
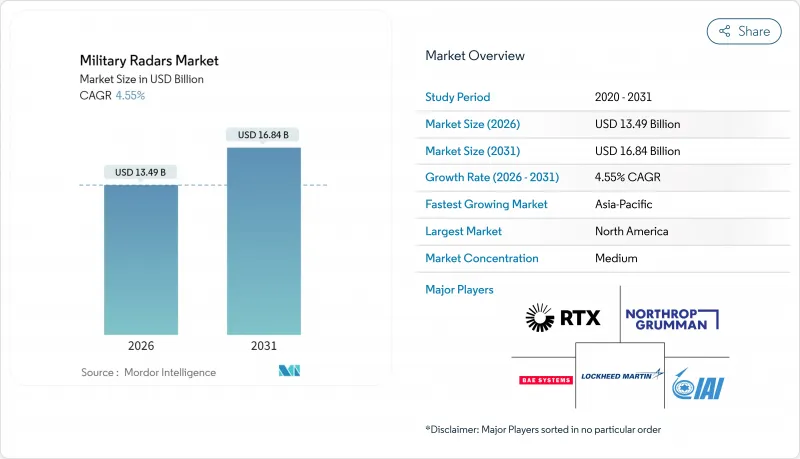
군용 레이더 시장은 2025년에 129억 달러로 평가되었으며, 2026년 134억 9,000만 달러에서 2031년까지 168억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예상됩니다.
예측 기간(2026-2031년)의 CAGR은 4.55%를 나타낼 것으로 전망됩니다.

증가하는 지정학적 긴장, 신속한 대 UAS(무인 항공기 시스템) 요건, 기계식 스캐닝 어레이에서 소프트웨어 정의 AESA(액티브 전자 스캔 어레이) 플랫폼으로의 이행이 수요를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 미국 우주개발청의 트래킹 레이어 등의 새로운 위성군은 우주 기반의 적외선 데이터가 몇 초 만에 지상 레이더에 목표를 이어받아 초음속·무리 위협에 대한 킬 체인을 강화하는 실례를 보여줍니다. 그러나 5G 주파수 대역 간섭 및 질화갈륨(GaN) 반도체공급 부족으로 인증주기가 장기화되고 프로그램 위험이 증가하고 있습니다. 플랫폼 수요는 양극화되고 있으며, 육상 시스템이 여전히 수익의 대부분을 차지하는 반면, 항공기 장착형 및 우주 센서는 가장 높은 R&D 비용 배분을 받고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 정의 레이더(SDR)가 기술 구성을 주도하는 동안, 초기 단계의 양자 프로토타입은 장기적인 파괴적 진보의 가능성을 시사합니다.
2024년 NATO 회원 23개국이 GDP 대비 2%의 방위비 목표를 달성하고 레이더 근대화 프로그램에 다액의 자금을 배분함으로써 방위 지출은 평시로서는 과거 최고를 기록했습니다. 폴란드의 47억 5,000만 달러 규모의 '비스와 계획'에서는 패트리어트 미사일과 지라프 4A 센서를 결합하여 동쪽 방향 400km의 감지 범위를 확대합니다. 대만은 2024년도의 레이더 예산을 7.7% 증액해, 천궁 III 요격 미사일의 페이즈드 어레이화를 단계적으로 추진했습니다. 일본도 북한 시험에서 드러낸 순항 미사일 방어의 약점을 보완하기 위해 초지평선 레이더를 조달했습니다. 이러한 계획은 적어도 중기적으로 군용 레이더 시장의 기반이 안정 될 것으로 예측됩니다.
극초음속 무기는 교전 가능 시간을 6분 미만으로 압축해 기존 센서에 과제를 가져옵니다. 미국은 2024년 8기의 추적 위성을 궤도에 투입해 지상 레이더에의 종말 요격 유도를 실시했습니다. NATO의 TWISTER 계획은 TRML-4D 지상 어레이와 우주 데이터 연계를 통해 활공체 추적을 실현하고 있습니다. 2019년 석유시설 공격을 받아 사우디아라비아가 47대의 KuRFS 레이더를 설치한 것은 대 드론 대책의 긴급성이 높아지고 있음을 나타냅니다. 우크라이나가 2024년에 200기 이상의 이동식 대 UAS 레이더를 전장에 도입한 것도 이 동향을 뒷받침하는 것입니다. 따라서 신속하게 배포 가능하고 소프트웨어 재구성 가능한 센서에 대한 수요가 세계 군용 레이더 시장의 성장 궤도를 밀어 올리고 있습니다.
군용 레이더 시스템에서 GaN 기술의 채택 확대는 GaN 반도체 재료의 세계 공급망에 부담을 주고 있습니다. GaN은 전력 밀도, 열효율 및 광대역 성능을 향상시켜 고급 AESA 레이더 시스템에 필수적입니다. 그러나 그 공급은 다양한 요인들에 의해 제한됩니다. 2024년 세계의 GaN 웨이퍼 생산 능력은 약 180만장(6인치 환산)에 달했지만 방위 프로그램만으로 그 총량의 거의 4분의 1을 차지하고 공급을 더욱 희박하게 했습니다. Wolfspeed사는 52주 리드타임을 보고하고 있으며 AN/TPY-4의 납품은 9개월 지연하고 있습니다. 갈륨의 정제량의 80%를 차지하는 중국은 2023년에 수출 라이선싱을 도입했고, 구미의 계약자는 대체 공급원의 확보와 인증을 강요했습니다. 미국 CHIPS법의 자금 배분에서는 GaN용이 5% 미만에 머물기 때문에 2027년 이전공급 개선은 전망 희박합니다. 이 병목 현상은 군용 레이더 시장의 단기 성장을 억제합니다.
2025년 군용 레이더 시장 수익의 38.74%를 육상 플랫폼이 차지했습니다. 이것은 NATO 동부전선 및 한반도에 있어서 대포병 시스템이나 통합 방공 시스템의 도입이 견인한 것입니다. 그러나 각국이 AESA 레이더의 개수를 가속하고 무인 조기 경계 노드를 전개하는 중, 항공기 탑재 센서는 연율 5.92%를 나타낼 전망입니다. E-7 웨지테일의 조달에 의해 노후화된 E-3가 대체되어, 노스롭 그라만사의 180 트랙 다목적 어레이가 도입됨으로써, 이 대처의 기세가 강조되고 있습니다. 예산상의 마찰에 의해 단기적인 해군 발주는 억제되고 있습니다만, 호주 호바트급함의 업그레이드나 일본의 이지스 장비함이 점증적인 수요를 지지하고 있습니다. 카펠라 스페이스와 같은 우주 기반 합성 개구 레이더 컨소시엄은 15분 간격의 재방문 시간을 목표로 하는 벤처 캐피탈을 주입하여 군용 레이더 시장 점유율을 저위도 이미지 영역으로 확대하려고 합니다. 예측 기간 동안 육상분야가 최대의 수익원으로 지속될 전망입니다. 그러나 항공기 탑재형 및 우주 도메인이 R&D 예산 증가분을 얻어 멀티 도메인 기동성으로의 점진적인 전환을 시사하고 있습니다.
추적·사격 관제 센서는 2025년 수익의 31.12%를 차지하며, 패트리어트, THAAD, 이지스의 지속적인 현대화를 반영했습니다. 한편 감시·조기 경계 레이더는 군용 레이더 시장에서 CAGR 6.18%의 가장 빠른 속도로 성장할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 독일의 F126 프리게이트함은 16발의 미사일 유도와 360도 연속 감시가 가능한 탈레스사제 「시파이어」를 채용하고 있어 기능 통합에 대한 수요를 나타내고 있습니다. 5년 전에는 거의 존재하지 않았던 대 드론 센서는 도시항공모빌리티(UAM)와 소비자용 드론의 보급에 따라 단거리에서의 저비용 검지가 요구되기 때문에 현재 두 자리 성장을 이루고 있습니다. 우크라이나가 이러한 시스템의 전장 가치를 입증함으로써 무기 감지 시스템과 대 드론 방어 시스템(C-RAM) 조달이 증가했습니다. 소프트웨어를 통한 모드 전환으로의 전환으로 운영자는 하드웨어를 교체하지 않고 새로운 임무를 업로드할 수 있어 군용 레이더 시장은 단일 용도의 품목을 넘어 다양화가 진행되고 있습니다.
북미는 2025년 군용 레이더 시장 수익의 36.95%를 차지했고 미국 방총성의 8,500억 달러를 넘는 지출(그중 48억 달러가 레이더 갱신·신규 도입에 충당)에 지지되었습니다. AN/TPY-4 및 LTAMDS 프로그램에서 알 수 있듯이이 지역은 소프트웨어 정의 아키텍처와 JADC2 지원 인터페이스에서 주도적 위치에 있습니다. 캐나다의 NORAD 현대화 계획은 북극권 수요를 창출하고 중기 수주 파이프라인을 유지하고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 6.86%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장하고 있으며, 이는 세계에서 가장 빠른 속도입니다. 인도의 6억 5,000만 달러 규모의 우텀 AESA 생산 라인, 일본의 4,200억 엔(26억 8,000만 달러)의 레이더 근대화 계획, 한국의 KF-21 탑재 AESA는 지역에서의 국산화와 오프셋의 동향을 종합적으로 나타내고 있습니다. 중국의 강경 자세로 인근 국가들은 조달을 가속화하고 있으며, 2030년대 초반까지 아시아태평양이 북미의 수익 주도권에 과제하는 태세가 갖추어지고 있습니다.
유럽의 성장은 완만하고 우크라이나에서 포병 무기를 사용한 후 자금이 탄약 비축으로 이동하고 있습니다. GDP의 4.7%를 차지하는 폴란드의 방위 지출과 독일의 3억 5,000만 유로(4억 345만 달러)에 이르는 TRML-4D 계약은 이 분야에 중점 투자를 부조하고 있습니다. 중동에서는 아랍에미리트(UAE)에 의한 해상 레이더 'SeaVue'를 포함한 MQ-9B 패키지(2억 9,000만 달러 상당) 등 외국 군사 판매(FMS)의 활용이 계속되고 있습니다.
반면 남미와 아프리카는 여전히 소규모 기여도에 머물렀고, 두 지역을 합친 매출은 전체의 8% 미만입니다. 전반적으로 지리적 분산은 순환 위험을 줄이고 군용 레이더 시장의 꾸준한 성장을 지원합니다.
The military radars market was valued at USD 12.90 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 13.49 billion in 2026 to reach USD 16.84 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.55% during the forecast period (2026-2031).
Mounting geopolitical tension, rapid counter-UAS requirements, and the transition from mechanically scanned arrays to software-defined AESA platforms are converging to reinforce demand. New constellations, such as the US Space Development Agency's Tracking Layer, demonstrate how space-based infrared data now hands off targets to ground radars in seconds, thereby tightening kill chains for hypersonic and swarm threats. Yet 5G spectrum encroachment and gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductor shortages prolong qualification cycles and elevate program risk. Platform demand is bifurcated: land systems still dominate revenue, but airborne and space sensors receive the highest R&D allocations. Software-defined radars (SDRs) lead the technology mix, while early quantum prototypes hint at the potential for disruptive long-term advancements.
Defense spending reached a peacetime record in 2024 as 23 NATO members finally met the 2% of GDP pledge, allocating sizable funds to radar modernization programs. Poland's USD 4.75 billion Wisla initiative couples Patriot missiles with Giraffe 4A sensors to extend detection 400 km east. Taiwan boosted its 2024 radar budget by 7.7%, targeting phased-array upgrades for Tien Kung III interceptors. Japan followed with over-the-horizon procurements to close cruise-missile gaps exposed during North Korean tests. Together, these programs ensure a steady baseline for the military radars market through at least the medium term.
Hypersonic weapons compress the engagement window to under six minutes, challenging legacy sensors. The US orbited eight tracking satellites in 2024 to cue ground radars for terminal intercept. NATO's TWISTER program links TRML-4D ground arrays with space feeds to track glide vehicles. Saudi Arabia's installation of 47 KuRFS radars following the 2019 oil-facility strike underscores the growing urgency for counter-drone measures. Ukraine's 2024 battlefield adoption of more than 200 mobile counter-UAS radars further validates the trend. The demand for rapid-deployable, software-reconfigurable sensors, therefore, elevates the global military radars market's growth trajectory.
The increasing use of GaN technology in military radar systems is straining the global supply chain for GaN semiconductor materials. GaN provides enhanced power density, thermal efficiency, and wide-band performance, making it critical for advanced AESA radar systems. However, its availability is constrained by various factors. Global GaN wafer capacity reached approximately 1.8 million six-inch-equivalent units in 2024; however, defense programs alone accounted for nearly one-quarter of that total, further tightening the supply. Wolfspeed reported 52-week lead times, pushing AN/TPY-4 deliveries nine months to the right. China, which refines 80% of gallium, imposed export licensing in 2023, forcing Western contractors to stockpile or certify alternative sources. US CHIPS Act funding earmarked less than 5% for GaN, so relief is unlikely before 2027. The bottleneck tempers near-term growth of the military radars market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Land platforms accounted for 38.74% of the military radars market revenue in 2025, driven by established counter-battery and integrated air defense deployments along NATO's eastern flank and the Korean Peninsula. However, airborne sensors are expanding at a rate of 5.92% annually as nations accelerate AESA retrofits and deploy unmanned early-warning nodes. The E-7 Wedgetail procurement replaces aging E-3s and introduces Northrop Grumman's 180-track multi-role array, underscoring the momentum behind this initiative. Budget friction constrains near-term naval orders, yet Australia's Hobart-class upgrades and Japan's Aegis-equipped vessels sustain incremental demand. Space-based synthetic-aperture consortia, such as Capella Space, inject venture capital that targets 15-minute revisit times, aiming to extend the military radars market share into low-latitude imaging. Over the forecast horizon, land will stay the largest revenue pool. Yet, airborne and space domains will claim a rising portion of R&D budgets, signaling a gradual shift toward multi-domain mobility.
Tracking and fire control sensors held 31.12% of 2025 revenue, reflecting continued Patriot, THAAD, and Aegis modernization, while surveillance and AEW radars are projected to notch a 6.18% CAGR, the quickest pace in the military radars market. Germany's F126 frigate has chosen Thales Sea Fire, which is capable of guiding 16 missiles and maintaining continuous 360° coverage, illustrating the demand for consolidated functions. Counter-drone sensors, which were almost nonexistent five years ago, are now experiencing double-digit growth as urban air mobility (UAM) and consumer drone proliferation require affordable detection at short ranges. Weapon-locating and C-RAM procurements accelerated after Ukraine demonstrated the battlefield value of these systems. The shift toward software-switchable modes enables operators to upload new missions without swapping hardware, thereby helping the military radars market diversify beyond single-purpose line items.
The Military Radars Market Report is Segmented by Platform (Land, Naval, and More), Product Type (Surveillance and Airborne Early Warning Radars, and More), Technology (Software-Defined Radar, and More), Range (Short, Medium, and Long), Component (Antenna, Transmitter, Receiver, Signal Processor, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America generated 36.95% of the 2025 revenue for the military radars market, buoyed by US Department of Defense outlays exceeding USD 850 billion, of which USD 4.8 billion was allocated to radar upgrades and new starts. The region leads in software-defined architectures and JADC2-ready interfaces, as exemplified by the AN/TPY-4 and LTAMDS programs. Canada's NORAD modernization adds Arctic demand, sustaining a medium-term pipeline.
The Asia-Pacific region is advancing at a 6.86% CAGR, the fastest rate worldwide. India's USD 650 million Uttam AESA production line, Japan's JPY 420 billion (USD 2.68 billion) radar modernization, and South Korea's KF-21 onboard AESA collectively illustrate regional indigenization and offset dynamics. China's assertive posture is driving its neighbors to accelerate procurement, positioning the Asia-Pacific region to challenge North American revenue leadership by the early 2030s.
Europe's growth is moderate as funds shift to munitions stockpiles after Ukraine's artillery usage. Poland's defense spending, accounting for 4.7% of its GDP, and Germany's EUR 350 million (USD 403.45 million) TRML-4D contract highlight targeted investments in the sector. The Middle East continues to utilize foreign military sales, with the UAE's MQ-9B package, including SeaVue maritime radars, valued at USD 290 million.
In contrast, South America and Africa remain smaller contributors, collectively accounting for less than 8% of revenue. Overall, geographic diversification helps mitigate cyclical risks and supports the steady growth of the military radars market.