
일반 항공 시장은 2025년 351억 5,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년 365억 9,000만 달러로 성장할 전망이며, 2031년까지 447억 6,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.
예측 기간(2026-2031년) CAGR은 4.12%로 성장이 전망되고 있습니다.

꾸준한 부의 창출, 기업의 수익성, 포인트-투-포인트 이동의 매력 증가가 이 기세를 지지하고 있습니다. 비즈니스 여행은 여전히 높은 수익 수요를 견인하고 있지만, 전기 수직 이착륙기(eVTOL) 프로그램의 인증 과정이 진행됨에 따라 시장 환경이 확산되고 있습니다. 분양 소유 플랫폼이 액세스를 확대하는 한편, 개발도상국에서의 인프라 정비가 새로운 노선을 개척하고 있습니다. 기존의 터빈 추진 시스템은 확고한 지위를 유지하고 있지만, 배터리 진보 및 지속 가능한 항공 연료(SAF)의 인센티브가 보다 깨끗한 운항의 기반을 마련하고 있습니다.
견조한 자산 확대가 프리미엄 기계 수요를 견인하고 있으며, 부유층(HNWIs)은 시간과 프라이버시를 특히 중시하고 있습니다. 2024년 상당한 수익 회복 이후 대기업은 경영진의 생산성 확보 및 혼잡한 허브 공항의 회피를 목적으로 항공기를 강화했습니다. 아시아태평양은 신규 부유층의 40%를 창출했지만, 공항 밀도에서는 여전히 지연을 취하고 있어 대륙간을 논스톱으로 비행 가능한 중형 및 대형 캐빈의 제트기에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있습니다. 기체 계획 담당자는 정기 항공사에 비해 추적 가능한 생산성 향상을 지적하고 구매 정당성을 강화하고 있습니다. 그 결과 안정적인 납품 파이프라인이 형성되고, 일반 항공 시장은 항공 업계 전체의 주기성으로부터 보호되고 있습니다.
북미의 비즈니스 제트기의 중앙 연령은 2024년에 20년을 넘었으며, 운항 회사는 구식 기체를 저연비 모델로 갱신하는 움직임을 가속시키고 있습니다. 최신 비행 갑판은 안전성과 연결성을 향상시켜 보수 비용을 초과하는 가치를 제공합니다. 유럽에서는 소음 규제의 강화에 의해 기준 부적합기의 조기 퇴역이 진행되어 신조기 수요를 밀어 올리고 있습니다. 여러 기계를 보유한 부문에서는 디지털에 의한 전기체의 건강 상태 모니터링이 기본 요건이 되었습니다. 따라서 현대화에 대한 지출은 수명주기 비용을 줄이고 운영 신뢰성을 향상시키는 전략적 투자로 자리매김하고 있습니다.
2024년에는 공급망 압박에 따라 부품 비용이 상승하여 항공기의 정가가 8-12% 상승했습니다. 연료 가격 변동 및 예비 부품 가격 상승은 시간당 운영 예산에 추가 압력을 가하고 있습니다. 보험 인수 회사는 조종사 부족 위험 평가를 배경으로 보험료를 인상했으며 금리 인상은 채무 상환 부담을 증가시켰습니다. 통화 약세인 신흥 시장에서는 달러 표시 거래가 더욱 저렴해졌습니다. 이러한 임박한 비용 장벽은 장기적인 펀더멘탈스가 건전함에도 불구하고 일부 구매 결정이 미루어질 수 있습니다.
비즈니스 제트는 2025년 일반 항공 시장 점유율의 46.36%를 차지했으며, 시간 엄수가 요구되는 기업 이동에 있어서의 우위성을 나타냈습니다. 대형 캐빈 플랫폼은 대륙간 직항편의 항속거리와 고쾌감 레이아웃으로 수익면에서 주도적 입장에 있습니다. 중형기는 지역 미션용으로 경제성의 밸런스가 잡히고 있는 한편, 라이트 제트는 단거리 이동을 목적으로 하는 오너 파일럿이나 전세 브로커를 매료하고 있습니다. 첨단 항공 이동성인 eVTOL 부문은 현재 상대적으로 소규모입니다. 그러나 인증 장애물이 낮아지면서 도시 혼잡이 보급을 촉진함에 따라 이 부문은 CAGR 3.62%가 예상됩니다. 회전익기는 여전히 포인트 투 포인트 긴급 운송 및 실용 임무에 필수적이지만, eVTOL 플랫폼에 의한 도시 지역의 경쟁이 심화되고 있습니다.
신규 설계의 다양한 개발 파이프라인은 OEM 각사의 확고한 자신감을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 조비 에비에이션은 2024년 미국 연방 항공국(FAA)의 주요 인증 기준을 달성하여 서비스 시작이 가까이 있음을 보여주었습니다. 터보프롭 및 피스톤 고정익기 카테고리는 활주로 제약에 의해 단거리 이착륙 성능이 요구되는 훈련, 화물 및 지역 접속의 틈새 시장에서 계속 활약하고 있습니다. 전반적으로 다양한 임무 세트가 일반 부문 시장을 단일 부문 부진으로부터 보호하는 역할을 합니다.
2025년 현재, 기존의 피스톤 엔진 및 터빈 엔진은 일반 항공 시장의 90.98%를 차지했습니다. 비즈니스 제트는 고도의 성능과 세계 정비 네트워크 지원을 통해 터빈 엔진이 주류입니다. 피스톤 엔진은 도입 비용이 낮기 때문에 훈련 장비의 주력으로 계속되고 있습니다. 전 전기 추진 시스템은 현시점에서는 소규모이지만, 배터리 에너지 밀도의 향상에 따라 CAGR 4.49%로 진전하고 있습니다. 하이브리드 전기 컨셉은 항속 거리의 과제를 해결하면서 초기의 지속가능성 목표를 달성하고 있습니다. 인증기관 및 제조업체와 제휴해 전동 추진 시스템의 안전 기준을 최종화하고 있으며, 이에 따라 2020년대 말까지의 광범위한 보급을 위한 기반이 갖추어지고 있습니다.
운영 비용의 이점, 특히 단거리 훈련 및 도시 간 셔틀 용도의 장점은 도입의 결정적인 요인으로 부상하고 있습니다. 지방 공항의 충전 인프라 정비 프로젝트는 재생에너지 의무화와 연동하여 생태계 정비를 가속화하고 있습니다. 그러나 배터리가 장거리 임무의 요구를 충족할 때까지 기존 터빈은 일반 비행 시장에서 주도권을 유지할 것으로 예측됩니다.
북미는 2025년 시점에서 일반 항공 시장 점유율의 51.12%를 차지하며 미국에서 20만기 이상의 가동기수와 고밀도 공항 네트워크가 기반을 두고 있습니다. 성숙한 자금 조달 경로, 종합적인 정비망, 풍부한 파일럿 인재가 지역의 주도적 지위를 강화하고 있습니다. 캐나다에서는 자원 탐사와 원격 지역에 대한 액세스에 항공을 활용하고, 멕시코에서는 관광 회랑에 있어서 프라이빗 차터기에 의한 포인트 투 포인트의 고급 여객 수송이 의존되고 있습니다. 기업의 재무 기반의 힘과 안정적인 잔존 가치의 성능은 지역 기체 현대화 사이클을 구축하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 6.33%로 가장 빠르게 성장이 전망되는 시장입니다. 중국이 금세기 말까지 500개의 일반 항공 공항을 정비할 계획은 지역의 항공 네트워크를 재구성합니다. 인도에서는 경제 성장이 전세 수요를 밀어 올리고 있으며, 인프라의 병목도 관민 연계에 의해 서서히 해소되고 있습니다. 일본과 한국은 높은 기술 도입률을 유지하고 항공전자기기 및 지속가능성 혁신을 촉진, 그 파급 효과는 세계 기체로 확산되고 있습니다. 호주 운항 회사는 인구 희박한 내륙 지역에서 광업 지원 및 의료 지원을 위해 계속해서 일반 에비에이션을 활용하고 있습니다.
유럽은 밀집한 기업 회랑과 정교한 전세 네트워크에 힘입어 확고한 점유율을 유지하고 있습니다. 엄격한 환경 규제가 기체 갱신을 가속시켜 OEM 제조업체에 지속 가능한 항공 연료 대응을 촉구하고 있습니다. EU의 조화화 노력이 마찰 완화를 도모하고 있는 반면, 브렉짓트 관련 관세 및 규제의 차이가 국경을 넘은 운항을 복잡화시키고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카에서는 천연 자원 프로젝트와 VIP 수송이 수요를 지지하고 있지만, 규제 성숙도의 편차 및 인프라의 부족이, 단기적인 기체 확대를 억제하고 있습니다.
The general aviation market was valued at USD 35.15 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 36.59 billion in 2026 to reach USD 44.76 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.12% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
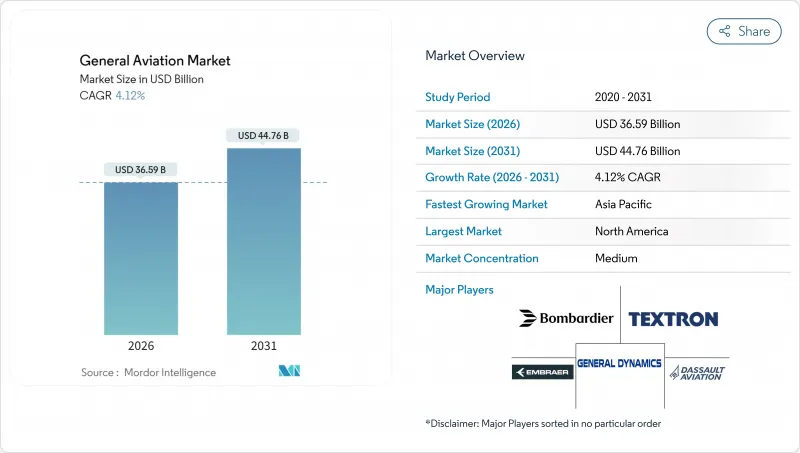
Steady wealth creation, corporate profitability, and the rising appeal of point-to-point travel underpin this momentum. Business travel continues to dominate high-yield demand, yet the landscape is widening as electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) programs advance certification processes. Fractional ownership platforms widen access, while infrastructure upgrades in developing economies open new routes. Established turbine propulsion retains a firm footing, but battery advances and sustainable aviation fuel incentives set the stage for cleaner operations.
Robust wealth expansion feeds premium aircraft demand as high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) place a premium on time and privacy. After a strong 2024 earnings rebound, large corporations added aircraft to secure executive productivity and bypass congested hubs. Asia-Pacific generated 40% of new wealth pools, yet still lags in airport density, intensifying demand for mid-size and large-cabin jets capable of nonstop intercontinental legs. Fleet planners cite trackable productivity gains over scheduled airlines, reinforcing purchase justification. The result is a stable delivery pipeline that shields the general aviation market from broader airline cyclicality.
North America's median business jet age crossed 20 years in 2024, spurring operators to replace legacy cabins with fuel-efficient models. Modern flight decks deliver safety and connectivity upgrades that outweigh retrofit costs. Europe's tightening noise rules are grounding non-compliant units sooner, lifting new-build demand. For multi-aircraft departments, digital fleet-wide health monitoring is now a baseline requirement. Modernization spending is thus framed as a strategic investment that lowers lifecycle costs and enhances dispatch reliability.
Aircraft sticker prices climbed 8-12% in 2024 as supply-chain strain pushed component costs upward. Fuel volatility and spares inflation added pressure to hourly operating budgets. Insurance underwriters raised premiums amid pilot-shortage risk assessments, while rising interest rates increased debt-service burdens. For currency-weak emerging markets, dollar-denominated transactions became even less affordable. These immediate cost hurdles may defer some purchase decisions despite healthy long-term fundamentals.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Business jets accounted for 46.36% of the general aviation market share in 2025, reflecting their dominance in time-critical corporate travel. Large-cabin platforms lead in revenue thanks to nonstop intercontinental range and high-comfort layouts. Mid-size variants offer balanced economics for regional missions, whereas light jets attract owner-pilots and charter brokers targeting short hops. The advanced air mobility eVTOLs segment is comparatively small today. Yet, this segment is set for a 3.62% CAGR as certification hurdles fall and urban congestion drives adoption. Rotorcraft remain indispensable for point-to-point emergency and utility roles but face growing urban competition from eVTOL platforms.
A diverse pipeline of clean-sheet designs underscores OEM confidence. Joby Aviation reached key FAA milestones in 2024, signaling imminent service entry. Turboprop and piston fixed-wing categories continue to serve training, cargo, and regional connectivity niches where runway constraints favor short-field performance. Overall, variety across mission sets insulates the general aviation market from a single-segment downturn.
Conventional piston and turbine engines comprised 90.98% of the general aviation market in 2025. Turbine powerplants prevail in business jets for their high-altitude performance and global maintenance network support. Piston engines remain the mainstay of training fleets, benefiting from lower entry costs. Although only a small base today, all-electric propulsion is advancing at a 4.49% CAGR as battery-energy density improves. Hybrid-electric concepts are bridging range gaps while meeting early sustainability goals. Certification authorities are working alongside manufacturers to finalize electric-propulsion safety codes, setting the stage for broader adoption by decade's end.
Operating-cost advantages, especially in short-hop training or urban shuttle applications, are emerging as pivotal adoption drivers. Charging-infrastructure projects at regional airports pair with renewable-energy mandates, accelerating ecosystem readiness. Still, until batteries meet longer-range mission needs, conventional turbines will retain primacy in the general aviation market.
The General Aviation Market Report is Segmented by Aircraft Type (Business Jets, and More), Propulsion Type (Conventional Piston/Turbine, Hybrid-Electric, and More), Ownership Model (Full Private Ownership, and More), End-User Application (Business/Corporate Transport, Personal and Leisure Flying, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America secured 51.12% of the general aviation market share in 2025, anchored by the United States' 200,000-plus active fleet and dense airport grid. Mature financing channels, comprehensive maintenance coverage, and a deep pilot pool reinforce regional leadership. Canada leverages aviation for resource exploration and remote-community access, whereas Mexico's tourism corridors rely on private charters for point-to-point luxury traffic. Corporate balance-sheet strength and consistent residual-value performance build regional fleet modernization cycles.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing arena with a 6.33% CAGR forecast through 2031. China's plan to establish 500 general aviation airports by the decade's end reshapes local air connectivity. India's economic upswing is lifting charter activity despite infrastructure bottlenecks that are gradually easing via public-private partnerships. Japan and South Korea maintain high technology adoption rates, catalyzing avionics and sustainability innovations that ripple across global fleets. Australian operators continue to exploit general aviation for mining and medical outreach in sparsely populated interiors.
Europe commands a solid share, supported by dense corporate corridors and a sophisticated charter network. Stringent environmental rules are accelerating fleet renewals and pushing OEMs toward sustainable aviation fuel compatibility. Though ongoing EU harmonization efforts seek to mitigate friction, Brexit-related customs and regulatory divergence complicate cross-border operations. Natural-resource projects and VIP transport underpin demand in the Middle East and Africa, but varying regulatory maturity and infrastructure gaps temper near-term fleet expansion.