
인도의 산업 자동화 시장은 2025년 172억 8,000만 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 197억 1,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 380억 2,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
예측 기간(2026-2031년) 동안의 CAGR은 14.05%로 전망되고 있습니다.

지속적인 정책 지원, 구식 플랜트의 급속한 근대화, 센서 가격의 하락이 함께 작용하여 두 자릿수 성장이 지속되고 있습니다. 생산연동형 인센티브제도가 현금 급여를 인더스트리 4.0 대응도와 연동시킴으로써 외국 직접투자가 급증하여 생산성과 수출 경쟁력을 높이는 기존 설비의 개보수 붐을 일으켰습니다. 다국적 기업은 공급망의 단축과 수입 관세 회피를 위해 현지 생산 거점을 확대하고 중견 기업은 자본 제약을 극복하기 위해 클라우드 기반 실행 소프트웨어를 도입했습니다. 한편, 민간 주도의 5G 파일럿 사업과 엣지 컴퓨팅 플랫폼은 지연 우려를 낮추고, 가공 플랜트에서 예지보전의 도입을 촉진했습니다. 사이버 보안 대책과 숙련 노동력 확보는 계속 주시해야 할 점이지만, 정책 주도의 업그레이드 사이클에 의해 수요는 견조한 성장 궤도를 유지하고 있습니다.
2024년 이후 유입된 외국 직접투자에 의해 공장 자동화 전체의 예산이 확대되었습니다. 지멘스는 드라이브와 컨트롤러의 생산 확대에 100억 루피(1억 2,050만 달러)를, 미쓰비시 전기는 현지 조립 라인에 22억 루피(2,650만 달러)를 각각 투자했습니다. 이러한 기존 설비의 업그레이드는 신규 설비 투자보다 확장성과 모듈성이 뛰어난 장비를 부각시켜 신속한 투자 회수와 높은 설비 가동률을 실현합니다. 구자라트, 마하라슈트라, 타밀 나두의 클러스터는 관련 공급업체를 유치하여 밸류체인 전반에 걸쳐 기술 노하우를 보급하고 있습니다. 수출 지향 제조업체는 세계의 품질 기준과도 부합하여 고급 모션 컨트롤, 에너지 절약형 드라이브 및 기계 안전 시스템에 대한 수요를 높입니다.
생산연동형 인센티브(PLI) 프로그램은 2025년까지 1,402억 루피(16억 9,000만 달러)를 인더스트리 4.0에 대한 적합성을 입증하는 조건부로 개별 산업에 지급했습니다. 자동차 제조업체의 신청자는 PLC 제어 스테이션과 실시간 품질 모니터링을 갖춘 완벽하게 네트워크화된 생산 라인을 입증하지 않으면 단계적 수혜를 유지할 수 없습니다. 전자기기 제조업체는 더욱 엄격한 기준에 직면하고 있으며, 예지보전 능력이나 하청업체 전체에서의 100% 추적 가능성 등이 요구됩니다. 이 규정 설계는 Tier 1 공급업체가 Tier 3 공급업체와 호환되는 자동화 레이어의 도입을 요구하므로 다운스트림 수요를 증폭시켜 부품, 공구 및 포장 파트너 전반에 걸쳐 시장 견인력을 두 배로 높입니다.
중소 부품 벤더는 EBITDA 마진이 8-12%이며, 매출금 회수 사이클이 90-120일로 길기 때문에 자동화에 충당되는 유동 자금이 한정되어 있습니다. 종합적인 설비 업그레이드에는 연간 매출의 15-20%에 상당하는 자본이 필요하며, 많은 기업은 보조금이 있는 대출 없이는 이 장애물을 넘을 수 없습니다. 신용 보증 시스템은 대출자의 위험 가중치를 줄이지만 담보 요건과 승인 지연은 여전히 신속한 도입을 방해합니다. 이로 인해 Tier 1 및 Tier 2 기업이 빠르게 디지털화를 추진하는 반면, Tier 3 기업이 지연되는 양극화된 생태계가 형성되어 OEM이 중시하는 동기 생산 모델이 손상될 수 있습니다.
2025년 시점에서 산업용 제어 시스템은 인도의 산업 자동화 시장 점유율의 37.15%를 차지했으며 자동차 분야에서의 견조한 PLC 수요와 화학 분야에서의 DCS 도입이 이를 뒷받침되고 있습니다. 한편, 소프트웨어 수익은 클라우드 기반 제조실행시스템(MES)의 구독 판매화로 진입장벽이 저하되어 15.05%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장하고 있습니다. 인도의 산업 자동화 시장에서 소프트웨어 솔루션의 규모는 2026년부터 2031년까지 두배로 증가할 것으로 예측됩니다. 이는 중견 기업이 ERP, MES, 품질 분석을 단일 스택에 통합하는 움직임 때문입니다. 필드 디바이스는 저렴한 센서의 보급과 제철소 및 식품 가공 플랜트에서의 예지보전의 도입 확대에 의해 성장했습니다. 서비스 수익도 증가하고 있으며 하이브리드 아키텍처에는 지속적인 사이버 패치 적용과 모델 재교육이 필요합니다.
강화된 사이버 보안 모듈과 역할 기반 접근 제어는 현재 대부분의 제어 시스템 업그레이드에 내장되어 있으며 보험 회사의 모니터링 강화 노력을 뒷받침합니다. 한편, 제품 수명주기 관리 소프트웨어는 규제 감사 추적이 디지털 방식으로 서명된 설계 개정을 요구하기 때문에 자동차 및 항공우주 분야에서 판매 주문을 획득하고 있습니다. 휴먼-머신 인터페이스는 태블릿형 터치스크린을 채택하여 운영자 교육 기간을 3일 미만으로 단축했습니다. 이러한 변화로 인해 수익은 지속적인 소프트웨어 구독 및 매니지드 서비스로 전환되고 있지만 하드웨어는 여전히 기반을 유지하고 있습니다.
프로그래머블 자동화는 2025년 수익의 41.45%를 차지했으며, 빠른 레시피 변경이 필요한 혼합 모델 조립 라인에서 뒷받침되었습니다. 그러나 공장이 AI, 머신 비전, 엣지 분석을 폐루프 최적화에 통합함에 따라 통합형 및 초자동화는 16.35%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 확대되고 있습니다. 타타 스틸과 같은 조기 도입 기업은 기존 SCADA 시스템에 AI 예측 모델을 오버레이하여 예기치 못한 다운타임을 20% 줄였습니다. 현재의 도입 곡선이 유지되면 초자동화에 대한 인도의 산업 자동화 시장의 규모는 2031년까지 123억 5,000만 달러에 달할 가능성이 있습니다.
초자동화로의 전환에는 통합된 데이터 계층이 필수적이므로 공급업체는 MQTT 브로커 및 OPC-UA 게이트웨이를 컨트롤러 업그레이드 및 세트로 제공합니다. 2025년에는 운영자가 AI 지원 워크플로에 대응할 수 있도록 멀티스킬 연수 프로그램에 대한 투자가 증가하여 직원 재교육 예산이 25% 증가했습니다. 규제 감사는 추적성 확보를 위해 전체 프로세스 매개변수를 기록하는 자동화 시스템을 권장하며 통합 스택으로의 전환이 더욱 가속화되고 있습니다.
The India industrial automation market was valued at USD 17.28 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 19.71 billion in 2026 to reach USD 38.02 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 14.05% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
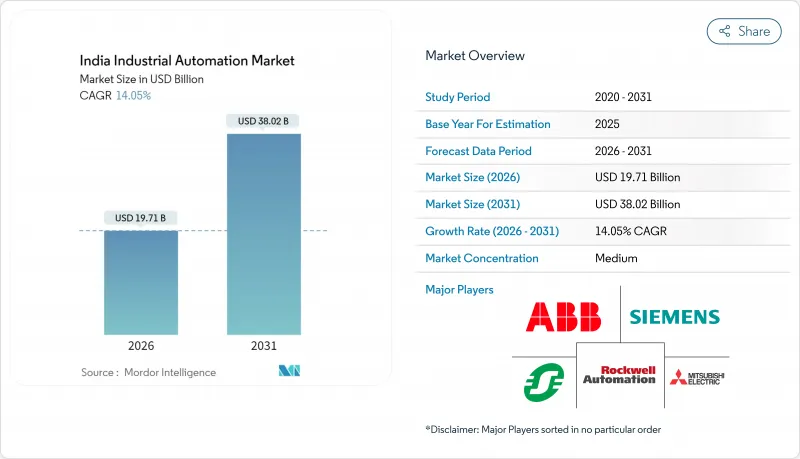
Ongoing policy support, rapid modernization of legacy plants, and falling sensor prices together sustain double-digit expansion. Foreign direct investment swelled after the Production Linked Incentive program linked cash disbursements to Industry 4.0 readiness, triggering a wave of brownfield retrofits that lift productivity and export competitiveness. Multinationals increased local manufacturing footprints to shorten supply chains and avoid import duties, while mid-tier enterprises adopted cloud-based execution software to overcome capital constraints. Meanwhile, private 5G pilots and edge computing platforms reduced latency concerns and encouraged predictive maintenance rollouts in process plants. Cybersecurity readiness and skilled labour availability remain watchpoints, yet the policy-driven upgrade cycle keeps demand on a strong growth path.[1]
Foreign direct investment flowing into the country after 2024 elevated overall factory-automation budgets. Siemens committed INR 10,000 million (USD 120.5 million) to expand production of drives and controllers, while Mitsubishi Electric directed INR 2,200 million (USD 26.5 million) toward local assembly lines. These brownfield upgrades emphasize scalable, modular equipment rather than greenfield capacity, enabling faster returns and higher asset utilization. Clusters in Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu attract allied suppliers, spreading technical know-how along the value chain. Export-oriented manufacturers also integrate global quality benchmarks, tightening demand for advanced motion control, energy-efficient drives, and machine safety systems.
The Production Linked Incentive program disbursed INR 140,200 million (USD 1.69 billion) by 2025 to discrete industries on the condition of demonstrable Industry 4.0 compliance. Automotive applicants must showcase fully networked production lines with PLC-controlled stations and real-time quality monitoring to keep receiving tranche payments. Electronics manufacturers face even stricter benchmarks such as predictive maintenance capability and 100 percent traceability across subcontractors. This rule design amplifies downstream demand because Tier-1 suppliers press Tier-3 vendors to install compatible automation layers, multiplying market pull across component, tooling, and packaging partners.
Smaller component vendors often operate on 8-12% EBITDA margins and face 90-120-day receivable cycles, leaving limited free cash for automation. Comprehensive upgrades can require capital equal to 15-20% of annual revenue, a hurdle that many cannot clear without subsidized loans. While the credit guarantee scheme reduces risk weightings for lenders, collateral requirements and approval delays still deter quick uptake. This creates a bifurcated ecosystem where Tier-1 and Tier-2 firms digitize rapidly while Tier-3 lags, potentially undermining the synchronous production models favoured by OEMs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Industrial control systems retained 37.15% India industrial automation market share in 2025, anchored by robust PLC demand in automotive and DCS rollouts in chemicals. Software revenue, however, is climbing at a 15.05% CAGR as cloud-hosted manufacturing execution suites become subscription-priced, lowering entry hurdles. The India industrial automation market size for software solutions is projected to double between 2026 and 2031 as mid-tier firms integrate ERP, MES, and quality analytics into a single stack. Field devices gained from cheaper sensors, expanding predictive-maintenance deployments in steel mills and food processing plants. Service revenue also rose because hybrid architectures need ongoing cyber-patching and model retraining.
Enhanced cybersecurity modules and role-based access controls now come bundled inside most control-system upgrades, addressing rising insurance scrutiny. Meanwhile, product lifecycle management software wins orders in automotive and aerospace because regulatory audit trails demand digitally signed design revisions. Human-machine interfaces adopt tablet-style touchscreens, shortening operator training to under three days. Collectively, these shifts pivot revenue toward recurring software subscriptions and managed services, though hardware remains foundational.
Programmable automation accounted for 41.45% revenue in 2025, favoured for mixed-model assembly lines that need rapid recipe changes. Yet integrated hyper-automation is expanding at a 16.35% CAGR as plants converge AI, machine vision, and edge analytics into closed-loop optimization. Early adopters like Tata Steel logged a 20% cut in unplanned downtime after overlaying AI predictive models on legacy SCADA. The India industrial automation market size tied to hyper-automation could reach USD 12.35 billion by 2031 if current adoption curves hold.
Transitioning to hyper-automation requires unified data layers, so vendors bundle MQTT brokers and OPC-UA gateways with controller upgrades. Workforce retraining budgets rose 25% in 2025 as firms invest in multi-skilling programs to align operators with AI-assisted workflows. Regulatory audits now prefer automation systems that log every process parameter for traceability, further reinforcing the move toward integrated stacks.
The India Industrial Automation Market Report is Segmented by Solution (Industrial Control Systems, Field Devices, Software, and Services), Automation Type (Fixed, Programmable, Flexible, and Integrated), End-User Industry (Automotive, Oil and Gas, Food and Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Power, Electronics, and More), and Deployment Mode (On-Premise, Cloud, and Hybrid). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).