이중 특이성 항체는 암 치료의 획기적인 IP입니다.
암에 대한 이중 특이성 항체(bsAb)의 개발은 괄목할 만한 임상적 진전과 함께 급속한 성장을 보이고 있습니다. 최근 데이터에 따르면, 임상시험 중인 bsAb의 85% 이상이 암 치료제이며, 현재 약 600개의 bsAb가 임상시험 중에 있습니다. 현재까지 11개의 bsAb가 암 치료제로 승인되었으며, 그 중 10개의 bsAb가 미국 FDA에 의해 승인되었습니다. 이러한 확대는 이 혁신적인 치료제에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있음을 반영합니다. 이중 특이성 항체는 두 개의 서로 다른 항원에 동시에 결합하도록 설계된 단백질입니다. 이중 특이성 항체는 두 유형의 세포를 연결하거나(in-trans 결합), 하나의 세포막에 있는 두 분자에 결합(in-cis 결합)합니다. 세포를 가교하는 BsAb가 가장 큰 그룹이며, T 세포 리디렉션이 가장 일반적이며, T 세포 인게이저는 세포독성 T 세포와 종양 세포 모두에 결합하여 종양에 대한 직접적인 면역반응을 촉진합니다. 2024년 12월, 미국 FDA는 뉴클레그린1(NRG1) 유전자 융합체를 보유하고 전신 치료 전 또는 전신 치료 후 병이 진행된 절제 불가능한 또는 전이성 진행성 비소세포폐암(NSCLC) 또는 NRG1 유전자 융합체를 보유하고 전신 치료 전 또는 전신 치료 후 병이 진행된 비소세포폐암(NSCLC)에 대한 치료제로 승인했습니다. 전신치료 전 또는 전신치료 후 병이 진행된 절제불능 또는 전이성 진행성 췌장선암 성인 환자를 대상으로 HER2 x HER3 bsAb의 조기 승인을 받았습니다. 그러나 생산의 복잡성, 독성(사이토카인 방출 증후군, 면역관문억제제 세포 관련 신경독성 증후군, 수액 관련 반응), 분자 안정성 및 반감기 최적화의 필요성 등의 과제가 남아있습니다. 이러한 장애물을 극복하기 위해 첨단 항체 공학 기술, 새로운 분자 포맷 개발 등 혁신적인 접근법이 모색되고 있습니다.
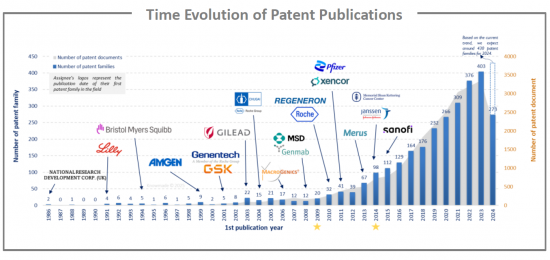
1986년부터 2000년대 초까지 특허 출원 건수는 적었지만 2010년 이후 크게 증가하여 2023년까지 400개 이상의 특허군이 탄생했으며, 1980년대, 1990년대, 2000년대 초에는 최초의 비대칭 포맷 개발, 최초의 T 세포 리다이렉션 시연, 최초의 재조합 단편 기반 포맷, 최초의 종 제한적 경쇄(LC) 페어링 문제 해결, 상보적 개발, 최초의 T 세포 리다이렉션 시연, 최초의 재조합 단편 기반 포맷, 종 제한 LC 페어링을 통한 경쇄(LC) 결합 문제 해결, 상보적 중쇄(HC)와 공통 LC를 사용하여 사슬 결합 문제 해결, 최초의 대칭형 포맷, 천연 인간 IgG4가 이중 특이성 발견, 이중 가변 도메인-Ig 대칭형 포맷의 개발 등 학술 연구 분야에서 많은 진전을 이루었습니다. 이러한 모든 혁신은 bsAb의 확립에 기여했습니다. 그리고 2009년, bsAb의 catumaxomab(T 림프구 항원 CD3 x 상피세포 접착분자(EpCAM)가 악성 복수의 치료제로 유럽연합(EU)의 승인을 받았습니다. 5년 후, blinatumomab(CD3xB 림프구 항원 CD19)이 FDA의 승인을 받았으며, 2015년 EU에서도 승인을 받았습니다.
이 보고서는 이중 특이성 항체 및 암의 특허 현황을 조사 분석하여 공개 특허의 시계열 추이, 특허 출원 국가, 특허의 법적 지위 등 IP 동향과 함께 주요 특허권자 순위, 주요 기업의 IP 포지션 및 특허 포트폴리오의 상대적 강점 등의 정보를 제공합니다.
Bispecific Antibodies Mark a Breakthrough in Cancer Therapy Intellectual Property.
The development of bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) in oncology is experiencing rapid growth, accompanied by significant clinical advancements. According to recent data, more than 85% of bsAbs in clinical trials are cancer treatments, with approximately 600 bsAbs currently in clinical trials. To date, 11 bsAbs have received regulatory approval for use in cancer, ten of them by the US FDA. This expansion reflects the growing interest in these innovative therapeutic agents. Bispecific antibodies are engineered proteins designed to bind simultaneously to two distinct antigens. They can bridge two cell types (in-trans binding) or engage two molecules on the membrane of one cell (in-cis binding). BsAbs that bridge cells represent the largest group, with T cell redirection as the most common denominator. T-cell engagers bind both cytotoxic T cells and tumor cells, promoting a direct immune response against the tumor. Several bsAbs have recently received regulatory approvals. In December 2024, the U.S. FDA granted accelerated approval of a HER2 x HER3 bsAb for adults with advanced, unresectable, or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring a neuregulin 1 (NRG1) gene fusion with disease progression on or after prior systemic therapy, or advanced, unresectable, or metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma harboring an NRG1 gene fusion with disease progression on or after prior systemic therapy. However, challenges remain, such as the complexity of production, toxicities (cytokine release syndrome, immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome, infusion-related reactions), and the need to optimize the stability and half-life of the molecules. Innovative approaches, such as advanced antibody engineering technologies and the development of new molecular formats, are being explored to overcome these obstacles. Understanding the intellectual property position and strategy of these various players is crucial in this evolving context. Detecting business risks and opportunities, anticipating emerging technologies, and enabling strategic decisions to strengthen market position can be achieved through this knowledge.

Between 1986 and the early 2000s, the number of patent publications is low but increasing. From 2010, the field is experiencing a significant acceleration, culminating in 2023 with more than 400 patent families. In the 1980s and 1990s and early 2000s, many advances were made in academic research such as the generation of the 1st asymmetric format, the 1st demonstration of T cell redirection, the 1st recombinant fragment-based formats, the 1st solution to light chain (LC) association issue through species-restricted LC pairing, the 1st solution to chain-association issue through use of complementary heavy chain (HC) (knobs into holes) and common LC, the 1st symmetric format, the discovery that natural human IgG4 is bispecific, the dual variable domain-Ig symmetric format pioneered, etc. All these innovations have contributed to the establishment of bsAbs. Then, in 2009, the bsAb catumaxomab (a T lymphocyte antigen CD3 x epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM)) received the European Union approval for the treatment of malignant ascites. Five years later, the blinatumomab (CD3xB lymphocyte antigen CD19) was FDA approved. It has been approved in the EU in 2015.
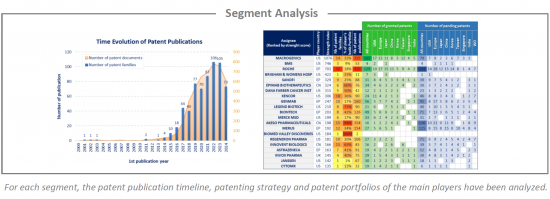
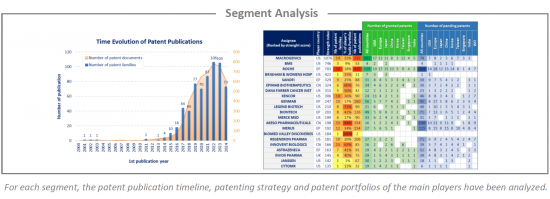
Bispecific Ab & Cancer have been investigated and the selected patent families labeled according to technologies to which they relate. This IP landscape features the following 3 types of segmentation: Tumor Antigens (ERBB family, BCMA, BRCA, mesothelin, PSMA, CEA, claudin, EPCAM, mucin, NKG2D, VEGF, CEACAM, MAGE, ROR1, c-Met and nectin), Immune Checkpoints (PD1 / PDL1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, TIM-3, OX40, ICOS, B7-H3, TIGIT and BTLA) and T cells (CD3).
Currently, there is a significant number of EP oppositions which reflects the strategic issues of bispecific antibody & cancer for companies. For each opposed patent, the application date, assignee, opponent, opposition year, and results are detailed.
Among the players owning patent families related to Bispecific Ab & cancer, 52 newcomers were identified. These companies are either start-up firms (6) or established companies (46) developing their first technology in the field. Most IP newcomers are based in the U.S. and in Asia. It is possible that one of these innovative companies could become one of the next healthcare unicorns that the big corporations will be tempted to acquire.
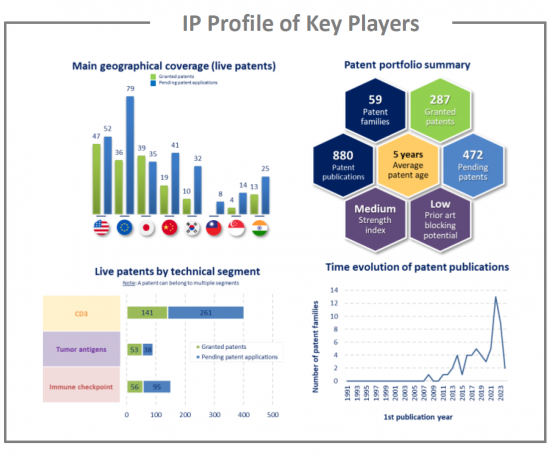
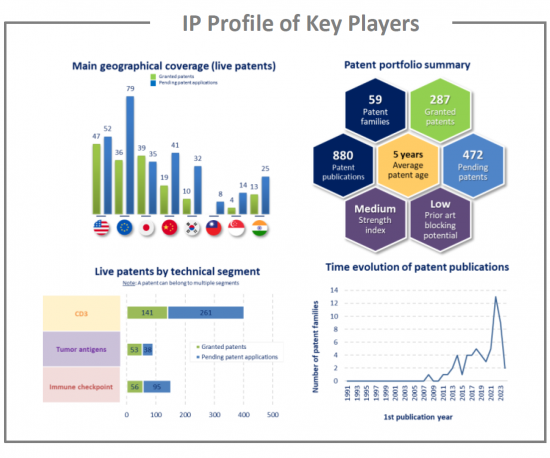
This IP study includes a selection and description of main players. The patent portfolio analysis of main players includes a description of the assignee, patent portfolio description, time evolution of patent publication, main geographical coverage and live patents by technical segment. This IP profile overview is followed by the description of the technological content of their key patents and by a table with its clinical trials.
Moreover, the report includes an Excel spreadsheet with the 2895 patent families analyzed in this study. This useful patent database allows for multi-criteria searches and includes patent publication numbers, hyperlinks to the original documents, priority dates, titles, abstracts, patent assignees, each patent's current legal status and segmentation. The report also includes a Patent Online Database which legal status are updated for each patent document.
ROCHE, AMGEN, JANSSEN, GENMAB, XENCOR, REGENERON PHARMACEUTICALS, GENENTECH - ROCHE, MACROGENICS, DRAGONFLY THERAPEUTICS, SANOFI, CHUGAI PHARMACEUTICAL, MERCK MSD, MERUS, BMS, SAMSUNG, JIANGSU HENGRUI PHARMACEUTICALS, ABBVIE, HEFEI TG IMMUNOPHARMA, MARENGO THERAPEUTICS, etc.