
이미징 레이더는 기본적인 범위와 속도 측정만 가능한 기존 레이더의 한계를 극복하기 위해 설계된 차세대 레이더 센싱 기술입니다. 범위, 속도, 방위각, 고도각을 동시에 획득함으로써 이미징 레이더는 고해상도 3D/4D 인식을 실현합니다. 이러한 고밀도 레이더 점군으로 물체 분류, 자유 공간 감지, 매핑, 장면 재구성 등의 고급 인식 기능을 가능하게 합니다. 악천후, 저조도, 복잡한 작동 환경에서의 견고성으로 인해 이미징 레이더는 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 자율 시스템의 기초가 되고 있습니다. ADAS, L2-L4 자율주행, 로보택시 플랫폼 등 육상 모빌리티부터 공중 드론, 해양 선박, 로봇, 우주, 국방 분야까지 그 범위가 넓어지고 있습니다. 특허 활동의 급속한 가속화는 이러한 기세를 반영하고 있습니다. 전 세계 10,600개 이상의 특허 패밀리(발명품)로 분류된 2만 2,200건 이상의 특허 출원이 확인되었으며, 그 중에는 이미징 레이더 영역과 연관성이 높은 2,800건 이상의 핵심 특허군이 포함되어 있습니다. 이러한 강력한 지적재산권(IP) 역학은 이미징 레이더가 보완적인 센서에서 주요인식 모달리티로 전환하고 있으며, 자율성의 미래를 형성하고 첨단 센싱 분야에서 가장 경쟁력 있는 IP 전장 중 하나를 주도하고 있음을 보여줍니다.
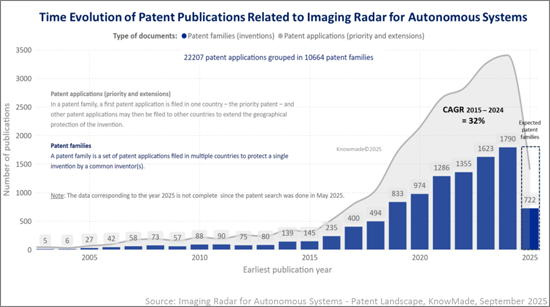
이미징 레이더의 특허 상황은 그 어느 때보다 가속화되고 있습니다. 2015-2024년 이미징 레이더 특허군의 공개 건수는 145건에서 1,790건으로 1,100% 이상 증가했으며, CAGR은 32%로 폭발적인 혁신의 시대를 맞이하고 있습니다. 이러한 급격한 증가는 4D 이미징 레이더, AI에 의한 인식, 멀티센서 융합으로의 기술적 전환을 반영하고 있습니다. 미국과 중국이 이 분야를 석권하고 있으며, 전 세계 출원 건수의 대부분을 차지하고 있는 반면, 유럽은 Bosch, ZF, Valeo등의 Tier-1공급업체를 통해 강력한 지위를 유지하고 있습니다. Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, General Motors, Alphabet - Waymo, Huawei-Yinwang, Magna등의 기존 기업은 레이더 하드웨어, 인식 소프트웨어, 센서 융합에 걸친 다양한 특허 포트폴리오를 보유하고 있습니다. 보유하고 있습니다. 동시에 Arbe Robotics, Under, Aptiv, Metawave 등의 전문 혁신가들은 4D 레이더 칩셋, 점군 처리, 실시간 환경 인식으로 타겟팅된 포트폴리오를 구축하고 있습니다. Xidian University, UESTC, BUAA, AIRCAS를 비롯한 학술기관은 파형, 안테나 설계, 빔 포밍의 기초적인 기술 혁신을 지속적으로 형성하고 있습니다. 산업계 리더, 스타트업, 연구기관의 복잡한 상호 작용은 첨단 센싱 분야에서 가장 경쟁력 있는 IP 영역 중 하나를 정의하고 있습니다.
이미징 레이더의 특허는 육상, 항공, 해상, 우주, 로봇, 국방의 6가지 주요 용도로 분류됩니다. 또한 특허 현황은 파형 설계 및 시스템 플랫폼에서 교정, 인식, 센서 융합에 이르기까지 11개의 주요 실현 기술을 포괄하는 5가지 기술 계층으로 구성되어 있습니다. 당사의 분석에 따르면 육상 모빌리티는 ADAS, 레벨 2-4 수준의 자율성, 로봇 택시의 보급으로 인해 가장 활발하고 기술적으로 진보한 분야입니다. UAV 네비게이션, 해상 센싱, 국방 분야 등 다른 영역도 확장하고 있습니다. 전체 기술 스택에서 기술 혁신은 FMCW 및 MIMO 신호 처리에서 AI 강화 인식 및 다중 센서 융합으로 확장되어 차세대 자율성에서 이미징 레이더의 핵심적인 역할을 강력하게 보여주고 있습니다.
이 보고서에서는 세계 자율 시스템용 이미징 레이더 산업에 대해 조사 분석하였으며, 1,600건 이상의 특허 엑셀 데이터베이스와 함께 세계 특허 동향 해설, 주요 기업의 IP 프로파일 등을 수록했습니다.
|
|
등
The global IP battlefield is heating up: who are the key players, and which technologies will shape the future of imaging radar for autonomous mobility?
Imaging radar represents the next generation of radar sensing technologies, designed to overcome the limitations of conventional radars that provide only basic range and velocity measurements. By simultaneously capturing range, velocity, azimuth and elevation, imaging radar produces high-resolution 3D/4D perception. These dense radar point clouds enable advanced perception functions including object classification, free space detection, mapping and scene reconstruction. Thanks to its robustness in adverse weather, low light and complex operating environments, imaging radar is becoming a cornerstone for safe and reliable autonomous systems. Its deployment spans terrestrial mobility such as ADAS, L2-L4 autonomous driving and robotaxi platforms, as well as aerial drones, marine vessels, robotics, space, and defense applications. The rapid acceleration of patenting activity reflects this momentum. More than 22,200 patent applications grouped into over 10,600 patent families (inventions) have been identified worldwide, including more than 2,800 core patent families that demonstrate a high degree of relevance to the imaging radar domain. This strong intellectual property (IP) dynamic demonstrates that imaging radar is transitioning from a complementary sensor to a primary perception modality, shaping the future of autonomy and driving one of the most competitive IP battlefields in advanced sensing.
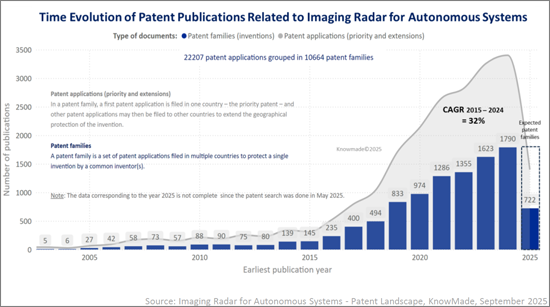
The patent landscape for imaging radar has experienced an unprecedented acceleration. From 2015 to 2024, imaging radar patent family publications grew from 145 to 1,790, an increase of over 1100% and a CAGR of 32% marking a period of explosive innovation. This surge reflects the technological transition toward 4D imaging radar, AI-driven perception and multi-sensor fusion. The United States and China dominate the field, together accounting for more than half of global filings, while Europe maintains a strong position through Tier-1 suppliers such as Bosch, ZF and Valeo. Established players including Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, General Motors, Alphabet - Waymo, Huawei-Yinwang and Magna hold diversified patent portfolios that span radar hardware, perception software and sensor fusion. At the same time, specialized innovators such as Arbe Robotics, Uhnder, Aptiv and Metawave are building targeted portfolios in 4D radar chipsets, point cloud processing and real-time environmental perception. Academic institutions, notably Xidian University, UESTC, BUAA and AIRCAS, continue to shape foundational innovation in waveforms, antenna design and beamforming. This complex interplay of industrial leaders, startups and research institutes defines one of the most competitive IP domains in advanced sensing.
Imaging radar patents are classified into six main application domains: terrestrial, aerial, marine, space, robotics and defense. The patent landscape has been further structured into five technology layers encompassing 11 key enabling techniques, ranging from waveform design and system platforms to calibration, perception and sensor fusion. Our analysis indicates that terrestrial mobility is the most active and technically advanced area, driven by ADAS, Level 2 to Level 4 autonomy and robotaxi deployment. Other domains such as UAV navigation, maritime sensing and defense applications are also expanding. Across the technology stack, innovation spans from FMCW and MIMO signal processing to AI-enhanced perception and multi-sensor fusion, highlighting the central role of imaging radar in next generation autonomy.
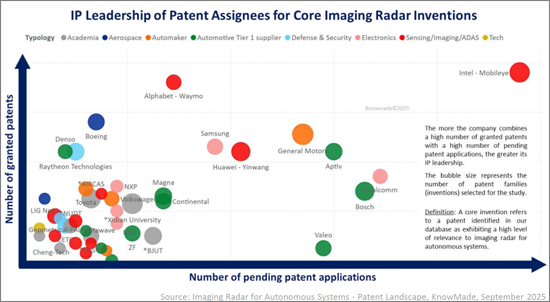
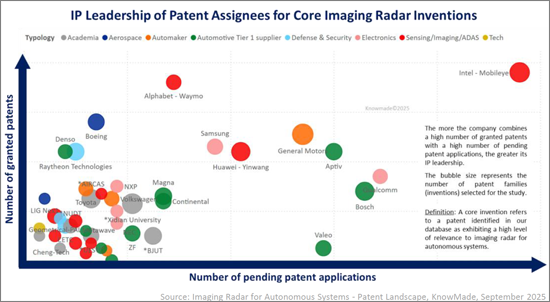
The imaging radar IP landscape is highly dynamic. Established OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers maintain strong positions, but new entrants are rapidly reshaping the field, with radar startups and ADAS suppliers particularly active. IP leadership now depends not only on the size of a portfolio but also on enforceability, geographic reach and technological impact. Companies such as GM, Intel-Mobileye, Bosch and Huawei-Yinwang combine extensive portfolios with a high volume of patent applications, while patent assignees like Arbe Robotics and Uhnder have demonstrated high IP strength and influence per patent.
In addition to individual patent portfolios, the IP ecosystem is shaped by sub-brands, joint ventures with shared IP ownership and co-owned patent families, all of which highlight the strategic role of IP in driving both competition and collaboration.
This report provides in-depth insights into the IP strategies of the main actors shaping the imaging radar domain. It includes detailed profiles of General Motors, Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, Huawei-Yinwang, Magna and Alphabet-Waymo, covering portfolio dynamics, notable granted and pending patents, legal status and global coverage. Beyond these key players, the report delivers a comprehensive classification of all identified patent assignees including automakers, Tier-1 suppliers, sensing and ADAS companies, electronics manufacturers, technology firms, academia, and defense and aerospace players. Within each segment, we identify both the established IP leaders and the IP newcomers, providing a clear view of how innovation and competition are distributed across the ecosystem.
For executives, IP professionals and R&D teams, the report delivers a comprehensive overview of a fast-evolving and competitive technology space. By aligning patent intelligence with strategic planning, companies can strengthen their innovation roadmap, secure competitive advantage and position themselves at the forefront of autonomous mobility and advanced sensing.
This report includes an extensive Excel database with the 10,600+ patent families (inventions) analyzed in this study, including patent information (publication numbers, assignees, dates, title, abstract, etc.), hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), and structured classification by application segments (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, and defense), five technology layers with 11 key technique segments (FMCW, MIMO, beamforming, 4D imaging radar, SAR, ISAR, calibration, point cloud, SLAM, tracking, AI and sensor fusion), as well as the identified core inventions. This database supports advanced multi-criteria searches and provides direct access to updated records, enabling users to benchmark portfolios, monitor competitors, identify potential partners or acquisition targets and evaluate freedom-to-operate constraints.
|
|
and more.