
선박용 윤활유 시장은 2025년 24억 3,000만 리터에서 2026년에는 24억 8,000만 리터로 성장하여 2026년부터 2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 1.86%를 나타낼 전망입니다. 2031년까지 27억 1,000만 리터에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.

이 안정적인 상승세는 특히 IMO 2020 유황규제 강화와 같은 환경규제의 엄격화 외에도 선대의 꾸준한 확대와 근대화 프로그램이 추진하는 고품질 윤활유에 대한 수요 증가를 반영하고 있습니다. 선박 소유자는 초저황 연료의 연소 및 듀얼 연료 LNG 엔진의 가동 시 엔진 청정성을 유지하는 윤활유를 점점 더 중시하고 있습니다. 이러한 변화로 인해 감속항행으로 인한 항해당 소비량 감소에도 불구하고 평균 판매가격은 상승세입니다. 해상풍력발전시설의 건설 증가와 다이나믹 포지셔닝선의 배치 확대로 고성능 유압 작동유 및 스러스터유 수요가 더욱 높아지고 있습니다. 세계의 배합 네트워크, 견고한 기술 서비스 및 디지털 상태 모니터링 플랫폼을 갖춘 공급업체는 선박용 윤활유 시장이 서비스 집약적 계약으로 전환하는 동안 더 큰 가치를 얻는 입장에 있습니다.
컨테이너 취급량 증가와 견조한 벌크 상품 유통은 효율화 기술에 의한 항해당 소비량 삭감에도 불구하고 윤활유 수요를 지원하고 있습니다. 다양화된 공급망은 항행 거리를 연장하고 최적화된 항로 설정은 항구 간의 엔진 가동 시간을 연장합니다. 이 두 가지 모두 윤활유의 총 수요를 높이고 있습니다. 양자강조선 등 아시아 조선소는 수주가 가득하며 다년간 서비스 계약으로 이어지는 다량의 최초 충전 수요가 보장되고 있습니다. 해안 항로의 항해 빈도 증가는 감속 항행 관행을 상쇄하고 연간 가동 시간의 순 증가를 초래합니다. 그 결과 모든 주요 선박 등급에서 윤활유 사용량 증가가 기록되어 선박용 윤활유 시장의 꾸준한 확대가 보장됩니다.
중국의 조선 능력 확대와 인도의 항만 정비에 의해 노후화한 선박의 대체가 진행되어, 고온 대응의 선진 엔진을 탑재한 설계가 주류가 됩니다. 이러한 엔진에는 고염기가 및 고내산화성을 갖춘 합성유 또는 반합성유가 적합합니다. 집중윤활시스템과 선내센서의 도입으로 운항회사는 프리미엄윤활유 공급과 연동한 상태감시형 보수계약으로의 이행이 가능해집니다. 일본과 한국의 조선회사는 LNG 운반선에 듀얼 연료 엔진을 추가하고 가스와 디젤 사이클에서 발생하는 산을 중화하는 특수 실린더 오일 수요를 더욱 높이고 있습니다. 장기적으로는 이 지역의 선대 갱신 규모가 세계의 선박용 윤활유 시장에서 가장 큰 절대적 성장을 지원하는 기반이 됩니다.
환경 대응 윤활유(EAL)는 광물유 등급에 비해 대폭적인 가격 프리미엄이 설정되어 있으므로 일부 운항회사에서는 사용량을 제한하거나 교환 간격을 연장하여 운용 예산을 억제하는 움직임을 볼 수 있습니다. 바이오 베이스 오일은 주 추진기관에서 전형적인 고온 환경 하에서는 산화 안정성이 약하며, 보조 기어나 선미 베어링 용도로의 보급이 제한되어 있습니다. 식품·바이오연료 섹터와의 원료 경쟁이 가격 변동성을 높이고, 베이스 오일의 생산 능력 부족이 대규모 도입의 장벽이 되고 있습니다. 식물 유래 대체품은 특수 보관 방법과 엄격한 수분 관리가 필요할 수 있으며 선원의 업무를 복잡하게합니다. 이러한 과제로 인해 규제면에서 인센티브가 여전히 강함에도 불구하고 판매량 증가는 둔화되고 있습니다.
트렁크 피스톤 엔진 오일(TPEO)은 2025년 선박용 윤활유 시장 점유율의 41.85%를 차지했습니다. 저속·중속 엔진은 섬프 용량이 크고 기본 수치를 유지하기 위해 정기적인 보충이 필요하기 때문입니다. 현대 듀얼 연료선의 연장 드레인 프로그램은 저황 연료 블렌드의 산을 중화하기 때문에 여전히 높은 알칼리성 TPEO에 의존하고 있습니다. 2024년부터 2025년까지 컨테이너선 및 장미화물선의 운항사업자가 뛰어난 퇴적물 억제 성능을 가진 신뢰성 높은 브랜드를 선호했기 때문에 TPEO의 선박용 윤활유 시장 규모는 견조하게 추이했습니다. 보조기관용 시스템 오일에 대한 병행 수요가 안정된 판매량을 지지하는 한편, 실린더 오일은 분리 분사 방식을 채용하는 2행정 엔진에서 틈새 역할을 유지하고 있습니다.
선미 베어링 오일 수요 동향은 가장 급속히 변화하고 있으며 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 2.04%를 나타낼 것으로 전망됩니다. 첨단 페이스 씰과 엄격한 제로 배출 규제의 도입으로 리터당 비용이 높음에도 불구하고 선주는 생분해성 합성 에스테르 오일로의 전환을 추진하고 있습니다. 기어유는 가혹한 부하 변동 하에서 가동하는 포드 추진 장치나 가변 피치 프로펠러의 채용 확대에 의해 완만한 수요 증가가 예상됩니다. 한편, 유압 작동유 수요량은 설치·서비스선에 탑재되는 자동화 갑판 기계나 동적 정위 시스템의 도입 상황에 연동합니다. 그리스 및 기타 특수 윤활유는 정기적인 베어링 유지 보수 및 선내 냉동 압축기와 같은 틈새 장비에 대한 수요를 지원합니다.
광물유는 2025년 시점에서 선박용 윤활유 시장의 71.95%를 차지했으며, 그 비용 효율과 폭넓은 OEM 승인이 반영되었습니다. 신뢰할 수 있는 세계 공급망을 통해 연료 공급 기지가 충분한 재고를 유지할 수 있으며, 운항자는 항해 전반에 걸쳐 사양을 준수할 수 있습니다. 합성 PAO와 에스테르 블렌드는 특히 LNG 운반선에 탑재된 고출력 엔진에서 높은 피막 강도와 내산화성이 추가 비용을 웃도는 프리미엄 틈새 시장을 독점하고 있습니다. 뛰어난 점도 지수 특성으로 인한 에너지 절약 효과는 구매 가격의 높이를 부분적으로 상쇄하고 성능이 중요한 시스템에서 점진적인 대체를 촉진합니다.
바이오 윤활유는 총량의 매우 일부이지만 유럽 및 미국 해안 수역에서 환경 대응 윤활유(EAL)의 의무화를 배경으로 CAGR 2.15%로 확대되고 있습니다. 식물 유래 에스테르는 우수한 윤활성과 낮은 독성을 가지고 있지만, 추진 엔진에서 열 스트레스를 줄이기 위해 산화 방지제 패키지가 필요합니다. 합성에스테르와 저점도 PAO를 혼합한 하이브리드 배합은 첨가제 응답성이 향상되어 중온역의 기어박스나 스러스터 시스템에의 적용 범위를 확대하고 있습니다. 원료의 가용성과 에스테르화 능력의 스케일 업은 바이오 제품의 주류 선박용 윤활유 시장으로의 침투 속도를 결정합니다.
본 「선박용 윤활유 시장 보고서」는 윤활유 유형(시스템 오일, 실린더 오일, 선미 축유 등), 기유(광물유, 합성유, 바이오 베이스), 선박 유형(장미 화물선, 탱커 - 컨테이너선 등), 용도(주 추진 엔진, 보조 엔진 및 발전기 등), 유통 경로(직접 공급, 유통업체 등), 지역(아시아태평양, 북미, 유럽 등)에서 분석했습니다.
아시아태평양은 2025년 선박용 윤활유 시장 점유율의 46.35%를 차지했으며, 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)2.05%로 확대될 것으로 전망됩니다. 중국의 신조선 납품의 우위성은 초기 충전량의 많음을 보증하고, 그 거대한 상선대는 지속적인 교환 수요를 견인하고 있습니다. 인도의 사갈마라 항만 근대화 계획 및 전용 해안 운송 회랑은 윤활유 소비를 촉진하고 있으며, 특히 아대륙 연안을 항해하는 장미 화물선과 유조선용 트렁크 피스톤 오일에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있습니다. 일본과 한국의 조선소는 높은 사양의 LNG 운반선과 듀얼 연료 추진 시스템을 추진하고 있으며, 이들은 고품질의 실린더 오일이 필요합니다. 이를 통해 첨단 배합 기준이 지역 전체에 퍼져 있습니다. 제조의 다양화 동향에 뒷받침된 동남아시아의 환적 거점은 지역 내 항로 거리를 연장하여 윤활유의 안정적인 수요를 유지하고 있습니다.
유럽은 엄격한 환경 규제로 환경 적합 윤활유(EAL) 및 저황 연료 대응 오일의 도입을 가속화하는 중요한 위치를 차지하고 있습니다. 2025년 5월 시행의 지중해 배출 규제 구역(ECA)에서는 연료와 윤활유의 적합성 검증이 의무화되어 깊은 기술적 전문 지식을 가진 브랜드 공급업체에 대한 선호가 강화되고 있습니다. 북유럽의 해상 풍력 발전의 확대는 한랭지 조건을 위해 특별히 고안된 합성 스러스터 오일 및 유압 작동유 수요를 증가시키고 있습니다. 발트해 및 북해 지역의 고급 배출 가스 규제로 인해 이 지역은 바이오 선미 축관 윤활유의 조기 도입 지역으로 자리매김하고 있습니다.
북미에서는 미국 대서양 해안의 해상 풍력 리스 사업이 추풍이 되어, 고성능 유압·스러스터 윤활유를 소비하는 신조 존스법 대응 설치선의 건조가 촉진되고 있습니다. 캐나다 북극권의 선박 및 오대호 무역에는 저온 유동성이 뛰어난 윤활유가 요구되고, 멕시코만의 해상 지원선은 기간이 되는 피스톤용·유압용 등급 수요를 지지하고 있습니다. 남미, 중동, 아프리카는 계속해서 성장 기회를 갖고 있습니다. 브라질의 프리솔트층 개발과 서아프리카의 심해 탐사가 OSV(오프쇼어 지원선)의 성장을 지원하지만, 통화 리스크와 정치 리스크가 투자를 억제하고 있습니다. 후자이라 등 중동의 벙커(연료 보급) 거점은 적재 수요의 기반이 되고 있지만, 지역의 지정학적 긴장에 의해 윤활유의 유통량이 일시적으로 혼란될 가능성이 있습니다.
The Marine Lubricants Market is expected to grow from 2.43 billion liters in 2025 to 2.48 billion liters in 2026 and is forecast to reach 2.71 billion liters by 2031 at 1.86% CAGR over 2026-2031.
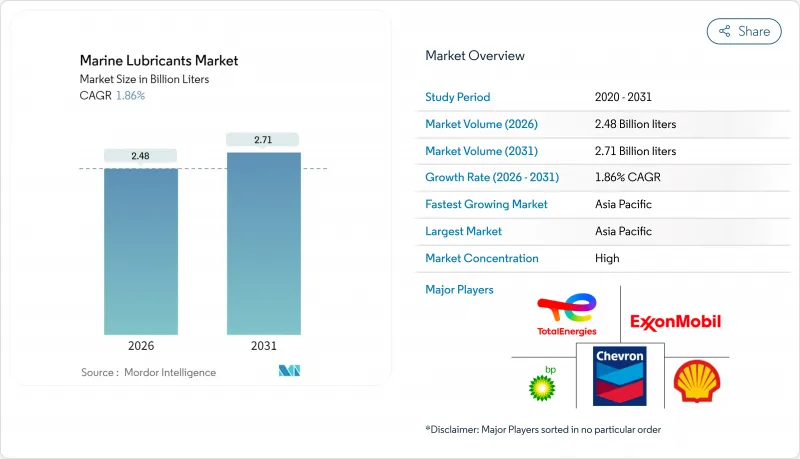
This stable upward trajectory reflects tightening environmental rules, notably the IMO 2020 sulfur cap, coupled with steady fleet expansion and modernization programs that push operators toward premium-grade formulations. Vessel owners increasingly favor lubricants that preserve engine cleanliness when burning very-low-sulfur fuel or operating dual-fuel LNG engines. This shift raises average selling prices even as slow-steaming lowers per-voyage consumption. Growing offshore wind construction, alongside greater deployment of dynamic-positioning vessels, further elevates demand for high-performance hydraulic fluids and thruster oils. Suppliers with global blending networks, robust technical service, and digital condition-monitoring platforms are positioned to capture greater value as the marine lubricants market migrates toward service-intensive contracts.
Container throughput growth and resilient bulk commodity flows sustain lubricant uptake even as efficiency technologies lower consumption per voyage. Diversified supply chains extend sailing distances, and optimized routing keeps engines running longer between ports, both of which lift total lubricant demand. Asian yards such as Yangzijiang Shipbuilding have full order books, guaranteeing sizable initial-fill requirements that convert to multi-year service contracts. Higher voyage frequency on near-shoring routes offsets slow-steaming practices, resulting in a net rise in annual operating hours. Consequently, every major vessel class registers incremental lubricant volume gains, ensuring steady expansion of the marine lubricants market.
China's enlarged shipbuilding capacity and India's port upgrades accelerate the replacement of aging vessels with designs carrying advanced, higher-temperature engines. These engines favor synthetic or semi-synthetic lubricants with elevated base-number and oxidation-resistance profiles. Installation of centralized lubrication systems and onboard sensors enables operators to migrate toward condition-based maintenance contracts bundled with premium lubricant supply. Japanese and South Korean builders are adding dual-fuel engines on LNG carriers, further raising demand for specialized cylinder oils that neutralize acid produced during gas-diesel cycles. Over the long term, the sheer scale of regional fleet renewal underpins the largest absolute gain in the marine lubricants market worldwide.
EALs command significant price premiums over mineral grades, prompting some operators to ration usage or extend drains to contain operating budgets. Bio-based oils exhibit weaker oxidative stability under the high temperatures typical in main propulsion engines, limiting penetration to auxiliary gear or stern-tube applications. Feedstock competition from food and biofuel sectors adds price volatility, while limited base-stock production capacity constrains large-scale adoption. Plant-based alternatives sometimes require specialized storage and stricter moisture control, adding complexity for ship crews. These challenges slow volume growth even though regulatory incentives remain strong.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Trunk piston engine oil (TPEO) accounted for 41.85% of the marine lubricants market share in 2025, as low-speed and medium-speed engines have large sump capacities and require regular top-ups to maintain the base number. Extended drain programs on modern dual-fuel ships still rely on high-alkalinity TPEO to neutralize acids derived from low-sulfur fuel blends. The marine lubricants market size for TPEO remained resilient during 2024-25 as container and bulker operators favored reputable brands with strong deposit control. Parallel demand for system oils in auxiliary engines supports steady volumes, while cylinder oils continue to hold a niche role in two-stroke engines that employ separate injection.
Demand dynamics shift fastest in stern-tube oils, projected to rise at a 2.04% CAGR through 2031. The use of advanced face seals and stricter zero-discharge regulations is pushing owners toward biodegradable synthetic esters, despite the higher cost per liter. Gear oils are expected to receive a modest uplift from the increasing adoption of podded propulsion and controllable-pitch propellers, which operate under extreme load fluctuations. Meanwhile, hydraulic fluid volumes track the rollout of automated deck machinery and dynamic-positioning systems used on installation and service vessels. Due to routine bearing maintenance and niche equipment such as onboard refrigeration compressors, greases, and other specialty lubricants.
Mineral oil captured 71.95% of the marine lubricants market size in 2025, reflecting its cost efficiency and wide-ranging OEM approvals. Reliable global supply chains enable bunkering hubs to maintain sufficient stocks, ensuring operators can adhere to specifications throughout their voyages. Synthetic PAO and ester blends dominate premium niches where high film strength and oxidation resistance outweigh added expense, especially on high-output engines fitted to LNG carriers. Superior viscosity index characteristics deliver energy savings that partly offset the higher purchase price, fostering gradual substitution in performance-critical systems.
Although just a fraction of the total volume, bio-based lubricants are advancing at a 2.15% CAGR, driven by EAL mandates in European and U.S. coastal waters. Plant-derived esters offer excellent lubricity and low toxicity, but require antioxidant packages to mitigate thermal stress in propulsion engines. Hybrid formulations blending synthetic ester with low-viscosity PAO demonstrate improved additive response, widening the application envelope into moderate-temperature gearbox and thruster systems. The availability of feedstock and the scale-up of esterification capacity will determine how quickly bio-based variants penetrate the mainstream marine lubricants market.
The Marine Lubricants Market Report is Segmented by Lubricant Type (System Oil, Cylinder Oil, Stern-Tube Oils, and More), Base Stock (Mineral Oil, Synthetic, Bio-Based), Ship Type (Bulker, Tanker, Container, and More), Application (Main Propulsion Engine, Auxiliary Engine and Generators, and More), Distribution Channel (Direct Supply, Distributor/Agent, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, and More).
Asia-Pacific retained 46.35% of the marine lubricants market share in 2025 and is projected to expand at a 2.05% CAGR through 2031. China's dominance in newbuild deliveries ensures high initial-fill volumes, while its massive merchant fleet drives continuous replacement demand. India's Sagarmala port modernization and dedicated coastal shipping corridors stimulate lubricant consumption, particularly for trunk piston oils in bulkers and tankers plying the subcontinent's coasts. Japanese and South Korean yards are pushing high-spec LNG carriers with dual-fuel propulsion that require premium cylinder oils, thereby spreading advanced formulation standards across the region. Southeast Asian transshipment hubs, supported by manufacturing diversification trends, lengthen regional voyage legs and sustain steady lubricant uptake.
Europe commands a pivotal position due to its stringent environmental rules that accelerate adoption of EALs and low-sulfur-compatible oils. The Mediterranean ECA, effective since May 2025, forces owners to validate fuel-lubricant compatibility, reinforcing preference for branded suppliers with deep technical expertise. Northern Europe's offshore wind build-out intensifies demand for synthetic thruster oils and hydraulic fluids specifically designed for cold weather conditions. Advanced emission controls in Baltic and North Sea zones position the region as an early adopter of bio-based stern-tube lubricants.
North America benefits from offshore wind leasing on the U.S. Atlantic seaboard, triggering newbuild Jones Act installation vessels that consume high-performance hydraulic and thruster lubricants. Canada's Arctic tonnage and Great Lakes trade need cold-flow-optimized oils, while Gulf of Mexico offshore support vessels sustain the baseline demand for trunk piston and hydraulic grades. South America and the Middle East and Africa remain emerging opportunities: Brazil's pre-salt activities and West Africa's deep-water prospects support OSV growth, but currency and political risks temper investment. Middle East bunker hubs like Fujairah anchor transshipment demand, although regional geopolitical tensions can intermittently disrupt lubricant volumes.