
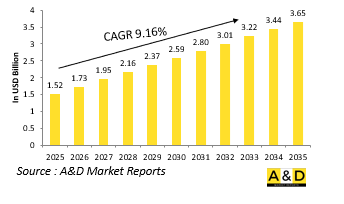
세계의 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 규모는 2025년에 15억 2,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2035년까지 36억 5,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있으며, 예측 기간 중(2025-2035년) 연간 평균 성장률(CAGR)은 9.16%로 전망되고 있습니다.

전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션은 고도의 군사 훈련의 요점이 되어, 파일럿이나 승무원이 현대의 전장에서의 작전에 불가결한 스킬을 개발할 수 있는 매우 현실적인 환경을 제공합니다. 이러한 시뮬레이터에 의해 군는 인원이나 장비를 불필요한 위험에 노출하지 않고, 시가전을 포함한 복잡한 임무 시나리오를 재현할 수 있습니다. 시뮬레이터는 협조성, 상황인식, 정밀조준에 중점을 둔 임무에 특화된 훈련모듈을 제공함으로써 부대가 이러한 요구에 대비할 수 있게 합니다. 전력 강화와 공동 작전에 대한 관심이 높아지는 가운데, 전투 헬기의 시뮬레이션은 다른 부대와 동맹군간의 상호 운용성과 결속도 지지하고 있습니다.
기술은 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션의 범위와 리얼리즘을 재정의하고 가상 훈련 환경에서 달성할 수 있는 것의 한계를 밀어 펼치고 있습니다. 난기류 등의 비행 다이내믹스를 재현해, 전투시의 스트레스 요인을 모방하는 것으로, 리얼함을 한층 더 높이고 있습니다. 또한 파일럿은 압력이 걸리는 환경에서 전술적인 의사결정을 닦을 수 있습니다. 또한, 전투 헬리콥터의 시뮬레이터에는 네트워크화된 환경이 포함되는 것이 많아져, 복수의 탑승원이 동시에 제휴한 미션으로 훈련할 수 있게 되어 있습니다. 실시간의 피드백, 성능 분석, 시나리오의 맞춤법을 바꾸고 있습니다. 새로운 센서 패키지, 전자전 시스템, 무기 플랫폼이 전투 헬리콥터에 통합됨에 따라, 시뮬레이션 기술도 병행해 진화해, 승무원의 숙련도와 적응력을 유지할 수 있게 되어 있습니다. 이러한 기술적 강화에 의해 시뮬레이션은 연습을 위한 툴일 뿐만 아니라,
전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 수요는 몇 가지 전략적 및 작전적 요청에 의해 형성되고 있습니다. 분쟁의 성격이 진화하고 있기 때문에 신속하고 연계된 유연한 항공 지원이 필요하다는 점입니다. 운용을 요구하는 경우가 많습니다. 시뮬레이션에 의해 항공기 탑승원은 관리된 조건하에서 이러한 시나리오를 상정한 훈련을 실시할 수 있어 대응 시간과 임무의 유효성을 향상시킬 수가 있습니다. 시뮬레이션은 관숙과 스킬 향상을 위한 위험이 없는 환경을 제공합니다. 또, 통합 훈련 환경이 항공 부대와 지상 부대의 제휴를 촉진하는데 도움이 되기 위해, 통합 부대의 운용이 중시되게 되어 있는 것도, 시뮬레이션의 활용을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 또한, 평시나 설비의 다운타임중에 즉응 태세를 유지할 필요성으로부터, 시뮬레이션은 전투 항공 전략에 있어서 불가결한
전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션의 동향은 지정학적 상황, 군사투자 전략, 운용상의 요건에 따라 지역에 따라 달라집니다. 이와 같이 설계되어 있습니다. 유럽에서는 다국간의 연계, 특히 NATO 회원국 간의 연계가 중시되고 있어 표준화된 훈련이나 합동 연습을 지원하기 위해 시뮬레이션이 활용 시나리오에는 국경 경비, 도시 분쟁, 반란 등 현대 안보상의 과제가 반영되는 경우가 많습니다. 전투 헬리콥터의 조달이 증가하고 있으며, 이에 따라 새로운 파일럿 훈련에 필요한 시뮬레이션 시스템의 조달도 증가하고 있습니다. 한편, 라틴아메리카와 아프리카에서는 보다 광범위한 국방 개혁과 근대화의 일환으로서, 시뮬레이터의 이용을 서서히 늘리고 있어 많은 경우, 현지의 훈련 인프라와 교리의 표준화를 개선하는 것을 목적.
돌격용 회전익기에서 주도권을 유지하기 위해 미국 육군은 Future Long-Range Assault Aircraft(FLRAA)의 출시를 Future Vertical Lift(FVL) 구상의 핵심 요소로 자리매김하고 있습니다. FLRAA는 미국 육군, 공군, 해군, 연안 경비대, 그리고 몇몇 동맹국에서 전술 유틸리티 헬리콥터의 기간기로서 오랫동안 활약해 온 상징적인 UH-60 Black Hawk를 대체하게 됩니다. 1979년 도입 이후, Black Hawk는 아프가니스탄, 이라크를 비롯한 세계 각지의 작전에서 중요한 전력이 되어 왔습니다. Sikorsky와 Honeywell과 같은 중요한 파트너가 이끄는 수많은 업그레이드가 이루어졌으며, 냉전 시대에 그 기원을 가지고 있음에도 불구하고 현대 전투 환경에서 효과적이고 적절한 존재로 남아 있습니다.
본 보고서에서는 세계 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장에 대해 조사했으며, 10년간의 부문별 시장 예측, 기술 동향, 기회 분석, 기업 프로파일, 국가별 데이터 등을 정리했습니다.
전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 보고서 정의
전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 세분화
지역별
기술별
시뮬레이션 유형별
구성 요소별
향후 10년간의 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 분석
이 장에서는 10년간의 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 분석을 통해 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장의 성장, 변화하는 추세, 기술 채택 개요 및 전반적인 시장 매력에 대한 자세한 개요를 제공합니다.
이 부문에서는 이 시장에 영향을 미칠 것으로 예상되는 상위 10개 기술과 이러한 기술이 시장 전체에 미칠 수 있는 영향에 대해 설명합니다.
세계 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 예측
이 시장의 10년간의 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 예측은 위의 전체 부문에서 자세히 다루고 있습니다.
지역 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 동향 및 예측
이 부문에서는 지역별 전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 동향, 촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제, 그리고 정치, 경제, 사회, 기술 등의 측면을 망라하고 있습니다. 또한 지역별 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석도 자세히 다루고 있습니다. 지역 분석의 끝에는 주요 기업 프로파일링, 공급업체 상황, 기업 벤치마킹가 포함됩니다. 현재 시장 규모는 일반적인 시나리오를 기반으로 추정됩니다.
북미
촉진요인, 억제요인, 과제
PEST
주요 기업
공급자 계층의 상황
기업 벤치마킹
유럽
중동
아시아태평양
남미
이 장에서는 이 시장에서 주요 방어 프로그램을 다루며 이 시장에서 신청된 최신 뉴스와 특허에 대해서도 설명합니다. 또한 국가 수준의 10년간 시장 예측과 시나리오 분석에 대해서도 설명합니다.
미국
방어 프로그램
최신 뉴스
특허
이 시장의 현재 기술 성숙도
캐나다
이탈리아
프랑스
독일
네덜란드
벨기에
스페인
스웨덴
그리스
호주
남아프리카
인도
중국
러시아
한국
일본
말레이시아
싱가포르
브라질
전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 기회 매트릭스
전투 헬리콥터 시뮬레이션 시장 보고서에 대한 전문가의 의견
The Global Combat Helicopter Simulation market is estimated at USD 1.52 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 3.65 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.16% over the forecast period 2025-2035.
Combat helicopter simulation has become a cornerstone of advanced military training, offering a highly realistic environment in which pilots and crews can develop critical skills for modern battlefield operations. These simulators allow armed forces to replicate complex mission scenarios including close air support, reconnaissance, anti-armor engagements, and urban warfare without exposing personnel or equipment to unnecessary risk. As global defense forces transition toward more agile, technology-enabled combat strategies, the role of rotary-wing assets continues to expand. Combat helicopters are expected to operate in varied and hostile environments, often at low altitudes and under intense threat conditions. Simulators enable forces to prepare for these demands by offering tailored, mission-specific training modules that emphasize coordination, situational awareness, and precision targeting. Globally, the integration of simulation into combat aviation training ensures that operational readiness is maintained even as airframes and mission profiles evolve. With rising focus on force multiplication and joint operations, combat helicopter simulation also supports interoperability and cohesion across different units and allied forces. As such, the global interest in simulation is not only about enhancing pilot skills, but also about preparing combat teams for the multifaceted nature of modern warfare.
Technology is redefining the scope and realism of combat helicopter simulation, pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in a virtual training environment. Modern simulators incorporate cutting-edge visual systems capable of rendering high-resolution terrain, day-night cycles, and weather conditions that impact rotorcraft performance and targeting accuracy. The use of motion platforms further enhances realism, replicating flight dynamics such as vibration, acceleration, and turbulence to mimic combat stressors. Integrated communication systems within the simulator enable realistic radio protocols and joint-force coordination training, fostering battlefield authenticity. Artificial intelligence is being increasingly used to simulate hostile forces, unpredictable combat scenarios, and civilian presence, allowing pilots to hone tactical decision-making in high-pressure environments. Furthermore, combat helicopter simulators now often include networked environments, where multiple aircrews can train simultaneously in coordinated missions, mirroring real-world operational dynamics. Real-time feedback, performance analytics, and scenario customization are transforming how pilots and gunners refine their techniques. As new sensor packages, electronic warfare systems, and weapons platforms are integrated into combat helicopters, simulation technology evolves in parallel to ensure that crews remain proficient and adaptive. These technological enhancements make simulation not only a tool for practice but a vital element in strategic capability development.
The demand for combat helicopter simulation is being shaped by several strategic and operational imperatives. One primary driver is the evolving nature of conflict, where asymmetric threats, hybrid warfare, and urban combat require rapid, coordinated, and flexible air support. Helicopters are frequently called upon to operate in environments with limited visibility, high threat levels, and rapidly changing mission parameters. Simulation enables aircrews to train for such scenarios under controlled conditions, improving response time and mission effectiveness. Another significant factor is the increasing complexity of rotary-wing platforms. Modern combat helicopters are equipped with advanced avionics, sensor systems, and networked communication suites that require thorough training to operate efficiently. Simulation provides a risk-free environment for familiarization and skill refinement. Additionally, defense budgets are under pressure globally, and simulation offers a cost-effective alternative to live-fly training, helping to reduce fuel usage, airframe wear, and logistical overhead. The growing emphasis on joint-force operations also drives simulation use, as integrated training environments help foster coordination between aviation and ground units. Moreover, the need to maintain readiness in peacetime or during equipment downtime makes simulation an indispensable part of combat aviation strategy, bridging gaps and reinforcing operational competence.
Combat helicopter simulation trends vary across regions based on geopolitical conditions, military investment strategies, and operational requirements. In North America, investment is focused on high-fidelity, full-mission simulators that support global deployment capabilities and integrated joint-force training. These systems are designed to replicate real-world combat environments and support interoperability among branches of the armed forces. In Europe, there is a strong emphasis on multinational coordination, particularly among NATO members, where simulation is being used to support standardized training and combined exercises. Scenarios often reflect contemporary security challenges, including border protection, urban conflict, and counterinsurgency. In the Asia-Pacific region, growing defense modernization programs are leading to increased procurement of combat helicopters and the corresponding simulation systems needed to train new pilots. Simulation is being prioritized to accelerate training pipelines and to ensure readiness in areas of maritime security and regional defense. In the Middle East, combat helicopter simulation is heavily focused on mission rehearsal for urban warfare, border security, and counterterrorism operations. Meanwhile, Latin America and Africa are gradually increasing their use of simulators as part of broader defense reforms and modernization, often with support from foreign defense partnerships aimed at improving local training infrastructure and doctrine standardization.
To preserve its leadership in assault-utility rotorcraft, the U.S. Army is positioning the launch of the Future Long-Range Assault Aircraft (FLRAA) as a central element of its Future Vertical Lift (FVL) initiative. This program aims to develop a next-generation fleet of advanced aircraft that will equip the military with the capabilities needed to deter threats, engage in combat, and achieve victory in future conflicts. FLRAA is set to replace the iconic UH-60 Black Hawk, which has long served as the backbone of the tactical utility helicopter fleet across the U.S. Army, Air Force, Navy, Coast Guard, and several allied nations. Since its introduction in 1979, the Black Hawk has been a critical asset in operations across Afghanistan, Iraq, and other global theaters. Over more than four decades, the helicopter has undergone numerous upgrades-spearheaded by Sikorsky and key partners like Honeywell-to ensure it remains effective and relevant in modern combat environments, despite its origins during the Cold War.
Combat Helicopter Simulation market Report Definition
Combat Helicopter Simulation market Segmentation
By Region
By Technology
By Type of Simulation
By Component
Combat Helicopter Simulation market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Combat Helicopter Simulation market analysis would give a detailed overview of Combat Helicopter Simulation market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Combat Helicopter Simulation market Forecast
The 10-year Combat Helicopter Simulation market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Combat Helicopter Simulation market Trends & Forecast
The regional Combat Helicopter Simulation market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Combat Helicopter Simulation market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Combat Helicopter Simulation market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.