
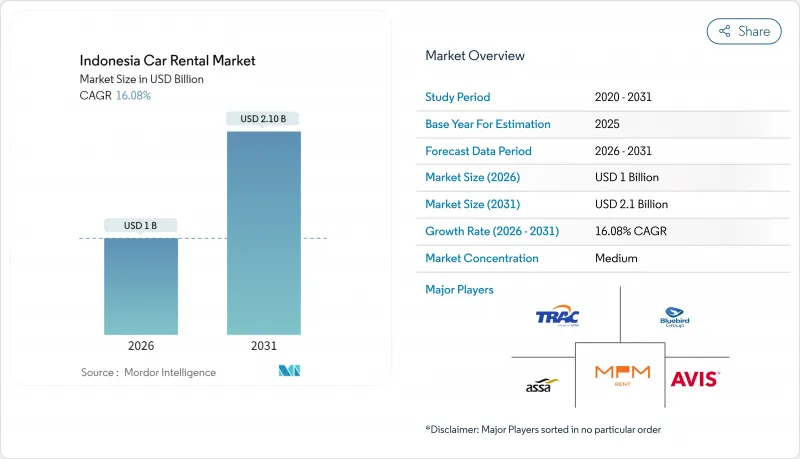
인도네시아의 렌터카 시장 규모는 2026년 10억 달러로 추정되고 있고, 2025년 8억 6,000만 달러에서 성장을 계속하고 있습니다. 2031년까지 21억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2026-2031년 CAGR 16.08%로 확대될 것으로 전망됩니다.

향후 5년간 가처분소득 증가, 중산계급 여행 예산 확대, 스마트폰의 보급이 지속적인 2자리 성장의 호조건을 마련할 전망입니다. 정부가 2025년에 1,460만-1,600만 명의 외국인 관광객 수용을 목표로 하고 있으며(2024년 1,390만 명에서 증가), 2024년 인도네시아 GDP 성장률 5.05%를 배경으로 비즈니스 여행이 회복되는 가운데 관광 수요의 견조함이 나타났습니다. 온라인 플랫폼은 투명성, 주문형 가용성, 디지털 결제에 대한 고객의 기대를 재정의하고 있습니다. 한편, 배터리 전기자동차(BEV)에 대한 새로운 우대 조치는 전기화를 미래의 수익원으로 자리매김하고 있습니다. 앱 기반 모빌리티 에코시스템이 라이드 셰어링과 일상적인 임대 경계를 모호하게 함에 따라 경쟁 압력이 치열해지고 있으며 기존의 사업자들은 차량 현대화 및 데이터 구동형 가격 전략을 가속화할 필요가 있습니다.
2024년 인도네시아는 약 1,390만 명의 국제 관광객을 맞아 국내 여행자 수가 10억 회를 넘어 국경 제한 완화 후 관광업의 급속한 회복을 보였습니다. 관광부는 도착 시 비자 확대와 '10개의 새로운 발리' 관광지 프로모션을 배경으로 2025년 방문 관광객 수가 1,460만-1,600만 명으로 증가할 것으로 예측했습니다. 코모도 섬과 롬복 섬 등 지방 공항에 대한 대규모 자본 투자에 의해 좌석수가 증가하고, 여행객의 흐름이 자바 섬 이외에도 분산되고 있습니다. 세계여행관광협의회(WTTC)는 2025년 관광 부문이 GDP에 4.6% 공헌할 것으로 예측했습니다. 관광객 기반의 확대는 특히 대중 교통이 제한된 섬들에서 렌터카와 운전자 패키지 수요를 직접 촉진하고 있습니다.
2024년 인도네시아의 디지털 경제는 900억 달러의 대대에 이르렀으며 전자상거래 거래의 급증에 힘입어 더욱 성장할 전망입니다. 2024년에는 온라인 예약이 총 거래의 상당한 비율을 차지하고 소비자가 즉시 가격 비교, 현금 없는 결제, 로열티 혜택을 제공하는 슈퍼 앱에 모여들면서 연간 현저하게 성장하고 있습니다. 블루버드 택시 및 고제크의 연계와 같은 제휴를 통해 기존 차량 사업자는 전국 규모의 고객 기반을 획득하면서 고객 획득 비용을 절감할 수 있습니다. 어그리게이터는 풍부한 데이터를 활용하여 동적 가격 설정 미세 조정, 차량 가동률 최적화, 보험 및 부대 서비스 실시간 업셀을 실현하고 있습니다.
2024년 인도네시아에서는 Grab과 Gojek이 방대한 온디맨드 배차를 처리했습니다. 제안된 Grab과 GoTo의 제휴는 배달, 결제, 라이드 쉐어를 단일 지갑으로 통합하여 네트워크 효과를 더욱 심화시킬 수 있습니다. 도시 지역 소비자는 교통 체증 및 주차장 부족을 피하기 위해 셀프 드라이브 렌탈보다 도어 투 도어 라이드 서비스를 선호합니다. 법인 여행자도 경비 관리 대시보드를 통해 라이드 쉐어를 예약해 기존의 공항 픽업 카운터를 회피하고 있습니다. 관련성을 유지하기 위해 임대 기업은 시간 단위 패키지, 항공사와의 로열티 연계, 앱 기반 상품화의 영향을 받기 어려운 틈새 시장을 위한 프리미엄 SUV 도입 등을 모색하고 있습니다.
2025년 인도네시아 렌터카 시장 수익의 68.84%를 온라인 채널이 차지하였고, CAGR 16.85%로 확대하고 있습니다. 이 장점은 스마트폰의 높은 보급률, 무현금 결제 급성장, 여행 계획, 지도, 디지털 지갑을 통합한 슈퍼 앱에 대한 소비자의 친화성을 반영합니다. 오프라인 여행사 카운터에 뒷받침된 인도네시아 렌터카 시장 규모는 2025년에도 여전히 큰 수익을 유지하고 있지만, 소규모 사업자가 가격에 민감한 관광객을 획득하기 때문에 어그리게이터 포털에 차량을 게재하는 움직임이 퍼져 점유율을 저하시키고 있습니다.
슈퍼 앱 에코시스템은 라이드 셰어링, 식품 배달, 디지털 뱅킹을 통합하여 하루 단위 대여 패키지의 크로스셀을 촉진합니다. 기존 브랜드는 클라우드 기반 예약 엔진, 푸시 알림에 의한 할인, AI 탑재 고객 서비스 채팅봇을 도입하여 테크 플랫폼과 동등한 사용자 체험을 실현하고 있습니다. 온라인으로 수집된 데이터를 통해 국적, 여행 목적 및 지출액에 근거한 세분화가 가능해져, 사업자는 주행거리 제한의 A/B테스트나 Wi-Fi 라우터의 번들 판매에 의한 증수를 도모할 수 있습니다.
단기 예약(1-30일 대여)은 계절적인 관광 피크로 2025년 인도네시아 렌터카 시장에서 57.88%의 점유율을 차지했습니다. 장기 계약은 2025년에 이 시장에서 현저한 수익을 넘어 17.12%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 확대가 전망되고 있습니다. 기업은 자본 보전 및 유지 보수 책임을 서비스 제공업체로 이전하기 위해 운영 리스를 채택합니다.
장기 패키지에는 일반적으로 운전자 급여, 정기 점검, 풀 보험이 포함되어 있으며 고객은 잔존 가치 변동 위험으로부터 보호됩니다. 플릿 관리자는 텔레매틱스를 도입하고 연료 소비와 예방 보전을 모니터링하여 가동 중단 시간을 줄입니다. 이 동향은 중고차 처분 채널도 확립하고 있어 3-5년 경과한 차량은 경매에 걸리거나 라이드 셰어링 드라이버에 매각되어 개인 간 재판매보다 신속하게 자본을 회수하고 있습니다.
2025년의 수익 구성비로는 관광 분야가 63.74%를 차지했지만, 비즈니스 모빌리티 분야가 다음 성장 엔진으로서 17.62%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 확대 중입니다. 인도네시아의 투자 적격 등급과 신속한 라이선싱 허가는 국제 기업의 이전을 촉진하고 이그제큐티브 픽업, 프로젝트 현장 셔틀 및 주재원 가족 수송에 대한 수요를 증가시키고 있습니다. 공장 종업원을 위한 당일 통근 패키지 및 BPO 종사자용 시너지 밴도 대응 가능한 수요 규모를 확대하고 있습니다.
관광 예약은 발리, 요그야카르타, 롬복에 집중되어 있으며, 셀프 드라이브 패키지에는 여정 큐레이션과 다국어 지원 GPS 네비게이션이 포함됩니다. 렌터카 회사는 인도네시아의 섬도국이라는 지역 특성과 도시간 철도망의 부족을 배경으로 공항 마중 서비스, SIM 카드 키트의 우선 준비, 24시간 대응의 로드 사이드 어시스턴스를 커스터마이즈하고 있습니다. 동시에 법인 계약에 의한 수입의 다양화가 진행되어 계절 변동을 완화함과 동시에 예측 가능한 차량 가동률을 실현하고 있습니다.
The Indonesian car rental market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 1.0 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 0.86 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 2.1 billion, growing at 16.08% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Over the next five years, rising disposable incomes, expanding middle-class travel budgets, and widespread smartphone adoption set a favorable backdrop for sustained double-digit growth. The government's target of welcoming between 14.6 and 16 million foreign visitors in 2025, up from 13.9 million in 2024, signals resilient tourism demand even as business travel rebounds on the back of Indonesia's 5.05% GDP growth in 2024. Online platforms are redefining customer expectations around transparency, on-demand availability, and digital payments, while new incentives for battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) position electrification as a future profit pool. Competitive pressure intensifies as app-based mobility ecosystems blur the line between ride-hailing and daily rentals, prompting traditional operators to accelerate fleet modernization and data-driven pricing strategies.
In 2024, Indonesia welcomed around 13.9 million international visitors and recorded over 1 billion domestic journeys, marking a swift rebound in its tourism sector following the easing of border restrictions. The Ministry of Tourism projects inbound visitors will rise to between 14.6 and 16 million in 2025, supported by visa-on-arrival expansion and marketing of the "10 New Balis" destinations. Significant capital investment in Komodo, Lombok, and other regional airports increases seat capacity and disperses travel flows beyond Java. The World Travel & Tourism Council projects the sector will contribute 4.6% to GDP in 2025. A larger tourist base directly lifts self-drive rentals and chauffeured packages, particularly in islands where public transport is limited.
In 2024, Indonesia's digital economy hit the USD 90 billion mark, buoyed by a surge in e-commerce transactions, with projections indicating further growth. Online rental bookings accounted for a substantial share of the overall transactions in 2024 and are growing significantly annually as consumers gravitate to super-apps offering instant price comparison, cashless payments, and loyalty rewards. Partnerships like Blue Bird taxis integrating with Gojek allow legacy fleets to unlock a nationwide customer base while cutting acquisition costs. Aggregators use rich data to fine-tune dynamic pricing, optimize fleet utilization, and upsell insurance or ancillary services in real time.
Grab and Gojek processed a significant number of on-demand rides in Indonesia during 2024. A proposed Grab-GoTo tie-up could deepen network effects, bundling deliveries, payments, and ride-sharing into a single wallet. Urban consumers prefer door-to-door rides over self-drive rentals to avoid congestion fees and parking scarcity. Corporate travelers also book ride-hailing through expense-management dashboards, bypassing traditional airport pickup counters. To stay relevant, rental firms are exploring hourly packages, loyalty linkage with airlines, and premium SUVs to serve niches less exposed to app-based commoditization.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Online channels generated 68.84% of the Indonesian car rental market revenue in 2025, climbing at a 16.85% CAGR. The dominance reflects deep smartphone penetration, a cashless payment boom, and consumer comfort with super-apps integrating trip planning, mapping, and digital wallets. Indonesia's car rental market size, attributed to offline travel-agency counters, remained at significant revenue in 2025 but is losing share as small operators list fleets on aggregator portals to reach price-sensitive tourists.
Super-app ecosystems combine ride-hailing, food delivery, and digital banking, encouraging cross-selling day-long rental packages. Legacy brands adopt cloud-based reservation engines, push-notification discounts, and AI-enabled customer-service chatbots to match the user experience of tech platforms. Data captured online allows segmentation by nationality, trip purpose, and spend, enabling operators to A/B test mileage caps or bundle Wi-Fi routers for incremental revenue.
Short-term bookings, defined as rentals lasting 1-30 days, held a 57.88% share in the Indonesian car rental market in 2025 due to seasonal tourism peaks. Long-term contracts surpassed the noteworthy revenue i the Indonesian car rental market in 2025 and are projected to expand at a 17.12% CAGR. Corporations adopt operating leases to preserve capital and shift maintenance responsibilities to service providers.
Long-term packages typically include driver salaries, periodic servicing, and full insurance, insulating clients from residual-value swings. Fleet managers deploy telematics to monitor fuel consumption and preventive maintenance, reducing downtime. The trend also anchors used-vehicle disposal channels, where cars aged three to five years are auctioned or sold to ride-hailing drivers, recouping capital faster than private resales.
Tourism accounted for 63.74% of revenue in 2025; however, business mobility is on course to become the next growth engine, expanding at an 17.62% CAGR. Indonesia's investment-grade rating and quick licensing approvals spur multinational relocations, raising demand for executive transfers, project-site shuttles, and expatriate family transport. Daily commuting packages for factory staff and shared vans for BPO workers also widen addressable volumes.
Tourism bookings concentrate in Bali, Yogyakarta, and Lombok, where self-drive packages include itinerary curation and GPS navigation in multiple languages. Car rental firms tailor airport meet-and-greet services, fast-track SIM card kits, and 24/7 roadside assistance, leveraging Indonesia's archipelagic geography and limited inter-city rail. In parallel, corporate contracts diversify income, cushioning seasonality and yielding predictable fleet-utilization ratios.
The Indonesia Car Rental Market Report is Segmented by Booking Type (Online and Offline), Rental Duration (Short-Term, Medium-Term and Long-Term), Application (Tourism and Leisure, Daily Commuting, and More), Vehicle Type (Economy/Hatchback and More), Fuel Type (ICE-Petrol, ICE-Diesel, and More), End-User (Corporate and Individual), Rental Channel, and Region. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).