
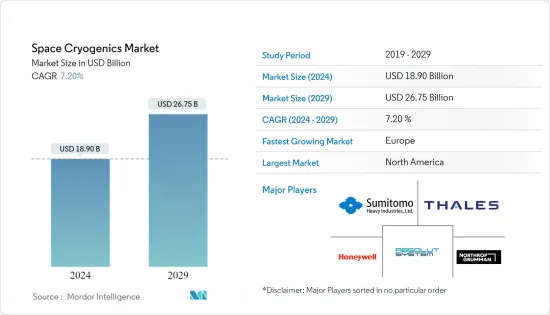
우주용 극저온 시장 규모는 2024년에 189억 달러로 추정 및 예측되고, 2029년에는 267억 5,000만 달러에 이를 전망이며, 예측 기간 중(2024-2029년)에 CAGR 7.20%로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.

우주용 극저온 시장의 성장은 우주선에 탑재되는 오퍼레이션의 간소화가 진행되고 있는 것에 기인하고 있습니다. 우주 미션이 복잡해지는 가운데, 장기간에 걸쳐 신뢰성 높은 성능을 발휘할 수 있는 극저온 시스템에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있습니다.
극저온 기술의 발전은 가혹한 우주 환경을 견디는 보다 견고하고 효율적인 극저온 시스템의 개발로 이어지고 있습니다. 우주 기반 응용 분야의 센서 및 콜드 일렉트로닉스와 같은 극저온 장치의 발전과 개척이 시장 성장의 원동력이 되었습니다.
극저온 센서와 콜드 일렉트로닉스는 재료 과학의 발전으로부터 혜택을 누리는 장치입니다. 저장 탱크, 단열재, 이송 시스템, 냉각 메커니즘을 포함한 극저온 인프라의 개발, 시험 및 배치에는 많은 재정 투자가 필요합니다. 따라서 극저온 설비에 필요한 높은 운영비와 자본 지출은 우주 극저온 시장의 성장을 방해하는 큰 요인이 되고 있습니다.
우주 과학 미션 부문은 우주 미션에서 크리오제닉스의 사용 증가로 예측 기간 동안 최대 수익 점유율을 차지할 것으로 예측됩니다. 세계적으로 우주 기관은 인공위성과 로켓 등 발사에 이니셔티브를 하고 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2023년 5월에는 인도 우주연구기관(ISRO)이 극저온 상단을 갖춘 GSLV 로켓을 이용하는 2세대 네비게이션 위성 발사에 성공했습니다. NVS-01은 정확하고 실시간 네비게이션을 제공하여 국가의 지역 네비게이션 시스템을 보완합니다.
2022년 11월 미국의 우주 기관인 NASA는 플로리다의 케네디 우주 센터에서 아르테미스-1 미션을 발사했습니다. 발사 중, 코어 스테이지 엔진은 발사 8분 후에 정지하고 로켓의 나머지 부분으로부터 분리되었습니다. 그 후 중간 극저온 추진 단계(ICPS)가 오리온 우주선 추진에 사용되었습니다. 오리온 우주선의 네 개의 태양전지판은 NASA에 의해 전개되었습니다. Orion은 ICPS에서 분리되어 '트랜스 루너 주입'을 완료했습니다. 현재 달 궤도를 향해 이동하고 있습니다. 이러한 개발은 예상되는 몇 년동안 이 부문을 이끌 것으로 예상됩니다.
우주용 극저온 기술 시장에서는 예측 기간 동안 진행 중 및 계획 중인 우주 이니셔티브의 결과로 유럽이 가장 높은 성장을 보일 것으로 예측됩니다. 예를 들어, 영국이 태양계 외 행성을 연구하기 위한 우주망원경의 창설을 주도하기 위해 2022년 영국 정부는 3,105만 달러의 투자를 발표했습니다. 이 자금은 이 나라가 Ariel의 페이로드 모듈, 극저온 냉각기, 광학 지상 지원 장비를 받는 동시에 미션의 과학적 운영과 데이터 처리를 계속 주도할 것으로 예상됩니다.
2023년 7월 프랑스 의회는 2024년부터 2030년까지 7년간 군사비 프로그램을 승인했습니다. 이 프로그램에는 우주 개발비로 67억 달러가 포함되어 있으며, 이는 전기 대비 45% 증가했습니다. 2023년 9월 독일 정부는 새로운 우주 전략을 발표하고 2030년까지 우주 여행의 목표와 기회를 제시했습니다.
2023년 10월 영국 우주청과 미국 우주 비행 서비스 회사인 Axiom Space는 영국 우주 비행사를 2주 동안 궤도로 보내는 것을 목표로 초기 협정에 조인했습니다. 영국과의 임무는 유럽 우주 기관이 상업 스폰서가 되어 지원합니다. 따라서 이 지역의 우주산업에서의 활동 증가는 우주용 극저온에 대한 수요 증가로 이어져 시장 수익의 성장을 가속할 것으로 기대되고 있습니다.
우주용 극저온 시장은 통합되어 대기업이 가장 높은 시장 점유율을 가지고 있습니다. 주요 시장 진출 기업으로는 THALES, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Absolut System, Sumitomo Heavy Industries Ltd, Honeywell International Inc. 등이 있습니다.
이 회사는 극저온 기술의 선두 주자이며 극저온 쿨러 공급업체입니다. 각 회사는 자동 제어, 원격 모니터링 및 유지 보수 기능을 제공하는 극저온 시스템의 연구 개발에 투자하고 있으며 우주선의 운영을 간소화하고 인위적 실수의 위험을 줄이는 데 도움이 됩니다. 극저온 시스템의 복잡성을 줄이고 사용 편의성을 향상시킴으로써 우주선 운영자는 복잡한 시스템 관리보다 미션 목표에 집중할 수 있습니다.
The Space Cryogenics Market size is estimated at USD 18.90 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 26.75 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 7.20% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The space cryogenics market growth can be attributed to the increasing simplicity of operations in onboard spacecraft. With space missions becoming more complex, the demand for cryogenic systems that can deliver reliable performance over extended periods is growing.
Advancements in cryogenic technologies are leading to the development of more robust and efficient cryogenic systems to withstand harsh space conditions. Advancements and developments in cryogenic devices, such as sensors and cold electronics in space-based applications, are driving market growth.
Cryogenic sensors and cold electronics are devices that benefit from the development of materials science. Substantial financial investments are required for the development, testing, and deployment of cryogenic infrastructure, which includes storage tanks, insulation, transfer systems, and cooling mechanisms. Hence, high operating expenses and capital expenditures required for cryogenic setups are major factors hindering the growth of the space cryogenics market.
The space science missions segment is expected to account for the largest share of revenue over the forecast period, owing to the increasing use of cryogenics in space missions. Globally, space organizations have been taking the initiative to launch satellites, rockets, and others. For instance, in May 2023, a second-generation navigation satellite that utilizes a GSLV rocket with a cryogenic upper stage was successfully launched by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). The NVS-01 will supplement the country's regional navigation system by delivering precise and real-time navigation.
In November 2022, the American space agency, NASA, launched the Artemis-1 mission at Florida's Kennedy Space Center. During the launch, the core stage engines shut down eight minutes after liftoff and separated from the rest of the rocket. After this, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) was used to propel the Orion spacecraft. The four solar panels of the Orion spacecraft were deployed by NASA. Orion decoupled from the ICPS and completed 'translunar injection.' It is now traveling toward the lunar orbit. Such developments are expected to lead the segment during the forecasted years.
In the space cryogenics market, Europe is projected to witness the highest growth as a result of the ongoing and planned space initiatives during the forecast period. For instance, to ensure that the United Kingdom leads the creation of a space telescope to study exoplanets, in 2022, the UK government announced an investment of USD 31.05 million. With this funding, the country is envisioned to continue leading the mission's scientific operations and data processing while also receiving the payload module, cryogenic cooler, and optical ground support equipment for Ariel.
In July 2023, the French parliament approved a seven-year military spending program for 2024-2030 that includes USD 6.7 billion for space programs, which is a 45% increase from the previous period. In September 2023, the German government presented a new Space Strategy and laid its goals and opportunities for space travel until 2030.
In October 2023, the UK Space Agency and a US spaceflight services company, Axiom Space, signed an initial agreement as they bid to send British astronauts into orbit for two weeks. The mission with the UK would be commercially sponsored and supported by the European Space Agency. Hence, increasing activities in the space industry in this region are leading to a rise in demand for space cryogenics, which is expected to drive growth in market revenue.
The space cryogenics market is consolidated, with leading players having the highest market share. Some of the key market players include THALES, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Absolut System, Sumitomo Heavy Industries Ltd, and Honeywell International Inc.
These companies are leaders in cryogenic technology and suppliers of cryogenic coolers. Companies are investing in the R&D of cryogenic systems that offer automated controls, remote monitoring, and maintenance capabilities to help streamline spacecraft operations and reduce the risk of human error. By reducing the complexity of cryogenic systems and enhancing their ease of use, spacecraft operators can focus on mission objectives rather than intricate system management.