
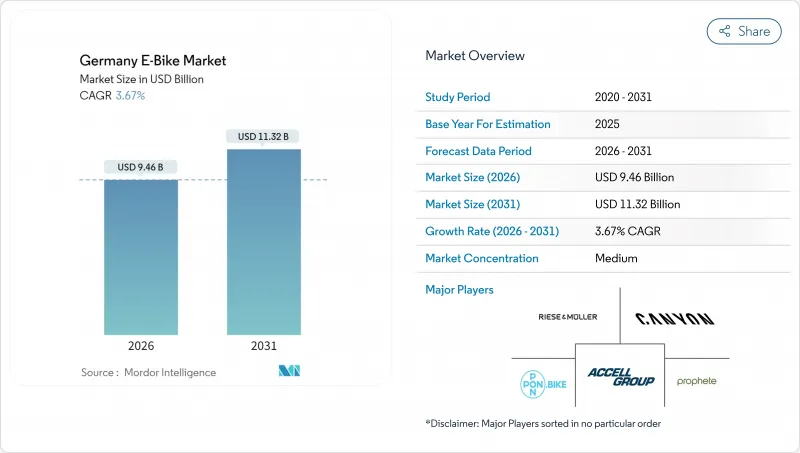
독일의 전기 자전거 시장은 2025년 91억 3,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년에는 94억 6,000만 달러로 성장할 전망이며, 2026-2031년 CAGR 3.67%로 성장을 지속하여, 2031년까지 113억 2,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

팬데믹 후 수요 급증이 정상화된 현재, 성장은 안정적인 교체 사이클, 상용 플릿 확대, 신규 도입의 점증으로 축발을 옮기고 있습니다. 평균 판매 가격이 안정화되는 가운데 배터리 규제, 기업 모빌리티 예산, 인프라 개선 등 성장세를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 경쟁 환경은 업계 재편, 재고 조정, 양판지향에서 수익성 중시로의 결정적인 전환을 반영하고 있지만, 2024년 기준에서 독일의 전기 자전거 시장은 여전히 자전거 총 판매 대수에 있어서 현저한 점유율을 차지하고 있습니다.
독일 연방 정부는 2030년까지 비전을 내건 전국 자전거 계획(NCP) 3.0을 발표했습니다. 이것은 전국적인 자전거 이용 촉진을 목적으로 한 전략적 이니셔티브입니다. NCP 3.0의 주요 목적은 독일에서 자전거의 매력과 안전성을 높이고 자전거 이용자의 주행 거리를 크게 증가시키는 것입니다. 전기 자전거는 총 자전거 대수에 차지하는 비율은 작은 반면, 자전거 이용 전체에 있어서 매우 중요한 역할을 하고 있습니다. 뮌헨에서는 2025년까지 보호된 자전거 전용 레인이 1,200km에 이를 예정이며, 한때는 자동차만이 이용 가능하게 되어 있던 통근 경로의 이용을 가능하게 합니다. 장거리 주행, 비탈길 주행의 보조, 날씨에 대한 영향이 적다고 하는 특성이, 도시 주민이 자동차를 전기 자전거로 치환하는 빈도가, 통상의 자전거보다 높은 이유를 설명하고 있습니다.
독일의 기업용 자전거 임대 붐은 주로 세제 정책에 의해 견인되고 있습니다. 2019년의 소득세법 개정에 의해 직원이 급여 공제로 자전거 또는 전동 어시스트 자전거를 리스하는 경우, 제조업체 정가의 극히 일부만을 월액 과세 대상의 복리 후생으로서 취급할 수 있게 되었습니다. 국가 자전거 계획 3.0에서는 통근 수단을 자동차로부터 전환하는 '중요 시책'으로서 기업용 자전거 리스를 자리 매김하고 있습니다. 단거리 통근의 대부분이 자전거 또는 전동 어시스트 자전거로 이행하면 연간 대폭적인 CO2 삭감 효과가 기대된다고 추정되고 있습니다. 총 급여 임대 제도를 통해 직원은 자전거 모델을 상당한 할인 가격으로 사용할 수 있습니다. 고용주는 매월 공제액의 예측 가능성을 평가하고 공급업체는 소매 가격 변동에 민감한 대량 계약의 안정성을 강조합니다.
2024년 조사에 따르면 소비자의 가격 의식이 높아져 많은 사람들이 고액의 임의 구매를 선도하는 경향이 보였습니다. 같은 해 평균 소매 가격은 하락했고 많은 일반 구매자들은 여전히 특정 가격대를 심리적 상한으로 인식하고 있습니다. 전국적인 인센티브가 없기 때문에 독일은 이웃나라 프랑스에 비해 순매입 지원액이 낮아 국경 마을에서의 월경 쇼핑을 촉진하고 있습니다.
2025년 독일의 전기 자전거 시장에서 페달 어시스트식 시스템이 79.35%를 차지했습니다. 이는 자전거와 동등한 법적 지위로 인해 보험 및 면허 요건이 면제되는 이점 때문입니다. 통근자가 장거리 루트에서 시속 45km의 순항을 요구하는 가운데, 스피드 페데렉은 3.76%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 기록하고 있습니다. 이 부문은 2026-2031년 독일의 전기 자전거 시장 확대에 특히 크게 기여할 전망입니다.
EPAC의 정의에 관한 규제 논의가 예측의 변동 요인이 됩니다. ZIV가 제안한 최대 출력 750W 제한과 1:4 어시스트 비율 유지는 비자동차 분류를 유지하기 위한 것입니다. 한편, LEVA-EU는 규제 강화가 화물 수송의 혁신을 저해한다고 반박하고 있습니다. 2026년에 예상되는 결정은 높은 어시스트 자전거가 목표로 하는 시장 규모를 확대 또는 축소할 수 있어 독일의 전동 어시스트 자전거 시장 점유율의 변화에 직접적인 영향을 미칩니다.
2025년의 수익 구성비에서는 도시 주행용이 70.92%를 차지했지만, 화물 및 실용 부문은 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 3.74%로 확대될 전망이며, 독일 전기 자전거 시장에서 가장 성장 현저한 분야입니다. 택배 회사 및 식료품 플랫폼이 도시 배출 규제 구역에 대한 대응으로서 라스트 마일 차량의 전동화를 진행하는 가운데, 화물 및 실용 용도의 이용이 급속하게 확대하고 있습니다.
2024년에는 화물용 유닛이 대폭적인 성장을 기록했으며, 전년 대비 현저한 증가를 보였습니다. 많은 차량이 주간 충전 없이 1 시프트를 완주할 수 있도록 1,000Wh 배터리를 표준 장비하고 있습니다. 베를린의 디젤 차량 규제와 함께 법인 주문은 안정적인 수요 유입을 약속하며 기존에는 소비자의 계절성에 좌우된 분기별 출하 사이클을 안정화시킵니다.
2025년 출하량 가운데 리튬이온팩이 99.82%를 차지했고, 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 3.67%로 성장을 지속할 전망이며, 독일의 전동자전거 시장 규모 확대의 대부분을 지원합니다. 대체 화학 기술은 여전히 1,000달러 미만의 엔트리 모델 및 실험적인 고체 배터리 파일럿 사업으로 제한됩니다.
EU 배터리 규제는 2027년 2월부터 디지털 여권의 의무화, 2028년까지 51%의 회수 목표를 도입합니다. 이러한 조치는 순환형 경제의 실천을 제도화하고, 리튬 이온 전지의 기존 우위성을 강화하는 동시에, 유럽에서의 셀 생산을 촉진하며, 스코프 3 배출량의 저감 및 수송 리스크의 저감을 도모합니다.
The German E-Bike market is expected to grow from USD 9.13 billion in 2025 to USD 9.46 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 11.32 billion by 2031 at 3.67% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Demand normalization after the pandemic surge now pivots growth toward steady replacement cycles, commercial fleet expansions, and incremental first-time adoption. Battery regulation, corporate mobility budgets, and improving infrastructure sustain forward momentum even as average selling prices stabilize. Competitive dynamics reflect consolidation, inventory rebalancing, and a decisive shift from volume chasing to profitability, yet the German E-Bike market continues to capture a notable share of total bicycle sales as of 2024.
Germany's Federal Government has unveiled the National Cycling Plan (NCP) 3.0, a strategic initiative aimed at promoting cycling across the nation, with a vision extending to 2030. NCP 3.0's primary objective is to enhance the appeal and safety of cycling in Germany, thereby aiming for a substantial uptick in the distance covered by cyclists . E-bikes, although forming a smaller portion of the total fleet, play a disproportionately significant role in overall bicycle usage. Protected lanes in Munich are set to reach 1,200 km by 2025, enabling commutes once considered car-only. Longer range, hill-flattening assistance, and lower weather sensitivity explain why urban residents substitute cars with e-bikes more often than with acoustic bikes.
Germany's corporate bike-leasing boom is largely driven by fiscal policy. A 2019 amendment to the Income Tax Act, which allows employees leasing bicycles or e-bikes through salary sacrifice to treat only a small portion of the manufacturer's list price as a monthly taxable benefit. The National Cycling Plan 3.0 highlights company-bike leasing as a "key action" to shift work-related travel from cars. They estimate a substantial annual CO2 saving if a significant portion of short commutes transitions to bicycles or e-bikes. Through gross-salary leasing, employees enjoy significant savings on bike models. Employers value the predictability of monthly deductions, while suppliers appreciate the stability of bulk contracts, which are less vulnerable to retail fluctuations.
In 2024, consumers became increasingly price-conscious, with many opting to delay significant discretionary purchases, according to surveys. In 2024, average retail prices declined, but many mainstream buyers still perceive a specific price point as a psychological ceiling. Without nationwide incentives, Germany ranks below neighboring France on net purchase support, encouraging cross-border shopping in border towns.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Pedal-assisted systems generated 79.35% of the Germany E-Bike market in 2025, benefiting from a bicycle-equivalent legal status that avoids insurance and license requirements. Speed Pedelecs post a 3.76% CAGR as commuters seek 45 km/h cruising on longer routes. This segment will contribute disproportionately to the expansion of the German e-bike market between 2026 and 2031.
Regulatory debate on EPAC definitions adds forecast volatility. ZIV's proposal to cap peak power at 750 W and maintain a 1:4 assist ratio aims to preserve the non-motor-vehicle classification. Advocacy group LEVA-EU counters that tighter rules would restrain cargo innovation. A decision expected in 2026 could widen or narrow the addressable market for high-assist bicycles, directly influencing Germany's E-Bike market share trajectories.
City/Urban riding held 70.92% of 2025 revenue, but the cargo/utility segment is on track for a 3.74% CAGR to 2031, the top growth lane within the German E-Bike market. Cargo/Utility usage follows closely as parcel companies and grocery platforms electrify last-mile fleets to meet city emission zones.
In 2024, the industry experienced significant growth in cargo units, reflecting a notable year-on-year increase, with many fleets now spec 1,000 Wh batteries to secure a full shift without midday recharging. Combined with diesel vehicle bans in Berlin, fleet orders promise steady demand inflows that stabilize quarterly shipment cycles previously driven by consumer seasonality.
Lithium-ion packs represented 99.82% of 2025 shipments and will chart a parallel 3.67% CAGR through 2031, underpinning most gains in the German E-Bike market size. Alternative chemistries remain relegated to sub-USD 1,000 entry bikes or experimental solid-state pilots.
The EU Battery Regulation introduces mandatory digital passports from February 2027 and collection targets of 51% by 2028. These measures institutionalize circular-economy practices, reinforcing lithium-ion incumbency while encouraging European cell production to cut embedded scope-3 emissions and lower transport risk.
The Germany E-Bike Market Report is Segmented by Propulsion Type (Pedal Assisted, Speed Pedelec, and More), Application Type (Cargo/Utility, City/Urban, and More), Battery Type (Lead Acid Battery, Lithium-Ion Battery, and More), Motor Placement (Hub (Front/Rear), Mid-Drive), Drive Systems, Motor Power, Price Band, Sales Channel, and End Use. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).