
간질환 치료제 시장은 2025년 234억 2,000만 달러에서 2026년에는 250억 8,000만 달러로 성장하고 2026년부터 2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 7.09%로 성장을 지속하여 2031년까지 353억 3,000만 달러에 달할 전망입니다.

견고한 수요는 획기적인 규제 당국의 승인, 바이러스성 간염 및 대사이상지방간질환(MASLD)의 세계적인 유병률 증가 및 RNA 기반 전달 플랫폼의 기술적 도약에 의해 뒷받침됩니다. 제조업체는 치료 효과를 극대화하기 위해 바이러스 유전자형, 섬유화 단계 또는 신진 대사 프로파일을 통해 환자를 계층화하는 동반진단을 통합한 정밀의료를 선호합니다. 한편, 다제 병용 요법의 연간 비용이 다섯자리에 이르는 가운데 병원의 약제위원회는 예산 증대의 압력에 직면하고 있으며 지속적인 바이러스학적 반응과 조직학적으로 확인된 섬유화 역전에 연동한 리스크 분담 계약에 관한 협상이 진행되고 있습니다.
간세포 암은 세계적으로 암 사망 원인의 3위를 차지하며 만성 간질환은 매년 450만명 이상의 미국인에게 영향을 미치고 있습니다. 이 역학적 급증은 항바이러스제, 면역요법, 질병조절 항섬유화제의 지속적인 도입을 촉진하고 있습니다. 아시아태평양에서는 바이러스성 간염의 부담이 더 높은 반면 서양 국가에서는 비만 및 당뇨병과 관련된 MASLD(대사이상지방간질환)의 증가에 직면하고 있습니다. 나이가 들수록 간의 재생 능력이 저하되기 때문에 노화는 질병의 유병률을 더욱 악화시킵니다. 각국의 보험제도는 질병을 조기에 발견하는 진단 프로그램의 확충, 근치적 치료의 대상이 되는 환자층의 확대, 간질환 치료제 시장의 활성화 등의 대응책을 강구하고 있습니다.
MASLD는 세계 인구의 약 25%에 영향을 미치고 간 이식의 적응증으로 가장 빠르게 증가하고 있습니다. 2024년 임상 증거에 따르면, 대사증후군 환자는 3-4단계 섬유화로 진행될 위험이 3배 높으며, 알코올 섭취는 질병 진행을 7년 앞당깁니다. FGF21 작용제 및 PPAR 조절제를 포함하는 이중 경로 약물은 현재 후기 임상시험 단계에 있습니다. 규제 당국은 MASLD의 다인자성을 인식하고 병용 요법을 검증하는 적응형 디자인을 지지합니다. 미국에서만 MASLD 관련 연간 지출은 1,030억 달러를 넘어섰으며, 보험사는 말기 질환으로의 진행을 회피하는 치료법에 대해 프리미엄 가격을 받아들이도록 지불자에게 촉구하고 있습니다.
면역억제요법은 감염증 위험을 40% 상승시킵니다. 신종 항섬유화제는 심기능 및 신기능 모니터링을 필수로 합니다. FDA는 NASH 치료제에 대해 시판 후 5년간의 안전성 조사를 요구하고 있습니다. 복잡한 투여 스케줄은 복약충실도를 억제하고 장기간의 실세계 데이터가 축적될 때까지 의사는 신중한 처방을 선택합니다. 개발 단계에서의 안전 위험을 조기에 파악하기 위해, 예측 독성학 및 간의 마이크로생리학적 모델에 대한 투자가 개발 기업들 사이에서 진행되고 있습니다.
항바이러스 요법은 2025년 간질환 치료제 시장에서 36.12%의 점유율을 유지했습니다. 전체 유전자형에 대응하는 직접 작용형 항바이러스제가 95%의 치유율을 유지하고 있는 것이 견인 요인입니다. 또한 2억 9,600만 명의 B형 간염 캐리어에 대한 만성 B형 간염 억제 요법이 지속적인 수익을 보장합니다. 한편, 항섬유화 및 항지방간제는 레스메티롬의 혁신 신약 승인과 MASLD 환자의 급증으로 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 10.22%로 확대될 것으로 전망됩니다. 면역억제제는 자가면역 간염의 틈새 시장을 유지하는 반면, 종양학에 초점을 맞춘 면역요법이 세포독성 화학요법을 대체하고 있습니다. 대사 개선제와 항염증제를 조합한 병용 요법이 처방 패턴을 확대하여 간질환 치료제 시장 규모를 확대하고 있습니다.
파이프라인의 분산이 진행됨에 따라 경쟁 환경이 변화하고 있습니다. 18개월 이내에 10가지 이상의 이중경로 작용 후보 약물이 2상 시험 단계에 돌입했습니다. 비침습적 섬유화 진행 점수에 기초한 성과연동형 계약은 특히 통합 의료 시스템의 시장 침투를 촉진하고 있습니다. 후기 단계에서의 항바이러스제 내성은 여전히 드물기 때문에 수명 주기 관리는 고정용량 배합제로 이행하여 복약 부담의 경감과 제네릭 의약품에 의한 시장 침식으로부터의 보호를 도모하고 있습니다.
2025년 간질환 치료제 시장의 점유율 42.35%는 환자 수가 많고 생명을 구하는 근치적 치료 요법에 의해 바이러스성 간염이 차지했습니다. WHO의 근절 목표는 조달 자금을 유지하고 중국과 인도의 국내 생산 노력으로 치료당 비용이 65% 감소했습니다. 이는 접근성을 확대하고 간질환 치료제 시장을 강화합니다. 한편, MASLD(대사이상지방간질환)는 세계적인 비만 증가에 따라 11.28%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 나타낼 전망입니다. 지방 간질환의 다인성 병인은 평균 판매 가격을 높이는 병용 요법의 구축을 촉진합니다.
알코올 관련 간질환은 중증 알코올성 간염의 90일 사망률을 25% 줄인 실적을 보유한 라수코스테롤이 FDA의 획기적 치료제로 지정되면서 새로운 주목을 받고 있습니다. 자가면역성 간질환은 규모가 작지만, 이식의 필요성을 지연시키는 생물학적 제제에 대해서 고액의 환급이 실현되고 있습니다. 희소유전성 질환 및 소아질환은 승인을 가속화하고 고가격 설정을 가능하게 하는 희소질환용 의약품 우대조치의 혜택을 받아 연구 위험을 완화하고 있습니다.
북미는 2025년 매출액의 42.10%를 차지하였으며 신규 승인 NASH 치료제의 급속한 보급과 전체 유전자형 HCV 항바이러스제의 광범위한 보험 적용이 기반이 되고 있습니다. 학술연구기관의 존재가 후기 임상시험의 피실험자 등록을 가속화하고, 세제우대조치가 연구개발을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 그러나 치료비 상승으로 적응증 기반 리베이트를 협상하는 약물 혜택 관리 회사의 모니터링이 강화되었습니다.
아시아태평양은 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 12.45%로 가장 빠르게 성장할 것으로 예상되는 지역입니다. 중국에서만 8,000만명의 만성 B형 간염 환자가 있으며, 국가보험 적용이 일차선택제인 테노포비르의 후발의약품으로 확대되어 치료 대상 인구가 증가하고 있습니다. 일본의 신속심사제도는 획기적인 생물학적 제제의 승인기간을 단축하고, 한국의 생명공학세제 우대조치는 국내 RNAi 파이프라인을 촉진하고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 의료기술평가기관이 신규 승인 전 비용효과를 중시하기 때문에 꾸준하고 완만한 성장이 나타나고 있습니다. 유럽의약청(EMA)이 미국 식품의약품국(FDA)의 과학적 조언과 무결성을 도모함으로써 병행 신청은 원활화되었지만, 가격 및 수량 합의에 따라 국가별 발매가 1년 이상 지연될 가능성이 있습니다. 중동, 아프리카 및 남미는 세계 수익에서 차지하는 비율이 낮지만, 다자간 도너 프로그램과 단계적 가격 설정 모델에 의해 WHO 추천 요법에 대한 접근성이 개선되면서 간질환 치료제 시장은 점차 확대되고 있습니다.
The Liver Diseases Therapeutics Market is expected to grow from USD 23.42 billion in 2025 to USD 25.08 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 35.33 billion by 2031 at 7.09% CAGR over 2026-2031.
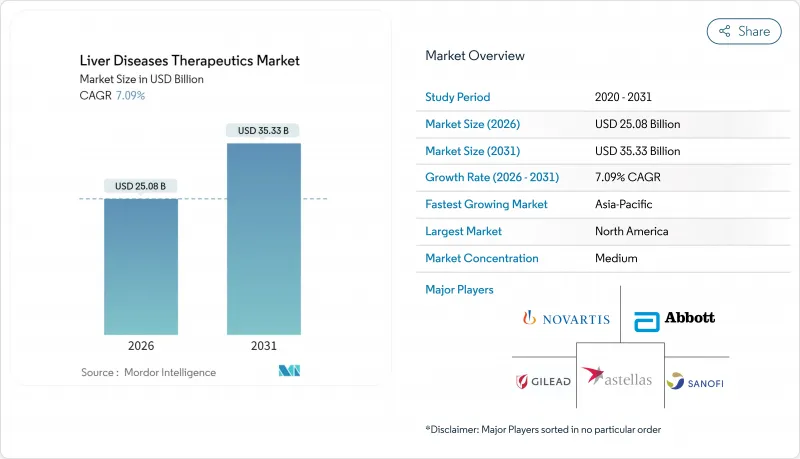
Robust demand is underpinned by breakthrough regulatory approvals, the rising global prevalence of viral hepatitis and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), and technological leaps in RNA-based delivery platforms. Manufacturers prioritise precision medicine, integrating companion diagnostics that stratify patients by viral genotype, fibrosis stage, or metabolic profile to maximise treatment benefit. Meanwhile, hospital formulary committees face escalating budget pressures as multi-drug regimens reach five-digit annual costs, prompting negotiations around risk-sharing contracts linked to sustained virologic response or histology-confirmed fibrosis reversal.
Hepatocellular carcinoma ranks as the third-leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, while chronic liver disease affects more than 4.5 million Americans each year. This epidemiological surge stimulates sustained uptake of antivirals, immunotherapies, and disease-modifying antifibrotics. Asia-Pacific carries a heavier viral hepatitis burden, whereas Western economies confront rising MASLD linked to obesity and diabetes. Aging populations compound disease prevalence because hepatic regenerative capacity declines with age. National payer systems respond by broadening screening programmes that detect disease earlier, expanding the addressable pool for curative therapies and boosting the liver disease therapeutics market.
MASLD touches roughly 25% of the global population, making it the fastest-growing indication for liver transplantation. Clinical evidence from 2024 shows metabolic-syndrome patients possess triple the risk of advancing to stage 3-4 fibrosis, and concurrent alcohol use accelerates disease by seven years. Dual-pathway drugs, including FGF21 agonists and PPAR modulators, are now in late-phase trials. Regulators embrace adaptive designs that test combination regimens, acknowledging MASLD's multifactorial nature. In the United States alone, MASLD-related spending exceeds USD 103 billion annually, prompting insurers to accept premium pricing for therapies that avert progression to end-stage disease.
Immunosuppressive regimens elevate infection risk by 40%; new antifibrotic agents mandate cardiac and renal monitoring. FDA now demands five-year post-marketing safety studies for NASH drugs. Complex dosing schedules undermine adherence, and physicians adopt conservative prescribing until long-term real-world data mature. To curb attrition, sponsors are investing in predictive toxicology and microphysiological liver models that flag safety liabilities earlier in drug development.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Anti-viral therapies retained 36.12% share of the liver disease therapeutics market in 2025, propelled by pan-genotypic direct-acting antivirals that sustain 95% cure rates. Chronic hepatitis B suppression for 296 million carriers assures durable revenue. Meanwhile, antifibrotic/antisteatotic agents are projected to log a 10.22% CAGR to 2031, benefitting from Resmetirom's first-in-class approval and a ballooning MASLD population. Immunosuppressants maintain a niche for autoimmune hepatitis, whereas oncology-focused immunotherapies increasingly supplant cytotoxic chemotherapies. Combination regimens blending metabolic correctors with anti-inflammatory agents are expanding prescribing patterns, lifting the liver disease therapeutics market size.
The competitive narrative is evolving as pipeline dispersion intensifies; more than a dozen dual-pathway candidates have entered Phase II within 18 months. Pay-for-performance contracts tied to non-invasive fibrosis regression scores bolster market uptake, especially among integrated health systems. As late-line antiviral resistance remains rare, lifecycle management pivots to fixed-dose combinations that lessen pill burden and shield franchises from generic erosion.
Viral hepatitis contributed 42.35% of liver disease therapeutics market share in 2025 due to sheer patient volume and life-saving curative regimens. WHO elimination targets sustain procurement funding, and domestic production efforts in China and India lower per-course costs by 65%, broadening access and reinforcing the liver disease therapeutics market. MASLD, however, will post an 11.28% CAGR as obesity climbs worldwide. Steatotic liver disease's multifactorial pathogenesis encourages combination therapy architectures that elevate average selling prices.
Alcohol-related liver disease receives fresh attention following FDA Breakthrough Therapy status for larsucosterol, which demonstrated 25% reduction in 90-day mortality in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Autoimmune liver diseases, although representing a smaller segment, achieve premium reimbursement for biologic agents that delay transplant need. Rare genetic and paediatric disorders benefit from orphan incentives that speed approvals and permit higher pricing benchmarks, cushioning research risk.
The Liver Disease Therapeutics Market Report is Segmented by Treatment Type (Anti-Viral Drugs, Immunosuppressants, and More), Disease Type (Viral Hepatitis A-E, and More), Drug Class (Small-Molecule Orals, and More), Route of Administration (Oral, Injectable), End User (Hospitals, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America captured 42.10% of revenue in 2025, underpinned by rapid adoption of newly approved NASH drugs and broad insurance coverage for pan-genotypic HCV antivirals. The presence of academic centres accelerates enrolment in late-phase trials, and tax credits support R&D. Yet ballooning therapy prices heighten scrutiny from pharmacy benefit managers that negotiate indication-based rebates.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing territory at a 12.45% CAGR to 2031. China alone houses 80 million chronic hepatitis B patients, and national reimbursement now covers first-line tenofovir generics, expanding the treated population. Japan's fast-track review system shortens approval timelines for breakthrough biologics, while South Korea's biotech tax incentives spur domestic RNAi pipelines.
Europe witnesses steady, slower growth as health technology assessment agencies seek cost-effectiveness before authorising new entries. EMA alignment with FDA scientific advice has smoothed parallel submissions, but price-volume agreements can delay country-level launches by more than a year. Middle East & Africa and South America together account for minor share of global revenue; however, multilateral donor programmes and tiered pricing models improve access to WHO-preferred therapies, gradually enlarging the liver disease therapeutics market.