
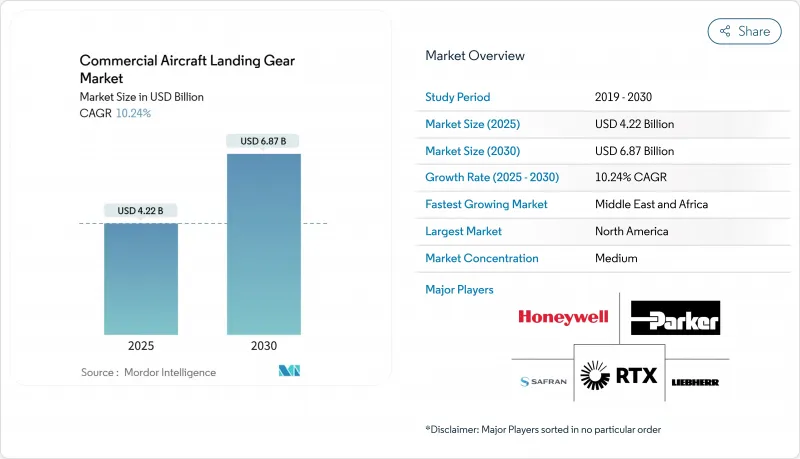
민간 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장 규모는 2025년에 42억 2,000만 달러, 2030년에는 68억 7,000만 달러로 증가할 것으로 예상되며, 10.24%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 보일 것으로 예측됩니다.

연비 효율이 높은 항공기에 대한 강한 수요, 보잉과 에어버스의 지속적인 생산 증가, 경량화 재료의 급속한 발전은 민간 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장을 전반적으로 끌어올렸습니다. 항공사는 이산화탄소 감축 목표를 달성하기 위해 항공기 업데이트 프로그램을 강화했습니다. 동시에, 통합 건강 모니터링 시스템은 랜딩기어를 상품에서 데이터가 풍부한 자산으로 발전시켜 예지보전의 새로운 수익원을 개척했습니다. 북미는 성숙한 교체 주기로 인해 선두를 유지했습니다. 그러나 중동 및 아프리카는 협동체 및 지역 항공기의 대규모 항공기를 필요로 하는 새로운 공항 인프라에 대한 정부의 1조 달러 융자 지원으로 인해 가장 역동적인 지역으로 부상했습니다. 특히 단조 티타늄공급망 제약은 애프터마켓 수요를 지속적으로 증가시켜 항공사가 장기 서비스 계약을 체결하도록 유도했습니다. MRO 공급업체와 티어원 공급업체 간의 통합은 항공사에 통합된 지원 옵션을 제공하는 동시에 경쟁력을 강화했습니다.
보잉과 에어버스는 2043년까지 8만 7,000대 이상의 항공기를 납품하겠다는 목표를 발표했지만, 단조품 및 패스너 부족이 지속되면서 당분간 생산량 증가는 부진할 것으로 보입니다. 미국 정부책임국의 조사에 따르면, 부품 공급업체의 60%가 적시 납품에 어려움을 겪고 있으며, 항공사는 항공기를 더 오래 사용해야 합니다. 이러한 지연은 장기 서비스 계약을 촉진하고 독립형 MRO의 활동을 활성화시켰습니다. 항공기 생산률이 회복됨에 따라 메인 기어 어셈블리와 노즈 기어 어셈블리의 단위 수요는 증가할 것으로 보입니다.
배기가스 규제 강화와 연료비 상승으로 항공사들은 구형 항공기 퇴출에 박차를 가하고 있습니다. 보잉은 2043년까지 납품 예정 기종 43,975대 중 21,100대를 교체할 것으로 예상하고 있으며, 신기술을 도입한 기체로의 구조적 전환을 강조하고 있습니다. 사프란이 생산하는 카본 브레이크는 항공기 1대당 최대 320kg의 무게를 줄이고, 연료 연소 모델에 직접 투입되어 랜딩기어 오버홀 빈도를 감소시켰습니다. 항공사들은 나중에 개조하는 것이 아니라 주문 시점에 첨단 장비 옵션을 지정하여 OEM의 주문 장부를 강화하는 동시에 레거시 시스템과의 기술 격차를 확대했습니다.
지정학적 긴장 속에서 항공우주용 티타늄 가격이 급등하면서 가격에 민감한 지역 항공사와 구매력이 없는 소규모 OEM의 예산이 늘어났습니다. 추가 제조 관련 인증의 장애물도 개발 주기를 연장시켜 예상되는 비용 절감 효과를 상쇄시켰습니다. 프리미엄 제품과 비용적으로 최적화된 대체 제품 간의 격차가 확대되고, 신흥국 시장에서의 차량 업그레이드가 지연될 수 있는 경제적 리스크.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 촉진 및 억제요인은 다음과 같습니다.
주익 시스템은 2024년 매출의 64.20%를 차지했고, 항공기의 이륙 중량 제한을 규정하는 구조적 하중을 담당하고 있습니다. 민간 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장의 큰 조각으로 인해 Tier 1 공급업체는 R&D 비용을 고부가가치 어셈블리에 분산시킬 수 있었습니다. 티타늄 합금과 고강도 강철로 만들어진 스켈레톤 빔은 피로 수명을 유지하면서 무게를 줄이고 항공사가 평가하는 성능 향상을 가져왔습니다.
노즈 기어 부문은 통합 전기 작동 및 실시간 무게 균형 센서와 같은 혁신이 기어 트레인의 이 부분에 집중되면서 10.98%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 전망을 보였습니다. 노즈시스템의 상용 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장 규모는 전기기계 부품에 특화된 신규 진출기업들을 끌어들여 빠르게 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다. 공급업체들은 메인 어셈블리보다 낮은 기술 진입장벽과 짧은 인증 주기를 활용하여 경쟁을 심화시키면서 전반적인 기술 채택을 가속화하고 있습니다.
B737 MAX와 A320neo로 대표되는 협동체 프로그램은 2024년 매출의 55.45%를 차지했으며, 민간 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장에서 매우 중요한 역할을 할 것임을 분명히 했습니다. 생산률의 상승은 선박 세트 수요에 직접적으로 반영되어 주 다리 공급업체는 10년동안 예측 가능한 수량을 확보 할 수있었습니다.
리저널젯은 엠브라에르의 E2 프로그램과 2차 시장에서의 새로운 노선 최적화 전략으로 인해 2030년까지 10.54%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 보일 것으로 예측됐습니다. 리저널 제트 상용 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장 규모는 특히 슬롯에 제약이 있는 공항이 소형 항공기를 선호하는 아시아태평양과 북미에서 협폭동체 항공기와의 격차를 일부 해소할 것으로 보입니다.
상용 항공기 랜딩기어 시장 보고서는 랜딩기어 유형(주 랜딩기어, 노즈 랜딩기어), 항공기 유형(협폭동체, 광폭동체, 지역 제트기), 최종 사용자(OEM, 애프터마켓), 하위 시스템(액추에이션 시스템, 조향 시스템, 기타), 지역(북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 중동 및 아프리카, 기타)으로 구분하여 분석하였습니다. 조향시스템, 기타), 지역(북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 남미, 기타)으로 구분하고 있습니다. 시장 예측은 금액(USD)으로 제공됩니다.
북미는 2024년 38.98%의 점유율을 유지했으며, 오클라호마시티, 마이애미, 몬트리올에 걸친 풍부한 단일 통로 제트기 도입 기반과 견고한 오버홀 생태계를 기반으로 하고 있습니다. 이 지역의 항공사들은 공급망 변동성을 헤지하기 위해 다년간의 서비스 계약을 체결하여 민간 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장 수요를 안정화시켰습니다.
유럽은 한 자릿수 중반의 꾸준한 성장세를 이어갔습니다. 에어버스는 A321neo의 확장을 위해 기어십 세트 수주를 가속화하고 있으며, 지속가능성 관련 법규로 인해 전기 택시 프로그램이 급물살을 타고 있습니다. 청정항공에 따른 EU의 연구 자금 지원은 기술 검증 리스크를 낮추고 상용 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장에 대한 공급업체의 진입을 확대했습니다.
중동 및 아프리카는 각 국가가 새로운 공항에 1조 달러를 투자하고 에티오피아항공, 에미레이트항공, 사우디아라비아와 같은 항공사가 노선망을 확장함에 따라 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 12.45%로 가장 빠른 성장세를 보일 것으로 예측됩니다. 보잉은 아프리카의 항공기 보유 대수가 두 배로 늘어나면서 민간 항공기 랜딩 기어 시장에 큰 증가 여력이 생길 것으로 전망하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 인도와 인도네시아의 공항 계획에 힘입어 이러한 확장 패턴을 반영했습니다. 국가 융자 및 급성장하는 저가 항공사가 대형 협동체를 주문하면서 랜딩 기어 및 애프터마켓 지원에 대한 수요가 증가했습니다. 남미는 거시경제의 역풍에도 불구하고 아비앙카항공, 라탐항공, GOL항공의 기재 현대화로 인해 완만한 성장을 기록했습니다.
The commercial aircraft landing gear market size reached USD 4.22 billion in 2025 and is projected to rise to USD 6.87 billion by 2030, translating into a 10.24% CAGR.
Strong demand for fuel-efficient fleets, continued production ramp-up at Boeing and Airbus, and rapid advances in lightweight materials collectively propelled the commercial aircraft landing gear market. Airlines intensified fleet renewal programs to meet carbon-reduction goals. At the same time, integrated health-monitoring systems elevated landing gear from a commodity to a data-rich asset, opening new revenue streams in predictive maintenance. North America preserved its leadership owing to its mature replacement cycle. Still, the Middle East and Africa emerged as the most dynamic regions as governments financed USD 1 trillion in new airport infrastructure that required large fleets of narrowbody and regional aircraft.Supply-chain constraints, notably in forged titanium, kept aftermarket demand elevated and encouraged carriers to sign long-term service agreements. Consolidation among MRO providers and tier-one suppliers added competitive intensity while giving airlines more integrated support options.
Boeing and Airbus published delivery targets that implied more than 87,000 airplanes through 2043, yet persistent shortages in forgings and fasteners slowed near-term output. A US Government Accountability Office survey showed 60% of component suppliers struggling with timely deliveries, forcing airlines to keep airframes in service longer. That lag boosted long-term service agreements and lifted activity across independent MROs. As build rates recover, unit demand for main and nose gear assemblies will rise because each new aircraft order triggers one complete shipset, shielding the commercial aircraft landing gear market from cyclical turbulence.
More restrictive emissions standards and high fuel costs drove carriers to accelerate the retirement of older jets. Boeing estimated 21,100 replacements among the 43,975 deliveries it envisioned through 2043, underscoring a structural pivot toward new-technology fleets. Carbon brakes manufactured by Safran eliminated up to 320 kg per aircraft, fed directly into fuel-burn models, and reduced landing gear overhaul frequency. Airlines began specifying advanced gear options at the point of order rather than retrofitting later, strengthening OEM orderbooks while widening the technology gap with legacy systems.
Prices for aerospace-grade titanium spiked amid geopolitical tension, stretching budgets for carriers in price-sensitive regions and smaller OEMs that lack purchasing power. Certification hurdles around additive manufacturing also lengthened development cycles and offset projected cost savings. The economic risk of widening the gap between premium products and cost-optimized alternatives, potentially delaying fleet upgrades in developing markets.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Main landing gear systems represented 64.20% of 2024 revenue, carrying the structural loads defining aircraft take-off weight limits. This sizeable slice of the commercial aircraft landing gear market enabled tier-one suppliers to spread R&D costs across high-value assemblies. Skeletonized beams made of titanium alloys and high-strength steels reduced weight while maintaining fatigue life, generating incremental performance gains valued by airlines.
The nose-gear segment showed a 10.98% CAGR outlook because innovations such as integrated electrical actuation and real-time weight-and-balance sensors concentrated in that part of the gear train. The commercial aircraft landing gear market size for nose systems is expected to expand rapidly, attracting new entrants specializing in electromechanical components. Suppliers leveraged lower technical entry barriers and shorter certification cycles than main assemblies, increasing competition yet accelerating overall technology adoption.
Narrowbody programs, led by the B737 MAX and A320neo families, delivered a 55.45% share of 2024 revenue, underlining their pivotal role in the commercial aircraft landing gear market. Higher build rates translated directly into shipset demand and gave main-gear suppliers predictable volume through the decade.
Regional jets posted a projected 10.54% CAGR to 2030, powered by Embraer's E2 program and new route-optimization strategies in secondary markets. The commercial aircraft landing gear market size for regional jets will close part of the gap with narrowbodies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America, where slot-constrained airports favor smaller-gauge aircraft.
The Commercial Aircraft Landing Gear Market Report is Segmented by Landing Gear Type (Main Landing Gear and Nose Landing Gear), Aircraft Type (Narrowbody, Widebody, and Regional Jet), End User (OEM, Aftermarket), Sub-Systems (Actuation System, Steering System, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America retained a 38.98% share in 2024, supported by a deep installed base of single-aisle jets and a robust overhaul ecosystem spanning Oklahoma City, Miami, and Montreal. The region's carriers locked in multi-year service agreements to hedge against supply-chain volatility, stabilizing demand for the commercial aircraft landing gear market.
Europe followed with steady mid-single-digit growth. Airbus accelerated gear-shipset orders to feed its A321neo expansion, while sustainability legislation fast-tracked electric taxi programs. EU research funding under Clean Aviation lowered technology-validation risk and broadened supplier participation in the commercial aircraft landing gear market.
The Middle East and Africa are on track for the quickest 12.45% CAGR through 2030 as states invest USD 1 trillion in new airports and carriers such as Ethiopian Airlines, Emirates, and Saudia expand route networks. Boeing predicted Africa's fleet would double, creating a sizeable incremental pool for the commercial aircraft landing gear market.
Asia-Pacific mirrored this expansion pattern, anchored by Indian and Indonesian airport programs. State-backed financing and fast-growing low-cost carriers placed large narrowbody orders, lifting forward demand for landing gear and aftermarket support. South America recorded moderate growth, hindered by macroeconomic headwinds, yet benefited from fleet modernization at Avianca, LATAM, and GOL.