
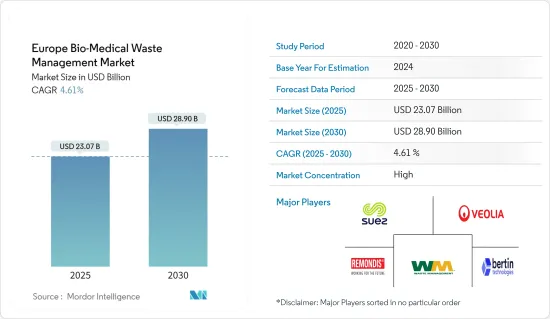
유럽의 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장 규모는 2025년에 230억 7,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 연평균 성장율(CAGR)은 4.61%로, 2030년에는 289억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.
유럽의 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장은 엄격한 규제 조치, 의료 활동의 급증, 생체 의료 폐기물의 적절한 처리에 대한 관심 증가로 인해 산업이 급성장하고 있습니다.
유럽 병원에서는 매년 약 600만 톤의 의료 폐기물이 발생하며, 그 중 약 1/3이 수술실에서 발생합니다. 이 고형 폐기물의 대부분은 체액으로 오염되지 않는 한 재활용이 가능합니다. 병원 폐기물의 2-3%에 불과한 감염성 폐기물은 생물학적 위험 폐기물에서 발견되는 50-70%에 비해 훨씬 적습니다.
독일의 의료 산업은 특수한 처리가 필요한 소량의 폐기물을 발생시킵니다. 독일의 연간 의료 폐기물 중 약 5,000kg, 즉 최대 5%가 감염성 폐기물의 범주에 속합니다. 이는 감염 위험으로 인해 위험한 것으로 간주되어 폐기물 목록 규정(Abfallverzeichnisverordnung, AVV)에 따라 분류됩니다.
의료 폐기물(HCW)의 발생률은 다양합니다. 이는 폐기물 관리 관행, 의료 시설의 특성 및 전문성, 재사용 가능한 장비의 가용성, 일일 환자 수에 영향을 받습니다. 개발도상국은 일반적으로 선진국에 비해 등록된 HCW 생산량이 적습니다. 예를 들어, 유럽에서 HCW 생산량은 하루 병상당 3.5-4.4kg이며, 구체적인 수치로 노르웨이는 병상당 3.9kg, 그리스는 병상당 0.3-3.6kg, 프랑스는 2.7-3.3kg 등 다양합니다..
유럽의 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장은 의료 시설, 연구 센터, 진단 연구소의 확대로 인한 의료 폐기물 증가에 힘입어 꾸준히 성장하고 있습니다. 이러한 성장 추세는 특히 코로나19 기간 동안 급증하는 의료 수요에 힘입어 지속될 것으로 예상되며, 효과적인 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리의 중요성이 강조되고 있습니다.
유럽연합과 각국 정부의 규제는 공중 보건과 환경 보호를 강조하며 바이오 의료 폐기물의 적절한 폐기 및 처리의 필요성을 강조하고 있습니다. 멸균, 소각, 화학 처리와 같은 폐기물 처리의 혁신을 비롯한 기술 발전으로 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리의 효율성과 안전성이 향상되고 있습니다.
인구 고령화와 함께 병원, 진료소, 연구 시설의 수가 증가함에 따라 바이오 의료 폐기물의 양도 증가하고 있습니다. 또한 부적절한 바이오 의료 폐기물 처리와 관련된 위험에 대한 인식이 높아지면서 전문 폐기물 관리 서비스에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다.
이러한 첨단 폐기물 처리 기술과 규정 준수는 매우 중요하지만, 특히 소규모 의료 기관의 경우 상당한 비용이 발생합니다. 폐기물 관리 서비스 제공업체는 유럽 국가에 널리 퍼져 있는 복잡하고 다양한 규정을 준수하는 데 어려움을 겪고 있습니다.
의료 산업의 확장은 특히 개발도상국에서 의료 폐기물 발생을 크게 증가시켰습니다. 팬데믹 기간 동안 병원 입원이 급증하면서 바이오 의료 폐기물의 생산량은 더욱 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다. 일반적인 개발도상국의 의료 폐기물 발생량은 하루 평균 병상당 0.5-2.5kg으로, 인구 통계와 의료 서비스에 따라 크게 달라집니다. 전염병이 증가함에 따라 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장은 크게 성장할 준비가 되어 있습니다. 또한 미생물, 인체 해부학 및 동물 폐기물의 축적이 증가함에 따라 이 시장은 더욱 확대될 것입니다.
2004년 WHO 정책 보고서와 스톡홀름 협약은 의료 폐기물 소각의 위험성을 강조하며 중금속, 산성 가스, 일산화탄소, 유기 화합물, 병원균을 예로 들며 의료 폐기물 소각의 위험성을 강조했습니다. 개발도상국에서는 여전히 소규모 소각이나 매립이 일반적인 방법입니다. 이와 대조적으로 많은 선진국에서는 다이옥신이 없는 기술을 선호하는 의료용 소각로를 단계적으로 폐지하고 있습니다. 특히 아일랜드, 포르투갈, 독일과 같은 국가에서는 탄소 배출량 감축 목표와 폐기물 에너지화 솔루션으로의 전환에 따라 소각장을 폐쇄하거나 소각장 사용을 유예하고 있어 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장의 잠재력이 더욱 커지고 있습니다.
급속한 인구 고령화와 엄격한 의료 폐기물 규제로 인해 유럽은 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장에 유리한 환경을 제공합니다. 예를 들어 서유럽은 병상당 3-6kg의 바이오 의료 폐기물 통계를 보고하고 있어 일일 폐기물 발생량에서 세계 선두를 달리고 있습니다. 강력한 폐기물 처리 인프라와 높은 폐기물 배출량을 고려할 때, 이러한 선진 지역은 전 세계 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장을 지배할 준비가 되어 있습니다.
바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장은 특히 개발도상국의 의료 폐기물 급증에 힘입어 상당한 성장세를 보일 것으로 예상됩니다. 또한 유럽과 같은 선진 지역을 중심으로 폐기물 관리에 대한 엄격한 규제와 기술 혁신이 시장의 전망을 더욱 밝게 하고 있습니다.
독일은 정교하고 엄격하게 규제되는 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시스템을 자랑합니다. 그 핵심은 폐기물 예방, 재활용, 재사용 및 폐기를 감독하는 폐쇄 물질 순환 폐기물 관리법입니다. 또한 국내 의료 기관은 감염 관리 및 안전 의무를 준수해야 합니다.
예를들어, 병원은 안전 및 법적 기준을 준수할 책임이 있는 폐기물 처리 감독관을 임명합니다. 또한 폐기물 처리를 시설의 품질 관리에 통합합니다. 특히 의료 폐기물의 75-90%는 생활 폐기물과 유사하기 때문에 지자체 채널을 통해 재활용 또는 소각하기에 적합합니다.
시설에서는 바늘이나 메스 같은 위험한 품목을 구멍이 뚫리지 않고 누출되지 않으며 잠금장치가 있는 용기에 담아 처리합니다. 폐기물 분리는 발생지에서 시작되며, 별도의 쓰레기통과 주머니가 이 과정을 돕습니다. 병원균 오염을 고려할 때 이 폐기물의 처리는 전문 업체에서 처리합니다.
독일에서는 바이오 의료 폐기물을 관리하는 주요 기술로 소각, 화학 소독, 습식 열처리(증기 멸균), 마이크로파 조사, 토지 처분, 수익화 등이 있습니다.
바이오 의료 폐기물 관리를 위한 국가의 전략은 세심한 분리, 안전한 처리, 친환경적인 폐기 관행에 중점을 두고 있습니다. 또한 재활용과 비용 효율성도 강조합니다. 이 포괄적인 시스템은 의료 전문가, 대중, 환경을 의료 폐기물과 관련된 위험으로부터 보호하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
엄격한 규제와 첨단 기술을 지원하는 독일의 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시스템은 환경 및 공중 안전에 주목하면서 의료 폐기물의 확실한 처분과 재활용을 보장합니다.
유럽의 바이오 의료 폐기물 관리 시장은 중간에서 높은 수준의 시장 집중도를 보이고 있으며, 주요 업체들이 지배력을 행사하고 있습니다. 이들은 첨단 기술을 활용하고 엄격한 규정을 준수하며 종합적인 폐기물 관리 솔루션을 제공합니다. 주요 기업으로는 SUEZ Group, Veolia Environmental Services, Remondis Medison, WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC, Bertin Technologies 등이 있습니다.
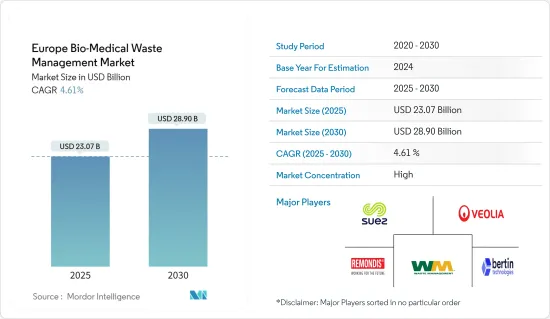
The Europe Bio-Medical Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 23.07 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 28.90 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.61% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
The European bio-medical waste management market plays a pivotal role in the waste management industry, spurred by strict regulatory measures, a surge in healthcare activities, and an amplified focus on properly disposing of bio-medical waste.
European hospitals generate around 6 million tons of medical waste yearly, about one-third of which originates in operating rooms. Most of this solid waste is potentially recyclable unless contaminated by bodily fluids. Infectious waste, constituting only 2-3% of hospital waste, is significantly less than the 50-70% found in biohazard waste streams.
Germany's healthcare industry generates a small portion of waste that requires specialized handling. Approximately 5,000 kilograms, or up to 5%, of the country's annual healthcare waste falls under the category of infectious waste. This subset is deemed hazardous due to its infection risk and is thus classified under the Abfallverzeichnisverordnung (AVV), or waste directory regulation.
The production rate of healthcare waste (HCW) varies. It is influenced by waste management practices, the nature of healthcare facilities and their specializations, the availability of reusable equipment, and the daily patient load. Developing nations typically report lower registered HCW production than their developed counterparts. For instance, in Europe, HCW production rates range from 3.5 to 4.4 kg/bed/day, with specific figures like Norway at 3.9 kg/bed/day, Greece varying from 0.3 to 3.6 kg/bed/day, and France at 2.7 to 3.3 kg/bed/day.
Europe's bio-medical waste management market is consistently growing, primarily fueled by the mounting medical waste from expanding healthcare setups, research centers, and diagnostic labs. This growth trend is expected to persist, bolstered by the surging healthcare demands, especially during COVID-19, underscoring the criticality of effective bio-medical waste management.
Regulations from entities like the European Union and national governments underscore the need for proper disposal and treatment of bio-medical waste, emphasizing public health and environmental protection. Technological advancements, including innovations in waste treatment like autoclaving, incineration, and chemical treatments, are boosting the efficiency and safety of bio-medical waste management.
As the number of hospitals, clinics, and research facilities rises, along with the aging demographic, the volume of bio-medical waste also increases. Moreover, a heightened awareness of the risks associated with improper bio-medical waste disposal is spurring the demand for professional waste management services.
While these advanced waste treatment technologies and regulatory compliance are crucial, they come at a significant cost, especially for smaller healthcare entities. Waste management service providers face challenges in navigating the intricate and varied regulations prevalent across European nations.
The healthcare industry's expansion has significantly boosted medical waste generation, especially in developing nations. With the surge in hospital admissions during the pandemic, the production of bio-medical waste is set to escalate. In a typical developing country, the volume of medical waste generated, averaging 0.5-2.5 kg per bed per day, hinges largely on demographics and healthcare services. As infectious diseases increase, the bio-medical waste management market is primed for substantial growth. Furthermore, the mounting accumulation of microbiological, human anatomical, and animal waste will further expand this market.
In 2004, a WHO policy paper and the Stockholm Convention underscored the risks of incinerating healthcare waste, highlighting heavy metals, acid gases, carbon monoxide, organic compounds, and pathogens. The prevalent methods in developing nations remain small-scale incineration or landfilling. In contrast, many developed countries are phasing out healthcare incinerators favoring dioxin-free technologies. Notably, nations like Ireland, Portugal, and Germany have either shuttered incinerators or placed moratoriums on them, driven by their carbon emission reduction goals and a shift toward waste-to-energy solutions, which, in turn, augments the bio-medical waste management market's potential.
With its rapidly aging population and stringent healthcare waste regulations, Europe presents a favorable landscape for the bio-medical waste management market. Western Europe, for instance, reports bio-medical waste statistics of 3-6 kg per bed, making it a global leader in daily waste generation. Given their robust waste disposal infrastructure and higher waste output, these developed regions are poised to dominate the global bio-medical waste management market.
The bio-medical waste management market is poised for substantial growth, fueled by a surge in medical waste, especially in developing nations. Additionally, stringent regulations and technological innovations in waste management, notably in advanced regions such as Europe, are bolstering the market's prospects.
Germany boasts a sophisticated and tightly regulated system for managing bio-medical waste. At its core is the Closed Substance Cycle Waste Management Act, which oversees waste prevention, recycling, reuse, and disposal. In addition, healthcare institutions in the country must adhere to infection control and safety mandates.
Hospitals, for instance, appoint a waste disposal overseer responsible for ensuring compliance with safety and legal standards. They also integrate waste disposal into the facility's quality management. Notably, 75-90% of healthcare waste mirrors domestic waste, making it suitable for recycling or incineration via municipal channels.
Facilities handle hazardous items like needles and scalpels in puncture-resistant, leak-proof, and lockable containers. Waste separation begins at the source, with distinct bins and sacs aiding the process. Given its pathogen contamination, specialized companies handle the disposal of this waste.
In Germany, the primary technologies for managing bio-medical waste encompass incineration, chemical disinfection, wet thermal treatment (steam sterilization), microwave irradiation, land disposal, and monetization.
The nation's strategy for bio-medical waste management centers on meticulous segregation, secure handling, and eco-conscious disposal practices. It also underscores recycling and cost-efficiency. This comprehensive system aims to shield healthcare professionals, the public, and the environment from the risks linked to medical waste.
Germany's bio-medical waste management system, supported by stringent regulations and advanced technologies, ensures the secure disposal and recycling of medical waste, with a primary focus on environmental and public safety.
The European bio-medical waste management market exhibits a moderate to high level of market concentration, with key players wielding dominance. They leverage cutting-edge technologies, adhere to strict regulations, and offer holistic waste management solutions. Some key players are SUEZ Group, Veolia Environmental Services, Remondis Medison, WM Intellectual Property Holdings LLC, and Bertin Technologies.