단계를 62.5% 줄이고 증가하는 작업량을 관리하는 기술의 역할을 명확하게 보여줍니다.
ISO 15189:2022는 리스크 관리 및 포인트 오브 케어 통합의 기준을 높이고 검사 시설을 추적성과 독립성을 입증하는 외부 조달 관리로 밀어 올립니다. 새로운 버전 하에서 미국 최초의 인증은 세계 컴플라이언스 기운으로의 조기 전환을 보여주었습니다. 검사 시설의 전환 기간은 3년이며 분자 품질 관리 시장 제품에 대한 지속적인 수요를 지원합니다.
분자 품질 관리의 경제성은 특히 검사의 복잡성이 증가함에 따라 제한된 예산으로 운영되는 검사실에서 큰 과제가 되고 있습니다. NGS 분석은 순차 PCR에 비해 환자 관리의 총 비용을 줄이지만 여전히 비싼 다중 항목 제어가 필요하며 샘플 당 비용의 4-7%를 차지할 수 있으며 소규모 실험실에서는 자명한 마진이 아닙니다. 고정 관리 비용은 검사량이 겸손한 경우에는 잘 늘리지 않으며 검사실은 교체 간격을 늘려야 하며 분석의 견고성이 저하될 수 있습니다.
ISO15189의 문서화 요건을 충족하고 플랫폼의 편향을 완화하는 벤더 중립적인 검증 툴에 대한 검사 시설의 기호를 반영해, 2024년의 분자 품질 관리 시장 점유율은 58.11%로 독립 컨트롤이 우위를 차지했습니다. 바이오 래드의 유니티 데이터 관리 네트워크는 38,000개의 실험실에서 사용되며 타사 컨트롤이 상호 비교를 집계하고 시스템 편차를 신속하게 감지하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 독립적인 제품은 호흡기 병원체를 위한 다중 분석 패널에서 주문 종양학 변이체에 이르기까지 다양한 실험실이 다양한 장치들 사이에서 표준화되도록 합니다.
장치별 컨트롤은 규모가 작지만 자동화 및 통합된 샘플에서 응답으로 플랫폼이 확대됨에 따라 2030년까지의 CAGR은 7.55%가 될 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 제조업체가 조정한 안정성과 로트 간의 일관성은 검증 시간을 절약하고 높은 처리량 환경에서 결정적인 이점을 제공합니다. 그러나 벤더 락에 대한 우려는 여전히 남아 있으며, 독립적인 컨트롤이 숙련도 체계에 대한 참조 옵션으로 남아 있습니다. 그러므로 분자 품질 관리 시장은 실험실이 인증을 위해 독립적인 대조군을 도입하는 반면, 일상적인 워크플로우의 연속성을 위해 장비별 재료에 의존하는 듀얼 소싱 모델에 기울고 있습니다.
PCR 기반 제품은 2024년 매출의 69.52%를 차지했으며, 납기와 비용이 폭을 넓힐 수 있는 대량의 감염증 검사에 지지되고 있습니다. 이러한 대조군은 보통 바이오 세이프티를 위해 비감염성 입자에 캡슐화된 안정화 바이러스 또는 박테리아 핵산을 포함합니다.
한편 NGS 기반 컨트롤은 CAGR 7.23%로 진전하고 있습니다. 이것은 암 영역에서 다중 진 패널로의 이동과 유전성 질환에서 종합적인 유전체 프로파일링의 사용 증가를 반영합니다. 샘플 준비 QC 키트는 시퀀싱 전에 라이브러리의 복잡성, 단편 크기 및 어댑터의 라이게이션 효율을 평가하여 비용이 많이 드는 재실행을 줄입니다. NGS 패널의 분자 품질 관리 시장 규모는 상환이 개선되고 시퀀싱 비용이 계속 감소함에 따라 확대될 전망입니다. 등온 증폭 컨트롤은 신속한 정성적 응답으로 충분한 포인트 오브 케어 STI 검사 등 틈새 이용 사례를 차지하고 있습니다.
2024년 매출은 북미가 38.14%로 최고였습니다. 좋은 상환, 많은 검사량, FDA의 틀로 인해 제3자 관리가 모범 사례에서 규제상 필요한 것으로 승격한 것이 뒷받침되었습니다. CLIA의 성능 기준치의 엄격화는 검사 시설이 인증을 유지하기 위해 QC 빈도를 늘려 수요를 더욱 높입니다. 캐나다의 의료기기 규제의 현대화는 혁신적인 품질 관리에 대한 가속적인 길을 지원하고 이 지역의 꾸준한 성장을 지원합니다.
아시아태평양은 CAGR 8.33%에서 가장 급성장하고 있는 지역으로, 정부의 유전체학 프로그램과 민간 진단 체인의 확대에 추진되고 있습니다. 일본에서는 NGS 종양학 패널이 상환되고, 한국에서는 세포 및 유전자 치료 제조에 대한 투자가 이루어지고 있으며, NGS 워크플로우의 QC 소비량이 증가하고 있습니다. 중국 국내 장비 제조업체는 QC 로트 추적 소프트웨어의 통합을 늘리고 현지 수요를 높이고 있습니다. 분단된 규제에도 불구하고, 분자 품질 관리 시장은 ISO 15189와 IVDR 원칙에 따른 품질 기준의 조화를 추진하는 APAC로부터 혜택을 받아 국경을 넘어 제품 채용을 촉진하고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 IVDR의 실시에 의해 검사기관이나 제조업체가 품질 문서의 업그레이드를 강요받고 있기 때문에 일관되게 한 자리대 중반의 성장을 나타내고 있습니다. 영국의 국민보건서비스(National Health Service)는 ISO 15189:2022 준수를 요구하는 중앙검사실 계약을 맺고 있으며 QC의 이용을 조달 템플릿에 통합하고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카와 남미는 아직 개발 도상이지만, 새로운 표준 검사실이 개설된 경우에는 2자리 증가를 나타내고 있습니다. 이 지역에서는 다자간 기관이 자금을 제공하는 감염증 감시 프로젝트에서 제3자 관리가 규정되어 있는 경우가 많으며, 공급업체는 조기에 발판을 얻을 수 있습니다.
The Molecular Quality Controls Market size is estimated at USD 225.31 million in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 312.70 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.78% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Robust growth rests on three forces: the United States Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) Laboratory Developed Tests (LDT) Final Rule, the global push for ISO 15189:2022 accreditation, and laboratories' rapid shift from single-analyte to multiplex and next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing. Independent, third-party controls remain the default tool for demonstrating analytic accuracy, while instrument-specific controls gain momentum as laboratories integrate automation and middleware. Demand is reinforced by oncology's expanding need for comprehensive genomic profiling, rising external-quality assessment (EQA) mandates, and the clinical move toward point-of-care molecular platforms that must still meet centralized quality standards. Conversely, high per-run control costs, supply bottlenecks for rare pathogen reference materials, and overlapping regulatory pathways temper near-term spending.
Diagnostic laboratories processed unprecedented volumes during the COVID-19 public-health emergency, with the FDA authorizing 291 molecular assays, demonstrating the scalability of high-throughput platforms. Post-pandemic, volume remains elevated as labs extend molecular testing to pharmacogenomics, antimicrobial resistance surveillance, and hereditary cancer panels. Each multiplex target adds validation layers, compelling laboratories to rely on robust third-party controls to avoid analytical drift. Digital QC dashboards integrated with laboratory information systems have trimmed manual verification steps by 62.5%, underscoring technology's role in managing rising workloads.
ISO 15189:2022 raises the bar for risk management and for point-of-care integration, pushing laboratories toward externally sourced controls that demonstrate traceability and independence. The first U.S. accreditation under the new version signaled an early inflection toward global compliance momentum. Laboratories have three years to transition, anchoring sustained demand for molecular quality controls market products.
The economics of molecular quality controls present significant challenges for laboratories operating under constrained budgets, particularly as test complexity increases. NGS assays cut the overall cost of patient care compared with sequential PCR yet still demand expensive multi-analyte controls that can account for 4-7% of per-sample cost, a margin non-trivial to small laboratories. Fixed control costs scale poorly when test volumes are modest, prompting labs to stretch replacement intervals and potentially compromise analytical robustness.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Independent controls dominated with a 58.11% molecular quality controls market share in 2024, reflecting laboratories' preference for vendor-neutral verification tools that satisfy ISO 15189 documentation requirements and mitigate platform bias. Bio-Rad's Unity Data Management network, active in 38,000 labs, illustrates how third-party controls aggregate peer comparisons to detect systemic deviations quickly. Independent products span multi-analyte panels for respiratory pathogens to custom oncology variants, allowing labs to standardize across diverse instruments.
Instrument-specific controls, though smaller, are projected to post a 7.55% CAGR through 2030 as automation and integrated sample-to-answer platforms expand. Manufacturer-tuned stability and lot-to-lot consistency save validation time, a decisive advantage in high-throughput environments. Yet vendor-lock fears linger, keeping independent controls the reference option for proficiency schemes. The molecular quality controls market therefore gravitates toward a dual-sourcing model in which labs deploy independent controls for accreditation while relying on instrument-specific materials for daily workflow continuity.
PCR-based products retained 69.52% revenue in 2024, anchored by high-volume infectious disease testing where turnaround time and cost trump breadth. These controls typically contain stabilized viral or bacterial nucleic acids encapsulated in non-infectious particles for biosafety.
NGS-based controls, however, are advancing at a 7.23% CAGR, reflecting oncology's shift toward multi-gene panels and the rising use of comprehensive genomic profiling in hereditary disorders. Sample-preparation QC kits assess library complexity, fragment size, and adapter ligation efficiency before sequencing, reducing costly reruns. The molecular quality controls market size for NGS panels is poised to expand as reimbursement improves and sequencing costs continue to decline. Isothermal amplification controls occupy niche use cases such as point-of-care STI testing, where rapid qualitative answers suffice.
The Molecular Quality Controls Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Independent Controls, Instrument-Specific Controls), Technology (PCR-Based, NGS-Based, Isothermal/Other NAAT), Application (Infectious Diseases, Oncology, and More), End-User (Clinical Laboratories, IVD Manufacturers and CROs, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America led with 38.14% revenue in 2024, buoyed by strong reimbursement, high test volume, and the FDA's framework that elevates third-party controls from best practice to regulatory necessity. CLIA's stricter performance thresholds compound demand as laboratories widen QC frequency to retain accreditation. Canada's modernization of medical-device regulations supports accelerated pathways for innovative quality controls, sustaining steady regional growth.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing geography with an 8.33% CAGR, propelled by government genomics programs and expanding private diagnostic chains. Japan's reimbursement of NGS oncology panels and South Korea's investment in cell-and-gene therapy manufacturing both translate to higher QC consumption for NGS workflows. China's domestic instrument makers increasingly embed QC lot-tracking software, amplifying local demand. Despite fragmented regulations, the molecular quality controls market benefits from APAC's push to harmonize quality standards with ISO 15189 and IVDR principles, fostering cross-border product adoption.
Europe exhibits consistent mid-single-digit growth as IVDR implementation compels laboratories and manufacturers to upgrade quality documentation. The United Kingdom's National Health Service awards central laboratory contracts that require ISO 15189:2022 compliance, embedding QC use in procurement templates. Middle East & Africa and South America remain nascent but show double-digit incremental gains where new reference laboratories open. In these regions, infectious-disease surveillance projects funded by multilateral agencies often stipulate third-party controls, giving suppliers an early foothold.