
희귀의약품 시장은 2025년에 2,309억 1,000만 달러가 되고, 2030년에는 3,125억 3,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, CAGR은 6.24%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

지속적인 성장은 규제 우대 조치, 유전자 및 세포 치료의 돌파구, 7,000개가 넘는 희귀질환의 근본적인 미충족 요구를 반영합니다. 생물학적 제형, 특히 유전자 요법과 단일클론항체의 이점은 한 번에 치료하는 치료에 대한 축족을 강조합니다. 북미는 강력한 지정 프로그램과 강력한 상환을 배경으로 선도하고 있으며, 아시아태평양은 정책의 틀이 확대됨에 따라 기세를 늘리고 있습니다. 경쟁정보에서는 대기업 제약기업이 파이프라인의 두께를 확보하기 위해 전문 바이오테크놀러지 기업을 인수하고 인공지능을 활용한 적응시험으로 개발사이클을 단축하여 독점기간 연장을 활용하고 있습니다.
유전자 치료는 대증 요법이 아닌 원인 변이를 표적으로 함으로써 희귀의약품 시장을 재정의하고 있습니다. 2024년 11월에 FDA가 승인한 방향족 L-아미노산 탈탄산효소 결핍증에 대한 KEBILIDI는 한 번의 방울로 임상적으로 의미 있는 운동 기능의 개선을 보였습니다. 유럽에서도 비슷한 기세가 있었고, 2024년에 LENMELDY가 EMA로부터 메타크로매틱 백질 이영양증에 대한 승인을 받았고, 바이오마커 주도의 가속화 경로가 검증되었습니다. CRISPR 편집과 아데노 관련 바이러스 전달의 융합은 전 세계 유병률이 1,000명 미만이더라도 실행 가능한 비즈니스 모델을 가능하게 합니다. 코스당 200만 달러를 초과할 수도 있는 프리미엄 가격은 제조업체가 구축해야 하는 특수 인프라에 대한 수익을 지원하는 것입니다. 수직 통합된 벡터 제조 라인이 있는 이른 무버는 강력한 진입 장벽과 가격 결정력을 획득합니다.
인공지능 플랫폼은 중간 효과와 안전성 신호를 기반으로 프로토콜을 조정할 수 있어 환자에 대한 노출을 줄이고 고정 설계와 비교하여 타임라인을 18-24개월 단축합니다. 2024년 AI에 관한 FDA 워크숍에서는 문서화에 대한 기대가 명확해지고, 보다 신속하면서도 설명 가능한 패스웨이가 촉진되었습니다. 머신러닝 알고리즘은 환자의 계층화를 향상시킵니다. 이를 통해 스폰서는 더 작은 N 크기로 규제 수준의 증거를 얻을 수 있으며 독점권 절벽을 앞둔 희귀의약품 시장에 신속하게 진입 할 수 있습니다. 현재는 사내에 데이터 사이언스 팀을 가진 대기업이 적응 시험 능력을 독점하고 있어 경쟁과의 차이를 넓히고 있습니다.
연간 치료비의 중앙값은 2024년에 25만 6,000달러를 넘고, 단회 투여의 유전자 치료는 빈번하게 200만 달러를 넘었습니다. 지불자는 사전 승인 및 결과 기반 계약으로 대응하며, 특히 치료가 이후 더 광범위한 집단으로 확장되는 경우에 대응합니다. 유럽의 HTA 기관은 상시 이후 지속적인 이익의 증거를 요구하고 있으며, 스폰서는 장기 레지스트리에 자금을 제공하도록 강요되고 있습니다. 따라서 가격 전략은 혁신에 대한 투자 회수와 상환의 실행 가능성을 유지하는 미묘한 균형을 유지하고 있습니다.
생물제제는 2024년 매출의 65.65%를 차지했고 2030년까지의 CAGR은 8.84%로 저분자를 상회할 전망입니다. 2024년 FDA 승인의 25%는 단일클론항체 또는 유전자 치료로 정밀 개입을 가능하게 하는 모달리티 플랫폼에 대한 선호가 지속됨을 보여주었습니다. 생물학적 제제의 희귀의약품 시장 규모는 2030년까지 2,050억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 고가로 거래되는 일회성 치료제에 의해 지원되고 있습니다. 비생물학적 제형은 재사용된 저분자 화합물에 의한 대사성 질환에서 여전히 점유율을 유지하고 있지만, 유전자 의약품이 보다 효과적으로 근본적인 효소 결핍을 해결함에 따라 경쟁과의 차별화가 좁아지고 있습니다. 한편, 저분자 의약품 제조업체는 제제 혁신과 라이프사이클 매니지먼트에 의존하고 있습니다.
두 번째 단락 유전자 치료의 모범 사례로는 겸상 적혈구증에 대한 LYFGENIA와 방향족 L-AAD 결핍증에 대한 KEBILIDI가 있으며, 모두 단일 투여로 획기적인 임상 효과를 나타냅니다. 제조의 복잡성이 진입 장벽을 높이고 있으며, 그 결과 CDMO와의 제휴와 사내 벡터 능력이 인수의 계기가 되고 있습니다. 규제 당국은 확실한 효력 측정과 장기 후속 조치를 요구하고 있으며, 각 회사는 학제 간 감시 프로그램을 수립하고 있습니다. 지적 재산 전략은 캡시드 공학과 프로모터 최적화에 중점을 두고 시장 경쟁력을 강화하고 있습니다.
종양성 질환은 2024년에 40.53%의 점유율을 유지했지만, 혈액 악성 종양의 포화가 나타날수록 성장 속도는 둔화됩니다. 2024년 암 영역의 희귀의약품 시장 점유율은 41%였지만, 새로운 카테고리가 가속됨에 따라 약간 저하될 것으로 예측됩니다. EMA에 의한 재발 여포성 림프종에 대한 Ordspono의 승인은 T 세포 유도 항체의 기술 혁신이 계속되고 있음을 뒷받침합니다. 그러나 혈액·면역질환 영역에서는 콘시주맙이나 피투실란 등의 인자 보충제가 CAGR 10.35%를 나타낼 전망입니다.
두 번째 단락 SOD1-ALS에 대한 토페르센을 포함한 신경계 유전자 치료는 파이프라인의 폭을 넓히고 바이오마커 주도의 승인을 강조합니다. 대사질환 프로그램은 차세대 효소 보충요법이나 mRNA 요법을 활용하고, 바이러스성 출혈열과 같은 감염증의 희소질환은 틈새 자금을 모은다. 투자자는 이러한 부문에서 포트폴리오의 가중치를 평가할 때 치료의 신규성과 규제 기세를 추적합니다.
북미는 2024년 세계 매출의 42.82%를 차지했으며, 희귀의약품법에 근거한 7년간의 독점권과 25%의 임상시험세액 공제의 혜택을 계속 받았습니다. WHIM 증후군에 대한 XOLREMDI와 고위험 골수이형성 증후군에 대한 RYT-ELO의 최근 FDA 승인은 규제 당국의 대응력을 보여줍니다. 그럼에도 불구하고, 인플레이션 억제법은 제품이 단일 희귀 질병 의약품(오판)의 효능과 효과를 넘어서면 가격 재협상 위험을 초래하기 때문에 라벨을 확장하려면 전략적주의가 필요합니다.
유럽은 10년간의 독점권과 수수료 경감을 제공하는 EMA의 집중화된 절차를 강점으로 희귀의약품 시장의 대부분을 차지하고 있습니다. 중요 의약품법(Critical Medicines Act)은 지역 생산 탄력성을 구축하고 공급 부족을 합리화하는 것을 목표로 하고 있지만 개혁 초안에서는 규제 당국의 데이터 보호를 9년간 단축하는 것이 제안되어 투자 의욕을 감퇴시킬 가능성이 있습니다. 매니지드 엔트리 계약과 결과 기반 계약이 지불 측의 협상을 지배하고 지출을 억제하면서 액세스를 확보하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 11.62%로 가장 급성장하고 있는 지역으로, 중국의 CARE 프로그램과 인도의 희소질환 정책 보조금에 지지되고 있습니다. 이 지역은 인구가 많기 때문에 임상시험의 모집이 용이하고, 가처분 소득 증가도 프리미엄 요법을 지지하고 있습니다. 그러나 보험 상환이 단편적이며 역학 데이터도 다양하기 때문에 즉각적인 도입에는 한계가 있으며, 스폰서는 지역별 참여 전략을 개발해야 합니다.
The orphan drugs market stood at USD 230.91 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 312.53 billion by 2030, progressing at a 6.24% CAGR.
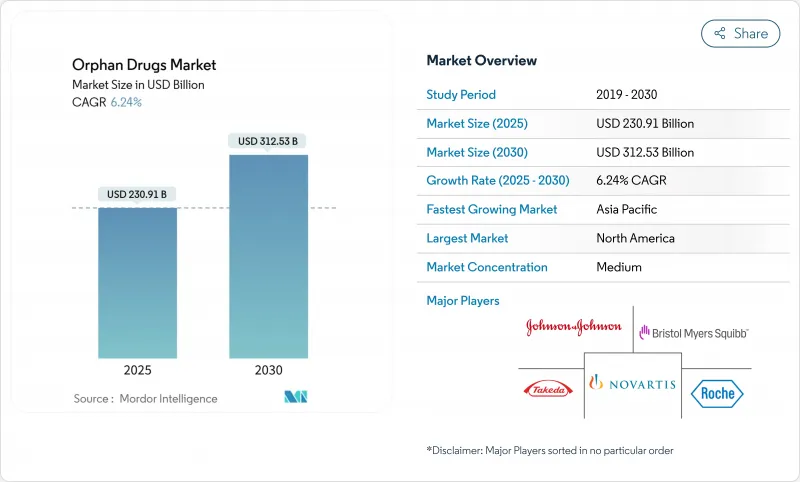
Sustained growth reflects regulatory incentives, gene- and cell-therapy breakthroughs, and persistent unmet needs across more than 7,000 rare diseases. Dominance of biologics, particularly gene therapies and monoclonal antibodies, underscores the pivot toward curative one-time treatments. North America leads on the back of robust designation programs and strong reimbursement, while Asia-Pacific gains momentum as policy frameworks expand. Competitive dynamics show large pharmaceutical firms acquiring specialty biotech innovators to secure pipeline depth, and artificial-intelligence-enabled adaptive trials are compressing development cycles to capitalize on extended exclusivity periods.
Gene therapy is redefining the orphan drugs market by targeting causal mutations rather than symptomatic pathways. The November 2024 FDA approval of KEBILIDI for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency demonstrated clinically meaningful motor improvements after a single infusion. Similar momentum appears in Europe, where LENMELDY secured EMA clearance for metachromatic leukodystrophy during 2024, validating accelerated biomarker-driven pathways. A convergence of CRISPR editing with adeno-associated virus delivery enables viable business models even when global prevalence is below 1,000 individuals. Premium pricing that can exceed USD 2 million per course underpins returns on the specialized infrastructure that manufacturers must build. Early movers with vertically integrated vector manufacturing lines attain formidable entry barriers and pricing power.
Artificial-intelligence platforms allow protocol adjustments based on interim efficacy and safety signals, reducing patient exposure and shaving 18-24 months off timelines relative to fixed designs. The FDA workshop on AI in 2024 clarified documentation expectations, fostering faster yet accountable pathways. Machine-learning algorithms enhance patient stratification, critical in trials where cohorts seldom exceed 200 participants. Sponsors thereby achieve regulatory-grade evidence with smaller N sizes, enabling rapid entry into the orphan drugs market ahead of exclusivity cliffs. Large firms with in-house data-science teams now dominate adaptive-trial capability, widening the competitive gap.
Median annual therapy costs surpassed USD 256,000 in 2024, and single-dose gene therapies frequently exceed USD 2 million. Payers respond with prior authorization and outcomes-based contracts, especially when treatments later expand into broader populations. European HTA bodies increasingly demand post-launch evidence of durable benefit, pushing sponsors to fund long-term registries that add material expense. Pricing strategy therefore remains a delicate equilibrium between recouping innovation investment and maintaining reimbursement viability.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Biologics accounted for 65.65% of revenue in 2024 and will outpace small molecules at an 8.84% CAGR through 2030. Twenty-five percent of FDA approvals in 2024 were monoclonal antibodies or gene therapies, signaling sustained preference for modality platforms enabling precision interventions. The orphan drugs market size for biologics is forecast to reach USD 205 billion by 2030, buoyed by one-time curative therapies that command premium price tags. Non-biologics still retain share in metabolic disorders via repurposed small molecules, yet competitive differentiation is narrowing as genetic medicines address underlying enzymatic deficits more effectively. Manufacturers scaling viral vector plants gain cost leverage, whereas small-molecule producers rely on formulation innovation and life-cycle management to remain relevant.
Second paragraph: Gene-therapy exemplars include LYFGENIA for sickle-cell disease and KEBILIDI for aromatic L-AAD deficiency, both demonstrating transformative clinical benefit with single administrations. Manufacturing complexity elevates barrier to entry; consequently, CDMO partnerships and in-house vector capacity have become acquisition triggers. Regulatory bodies demand robust potency assays and long-term follow-up, prompting companies to establish multidisciplinary surveillance programs. Intellectual-property strategies focus on capsid engineering and promoter optimization, consolidating competitive moats within the orphan drugs market.
Oncologic diseases retained 40.53% share in 2024 but exhibit a slower growth pace as saturation in hematologic malignancies emerges. The orphan drugs market share for oncology stood at 41% in 2024 and is expected to edge marginally lower as newer categories accelerate. EMA approval of Ordspono for relapsed follicular lymphoma underscores continued innovation in T-cell-redirecting antibodies. However, hematologic and immunologic diseases are advancing at a 10.35% CAGR propelled by factor-replacement alternatives such as concizumab and fitusiran.
Second paragraph: Neurologic gene therapies, including tofersen for SOD1-ALS, broaden the pipeline and highlight biomarker-driven approvals. Metabolic disease programs leverage next-generation enzyme replacement and mRNA therapy, while infectious-disease rarities such as viral hemorrhagic fevers attract niche funding. Investors track therapeutic novelty and regulatory momentum when assessing portfolio weightings across these segments.
The Orphan Drugs Market Report is Segmented by Drug Type (Biologics and Non-Biologics), Disease Area (Oncologic Diseases, Hematologic & Immunologic Diseases, Neurologic Diseases, and More), Route of Administration (Parenteral, Oral, and More), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America captured 42.82% of global revenue in 2024 and continues to benefit from 7-year exclusivity under the Orphan Drug Act plus the 25% clinical-trial tax credit. Recent FDA approvals of XOLREMDI for WHIM syndrome and RYT-ELO for high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes illustrate regulator responsiveness. Nonetheless, the Inflation Reduction Act introduces price-renegotiation risk if products expand beyond single orphan indications, prompting strategic caution on label extensions.
Europe holds a significant portion of the orphan drugs market on the strength of centralized EMA procedures that offer 10-year exclusivity and fee relief. The Critical Medicines Act seeks to build regional manufacturing resilience and streamline shortages, but draft reforms propose reducing regulatory-data protection to nine years, potentially tempering investment enthusiasm. Managed-entry agreements and outcome-based contracts dominate payer negotiations, ensuring access while controlling spend.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region at 11.62% CAGR to 2030, underpinned by the CARE program in China and India's rare-disease policy grants. The region's large populations ease trial recruitment, and rising disposable incomes support premium therapies. Still, fragmented reimbursement and variable epidemiological data limit immediate uptake, requiring sponsors to develop localized engagement strategies.