
인도네시아의 데이터센터 시장은 2025년 16억 1,000만 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 18억 3,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 34억 8,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.
예측 기간(2026-2031년)에 있어서 CAGR은 13.71%를 나타낼 것으로 전망되고 있습니다.

IT 부하 용량 측면에서 시장은 2025년 1,440메가와트에서 2030년까지 3,560메가와트로 성장하며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 19.89%를 나타낼 것으로 예상됩니다. 시장 부문의 점유율 및 추정치는 MW 단위로 계산 및 보고됩니다. 하이퍼스케일러의 급속한 전개, 경제특구에서 100% 외자소유를 인정하는 면세조치, 2억 7,200만명의 주민에 있어서 디지털 소비의 급증에 의해 인도네시아의 데이터센터 시장은 동남아시아에서 가장 역동적인 디지털 인프라 프론티어의 하나로 자리매김하고 있습니다. 자카르타는 고밀도 광섬유 네트워크와 해저 케이블 육상 포인트를 갖기 때문에 용량 전개를 주도하는 반면 바탐은 싱가포르에의 근접성으로부터 파급 수요를 모아 신규 건설을 가속화하고 있습니다. 코로케이션이 여전히 도입의 대부분을 차지하는 것, 엄격한 데이터 거주지법에 대응을 목적으로 세계의 클라우드 제공업체가 플랫폼의 현지화를 진행하는 가운데, 하이퍼스케일 투자는 연간 21% 이상의 속도로 확대하고 있습니다. Tier 3 설계는 기본 아키텍처로 정착되어 있으며, 이는 Tier 4의 고비용을 피하면서 동시 유지보수성을 요구하는 기업의 요구를 반영합니다. 또한 PLN(인도네시아 국영전력회사)과의 장기전력 구매계약에 의해 AI 대응 구성을 지원하는 재생가능에너지에 의한 메가와트 단위의 전력공급이 실현되고 있습니다.
AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft 각사는 멀티 AZ 리전의 가동 또는 발표를 진행하고 있어 국내 워크로드용으로 20밀리초 미만의 레이턴시를 보증합니다. 자카르타와 바탐은 250MW가 넘는 대규모 코로케이션 계약의 파이프라인을 형성합니다. 2024년 10월에 가동을 시작한 Indosat-NVIDIA의 2억 5,000만 달러 규모의 AI 팩토리는 이미 20개 이상의 인도네시아 기업에 서비스를 제공하고 있으며, 생성형 AI 추론 수요를 충족하기 위해 18개월 이내에 H100에서 Blackwell GB200 GPU로의 전환을 계획하고 있습니다. 하이퍼스케일러의 엄격한 신재생에너지 조달 정책은 신재생에너지 증명서를 번들로 제공하는 PLN과의 장기 전력 계약을 장려하고 사업자가 지속가능성 목표를 달성할 수 있도록 지원합니다. 현지 통신 사업자는 최종 마일 연결과 관리 서비스를 결합하여 이익을 얻었으며, 이는 핵심 시스템을 클라우드 마이그레이션하는 동안 기업 시장에서 고객 정착률을 높입니다. 이러한 배포로 인도네시아는 전 세계 트래픽 루트의 핵심이 되어 싱가포르와 쿠알라룸푸르에서 종단된 워크로드를 재분배하고 있습니다. 그 결과 발생하는 설비투자 사이클은 건설임금을 밀어 올려 숙련 노동자층을 감소시키고, 공급자와 폴리테크닉 기관 간 노동력 스킬 향상 협정의 필요성을 가속화하고 있습니다.
인도네시아에서는 특별경제구(SEZ) 내의 데이터센터 프로젝트에서 100% 외자소유를 인정하고 있으며, 디지털 인프라 투자에 대한 가속상각을 적용함으로써 신규 건설 프로젝트의 실효 IRR 기준을 250-300베이시스 포인트 인하하고 있습니다. 치카랑과 바탐의 SEZ에서는 수입설비에 대한 부가가치세(VAT)를 0%로 하고 초기설비투자액을 약 11% 삭감하고 있습니다. 간소화된 온라인 단일 신청(OSS) 시스템은 적합 프로젝트 승인 기간을 24주에서 최소 10주로 단축합니다. 이러한 우대조치로 한국투자파트너스와 시나르 머슬랜드, 디지털 리얼티와 미트라 아디타마 등의 합작사업이 유치되어 2024년 이후 총 7억 5,000만 달러 이상의 투자를 표명하고 있습니다. 정책 입안자는 디지털 인프라를 2025년까지 1,300억 달러 규모의 디지털 경제 목표 달성의 기반으로 자리매김했고, 정권 교체 하에서도 세제 우대 조치의 계속을 보증했습니다. 관세 면제로 장벽이 줄어들었지만 개발자는 건축자재에 대한 엄격한 현지 조달 요구 사항을 충족해야하며 인도네시아의 EPC 계약자와의 제휴가 촉진되고 있습니다.
석탄은 여전히 국내 발전 구성의 40.5%를 차지하고 있으며, 사업자는 스코프 2 배출량의 영향을 받아 다국적 클라이언트의 넷 제로 의무와 모순되는 상황에 있습니다. PLN(인도네시아 국영전력회사)이 123조 루피아(80억 달러)의 보조금에 의존하고 있는 상황은 재생가능에너지의 급속한 확대를 제약하고 있으며, 데이터센터 개발자는 탄소예산을 달성하기 위해 Off-grid형 태양광+축전시스템과 바이오매스 혼소계약의 조달을 강요하고 있습니다. 신재생에너지 증서(RECs)는 공급이 수요를 따라잡지 못하고 있기 때문에 고가로 거래되고 전력비용에 약 6달러/MWh를 올리고 있습니다. 하이퍼스케일러 기업은 가상 PPA를 협상하고 있지만, PLN이 송전망으로의 전력 주입권의 분리를 완료할 때까지 카운터 파티 리스크에 직면합니다. 더욱 복잡하게도 인도네시아 은행의 데이터센터 인증 체크리스트는 라이프사이클 탄소 공개가 요구되고 BFSI 클라이언트의 감사 부담이 증가하고 있습니다. 2030년대에 파푸아의 대규모 수력 발전이 공급될 때까지 인도네시아의 데이터센터 산업은 성장에 대한 의지와 급격한 탈탄소화 비용의 균형을 맞추어야 합니다.
2025년 대규모 시설은 인도네시아 데이터센터 시장의 46.12%를 차지했습니다. 이는 기업이 단일 캠퍼스 솔루션을 선호하는 경향을 반영하며, 이 솔루션은 내결함성이 있는 전력 공급, 캐리어 중립적인 연결성, 캠퍼스 전체의 PUE1.5 미만을 실현하고 있습니다. 텔콤의 치카란 확장에 의해 2025년까지 캠퍼스 용량이 60MW로 확대되는 것, 엣지 코넥스사가 부카시에서 각 30MW의 다단계 개발을 약속하고 있기 때문에 인도네시아의 대규모 건설 데이터센터 시장 규모는 더욱 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다. 반면에 분산형 기업이 사용자에 가까운 엣지 노드를 배치하는 경향 때문에 중형 시설은 21.18%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 시장을 견인하고 있습니다. 뉴트라 DC 등의 사업자는 이미 2급 도시권에서 'neuCentrIX' 브랜드의 마이크로 엣지 사이트 19 거점을 운영하고 있어 지역 요인이 소규모 시설 수요를 견인하고 있는 실태가 부각되고 있습니다. 메가/매시브 규모의 카테고리도 대두하고 있어 인도사트와 NVIDIA의 AI 팩토리가 장래의 확장을 위해서 80 MW를 확보하고 있는 사례가 현저합니다. 이는 GPU 클러스터가 랙당 80kW라는 고전력 밀도 설계를 촉진하는 경향을 뒷받침합니다. 소형 모듈형 데이터센터는 여전히 틈새 시장이며 주로 정부의 엣지 워크로드와 낙도에서 지역 연결 파일럿 사업을 지원합니다. 전반적으로, 사업자는 자카르타의 메가와트급 시설과 섬도부의 분산형 레이턴시 요건의 균형을 맞추기 위해 구축 템플릿의 다양화를 추진하고 있으며, 이에 따라 규모별 수요의 병행적인 지속을 도모하고 있습니다.
중규모 용량의 확대는 PLN(국영전력회사)이 수라바야와 반둥에서 실시하는 변전소 업그레이드에 의해 2027년까지 150MVA의 예비부하가 해방되는 대로 가속할 전망입니다. 이러한 도시 지역에서 4-6MW 포드를 개발하는 개발 사업자는 결제 처리에 5밀리초 미만의 낮은 지연을 필요로 하는 핀텍 기업 및 EC 플랫폼 수요를 수익화할 수 있습니다. 한편, 하이퍼스케일러는 10MW를 넘는 데이터홀 전체의 사전임대계약을 계속 체결해 대규모 사이트 확장의 기반을 굳히고 있습니다. 그 결과 프로젝트 금융 모델은 인도네시아의 10년간 면세 기간을 배경으로 자본 지출의 회수를 최적화하기 위해 다양한 수익원(도매 앵커 테넌트와 소매 엣지 케이지)을 결합하는 경우가 증가하고 있습니다. 이러한 하이브리드형 비즈니스 모델은 인도네시아의 데이터센터 시장이 규모와 도달 범위를 모두 확보할 수 있는 유연한 용량 계획을 장려하는 방법을 돋보이게 합니다.
2025년 시점에서 Tier 3 시설은 인도네시아 데이터센터 시장의 83.90%를 차지했으며, 티어 4 구축의 35% 비용 프리미엄을 수반하지 않고 BFSI(은행 및 금융 및 보험) 및 통신 분야의 SLA를 만족하는 병행 보수성을 실현하기 위해, 향후도 사실상의 표준 규격으로서 정착할 전망입니다. Tier 4 공급은 게임 퍼블리셔 및 고주파 거래업체가 내결함성 가동 시간을 요구하는 주요 캠퍼스 내의 제한된 스위트로 제한됩니다. 발릭파판과 족자카르타에서 IoT와 스마트시티의 파일럿 사업을 위한 엣지 전개에서는 라이프사이클 경제성이 중복성을 상회하기 때문에 Tier 1-2의 설치 면적이 계속되고 있습니다. 개인정보보호법에 근거한 규제체크리스트에서는 이중전원공급과 N1냉각이 의무화되어 있으며, 신규건설에 있어서 사실상 진입장벽으로 Tier3가 위치하고 있습니다. 뉴트라 DC의 치카란 시설은 업타임 티어 III 및 티어 IV의 인증을 취득하고 있으며, 모듈식 전기 스키드를 채용하여 티어 간의 원활한 이행을 실현. 랙 이전이 불필요해지는 이 특징은 단계적인 확장을 목표로 하는 기업에게 매력적입니다.
미래의 티어 설계는 WUE와 같은 지속가능성 지표를 통합하고 기존의 분류 체계는 포괄성을 잃을 것입니다. 사업자는 이미 옥상태양광발전을 도입해 연간 소비전력의 5%를 충당하고 있으며, PLN(인도네시아 국영전력회사)이 넷미터링 규칙을 확정하는 대로 이 수치는 두배로 될 것으로 전망되고 있습니다. 또한 GPU 고밀도 홀은 액체 냉각 루프를 필요로 하고 냉각 중복성이 홀 수준에서 랙 수준으로 이동하기 때문에 계층 분류가 복잡해집니다. 이러한 변화에도 불구하고, Tier 3는 비용, 컴플라이언스, 안정적인 가동 시간의 균형을 이루고 있으며, 기업 워크로드의 90%를 수용할 수 있기 때문에 인도네시아의 데이터센터 시장 성장에 핵심적인 존재가 될 것입니다.
인도네시아의 데이터센터 시장 보고서는 데이터센터 규모(대규모, 초대규모, 중간 규모, 메가, 소규모), 티어 유형(Tier 1.2, Tier 3, 티어 4), 데이터센터 유형(하이퍼스케일/자체 건설, 기업/엣지, 공동 위치), 최종 사용자(은행, 금융서비스 및 보험(BFSI), IT 및 ITES, 전자상거래, 정부, 제조, 미디어 및 엔터테인먼트)로 분류됩니다. 시장 예측은 IT 부하 용량(MW) 단위로 제공됩니다.
The Indonesia Data Center Market was valued at USD 1.61 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 1.83 billion in 2026 to reach USD 3.48 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 13.71% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
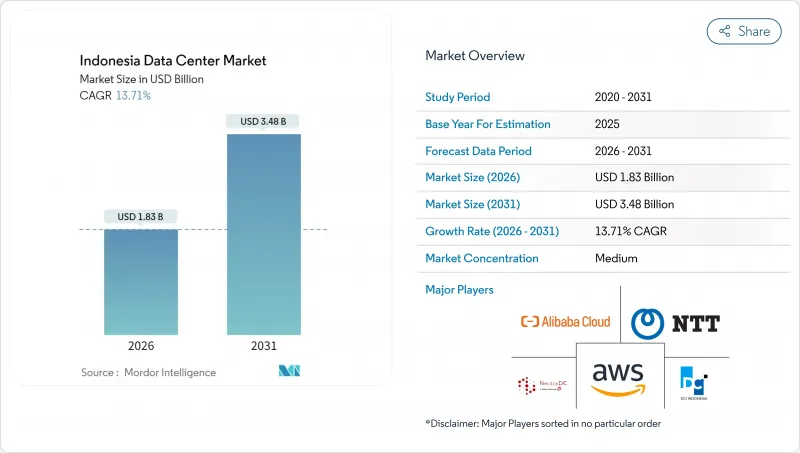
In terms of IT load capacity, the market is expected to grow from 1.44 thousand megawatt in 2025 to 3.56 thousand megawatt by 2030, at a CAGR of 19.89% during the forecast period (2025-2030). The market segment shares and estimates are calculated and reported in terms of MW. Rapid hyperscaler roll-outs, tax exemptions that allow 100% foreign ownership in Special Economic Zones, and a sharp rise in digital consumption among 272 million residents position the Indonesia data center market as one of Southeast Asia's most dynamic digital infrastructure frontiers. Jakarta dominates capacity deployment due to its dense fiber network and submarine cable landing points, while Batam's proximity to Singapore attracts spillover demand, accelerating greenfield builds. Colocation still commands most deployments, yet hyperscale investments are advancing more than 21% a year as global cloud providers localize platforms to comply with strict data-residency laws. Tier 3 designs remain the default architecture, reflecting enterprises' need for concurrent maintainability without the premium of Tier 4, and long-term PLN power-purchase agreements unlock renewable megawatt blocks that support AI-ready configurations.
AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft have each activated or announced multi-AZ regions, guaranteeing sub-20 ms latency for domestic workloads and driving a pipeline of wholesale colocation deals exceeding 250 MW in Jakarta and Batam. The Indosat-NVIDIA USD 250 million AI factory that went live in October 2024 already serves more than 20 Indonesian enterprises and plans to migrate from H100 to Blackwell GB200 GPUs within 18 months to satisfy generative-AI inferencing demand. Hyperscalers' strict renewable-energy procurement policies catalyze long-term power contracts with PLN that bundle renewable certificates, helping operators meet sustainability targets. Local carriers benefit by bundling last-mile connectivity and managed services, which embeds stickiness in an enterprise market still migrating core systems to the cloud. These deployments anchor Indonesia in global traffic routes, redirecting workloads that would otherwise terminate in Singapore or Kuala Lumpur. The resulting capex cycle raises construction wages and tightens the skilled-labor pool, hastening the need for workforce upskilling agreements between providers and polytechnic institutes.
Indonesia allows 100% foreign ownership in data-center projects located within Special Economic Zones and grants accelerated depreciation on digital-infrastructure investments, lowering effective project IRR thresholds by 250-300 basis points for greenfield builds. Cikarang and Batam SEZs each offer 0% VAT on imported equipment, shaving up-front capex by around 11%. The streamlined Online Single Submission (OSS) system compresses approval timelines from 24 to as little as 10 weeks for compliant projects. These incentives have attracted joint ventures such as Korea Investment Partners-Sinar Mas Land and Digital Realty-Mitra Aditama, which collectively announced more than USD 750 million in commitments since 2024. Policymakers view digital infrastructure as a cornerstone for the USD 130 billion digital economy target by 2025, ensuring continuity of fiscal privileges even under changing administrations. While tariff holidays lower barriers, developers must still meet stringent local content requirements for construction materials, prompting partnerships with Indonesian EPC contractors.
Coal still accounts for 40.5% of the national generation mix, exposing operators to Scope 2 emissions that conflict with the net-zero mandates of multinational clients. PLN's financial reliance on IDR 123 trillion (USD 8 billion) in subsidies constrains the rapid build-out of renewable energy, forcing data-center developers to source off-grid solar-plus-storage or biomass co-firing contracts to meet their carbon budgets. Renewable energy certificates (RECs) sell at premium prices because supply lags behind demand, adding roughly USD 6 per MWh to power costs. Hyperscalers negotiate virtual PPAs but face counterparty risk until PLN finalizes unbundling of grid-injection rights. Further complicating matters, Bank Indonesia's data center accreditation checklist now requires life-cycle carbon disclosures, increasing audit overhead for BFSI clients. Until large-scale hydropower from Papua is delivered in the 2030s, the Indonesian data center industry must balance growth aspirations with steep decarbonization expenses.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Large facilities held 46.12% of the Indonesia data center market share in 2025, reflecting enterprises' preference for single-campus solutions that offer resilient power, carrier-neutral connectivity, and campus-wide PUE below 1.5. The Indonesia data center market size for large builds is predicted to widen further as Telkom's Cikarang expansion raises its campus capacity to 60 MW by 2025, and EdgeConneX commits to multi-phase developments of 30 MW each in Bekasi. Medium-sized facilities, however, are pacing the field with a 21.18% CAGR because distributed enterprises deploy edge nodes closer to users. Operators such as NeutraDC already run 19 micro-edge sites branded neuCentrIX across tier-2 cities, highlighting how geography drives smaller footprints. Mega and massive categories are emerging, exemplified by the Indosat-NVIDIA AI factory that reserves 80 MW for future phases, underlining how GPU clusters skew power density design toward 80 kW per rack. Small modular data centers remain niche, mainly supporting government edge workloads and rural connectivity pilots on outer islands. Overall, operators are diversifying build templates to strike a balance between Jakarta megawatts and the islands' distributed latency needs, thus sustaining parallel demand across size cohorts.
Medium-size capacity gains are likely to accelerate once PLN's substation upgrades in Surabaya and Bandung unlock 150 MVA of spare load by 2027. Developers deploying 4 - 6 MW pods in those metros can monetize demand from fintechs and e-commerce platforms that require sub-5 ms latency for payment processing. Meanwhile, hyperscalers continue to sign pre-lease agreements for entire data halls exceeding 10 MW each, anchoring large-site expansions. As a result, project financing models increasingly bundle diversified revenue streams, wholesale anchor tenants plus retail edge cages, to optimize capex payback under Indonesia's 10-year tax-holiday horizon. The resulting hybrid business models underscore how the Indonesia data center market incentivizes flexible capacity planning to capture both scale and reach.
Tier 3 facilities captured 83.90% of the Indonesia data center market share in 2025 and will remain the de facto standard owing to concurrent maintainability that satisfies BFSI and telecom SLAs without the 35% cost premium of Tier 4 builds. Tier 4 supply is restricted to a handful of suites within major campuses where gaming publishers and high-frequency traders demand fault-tolerant uptime. Tier 1-2 footprints persist in edge deployments serving IoT and smart-city pilots in Balikpapan and Yogyakarta, where lifecycle economics trump redundancy. Regulatory checklists issued under the Personal Data Protection Law require dual-power feeds and N + 1 cooling, effectively making Tier 3 the entry barrier for new builds. NeutraDC's Cikarang complex holds both Uptime Tier III and Tier IV certifications and utilizes modular electrical skids to facilitate seamless transitions between tiers, eliminating the need to migrate racks, a feature that appeals to enterprises scaling over time.
Future tier designs will incorporate sustainability metrics such as WUE and render traditional classifications less comprehensive. Operators are already integrating rooftop solar that supplies 5% of annual consumption, a figure expected to double once PLN finalizes net-metering rules. In addition, GPU-dense halls demand liquid-cooling loops that complicate tier labels because cooling redundancy becomes rack-level rather than hall-level. Despite such shifts, Tier 3 will retain dominance because it balances cost, compliance, and reliable uptime for 90% of enterprise workloads, thereby remaining integral to Indonesia's data center market growth.
The Indonesia Data Center Market Report is Segmented by Data Center Size (Large, Massive, Medium, Mega, and Small), Tier Type (Tier 1 and 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4), Data Center Type (Hyperscale/Self-Built, Enterprise/Edge, and Colocation), End User (BFSI, IT and ITES, E-Commerce, Government, Manufacturing, Media and Entertainment, and More), and Hotspot. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of IT Load Capacity (MW).