
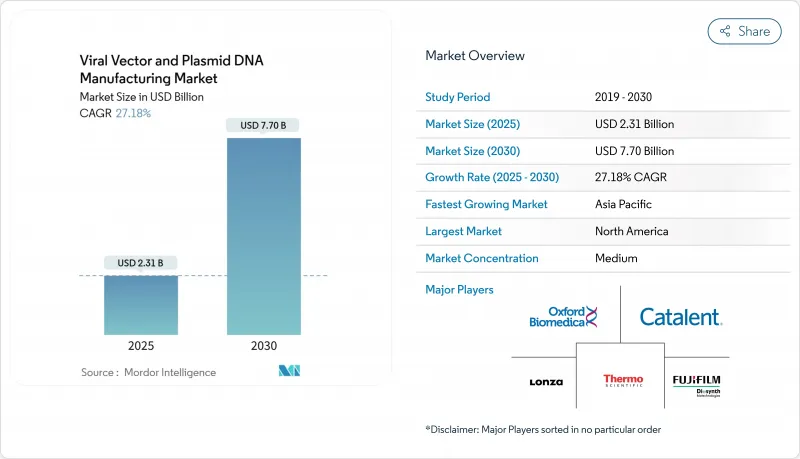
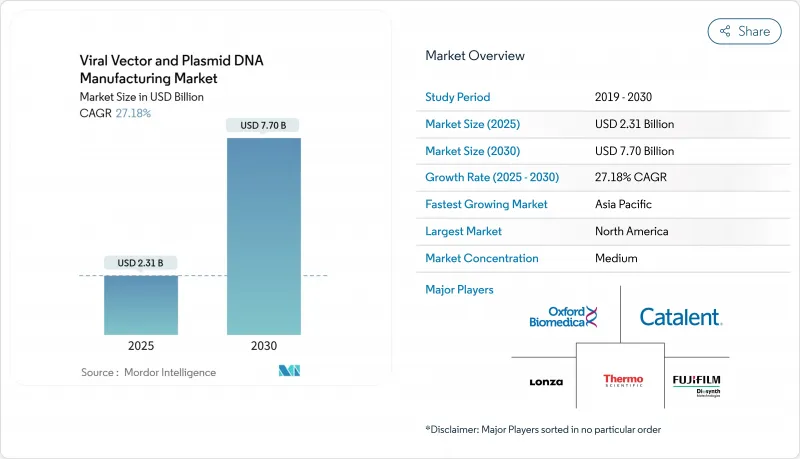
바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장 규모는 2025년 23억 1,000만 달러, 2030년 77억 달러에 이르고, CAGR 27.18%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다.
더 많은 유전자 치료가 규제 당국의 승인을 얻고, 맞춤형 의료가 일상화되고, 제조 기술이 상업 규모에 충분할 정도로 성숙함에 따라 수요가 가속화됩니다. 세계의 GMP 생산 능력은 임상 파이프라인에 상당히 늦어져 공급은 여전히 박박하고 있으며, 스폰서는 전문 CDMO를 향해 시설 확장 및 인수 파도에 이어 박차를 가하고 있습니다. 바이러스 벡터는 계속 출하량의 대부분을 차지하고 있지만, 개발자가 비용 억제, 스케일 업의 간소화, 면역원성의 억제를 시도하고 있기 때문에 비바이러스 접근이 견인 역할이 되고 있습니다. 북미는 계속 승인 취득과 의약품 개발비로 선도하고 있지만, 아시아태평양은 정부가 현지 생물 제제 허브에 자금을 공급하고 혁신 기업가 낮은 사업비를 추구하는 가운데 다음 공장군을 매료하고 있습니다.
희귀 유전성 질환과 만성 질환에 대한 정확한 진단을 받는 환자가 증가하고 있으며, 이러한 적응증의 대부분은 현재 승인 또는 후기 단계의 유전자 치료가 시야에 들어가고 있습니다. 최근 승인된 제바스킨이나 케빌리디와 같은 제품은 당국이 역사적으로 난치성 질환에 대한 선진적인 치료법을 적극적으로 인정하고 있음을 보여주며 안정적인 벡터 수요를 견인하고 있습니다. 노인으로의 역학적 전환은 만성 질환의 확산을 증폭시켜 일회성 유전자 치환 후보자의 내구성있는 풀을 만듭니다. 심사의 합리화나 시장독점권 등 희소질환에 대한 우대조치가 전망을 더욱 견고하게 하고 있습니다. 이러한 요인들이 결합되어 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장이 큰 볼륨을 갖게 되었습니다.
현재 2,000개가 넘는 유전자 치료 프로그램이 세계 등록되어 있으며, 아데노 관련 바이러스(AAV)가 여전히 가장 일반적인 페이로드가 되고 있습니다. Salepta의 rAAVrh74 템플릿에 대한 FDA의 플랫폼 기술 지정은 잘 특성화 된 벡터의 재사용을 장려하고 비용과 일정을 모두 줄입니다. 제약 제조업체는 노바티스의 4천만 유로 EU 벡터 공장과 같은 실제 상점에서 헌신으로 추종하고 있으며, 후기 단계의 자산 프레임을 확보하고 있습니다. 조기에 능력을 확보한 개발 기업은 2상 데이터에서 상시까지 신속하게 이행할 수 있습니다. 그러므로 안정적인 임상시험 대기열은 다년간 생산의 가시성을 보장하고 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장 전체의 확대를 지원합니다.
하나의 유전자 치료 과정에 100만 달러가 걸릴 수도 있고, 바이러스 벡터의 투입은 그 40%를 차지하는 경우가 많습니다. 브라질은 현지 생산으로 3만 5,000달러의 CAR-T 가격으로 가는 길을 보였으나, 대부분의 의료 시스템은 규모에 따른 지불을 고민하고 있습니다. 성과 기반 계약은 위험 분산에 도움이 되지만, 소규모 생명 공학 기업은 슬롯 확보 및 공장 건설에 상당한 선행 투자에 직면하고 있습니다. 자동화와 표준화된 플랫폼은 구제를 약속하지만, 수백만 달러의 자본 지출을 필요로 하기 때문에 자금력 있는 스폰서밖에 손을 낼 수 없습니다. 이러한 비용은 특히 저소득 지역에서 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장의 침투를 방해합니다.
2024년 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장의 55.45%는 바이러스 벡터이며, 이는 확립된 규제 전례와 강력한 형질감염 효율에 의해 지원되었습니다. 비바이러스성 벡터는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 29.65%로 가장 빠르며 면역 장애를 피하는 지질 나노입자, 폴리머 접합체, 일렉트로포레이션 시스템에 밀려 왔습니다. 플라스미드 DNA는 여전히 두 범주의 백본이며 바이러스 어셈블리의 출발 템플릿으로, 직접 주입 접근법에서 치료 구조물로도 기능하고 있습니다.
바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장 규모는 Casgevy 및 Elevidys와 같은 새로 승인된 제품이 상업 규모로 전환됨에 따라 더욱 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다. AAV와 렌티바이러스 계통은 내구성 있는 발현과 조직 향성에 의해 종양학과 희귀질환의 파이프라인을 지배하고 있습니다. 그러나 제조가 복잡하기 때문에 비용이 많이 들고 약물 스폰서는 확장 가능한 비 바이러스성 캐리어를 시도합니다. mRNA의 COVID-19 백신으로 얻은 지질 나노입자의 전문 지식은 플라스미드나 siRNA의 전달에 활용할 수 있어 비바이러스성 방법이 점유율을 깎아내는데 도움이 됩니다. 나노입자 전문가와 레거시 생물학적 제제 CDMO의 파트너십은 이미 공장 전체의 활용을 확대하기 시작했으며, 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장에서 두 가지 방법이 모두 공존한다는 것을 보여줍니다.
북미는 2024년 매출의 42.56%를 차지하며, FDA 리더십, 대규모 벤처 자금 풀, 깊은 임상시험 생태계에 의해 지원되었습니다. Lonza의 Vacaville 공장의 12억 달러 인수와 Charles River의 Vigene Biosciences 인수와 같은 대형 거래는 이 지역의 수직 통합에 대한 의욕을 보여줍니다. 숙련 노동자의 부족과 원재료의 운로는 여전히 존재하지만, 협력적인 노동력 프로그램과 리쇼어링 인센티브는 그 갭을 메우는 것을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 전반적으로 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장은 여전히 미국에서 가장 높은 가격 및 가장 신뢰할 수있는 규제 경로를 발견하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 다국적 기업과 국내 기업이 중국, 한국, 인도, 호주에 새로운 공장을 건설하고 있기 때문에 CAGR 28.65%의 가장 강한 전망을 보여줍니다. Vector Builder의 5억 달러를 투자한 광저우 캠퍼스와 WuXi Biologics의 지속적인 확장은 중요한 치료법의 현지화를 중시하는 베이징의 자세를 반영하며, 인도의 Bharat Biotech는 CGT 공장 설립에 7,500만 달러를 투자하고 있습니다. 지역 당국은 허가를 간소화하고 세액 공제를 제공함으로써 리터당 비용을 낮추고 환자에 대한 접근을 넓히고 있습니다. 이러한 움직임은 이 지역의 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장을 급속히 확대하여 세계 공급 라인을 다양화합니다.
유럽은 성숙하면서도 진화를 계속하고 있습니다. EMA 가이드라인은 예측 가능한 심사 스케줄을 주고, 국경을 넘은 컨소시엄은 호라이즌 유럽의 자금을 첨단 치료 인프라에 돌려줍니다. 노바티스가 슬로베니아에서 4,000만 유로를 투입하여 벡터를 확장한 것은 회원국간 상환에 편차가 있음에도 불구하고 기업의 자신감을 뒷받침합니다. 브레그지트 후 영국은 임상시험과 제조에 매력적인 나라가 되기 위해 병행 규제 체계를 추구하고 있습니다. 라틴아메리카와 중동 및 아프리카는 절대량으로 후진을 숭배하고 있지만, 브라질의 비용효과의 약진과 걸프 국가의 정부계 투자 차량은 새로운 생산능력 증강을 시사하고 있습니다. 이들을 종합하면 지리적 다양화는 위험을 분산시켜 바이러스 벡터 및 플라스미드 DNA 제조 시장에 탄력성을 부여하게 됩니다.
The viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market size stands at USD 2.31 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 7.70 billion by 2030, expanding at a 27.18% CAGR.
Demand accelerates as more gene therapies win regulatory approvals, personalized medicine becomes routine, and production technologies mature enough for commercial scale. Supply remains tight because global GMP capacity lags sharply behind the clinical pipeline, pushing sponsors toward specialized CDMOs and spurring wave after wave of facility expansions and acquisitions. Viral vectors continue to dominate shipments, yet non-viral approaches gain traction as developers try to curb cost, simplify scale-up, and limit immunogenicity. North America retains leadership in approvals and spend, but Asia-Pacific attracts the next tranche of factories as governments fund local biologics hubs and innovators chase lower operating outlays.
More patients receive precise diagnoses for rare genetic disorders and chronic conditions, and many of those indications now have either approved or late-stage gene therapies in view. Recently cleared products such as Zevaskyn and Kebilidi show that authorities are willing to green-light advanced treatments for historically intractable illnesses, driving steady vector demand. The epidemiological transition toward older populations amplifies chronic disease prevalence, creating a durable pool of candidates for one-time gene replacement. Rare-disease incentives, including streamlined reviews and market exclusivity, further fortify the outlook. Combined, these factors add material volume to the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market.
More than 2,000 gene-therapy programs now populate global registries, with adeno-associated viruses (AAV) still the most common payload. The FDA's Platform Technology Designation for Sarepta's rAAVrh74 template encourages reuse of well-characterized vectors, cutting both cost and timeline. Drug makers have followed with bricks-and-mortar commitments such as Novartis' EUR 40 million EU vector plant, ensuring slots for late-stage assets . Developers that secure capacity early can move rapidly from Phase II data to launch. The steady clinical queue therefore locks in multi-year production visibility and underpins expansion across the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market.
A single gene-therapy course can cost USD 1 million, and viral vector inputs often consume up to 40% of that bill. While Brazil showed a path to USD 35,000 CAR-T pricing through local production, most health systems struggle to pay at scale. Outcome-based contracts help spread risk, but smaller biotech firms still face heavy upfront investment to secure slots or build plants. Automation and standardized platforms promise relief, yet they require multimillion-dollar capital outlays that only deep-pocketed sponsors can afford. These costs temper penetration of the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market, especially in lower-income regions.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Viral vectors accounted for 55.45% of the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market in 2024, supported by well-established regulatory precedents and strong transfection efficiency. Non-viral vectors deliver the fastest 29.65% CAGR through 2030, propelled by lipid nanoparticles, polymer conjugates, and electroporation systems that bypass immunity hurdles. Plasmid DNA remains the backbone for both categories, serving as the starting template for viral assembly and as the therapeutic construct in direct injection approaches.
The viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market size for viral vectors is projected to widen further as newly approved products such as Casgevy and Elevidys transition to commercial scale. AAV and lentiviral lines dominate oncology and rare-disease pipelines thanks to durable expression and tissue tropism. Yet manufacturing complexity keeps cost high, motivating drug sponsors to trial scalable non-viral carriers. Lipid nanoparticle expertise gained in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines can be leveraged for plasmid and siRNA delivery, helping non-viral methods chip away at share. Partnerships between nanoparticle specialists and legacy biologics CDMOs have already started to expand total factory utilization, indicating that both modalities will coexist within the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market.
The Viral Vector and Plasmid DNA Manufacturing Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Plasmid DNA, Viral Vector, and Non-Viral Vector), Application (Cancer, Genetic Disorders, Infectious Diseases, Ophthalmic Disorders and More), Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, The Middle East and Africa, and South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America controlled 42.56% of 2024 revenue, sustained by FDA leadership, large venture funding pools, and a deep clinical-trial ecosystem. Major transactions like Lonza's USD 1.2 billion takeover of a Vacaville plant and Charles River's purchase of Vigene Biosciences illustrate the region's appetite for vertical integration. Skilled labor shortages and raw-material chokepoints do persist, but concerted workforce programs and reshoring incentives aim to close gaps. Overall, the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market still finds its highest pricing and most reliable regulatory pathway in the United States.
Asia-Pacific shows the strongest 28.65% CAGR outlook as multinational firms and domestic champions build new suites in China, South Korea, India, and Australia. VectorBuilder's USD 500 million Guangzhou campus and WuXi Biologics' continual expansions reflect Beijing's emphasis on localizing critical modalities, while India's Bharat Biotech commits USD 75 million to its inaugural CGT plant. Regional authorities streamline approvals and offer tax credits, bringing down cost per liter and widening patient access. These moves rapidly enlarge the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market in the region and diversify global supply lines.
Europe retains a mature yet evolving position. EMA guidelines give predictable review timelines, and cross-border consortia channel Horizon Europe funds into advanced-therapy infrastructure. Novartis' EUR 40 million Slovenian vector expansion underscores corporate confidence despite reimbursement variations across member states. Post-Brexit, the United Kingdom pursues parallel regulatory schemes to stay attractive for trials and manufacturing. Latin America and Middle East/Africa trail in absolute terms, but Brazil's cost-effectiveness breakthroughs and Gulf sovereign investment vehicles hint at fresh capacity additions. Collectively, geographical diversification spreads risk and adds resilience to the viral vectors and plasmid DNA manufacturing market.