
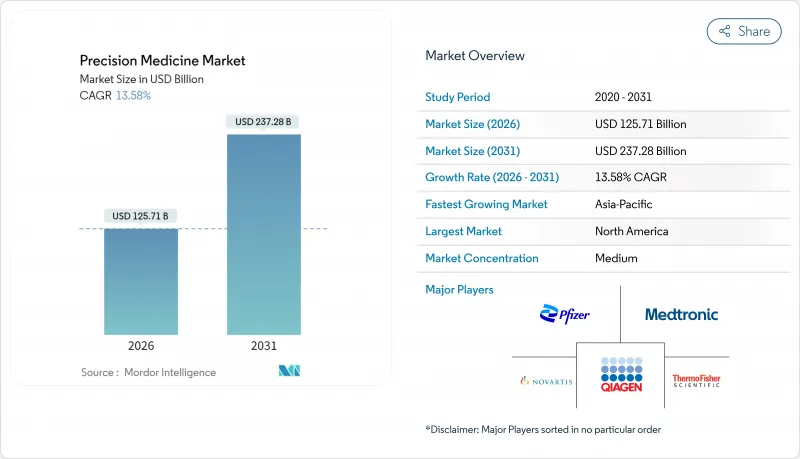
2026년 정밀의료 시장의 규모는 1,257억 1,000만 달러로 추정되며, 2025년 1,106억 8,000만 달러에서 성장하여, 2031년에는 2,372억 8,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
2026년부터 2031년까지의 연평균 성장률(CAGR)은 13.58%가 될 전망입니다.

시퀀싱 비용 감소와 인공지능 기반 분석 및 규제 측면에서의 유연성이 결합되어 건강 관리는 획일적인 치료에서 데이터 기반 맞춤형 개입으로 전환하고 있습니다. 미국, 중국, 인도의 유전체 프로그램은 대규모 멀티오믹스 데이터를 임상 의사결정 지원 도구에 제공하고 클라우드 기반 바이오인포매틱스 플랫폼은 돌연변이 발견에서 치료 선택까지의 시간을 단축하고 있습니다. 범암 동반진단의 진전에 의해 적응증 관련 의약품 시장이 확대되고, 약리유전체학용 신규 환급 코드가 검사의 비용 대비 효과를 향상시키고 있습니다. 한편, 주요 시장에서는 검사실 개발 검사(LDT)의 엄격한 감시로 컴플라이언스 비용은 상승하고 있지만, 검사 품질과 환자 안전성의 향상이 기대됩니다.
정부의 유전체 계획은 시퀀싱을 연구실에서 일상 진료로 이행시키는 기반 정비를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 미국 국립위생연구소(NIH)는 미국 병원 네트워크 6곳에 유전체 분석을 통합하는 학습형 의료 시스템에 대해 2,700만 달러의 자금을 제공했습니다. 중국의 '인간 유전체 프로젝트 2'는 8,000만 건의 유전체 시퀀싱을 목표로 돌연변이 해석을 위한 세계 최대 기준 패널을 구축하고 있습니다. 인도는 2025년에 10,000개의 개인 유전체를 공개했으며, 세계 데이터베이스에서 남아시아 지역의 공백을 보충했습니다. 스웨덴의 PROMISE 프로그램은 국가 등록부와 멀티오믹스 데이터를 연계하여 실시간 임상 의사결정을 뒷받침합니다. 이 프로젝트는 종합적으로 상호 운용 가능한 데이터 에코시스템을 구축하고 진단 정확도를 높여 새로운 신약 개발 타겟을 촉진합니다.
2024년 이후 15건 이상의 FDA 승인이 표적 치료제와 특정 바이오마커 검사를 연결하여 정밀 종양학의 대상 환자층을 확대하고 있습니다. 일루미나의 'TruSight Oncology Comprehensive'는 1회의 검사로 500개 이상의 바이오마커를 해석하는 최초의 FDA 승인 범암 체외 진단약이 되었습니다. FoundationOne CDx는 고형 종양 전체에서 NTRK 융합을 검출할 수 있어 환자를 라로트렉티닙 요법으로 인도합니다. Therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR 키트는 KRAS G12C 돌연변이를 가진 대장암에 대해 소토라십과 파니투무맙의 병용 요법을 지원합니다. 가던트 헬스의 Shield 혈액 검사는 평균 위험군 성인에서 83% 감도로 대장암을 검출하는 비침습적 선택을 제공합니다. 진단제 승인 증가는 제약 기업에 검사법과의 공동 개발을 강력히 촉구하고 바이오마커 가이드 요법의 선순환을 강화하고 있습니다.
유럽의 GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정)은 유전체 데이터를 고도로 민감한 정보로 취급하며 대부분의 오믹스 리포지토리가 지역 외부에서 운영되거나 복잡한 동의 규칙을 준수해야 합니다. 유럽 건강 데이터 공간(EHDS)에서는 EU 지역 외부 기관이 접근을 신청할 때 추가 서류가 요구되고 프로젝트의 타임라인이 장기화됩니다. 미국에서는 HIPAA가 임상 데이터를 규제하지만 많은 조사 데이터베이스는 그 범위를 벗어나 대서양 횡단 연구에 대한 추가 컴플라이언스 요구사항이 추가됩니다. 연합 학습과 같은 프라이버시 보호 기술은 유용하지만, 국경을 넘어서는 법적 해석의 완전한 정합에는 이르지 못했습니다. 그 결과 세계 컨소시엄은 지역별 계약 협상을 요구하고 따라서 거래 비용이 증가하고 대규모 연구가 지연되고 있습니다.
차세대 시퀀싱(NGS)은 2025년 정밀의료 시장의 33.78%를 차지하였으며 대부분의 동반 진단 및 약리유전체학 워크플로를 뒷받침합니다. 일루미나의 TruSight Oncology Comprehensive 분석(단일 측정으로 500개 이상의 바이오마커를 프로파일링)이 FDA 승인을 얻어 NGS는 광범위한 유전체 프로파일링의 전형적인 표준으로서의 지위를 확고히 했습니다. 현재 시퀀서는 클라우드의 바이오인포매틱스 파이프라인에 데이터를 제공하여 수시간 내에 행동 가능한 돌연변이를 확인합니다. 이를 통해 일상적인 진료에서도 유전체 보고서를 관리할 수 있습니다. 공간단백질체학과 고처리량 혈장 단백질 분석의 병행적인 진보는 오믹스 조사 범위를 DNA를 넘어 확장하고, 대사체학과 에피유전체학이 규제적 맥락을 추가하고 있습니다. 이러한 층의 통합은 약물 선택과 복용량 결정에 모두 도움이 되는 환자별 분자 서명을 만들 수 있습니다.
두 번째 기술의 파도는 인공지능(AI)과 머신러닝을 중심으로 전개되며 이 분야는 17.62%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 분야입니다. AI 툴은 돌연변이 어노테이션 스케일링, 종양의 악성도와 관련된 돌연변이 시그니처의 검출, 알고리즘에 의한 임상시험 참가자의 최적화를 실현합니다. 단백질체학 기업인 SomaLogic은 마이크로리터 단위의 샘플로부터 10,000종의 단백질을 측정하여 고밀도 데이터를 생성합니다. 이 데이터를 AI 모델이 분석하고 조기 질병 위험 점수로 변환합니다. 데이터세트가 확대됨에 따라 모델의 성능이 향상되고 추가 R&D 자금을 유치하는 자체 증폭 사이클이 생성됩니다. 시퀀싱의 지속적인 중요성과 AI 분석 기술의 급속한 보급은 차세대 시퀀싱(NGS)이 원시 데이터를 제공하고 지능형 소프트웨어가 임상 가치를 끌어내는 하이브리드 생태계를 시사합니다.
북미는 2025년에 47.85%의 수익 점유율로 정밀의료 시장을 견인했습니다. 이는 연방 정부의 유전체학 자금, 약리유전체학에 대한 보험 적용, 그리고 유연한 규제 정책에 의해 뒷받침됩니다. FDA가 2024년 7월에 발표한 실험실 개발 검사(LDT)의 틀은 연간 12억 9,000만 달러의 컴플라이언스 비용을 수반하지만, 이해관계자는 검사 품질의 향상에 의해 환자와 임상의의 신뢰가 강화될 것으로 예측됩니다(fda.gov). 캐나다는 '정밀의료를 위한 유전체학' 이니셔티브를 통해 유사한 진전을 뒷받침하고 있으며, 멕시코는 INMEGEN의 자원을 희귀질환 시퀀싱에 투입하고 있습니다. 이 지역에는 시퀀싱 벤더 주요 10개사의 대부분이 집중되어 있으며 AI 헬스 스타트업도 고밀도로 존재하기 때문에 기술과 임상 도입에 있어서 지속적인 리더십이 확보되고 있습니다.
유럽은 수익 규모로는 2위이지만 GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정)의 영향으로 국경을 넘어서는 데이터 교환의 진전은 지연되고 있습니다. 독일의 디지털 건강법은 익명화된 청구 데이터의 조사 이용 제한을 완화하여 다국적 임상시험의 유치가 기대됩니다. 스웨덴의 PROMISE 프로젝트는 전국 암 등록 데이터와 전체 유전체 시퀀싱, 전자의무기록을 연계하고 있으며, 기존의 개인정보보호법 내에서 조정된 데이터 전략이 기능하는 실례를 나타내고 있습니다. 영국, 프랑스, 이탈리아, 스페인은 각각 바이오뱅크의 용량 확대와 약리유전체 검사의 환급 스케줄 검토를 진행하고 있으며, 북미와의 도입 격차를 줄이고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 CAGR 14.12%로 가장 빠르게 성장하고 있으며 국가 유전체 계획과 건강 관리 비용 증가가 성장을 견인하고 있습니다. 중국의 '인간 유전체 프로젝트 2'와 AI 중심의 정밀의료 로드맵은 강력한 중앙 정부 자금과 지방 전개로 이어지고 있습니다. 인도의 '인도 유전체 계획'은 남아시아의 대표성 부족 현상을 해소하고 지역 특유의 약물 표적 발견을 촉진합니다. 일본은 표적요법 개발을 이끄는 국가 프로그램 아래 10만건의 암 유전체 해석을 추진하고 있습니다. 호주와 한국은 정부 보조금과 벤처 투자를 결합하여 멀티오믹스 거점을 구축하고 있으며, 싱가포르는 공립병원에서 AI 유전체학을 확대 중입니다. 동남아시아 및 중동 국가는 예측기간 중 캐치업 성장을 지원하는 규제 및 환급 기반의 정비를 추진하고 있습니다.
Precision Medicine market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 125.71 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 110.68 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 237.28 billion, growing at 13.58% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Falling sequencing costs, AI-driven analytics, and friendlier regulatory pathways are aligning to shift healthcare away from one-size-fits-all therapy toward data-rich, patient-specific interventions. Genomic programs in the United States, China, and India are feeding large multi-omics datasets into clinical decision support tools, while cloud-based bioinformatics platforms shorten the time from variant discovery to treatment choice. Progress in pan-cancer companion diagnostics is expanding label-linked drug markets, and new reimbursement codes for pharmacogenomics are improving test affordability. At the same time, stricter oversight of laboratory-developed tests in major markets is raising compliance costs but promises higher test quality and patient safety.
Government genomics programs are underwriting infrastructure that moves sequencing from research labs to routine care. The NIH funded USD 27 million for learning health systems that embed genomics into six U.S. hospital networks. China's Human Genome Project 2 plans to sequence 80 million genomes, creating the world's largest reference panel for variant interpretation. India released 10,000 personal genomes in 2025, filling South Asian gaps in global databases. Sweden's PROMISE program links national registries with multi-omics data to support real-time clinical decision making. Collectively, these projects create interoperable data ecosystems that lift diagnostic accuracy and spur new drug targets.
More than 15 FDA clearances since 2024 have tied targeted drugs to specific biomarker tests, widening the addressable patient pool for precision oncology. Illumina's TruSight Oncology Comprehensive became the first FDA-cleared pan-cancer in-vitro diagnostic that reads 500 plus biomarkers in one run. FoundationOne CDx now detects NTRK fusions across solid tumors, linking patients to larotrectinib therapy. The therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR Kit guides sotorasib plus panitumumab for KRAS G12C-mutated colorectal cancer. Guardant Health's Shield blood test adds a non-invasive option that detects colorectal cancer with 83% sensitivity in average-risk adults. Frequent diagnostic approvals give drug developers strong incentives to co-develop assays, reinforcing a virtuous cycle for biomarker-guided therapy.
GDPR in Europe treats genomic data as highly sensitive, forcing most omics repositories to operate outside the bloc or navigate complex consent rules. The European Health Data Space introduces extra documentation for any non-EU entity seeking access, lengthening project timelines. In the United States HIPAA governs clinical data, yet many research databases fall outside its scope, adding another compliance layer for cross-Atlantic studies. Privacy-preserving technologies such as federated learning help but cannot fully align legal interpretations across borders. Consequently, global consortia must negotiate region-specific contracts, raising transaction costs and delaying large-scale studies.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Next-generation sequencing captured 33.78% of the precision medicine market share in 2025, underpinning most companion diagnostics and pharmacogenomic workflows. FDA clearance of Illumina's TruSight Oncology Comprehensive assay, which profiles more than 500 biomarkers in one run, cements NGS as the gold standard for broad genomic profiling. Sequencers now feed cloud bioinformatics pipelines that flag actionable variants within hours, making genomic reports manageable during routine clinician visits. Parallel advances in spatial proteomics and high-throughput plasma protein analysis extend the reach of omics beyond DNA, while metabolomics and epigenomics add regulatory context. The integration of these layers enables the creation of patient-specific molecular signatures that inform both drug selection and dosing.
A second technology wave centers on artificial intelligence and machine learning, the fastest-growing segment at a 17.62% CAGR. AI tools scale variant annotation, detect mutational signatures linked to tumor aggressiveness, and optimize algorithmic trial enrollment. Proteomics firm SomaLogic measures 10,000 proteins from a microliter sample, producing high-density data that AI models translate into early disease risk scores. As datasets expand, model performance improves, generating a self-reinforcing cycle that attracts further R&D funds. The enduring centrality of sequencing, combined with the rapid adoption of AI analytics, suggests a hybrid ecosystem where NGS provides raw data while intelligent software unlocks its clinical value.
The Precision Medicine Market Report is Segmented by Technology (Big Data Analytics, Bioinformatics, and More), Application (Oncology, Neurology, Immunology, Cardiology, Infectious Diseases, and More), End User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America led the precision medicine market with a 47.85% revenue share in 2025, underpinned by federal genomics funding, payer coverage for pharmacogenomics, and an accommodating regulatory stance. The FDA's July 2024 framework for laboratory-developed tests introduces USD 1.29 billion in annual compliance spend, yet stakeholders anticipate higher assay quality that will reinforce patient and clinician confidence fda.gov. Canada supports similar progress through Genomics for Precision Health initiatives, while Mexico is channeling INMEGEN resources into rare-disease sequencing. Collectively, the region hosts most top-ten sequencing vendors and a high concentration of AI health startups, ensuring ongoing leadership in technology and clinical adoption.
Europe ranks second by revenue yet faces slower cross-border data exchange due to GDPR. Germany's Digital Health Act lifts restrictions on using anonymized claims data for research, which could attract multinational trials to the country. Sweden's PROMISE links national cancer registry data with whole-genome sequencing and electronic health records, illustrating how coordinated data strategy can work inside existing privacy law. The United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain are each expanding biobank capacity and revising reimbursement schedules for pharmacogenomic tests, narrowing the adoption gap with North America.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region with a 14.12% CAGR, propelled by national genome initiatives and rising healthcare spend. China's Human Genome Project 2 and its AI-centered precision health roadmap receive strong central funding and provincial rollouts. India's Genome India Project corrects South-Asian under-representation and boosts discovery of region-specific drug targets. Japan has committed to analyze 100,000 cancer genomes under a national program to guide targeted therapy development. Australia and South Korea are combining government grants with venture investment to build multi-omics hubs, and Singapore is scaling AI genomics in public hospitals. Southeast Asian and Middle East countries are laying regulatory and reimbursement groundwork that will support catch-up growth during the forecast horizon.