
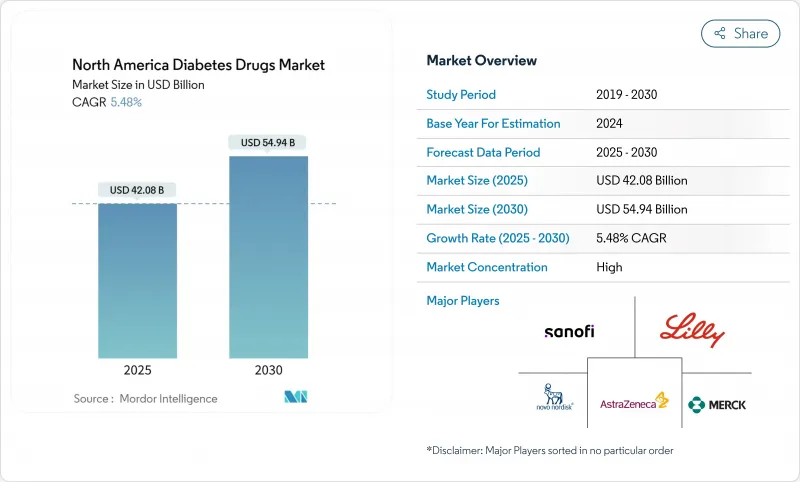
북미의 당뇨병 치료제 시장은 2025년 420억 8,000만 달러, 2030년에는 549억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

차세대 GLP-1 수용체 작용제의 급속한 보급과 함께 당뇨병과 비만 치료의 융합이 진행되고 있는 것이 시장 확대의 큰 요인이 되고 있습니다. 미국 처방약 지출은 2024년에 10.2% 증가했으며, GLP-1은 이미 가장 크고 급성장하는 치료비 범주로 선정되었습니다. 경구 항 당뇨병 치료제물은 주사제의 기술 혁신이 가속화되고 바이오 시밀러 인슐린 도입이 주요 부문에서 가격을 낮추고 있음에도 불구하고 치료량의 대부분을 계속 지배하고 있습니다. 메디케어와의 엄격한 협상, 국가별 가격 상한 규제, 지불자의 사전 승인 규칙이 처방 선택의 형태를 바꾸고 있지만, 치료법의 혁신으로 총 지출이 증가하는 경향이 있습니다. 제조 기지로서 멕시코의 상승과 온라인 약국의 확대는 또한 지역 전체의 경쟁 경제와 환자 접근을 변화시키고 있습니다.
GLP-1 수용체 작용제는 2형 당뇨병 환자의 88% 이상과 관련된 비만과 당뇨병 관리를 통합하는 약물입니다. Tirzepatide는 2023년 말까지 포도당 저하제의 처방 약 12%에 달했고, 당뇨병 이외의 체중 관리 사용자로부터의 인기는 대사 적응증 사이의 치료 모호함을 강조하고 있습니다. GLP-1/GIP의 이중 작용은 단일 표적 약물보다 더 큰 체중 감소와 HbA1c 감소를 가져오고, retatrutide와 같은 새로운 트리플 작용제는 48주에 24%의 체중 감소를 기록하고 새로운 임상 벤치마크를 설정했습니다. FDA의 신속한 승인은 보다 광범위한 심대사성 질환에 대한 적응을 확대하고 보험 상환의 시야를 넓히고, 처방자들은 이러한 치료법을 케어 패스의 초기 단계에서 채택하게 되었습니다.
지불자는 듀얼 및 트리플 인크레틴의 심혈관계 및 신장에 대한 유익성을 인식하기 위해 처방을 재조정하고 있습니다. Medicare의 가격 협상에서 기존 경구 약물에 큰 압력이 가해지면서 새로운 GLP-1 제제는 Tier-preferred의 보험 적용으로 노인의 자기 부담액이 감소하고 있습니다. 고용주의 의료보험제도는 결과지표에 연결된 비만과 당뇨병의 치료계약을 번들로 이용확대를 강화하고 있습니다.
미국의 지불 기관은 양호한 임상 프로파일에도 불구하고 GLP-1의 투여 개시를 지연시키거나 거부하는 다단계 치료 규칙을 계속 적용하고 있으며, 환자의 탈락과 시장 전체의 침투 지연으로 이어지고 있습니다. 메디케어 어드밴티지 플랜은 체중 관리 용도의 승인에 특히 신중하며, 이용 상한을 유지함으로써 초기 성장을 억제하고 있습니다.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 촉진요인 및 억제요인
경구제는 2024년 북미 당뇨병 치료제 시장의 68.23%를 차지했고 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 7.52%로 성장하여 주사제의 약진에도 불구하고 주도권을 유지할 것으로 예측됩니다. 카나글리플로진과 같은 SGLT-2 억제제는 심신 결과 데이터와 캐나다 보건부의 라벨링 업데이트를 기반으로 계속 증가하고 있습니다.
비인슐린 주사제는 GLP-1, 듀얼 GIP/GLP-1, 신흥의 트리플 효능제 클래스를 배경으로 급신장하고 있습니다. 트리플 메커니즘 치료제는 체중, 심혈관, 신장에 효과를 주는 프리미엄 치료제로 자리매김하며, 북미의 당뇨병 치료제 시장에서 처방전 1장당 가치를 높이고 있습니다. α-글루코시다아제 억제제는 고령자 코호트에서 틈새 시장을 유지하고 있으며, 여러 기전을 겸비한 배합제는 복약의 간편화와 복약 준수의 향상을 목표로 하고 있습니다.
2형 당뇨병 치료제는 계속해서 판매의 대부분을 차지하고 있지만, 1형 당뇨병 치료제도 가장 높은 성장을 보이고 있습니다. 주 1회 투여 세마글루티드를 자동 인슐린 제제와 통합함으로써 범위내 투여 시간이 69.4%에서 74.2%로 상승했습니다. 그 결과 1형 보조제인 북미 당뇨병 치료제 시장 규모가 확대되고 있습니다. β 세포 재생을 목적으로 한 유전자 치료 프로그램은 아직 상업화 전이지만 파이프라인의 충실을 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
The North America diabetes drugs market stood at USD 42.08 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 54.94 billion by 2030, translating to a 5.48% CAGR during the period.
A growing convergence of diabetes and obesity treatment, coupled with rapid uptake of next-generation GLP-1 receptor agonists, is providing much of the forward momentum. U.S. prescription drug spending climbed 10.2% in 2024, and GLP-1s already rank as the largest and fastest-growing therapeutic spend category.Oral anti-diabetics continue to control the majority of therapy volumes even as injectable innovation accelerates, and biosimilar insulin introductions are compressing prices in key segments. Tight Medicare negotiations, state price-cap statutes, and payer prior-authorization rules are reshaping formulary choices, yet therapeutic innovations keep total spending on an upward trajectory. Mexico's emergence as a manufacturing hub and the expansion of online pharmacies are also altering competitive economics and patient access across the region.
GLP-1 receptor agonists unify obesity and diabetes management, a nexus relevant to more than 88% of people with Type 2 diabetes. Tirzepatide reached roughly 12% prescription share of glucose-lowering drugs by end-2023, and its popularity among non-diabetic weight-management users underscores the therapeutic blur between metabolic indications. Dual GLP-1/GIP activity delivers greater body-weight and HbA1c reductions than single-target drugs, while emerging triple-agonists such as retatrutide have posted 24% weight loss at 48 weeks, setting new clinical benchmarks. Fast-tracked FDA approvals for wider cardiometabolic indications are expanding reimbursement horizons and encouraging prescribers to adopt these therapies earlier in care pathways.
Payers are recalibrating formularies to recognize the cardiovascular and renal benefits of dual and triple incretins. Medicare's price negotiations apply greater pressure on legacy oral agents, while newer GLP-1s gain Tier-preferred coverage, thus lowering out-of-pocket costs for seniors.Commercial insurers now classify obesity as a medical condition, unlocking pharmacotherapy budgets previously reserved for diabetes. Employer health plans are bundling obesity and diabetes care contracts tied to outcome metrics, reinforcing utilization growth.
US payers continue to impose multi-step therapy rules that delay or deny GLP-1 initiation despite favorable clinical profiles, leading to patient drop-out and slower overall market penetration. Medicare Advantage plans remain especially cautious in approving weight-management uses, preserving utilization caps that curb early growth.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Oral agents secured 68.23% of the North America diabetes drugs market in 2024 and are projected to expand at 7.52% CAGR through 2030, sustaining leadership despite injectable breakthroughs. SGLT-2 inhibitors such as canagliflozin continue to gain based on cardio-renal outcome data and Health Canada labeling updates.
Non-insulin injectables are climbing rapidly on the back of GLP-1, dual GIP/GLP-1, and emerging triple-agonist classes. Triple-mechanism drugs are positioned as premium therapies offering weight, cardiovascular, and renal benefits, thereby lifting value per prescription within the North America diabetes drugs market. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors retain a niche among geriatric cohorts, and combination pills that merge multiple mechanisms aim to simplify dosing and boost adherence.
Therapies for Type 2 diabetes continue to dominate revenue, yet Type 1 options are showing the strongest incremental gains. Integration of weekly semaglutide with automated insulin delivery lifted time-in-range metrics from 69.4% to 74.2%, a meaningful clinical advance. The resulting enthusiasm is expanding the North America diabetes drugs market size for Type 1 adjuncts. Gene-therapy programs aimed at beta-cell regeneration are still pre-commercial but underscore the pipeline depth.
The North America Diabetes Drugs Market Report is Segmented by Drug Class (Insulins [Biosimilar Insulin and More], Non-Insulin Injectable, Oral Anti-Diabetic and Combination Drugs), Diabetes Type (Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes), Drug Origin (Branded and Generic/Biosimilar), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).