
특급 배송 시장은 2025년에 2,553억 5,000만 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 2,704억 7,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 3,612억 6,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
예측기간(2026-2031년)의 CAGR은 5.92%로 전망되고 있습니다.

국경을 넘은 전자상거래 활동의 활성화, 디지털 무역회랑의 도입 확대, 의료용 콜드체인의 수요 가속 등의 요인이 시장 기반을 강화하고 있습니다. 한편, 에너지 가격과 인건비의 변동이 사업자의 수익성을 위협하는 상황이 계속되고 있습니다. 네트워크 규모는 여전히 주요 경쟁 우위성이지만, 자동화, 데이터 분석 및 대체 라스트마일 운송 모드에 대한 기술 투자는 민첩한 신규 진출기업이 틈새 시장에서 기존 기업에 도전할 수 있는 기회를 낳고 있습니다. 지역별 동향은 계속 변화하고 있으며, 북미는 성숙한 인프라와 소비자의 프리미엄 서비스에 대한 수요에 의해 최대의 점유율을 차지하는 한편, 아시아태평양은 모바일 퍼스트 상거래와 디지털 결제의 보급을 배경으로 가장 빠른 성장률을 나타내고 있습니다.
크로스보더 소포의 취급량은 2025년부터 2030년에 걸쳐 CAGR 7.44%로 증가할 전망이며, 시장 전체의 성장률을 크게 웃돌아 국제 조달로의 구조적 전환을 나타내고 있습니다. USMCA(미국, 멕시코 및 캐나다 협정)나 RCEP(환태평양 경제 동반자 협정) 등의 무역 협정에 의해 세관 데이터 교환이 효율화되고, 서류 절차가 간소화되어 평균 통관 시간이 약 1/3 단축되었습니다. 주요 특송 사업자가 설치한 전용 크로스보더 허브는 수개국에 걸친 유통망의 거점이 되어 서비스 기대치가 높음에도 불구하고 이익률을 유지하는 화물 집약을 가능하게 하고 있습니다. 국제 소포는 일반적으로 국내 소포보다 3-5배 높은 가격이 설정되므로 사업자에게 중요한 수익원의 다양화를 가져옵니다. 보세 창고, 디지털 통관 플랫폼, 지역 밀착형 라스트마일 협력에 대한 투자는 세계 재고 흐름을 동기화할 수 있는 네트워크 경쟁 우위를 더욱 확대할 것입니다.
당일 배송은 특히 인구 밀도가 높고 배송 루트 효율을 기대할 수 있는 대도시권에서는 신선함에서 필수 조건으로 변화하고 있습니다. 아마존 배송이 2024년 미국 90개 도시 이상에서 전개됨으로써 경쟁이 격화되고, 경쟁사는 마이크로플루필먼트 거점의 확충과 실시간 재고 가시화에 의해 수주에서 배송까지의 사이클 단축을 요구받고 있습니다. 도시 지역의 루트 최적화 알고리즘은 소포 1개당 배송 비용을 15-20% 절감합니다. 시간 엄수로 인한 프리미엄 수요와 비용을 중시한 저속 배송층이라는 양극화가 진행됨으로써 운송 사업자는 세분화 전략을 강화하고 차별화된 요금 체계를 적용하면서 차량 가동률의 합리화를 도모할 수 있게 되었습니다. 계절 프로모션과 함께 지속적인 수요 피크는 시간 단위 수요 변동에 대응하는 동적 가격 설정 및 예측형 인력 배치 모델의 도입을 사업자에게 촉진하고 있습니다.
연료비는 일반적으로 특송업체의 영업비용의 15-20%를 차지하므로 연료비 급등은 즉각적으로 수익에 영향을 미칩니다. 2024년에는 지정학적 긴장에 의해 원유 공급이 축소되었고, 페덱스는 유류비를 12.5% 늘렸습니다. 동시에 인력 부족이 심각해져 북미 및 서유럽 전역에서 운전기사 임금이 8-12% 상승했습니다. 전기화와 루트 계획 소프트웨어는 위험을 줄이지만 투자 회수에는 수년이 소요됩니다. 재무기반이 취약한 중소 지역 사업자는 운송량을 유지하기 위해 적극적인 가격설정을 실시하고 있으며 이는 이익률을 더욱 낮추고 있습니다. 지속적인 비용 변동으로 간선 운송 구간의 통합과 전력망 인프라가 일부 지역에서 대체 연료의 활용을 목적으로 하는 네트워크 재설계를 요구하고 있습니다.
전자상거래 화물은 2025년에 32.55%의 수익 점유율을 차지한 특급 배송 시장의 기반이었으며, 프로모션 캘린더와 연동한 예측 가능한 화물량의 급증을 가져와 데이터 구동형 루트 최적화를 촉진하고 있습니다. 성숙한 지역에서도 당일 배송 서비스의 보급으로 배송 빈도가 증가하고 소포 화물의 두 자릿수 성장이 계속되고 있습니다.
의료 분야에서는 2026년부터 2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 6.30%를 나타낼 것으로 전망되어 온도 및 추적 관리 체제에 대한 의존도가 높아지고 있습니다. 특송 사업자는 규제 요구사항을 충족하기 위해 검증된 포장재, 다중 냉각 시스템 및 운송 모니터링을 통합합니다. 제조업체는 부패 위험을 최소화하고 필요할 때 신속한 제품 회수를 가능하게 하는 배송 전체 과정의 가시성을 강조합니다. 이 시너지 효과로 특송 업계의 역할은 단순한 운송업체에서 생명과학 생태계의 전략적 공급망 파트너로 진화하고 있습니다.
국제 운송은 프리미엄 크로스보더 수요와 통관 마찰 감소를 배경으로 국내 운송에 비해 7.31%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)(2026-2031년)로 보다 빠른 성장이 예상됩니다. 보세 허브와 통관 업무에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 특송 사업자는 지정학적 긴장이 주요 위험임에도 불구하고 가격 결정력을 유지하고 있습니다. 국내 소포는 2025년 수익 점유율 65.72%를 차지하면서 규모의 경제효과를 가져온 한편, 격렬한 경쟁과 라스트마일 인건비 상승에 따른 이익률 축소에 직면하고 있습니다.
국제 수익은 통관 시간의 단축과 실시간 추적을 가능하게 하는 무역 회랑의 디지털화 이니셔티브로 혜택을 누리고 있습니다. 국경을 넘어선 물류와 관련된 특급 배송 시장의 규모는 예측기간 동안 공헌도를 확대할 전망이며, 민첩한 용량 관리와 양국 간 항공화물 협정의 필요성을 더욱 강화하고 있습니다.
북미는 2025년에 35.12%의 수익 점유율을 차지하였으며, 이 지역의 고급 전자상거래 보급률, 광범위한 고속도로 인프라, 높은 가처분 소득이 이를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 뉴욕, 로스앤젤레스, 토론토 등의 고밀도 도시권에서는 프리미엄 요금을 설정한 당일 배송 네트워크가 유지되고 있습니다. 미국은 USMCA(미국, 멕시코 및 캐나다 협정) 하에서 크로스보더 물류를 뒷받침하며, 관세의 안정성과 간소화된 통관 수속을 보증하고 있습니다. 반면 캐나다의 이중 언어 시장과 멕시코의 마킬라도라 회랑은 다양한 화물 구성을 제공합니다. 하지만 인건비 상승과 온실가스 보고의 엄격화가 당면의 수익성 과제가 되고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 모바일 월렛과 소셜커머스 플랫폼이 새로운 소비자층을 개척하는 가운데 2026년부터 2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 7.45%로 세계 시장의 성장을 견인할 것으로 예측됩니다. 중국의 소포밀도는 기타 국가를 압도하고 있지만 인도, 인도네시아, 베트남은 가맹점 유치에 대한 인센티브로 급속히 규모를 확대하고 있습니다. 지역 정부는 통합 디지털 무역 틀을 추진하고 있으며, 아세안의 단일 창구 통관 계획이 그 사례입니다. 이에 따라 규정 준수 화물의 통관 시간을 6시간 미만으로 단축하고 있습니다. 인프라의 병목 현상은 여전히 존재하지만 스마트 물류 허브와 지방 도시 공항에 대한 적극적인 투자로 인해 용량 부족을 해소하고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 관세 코드의 조화와 지역 내 자유화에 의한 단거리 크로스보더 거래가 기반이 되어 꾸준한 확대를 유지하고 있습니다. 차량의 전동화 의무화와 교통 체증 요금 인상으로 운영 비용은 상승하는 한편, 우선 배송 프레임의 지정이나 지속 가능한 선택을 요구하는 법인 고객의 선호로 인해 조기 도입 기업에게는 이점이 발생하고 있습니다. 동유럽 시장은 침투율이 낮아 성장의 여지가 크고, 소득 증가와 EU 자금에 의해 소포 이용이 급증하고 있습니다. 중동 및 아프리카 및 남미는 전체적으로 점유율은 작지만 인프라와 핀테크의 진전에 의해서 서비스를 제공 가능한 시장이 확대되어 한 자릿수 후반의 높은 성장률을 달성하고 있습니다. 장기 전망은 정치적 안정, 세관 근대화, 지방 도시와 국제 무역 경로를 연결하는 항공화물 회랑의 확장에 달려 있습니다.
The Express Delivery Market was valued at USD 255.35 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 270.47 billion in 2026 to reach USD 361.26 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.92% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
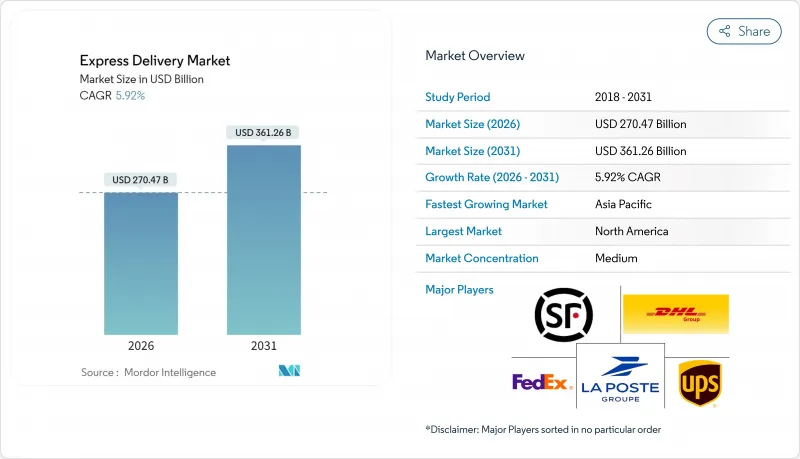
Intensifying cross-border e-commerce activity, rising adoption of digital trade corridors, and accelerating demand for healthcare cold chains are strengthening fundamentals, even as volatile energy prices and labor costs test operator profitability. Network scale remains the primary competitive moat, yet technology investments in automation, data analytics, and alternative last-mile modes are allowing agile entrants to challenge incumbents in niche pockets. Regional dynamics continue to evolve: North America commands the largest share due to mature infrastructure and consumer premium-service appetite, while Asia-Pacific registers the fastest growth on the back of mobile-first commerce and digital payment penetration.
Cross-border parcel volumes are climbing at a 7.44% CAGR (2025-2030), comfortably outpacing overall market growth and signaling a structural pivot toward international sourcing. Trade agreements such as USMCA and RCEP are streamlining customs data exchange and trimming paperwork, reducing average clearance times by almost one-third. Dedicated cross-border hubs established by major express carriers now anchor multi-country distribution and allow shipment consolidation that preserves margins despite higher service expectations. International parcels typically command prices three to five times domestic equivalents, providing operators with critical earnings diversity. Investment in bonded warehouses, digital customs platforms, and localized last-mile collaborations further widens the moat for networks able to synchronize global inventory flows.
Same-day fulfillment has shifted from novelty to a hygiene factor, especially in metropolitan catchments where population density supports route density economics. Amazon's 2024 roll-out to more than 90 U.S. cities accelerated competitive responses, forcing rivals to compress order-to-delivery cycles through micro-fulfillment build-outs and real-time inventory visibility. Urban route-optimization algorithms are trimming per-package costs 15-20%, but only when shipment density crosses critical thresholds. The bifurcation of premium time-sensitive demand and value-focused slower tiers enables carriers to sharpen their segmentation strategy, charging differentiated tariffs while rationalizing fleet utilization. Continuous demand peaks around seasonal promotions are pressuring operators to adopt dynamic pricing and predictive staffing models that align capacity with hourly volume swings.
Fuel typically constitutes 15-20% of an express carrier's operating cost base; hence, a sudden spike reverberates immediately through earnings. In 2024, FedEx lifted its fuel surcharge by 12.5% after geopolitical tensions tightened crude supply. Concurrent talent scarcity pushed driver wages up 8-12% across North America and Western Europe. Electrification and route-planning software mitigate exposure yet require multi-year payback. Smaller regional players lacking balance-sheet depth resort to aggressive pricing to retain volume, eroding margins further. Persistent cost volatility compels network redesign toward consolidation of linehaul legs and greater use of alternative fuels where grid infrastructure permits.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
E-commerce shipments remain the bedrock of the express delivery market with a revenue share of 32.55% in 2025, supplying predictable volume surges tied to promotional calendars and facilitating data-driven route optimization. Even mature geographies continue to register double-digit parcel growth as same-day propositions unlock incremental frequency.
Healthcare's 6.30% CAGR between 2026-2031 showcases mounting reliance on temperature-controlled, track-and-trace chains of custody. Express carriers are integrating validated packaging, redundant cooling systems, and in-flight monitoring to uphold regulatory obligations. Manufacturers value door-to-door visibility that minimizes spoilage risk and speeds product recalls when necessary. This synergy elevates the express delivery industry's role from mere carrier to strategic supply-chain partner within life-sciences ecosystems.
International shipments are expected to grow faster at a 7.31% CAGR (2026-2031), compared to domestic traffic, fueled by premium cross-border demand and reduced customs friction. Express carriers with bonded hubs and brokerage expertise command pricing power, even as geopolitical risks remain a watch point. Domestic parcels with a revenue share of 65.72% in 2025, while delivering scale economies, face margin compression from intense competition and rising last-mile labor costs.
International revenue benefits from trade corridor digitization initiatives that cut clearance times and enable real-time tracking. The express delivery market size tied to cross-border flows is on track to widen its contribution over the forecast horizon, reinforcing the need for agile capacity management and bilateral air-freight agreements.
The Express Delivery Market Report is Segmented by Destination (Domestic and International), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Model (Business-To-Business (B2B) and More), End User Industry (E-Commerce, Healthcare, and Others), Mode of Transport (Road, Air, and Others), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, Europe, Middle East and Africa, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America's 35.12% revenue share in 2025 underscores the region's advanced e-commerce penetration, expansive highway infrastructure, and high discretionary income. Dense urban agglomerations such as New York, Los Angeles, and Toronto sustain same-day networks that command premium tariffs. The United States anchors cross-border flows under the USMCA, ensuring tariff stability and simplified customs interfaces, while Canada's bilingual market and Mexico's maquiladora corridors contribute diversified volume mixes. Labor cost inflation and stricter greenhouse-gas reporting pose immediate profitability challenges.
Asia-Pacific is expected to lead global growth at a 7.45% CAGR between 2026-2031 as mobile wallets and social-commerce platforms unlock incremental shopper cohorts. China's parcel density dwarfs all peers, yet India, Indonesia, and Vietnam are scaling rapidly through merchant onboarding incentives. Regional governments promote integrated digital-trade frameworks, exemplified by ASEAN's single-window customs blueprint that trims clearance to under six hours on compliant shipments. Infrastructure bottlenecks persist, but aggressive investment in smart logistics parks and secondary-city airports is bridging capacity gaps.
Europe maintains steady expansion supported by harmonized customs codes and short-haul cross-border commerce facilitated by open internal borders. Fleet electrification mandates and escalating congestion charges elevate operating costs but also reward early adopters via preferred delivery slots and corporate customer preference for sustainable options. Eastern European markets offer under-penetrated growth avenues where rising incomes and EU funding accelerate parcel adoption. Middle East & Africa and South America collectively represent a smaller share yet deliver high-single-digit growth as infrastructure and fintech advances broaden serviceable addressable markets. Long-run prospects hinge on political stability, customs modernization, and expanded air-cargo corridors connecting secondary cities to global trade lanes.