
리튬이온 배터리용 할로겐화물 고체 전해질 관련 특허 출원 및 공개 동향을 분석하고, 특허 공개 건수 추이(국가별, 특허권자별), 부문별 주요 특허권자 및 신규 진출기업, 주요 기업의 포지셔닝 및 특허 포트폴리오 확대 정도, 재료 구성별/기술 과제별/기술 과제별 특허 리스트, 주요 기업의 IP 프로파일(주요 특허 포트폴리오 개요, 기술 커버리지, 지역적 커버리지 등) 등을 조사하였습니다. 기술 과제별 특허 리스트, 주요 기업의 IP 프로파일(특허 포트폴리오 개요, 기술적 커버리지, 지역적 커버리지, 주요 특허등) 등을 조사하고, 분석 대상 특허(총 330여 건)의 개요를 정리한 엑셀 파일을 첨부해 드립니다.
고체 리튬이온 배터리는 안전성과 높은 에너지 밀도라는 주목할 만한 장점으로 인해 최근 수십년간 큰 주목을 받고 있습니다. 이 유망한 차세대 리튬 배터리의 실용화를 위해서는 빠른 이온 운송과 우수한 안정성을 가진 고체 전해질(SE)이 필수적입니다. 이에 따라 황화물계 전해질, 산화물계 전해질 등 무기 고체 전해질에 대한 연구가 활발히 진행되어 왔습니다. 그러나 두 전해질 모두 전도성과 안정성의 최적 균형을 이루지 못하고 있습니다. 산화물은 입계 임피던스가 높고, 황화물은 안정성이 낮습니다. 그러나 할로겐화물 고체 전해질은 상온에서 높은 이온 전도도(>10-3 S.cm-1), 산화물 양극 재료와의 우수한 호환성, 우수한 화학적 안정성 및 확장성으로 인해 고체 리튬이온 배터리의 가장 유망한 대안 중 하나로 인식되고 있습니다.
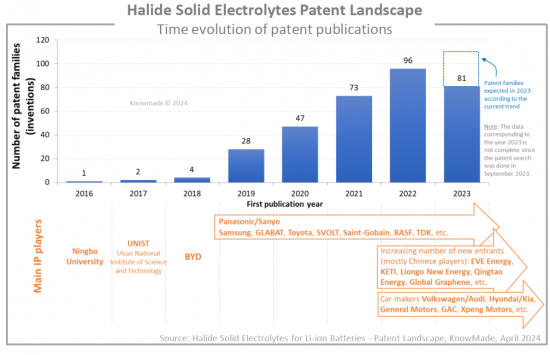
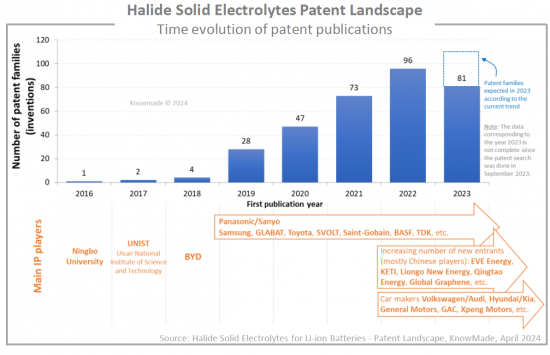
고체 리튬이온 배터리 관련 특허 모니터링을 통해 할로겐화물 고체 전해질에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다. 2023년 9월 현재, 리튬이온 배터리용 할로겐화물 고체 전해질 소재에 대한 특허가 330건 이상 출원되었습니다. 고체 배터리 산업에서 사업을 운영하는 기업은 기술, 경쟁, 지적재산권(IP) 관점에서 이러한 신흥 소재를 면밀히 검토하는 것이 매우 중요합니다.
이 보고서는 주요 특허권자(특허 양수인)의 특허 포트폴리오의 강점, 주요 특허권자(특허 양수인)의 주요 기술 및 활용 분야를 분석합니다. 또한 특허기술과 그 활용 현황 및 동향에 대한 개요를 제공합니다. 또한 이 분야의 선도기업과 신규 진입기업의 전략적 및 기술적 방향성을 검토하고 있습니다.
특허는 청구대상 물질 조성(LiMX4, Li3MX6, 할로겐화 물질 단독, 쉘을 갖는 할로겐화 물질, 다른 물질과 혼합된 할로겐화 물질), 청구대상 제조방법(메카니컬, 공융, 액상) 및 과제/해결방안, 발명에 의해 개시된 실온에서의 실온에서 가장 좋은 재료/이온 전도도에 따라 수작업으로 분류되어 있습니다.
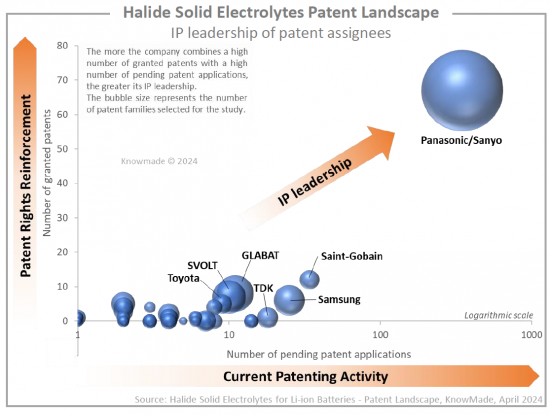
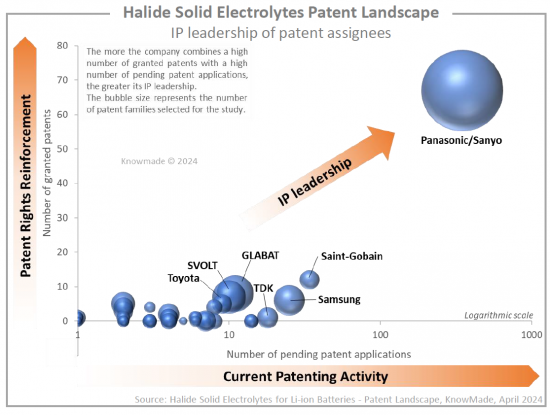
파나소닉/산요가 할로겐화물 고체 전해질 특허를 주도하고 있으며, 삼성, GLABAT, SVOLT, Saint-Gobain, TDK가 그 뒤를 잇고 있습니다. 또한 IP 분석을 통해 EVE Energy, 한국전자통신연구원(KETI), Liongo New Energy, Qingtao Energy, Samsung, GLABAT, SVOLT, Saint-Gobain, TDK 등이 2022년 이후 최초로 할로겐화물 관련 특허를 출원한 60개 이상의 IP 신규 시장 진출기업을 확인할 수 있었습니다. Energy, Qingtao Energy Development, Global Graphene 등이 있습니다. 특허 신규 시장 진출기업의 80%가 중국 출신입니다. 이 섹션에서는 주요 기업(Panasonic, Samsung, Saint-Govain, GLABAT, SVOLT, EVE Energy, University of Western Ontario, TDK, Toyota 등)이 보유한 IP 포트폴리오에 초점을 맞추었습니다. 각각의 할로겐화물 고체 전해질 관련 특허 포트폴리오에 대한 개요와 주요 특허 기술에 대한 설명을 제공합니다.
이 보고서에는 분석 대상의 모든 특허를 포함하는 광범위한 엑셀 데이터베이스도 포함되어 있습니다. 이 편리한 특허 데이터베이스는 다기준 검색이 가능하며, 특허 공개 번호, 업데이트된 온라인 데이터베이스에 대한 하이퍼링크(원문, 법적 지위 등), 우선일, 제목, 요약, 특허 양수인, 부문(과제/솔루션, 재료 구성, 할로겐화물의 구성, 합성 방법 등)를 포함하고 있습니다. 포함합니다.
Baoneng Group, Baowu Steel Group, BASF, Beijing Institute of Technology, BYD, China Automotive Battery Research Institute, China Electrics, Corning, EVE Energy, FAW(China First Automobile Works), Global Graphene, GRINM(General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals) / GRIMAT, GRIREM Advanced Materials, GTC Power, Guolian Automobile Power Battery Research Institute(GLABAT), Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy / Gotion, Hanyang University, Hyundai / Kia, Institute of Chemistry - Chinese Academy of Sciences, Korea Electronics Technology Institute(KETI), Liongo New Energy Technology, Nankai University, Nanmu Nanotechnology, Nichia, Panasonic / Sanyo, QingTao Energy Development, Rare Earth Functional Materials Innovation Center, Saint-Gobain, Samsung, Shenzhen University, Silver Leaf Element, Solvay, South University of Science & Technology of China(SUSTech), SVOLT / Fengchao Energy Technology, TDK, Toyota, Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, University of Maryland, University of Waterloo, University of Western Ontario, University of Science and Technology of China(USTC), Xi'an Jiaotong University, Yonsei University, Zengzhou New Century Materials Genome Institute, Zhejiang University 등
Solid-state Li-ion batteries have garnered significant attention in recent decades due to their notable advantages of safety and potential for high energy density. Solid electrolytes (SE) with rapid ionic transport and excellent stability are essential for the commercialization of this promising next-generation of Lithium batteries. Hence, there has been extensive exploration of inorganic solid electrolytes, including sulfide- and oxide-based electrolytes. Unfortunately, both have been unable to strike an optimal balance between conductivity and stability. Oxides suffer from high impedance of grain boundaries, while sulfides experience poor stability. However, halide-based solid electrolytes are increasingly being recognized as one of the most promising options for solid-state Li-ion batteries, owing to their decent room temperature ionic conductivity (>10-3 S.cm-1), good compatibility with oxide cathode materials, excellent chemical stability, and scalability.
The increasing interest in halide solid electrolytes has been observed while monitoring patents on solid-state Li-ion batteries. As of September 2023, over 330 patent families have been published on halide solid electrolyte materials for Li-ion batteries. It is now crucial for companies operating in the solid-state battery industry to closely examine these emerging materials from technological, competitive, and intellectual property (IP) perspectives.
In this context, Knowmade is releasing a new patent landscape report that focuses on halide solid electrolyte materials for Li-ion batteries. In this report, Knowmade's analysts have selected and analyzed over 860 patents and patent applications from more than 330 patent families (inventions) filed by 110+ different entities. The report provides a detailed analysis of the IP landscape and noteworthy patents concerning halide solid electrolyte materials. This new IP report is complementary to our previous patent landscape reports and patent monitors on solid-state batteries.
IP competition analysis should reflect the vision of players with a strategy to enter and develop their business in the solid-state Li-ion battery market. In this report, Knowmade's analysts provide a comprehensive overview of the competitive IP landscape and latest technological developments in this field. The report covers IP dynamics and key trends in terms of patents applications, patent assignees, filing countries, and patented technologies. It also identifies the IP leaders, most active patent applicants, and new entrants in the IP landscape. The report also sheds light on under-the-radar companies and new players in this field.
In this report, we analyze the strength of patent portfolios and the technology and application focus of key patent assignees. An overview of the current status and trends of patented technologies and their applications is also provided. Furthermore, the report examines the strategic and technological directions of both leading companies and newcomers in the field.
The patents have been manually categorized according the claimed material compositions (LiMX4, Li3MX6, halide material alone, halide material with a shell, halide material mixed with another material), the claimed manufacturing methods (mechano-chemical, co-melting, liquid-phase), as well as the challenges/solutions and the best materials/ionic conductivities at room temperature disclosed by the inventions.
Panasonic/Sanyo is leading the halide solid electrolytes patent landscape, challenged by Samsung, GLABAT, SVOLT, Saint-Gobain, and TDK. Additionally, the IP analysis allowed us to pinpoint over 60 IP newcomers who filed their first halide-related patents in 2022 or after: EVE Energy, Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI), Liongo New Energy, Qingtao Energy Development, Global Graphene, etc. 80% of new entrants in the patent landscape come from China. In a dedicated section, we focus on the IP portfolios held by key players (Panasonic, Samsung, Saint-Gobain, GLABAT, SVOLT, EVE Energy, University of Western Ontario, TDK, Toyota, etc.). For each, we provide an overview of their patent portfolio related to halide solid electrolytes and a description of their key patented technologies.
This report also includes an extensive Excel database with all patents analyzed in this study. This useful patent database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent publication numbers, hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), priority date, title, abstract, patent assignees, and segments (challenges/solutions, material composition, halide formula, synthesis methods, etc.).
Baoneng Group, Baowu Steel Group, BASF, Beijing Institute of Technology, BYD, China Automotive Battery Research Institute, China Electrics, Corning, EVE Energy, FAW (China First Automobile Works), Global Graphene, GRINM (General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals) / GRIMAT, GRIREM Advanced Materials, GTC Power, Guolian Automobile Power Battery Research Institute (GLABAT), Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy / Gotion, Hanyang University, Hyundai / Kia, Institute of Chemistry - Chinese Academy of Sciences, Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI), Liongo New Energy Technology, Nankai University, Nanmu Nanotechnology, Nichia, Panasonic / Sanyo, QingTao Energy Development, Rare Earth Functional Materials Innovation Center, Saint-Gobain, Samsung, Shenzhen University, Silver Leaf Element, Solvay, South University of Science & Technology of China (SUSTech), SVOLT / Fengchao Energy Technology, TDK, Toyota, Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, University of Maryland, University of Waterloo, University of Western Ontario, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), Xi'an Jiaotong University, Yonsei University, Zengzhou New Century Materials Genome Institute, Zhejiang University, and more.