
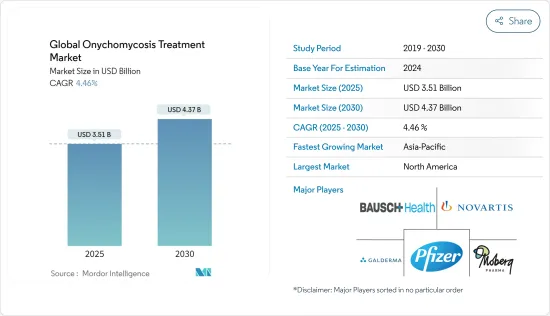
세계의 조진균증 치료 시장 규모는 2025년에 35억 1,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2030년) CAGR 4.46%로 확대되어, 2030년에는 43억 7,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

COVID-19의 대유행 이전에는 조진균증이 의심되는 모든 환자에게 임상 검사, 피부경 검사 및 진균 검사가 권장되었습니다. COVID-19의 유행이 확산됨에 따라 긴급성이 없는 통원은 연기되고 있으며, 조진균증의 진단 및 치료의 일부 요소에 원격 의료가 이용될 수 있습니다. 원격 진료는 조진균증이 의심되는 환자를 평가하는 데 사용할 수 있지만 이미 균학적 확인이 있는 환자에게 이상적입니다. 그 결과, COVID-19의 대유행은 시장에 단기적인 중단을 초래할 것으로 예측됩니다. 그러나 수익성장률은 예측기간 동안 회복될 것으로 예측되며, 세계의 조진균증 시장은 2자리 성장률로 증가할 것으로 예측됩니다.
조진균증은 통상적으로 손발톱의 비 피부 사상균 감염을 지칭하였으나, 현재는 모든 곰팡이에 의한 손발톱 감염을 지칭하는 일반적인 용어로서 사용되고 있습니다(손발톱 백선증은 특히 손발톱의 피부 사상균성 침습을 나타냅니다). 조진균증에는 표재성 조진균증, 원위 및 외측 손톱 아래 조진균증, 근위 손톱 아래 조진균증, 손톱내 조진균증, 전체 손톱 이영양증 조진균증 등의 유형이 있습니다. 손발톱 이영양증의 약 절반만이 곰팡이에 의해 유발되며, 따라서 조진균증은 진균성 피부 감염의 1/3을 차지합니다.
노년 인구 증가, 조진균증의 유병률 증가, 세계 당뇨병 인구 증가, 조진균증의 잠재적 위협에 대한 의식 증가가 조진균증 치료 시장의 주요 촉진요인입니다. 2020년에 발표된 'High prevalence of mixed infections in global onychomycosis'라는 제목의 논문에 따르면, 손톱발 백선증은 세계에서 10%의 유병률로 발생하는 것으로 추정되며 감염균은 Trichophyton rubrum이 가장 흔합니다. 또한 2021년 세계보건기구(WHO)의 데이터에 따르면 2030년에는 지구상의 6명 중 1명이 60세 이상의 노인이 될 것으로 예상됩니다. 60세 이상 인구는 2020년 10억 명에서 2050년 14억 명으로 증가할 것으로 예상됩니다. 2050년까지 60세 이상의 성인 인구는 전 세계적으로 2배(21억 명)로 증가합니다.
조진균증 치료에 사용할 수 있는 약물은 테르비나핀, 시클로피록스, 쥬브리아, 플루코나졸, 펜락, 시클로단, 케토코나졸, 스폴라녹스, 이트라코나졸, 케리딘, 에피나코나졸, 글리세오플빈 등을 포함합니다. 조진균증 치료는 약물이 첫 번째 선택 변함이 없으며 지속적으로 높은 성공률로 큰 시장 점유율을 차지합니다.
Elewski와 Charif의 조진균증 보고서에 따르면 노인 인구의 약 40%가 조진균증이며 65세 이상에서는 발톱 성장률이 약 40%에서 60% 감소합니다. 또한, 조진균증은 세계적으로 인구의 약 2%에서 26%가 앓고 있습니다. 그러나 조진균증에 감염된 사람 중 선진국에서 의사의 진단이나 치료를 받는 사람은 30% 미만입니다.
조진균증 치료 시장에서 약물 부문은 큰 점유율을 차지합니다. 제품의 높은 효능과 가용성으로 인해 예측 기간 동안에도 유사한 동향이 예상됩니다. 2021년 7월, Lupin은 미국 식품의약국(FDA)으로부터 타바보롤 외용액 5%의 미국 출시 승인을 받았습니다.
COVID-19의 유행은 공급망의 갈등으로 인해 의약품 유통이 세계적으로 혼란스럽고 2020년에는 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되었습니다. 그러나, 2020년 후반, 2021년, 그리고 그 이전 해에는 조진균증 시장이 회복되어 예측 기간 동안 플러스 성장을 보일 것으로 예상되었습니다.
북미는 높은 약값, 노인 인구 증가, 이 지역의 조진균증 및 당뇨병 환자의 유병률 증가로 인해 세계 조진균증 치료 시장에서 큰 점유율을 차지할 것으로 예상됩니다. 인구조사국의 2020년 인구추계에 따르면 5,500만 명 이상의 미국인이 65세 이상이며, 그 중 4분의 1이 캘리포니아, 플로리다, 텍사스의 3개 주에 살고 있습니다. 기타, 조지아주, 일리노이주, 미시간주, 뉴욕주 등 7개 주가 65세 이상 인구의 약 1/4을 차지하고 있습니다.
조진균증이 연령에 따라 증가하는 이유로는 손발톱의 외상 반복, 말초 순환 불량, 당뇨병, 면역 기능 저하, 병원성 진균에 오랫동안 노출되는 운동 부족, 발톱을 자를 수 없거나, 발 케어가 잘 되지 않는 등 다양한 요인을 들 수 있습니다. 국내기업은 시장개척을 위해 연구개발, M&A, 제품 출시 등 다양한 전략을 취하고 있습니다.
2020년 10월, 미국 Pfizer Inc.는 조진균증에 대한 임상 연구를 시작했다고 발표했습니다. 첫 번째는 AN2690 외용액이 손톱 무좀 치료에 효과적인지 여부를 결정하는 시험입니다. 다른 하나는 소아와 청소년을 대상으로 하는 원이부 조갑하 조진균증에 대한 타바보롤 5% 외용액의 안전성 및 약동학을 평가하는 개방표지시험이었습니다.
한편, COVID-19의 유행은 진단의 감소를 가져오고, 병원과 1차 케어 센터가 COVID-19 환자에게 중점을 옮겼기 때문에 조진균증 치료제 및 기타 치료법의 판매 수입에 영향을 주었습니다.
조진균증 치료 시장은 세분화되어 경쟁이 심하고 여러 주요 기업으로 구성되어 있습니다. 각 회사는 시장에서의 지위를 강화하기 위해 개발, 제휴, 제품 출시에 주력하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2020년 4월 미국 식품의약국은 Bausch Health사의 Jublia 승인을 확대했습니다. Jublia는 6세 이상 환자의 발톱 발톱 무좀을 치료하는 데 사용되는 외용제입니다.
현재 시장을 독점하고 있는 기업으로는 Bausch Health Companies Inc.(Valeant Pharmaceuticals Inc.), Galderma SA, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Moberg Pharma AB, Johnson & Johnson, Bayer AG, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., Ciplas Ltd, Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals Inc., Lumenis Ltd 등이 있습니다.
The Global Onychomycosis Treatment Market size is estimated at USD 3.51 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 4.37 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.46% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Clinical examination, dermoscopy, and mycological examination were recommended for all patients with suspected onychomycosis prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. Non-urgent in-patient visits are being postponed as the COVID-19 pandemic spreads, and telemedicine may be used to handle some elements of onychomycosis diagnosis and treatment. Telemedicine can be used to assess individuals with suspected onychomycosis, although it's best for those who have already had their mycological confirmation. As a result, the COVID-19 pandemic is projected to cause a short-term interruption in the market. However, the revenue growth rate is predicted to recover during the forecast period, and the global onychomycosis market is expected to increase at a double-digit rate.
Onychomycosis traditionally referred to a non-dermatophytic infection of the nail but is now used as a general term to denote any fungal nail infection (tinea unguium specifically describes a dermatophytic invasion of the nail plate). Onychomycosis is of different types, such as superficial onychomycosis, distal and lateral subungual onychomycosis, proximal subungual onychomycosis, endonyx onychomycosis, and total dystrophic onychomycosis. Only around half of nail dystrophies are caused by a fungus; hence onychomycosis accounts for one-third of fungal skin infections.
The increasing geriatric population, rising prevalence of onychomycosis, diabetic population worldwide, and growing awareness about the potential threats of onychomycosis are the key driving factors in the onychomycosis treatment market. According to an article titled, 'High prevalence of mixed infections in global onychomycosis,' published in 2020, onychomycosis is estimated to occur at a prevalence of 10% worldwide, with the infecting organism most commonly being Trichophyton rubrum. In addition, according to World Health Organization's (WHO) data in 2021, by 2030, one out of every six persons on the globe will be aged 60 years or older. The number of people aged 60 years and more is expected to rise from 1 billion in 2020 to 1.4 billion by 2050. By 2050, the global population of adults aged 60 years and above will have doubled (2.1 billion).
Some of the drugs available for the treatment of onychomycosis are terbinafine, ciclopirox, Jublia, Fluconazole, Penlac, ciclodan, ketoconazole, Sporanox, Itraconazole, Kerydin, efinaconazole, griseofulvin, and so on. For onychomycosis treatment, drugs remain the first-line treatment choice and hold a major market share owing to a consistently high success rate.
Elewski and Charif's onychomycosis report states that approximately 40% of the elderly population have onychomycosis and a reduction in nail growth rate ranges from about 40% to 60% in persons aged above 65 years. Furthermore, onychomycosis affects approximately 2% to 26% of different populations globally. However, less than 30% of individuals infected with onychomycosis seek medical advice or treatment in developed countries.
The drugs segment holds a significant share in the onychomycosis treatment market. It is anticipated to show a similar trend over the forecast period due to the products' highly effective nature and easy availability. In July 2021, Lupin received approval to launch Tavaborole Topical Solution 5% in the US from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the distribution of drugs was disrupted worldwide due to the supply chain disruptions and was expected to have an impact in 2020. However, in late 2020, 2021, and further years, the onychomycosis market was expected to recover and even show positive growth over the forecast period.
North America is expected to hold a major share in the global onychomycosis treatment market due to high drug costs, rising geriatric population, and increasing prevalence of onychomycosis and diabetic patient populations in this region. According to the Census Bureau's 2020 population estimates, more than 55 million Americans are aged 65 years or older, of which one-fourth live in one of three states, namely, California, Florida, and Texas. Seven other states, including Georgia, Illinois, Michigan, New York, account for roughly another quarter of the 65+ population.
The reasons for the age-related increase in onychomycosis include a variety of factors, like repeated nail trauma, poor peripheral circulation, diabetes, suboptimal immune function, longer exposure to pathogenic fungi, inactivity, or the inability to cut toenails or maintain good foot care. Various strategies, such as research and development, mergers and acquisitions, and product launches, are being adopted by domestic companies to strengthen their market position.
In October 2020, US-headquartered Pfizer Inc. announced that it had begun clinical studies concerning onychomycosis. The first one involved a study determining whether the AN2690 topical solution is an effective treatment for onychomycosis of the toenail. The second one was an open-label study to evaluate the safety and pharmacokinetics of the tavaborole 5% topical solution to treat distal subungual onychomycosis of the toenail in both children and adolescents.
On the other hand, the COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in decreased diagnosis and impacted the sales revenue of drugs and other treatment methods for onychomycosis as hospitals and primary care centers shifted their focus to COVID-19 patients.
The onychomycosis treatment market is fragmented and competitive and consists of several major players. Companies are focusing on developments, collaborations, and product launches to strengthen their market position. For instance, in April 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration expanded the approval of Jublia manufactured by Bausch Health. Jublia is a topical solution used to treat onychomycosis in the toenail(s) in patients aged six years and above.
Some of the players currently dominating the market are Bausch Health Companies Inc. (Valeant Pharmaceuticals Inc.), Galderma SA, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Moberg Pharma AB, Johnson & Johnson, Bayer AG, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd, Cipla Ltd, Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Lumenis Ltd.