
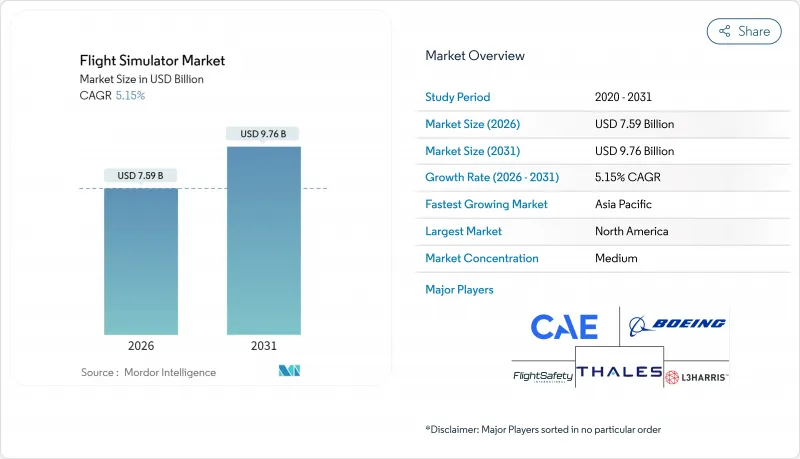
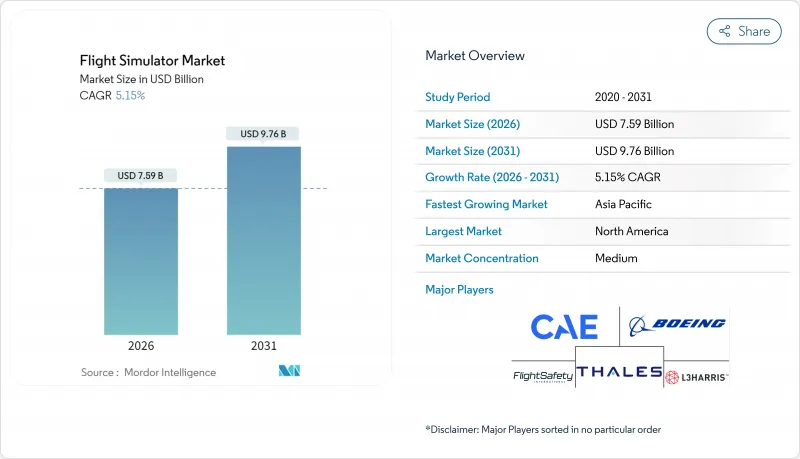
비행 시뮬레이터 시장은 2025년 72억 2,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 2026년에는 75억 9,000만 달러로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다. 2026-2031년에 걸쳐 CAGR 5.15%로 성장할 것으로 보이며, 2031년까지 97억 6,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 전망됩니다.
의무적 훈련 규정, 확대되는 조종사 부족 현상, 첨단 항공 이동 플랫폼으로의 전환은 팬데믹 이후 지연된 수요 회복이 잦아들고 있음에도 수요를 꾸준한 구조적 성장 궤도에 유지시키고 있습니다. 항공사와 군은 역량 기반 체계에 맞춰 교육 과정을 현대화하며, 안전 마진을 유지하면서 훈련 주기를 단축하는 몰입형 기술에 대한 지속적인 투자를 촉진하고 있습니다. 서비스 중심 비즈니스 모델이 조달 시장을 점차 장악하면서 운영사는 선행 자본 부담에서 벗어나고, 공급사는 평생 지원 서비스를 통해 수익을 창출할 수 있게 되었습니다. 지역별로는 북미가 규모 면에서 주도권을 유지하지만, 인도와 중국이 기록적인 항공기 주문 잔고를 처리하기 위해 경쟁하면서 아시아태평양 지역이 가장 빠른 역량 확장을 보이고 있습니다. 주요 공급업체 간 통합이 가속화되며, 기업들은 하드웨어, 소프트웨어, 훈련 분석을 단일 성과 기반 솔루션으로 묶는 수직적 통합을 추구하고 있습니다.
일시적 채택 중단 이후에도 세계의 조종사 공급망은 여전히 긴장 상태를 유지하며 풀모션 장치 활용도를 사상 최고 수준으로 끌어올리고 있습니다. 미국 지역 항공사들은 사직률이 감소했다고 보고하지만, 기체 증가 속도가 훈련 역량을 앞지르면서 장기적인 조종실 인력 수요를 충족시키지 못하고 있습니다. 호주는 팬데믹 기간 동안 25,000명의 항공 인력을 잃어, 보잉 오스트레일리아가 정비 일정을 유지하기 위해 기술자 견습생 정원을 두 배로 늘려야 했습니다. 인도가 50개 이상의 신규 아카데미 설립을 계획한 것은 신흥 시장들이 향후 15-20년 내 예상되는 30,000명의 조종사 부족을 메우기 위해 시뮬레이터를 제도화하는 방식을 보여줍니다. 이러한 구조적 부족은 초기 및 재교육용 장치에 대한 지속적인 수요를 촉진하여 비행 시뮬레이터 시장 전반에 걸쳐 수익 가시성을 확보합니다.
규제 기관들은 비행 장애 예방 및 복구 훈련을 법제화하여 기존 모범 사례를 법적 의무로 전환했습니다. 국제민간항공기구(ICAO)의 역량 기반 표준은 이제 미국 연방항공청(FAA)과 유럽항공안전청(EASA)의 규정 제정을 주도하며, 고충실도 시뮬레이션을 핵심 교육 과정에 포함시키고 있습니다. 다중 승무원 조종사 면허(MPL) 과정은 실기 비행 시간 요건을 더욱 단축시켜, 복잡한 시나리오를 재현하는 풀모션 및 혼합현실 장치로 훈련 예산을 전환시키고 있습니다. CBTA 프레임워크를 도입한 항공사들은 비행 경로 관리 및 승무원 자원 기술에서 측정 가능한 향상을 보고하며, 재훈련 주기 전반에 걸쳐 시뮬레이터 수요를 강화하고 있습니다.
고충실도 레벨 D 장치는 여러 공급업체가 제작한 정밀 광학 장치에 의존합니다. 항공우주 주요 업체들이 핵심 부품을 자체 프로그램으로 끌어들이면서 콜리메이트 디스플레이 어셈블리 납품이 지연되고, 이로 인해 인수 시험이 늦어지고 주문 잔고가 증가하고 있습니다. 업계 조사에 따르면 2차 항공전자 장비 공급업체의 60%가 B737 MAX 생산 확대를 훈련 장치 생태계 전반의 납품 지연을 초래하는 가장 큰 병목 현상으로 꼽았습니다. 이 부족 현상은 단가를 상승시키고 OEM이 항공사 계약을 비행학교 주문보다 우선시하도록 강요하여 동일한 투영 유리를 사용하는 혼합현실 트레이너의 도입을 늦추고 있습니다. 일부 운영사는 FAA 레벨-D 정확도에 미치지 못하는 임시 개조를 선택하여 규제 승인 및 수익 창출 서비스 시기를 지연시키고 있습니다. 새로운 공급업체가 광학 틈새 시장에 진입하지 않는 한, 강력한 수요 신호에도 불구하고 이러한 제약으로 인해 단기 성장이 제한될 것입니다.
풀 플라이트 시뮬레이터(FFS)는 2025년 수익의 거의 절반을 차지했습니다. 그러나 복합현실/가상현실(VR) 절차 훈련 장치는 10.23%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 비행 시뮬레이터 시장을 주도하고 있으며, 조종 조작 이외의 작업에서 몰입형 기술에 대한 운영자 측의 신뢰를 보여줍니다. 소형 VR 훈련기의 비용은 풀모션 장치의 일부에 불과해 항공사들이 승무원 기지에 다수 장비를 배치하고 출장 경비를 절감할 수 있게 합니다. 알래스카 항공의 Loft Dynamics VR B737 플랫폼 투자는 이러한 변화를 잘 보여주는 사례로, FAA 승인을 기다리는 여러 허브에 설치가 계획 중입니다.
몰입형 헤드셋과 모션 큐잉 기술의 결합은 이제 조종실 숙련 및 비상 훈련에 충분한 정확도를 제공하여, 부족한 레벨 D 시뮬레이터 용량을 최종 숙련도 점검에 활용할 수 있게 합니다. FAA가 버텍스 솔루션즈(Vertex Solutions) 및 바르조(Varjo)와 공동으로 추진 중인 XR 표준화 프로그램은 인증 절차를 가속화하여 지역 항공사 및 비행 학교로의 확산을 촉진할 전망입니다. 기기 가격 하락과 소프트웨어 생태계 성숙에 따라 혼합현실(MR) 트레이너는 2030년대 초까지 비행 시뮬레이터 시장 점유율을 확대할 것입니다.
북미는 확고한 항공사 허브, 군사 예산, FAA 규제 영향력 덕분에 2025년 지출의 39.45%를 유지했습니다. 그러나 아시아태평양 지역은 인도 및 중국 항공사들이 수천 대의 좁은 동체 항공기를 도입하고 은퇴자들이 지역 항공기 편대에서 이탈을 주도함에 따라 7.12%의 연평균 성장률(CAGR)을 기록할 예정입니다. 국내 훈련 역량은 이를 따라잡기 위해 급속히 확대되고 있으며, 세계의 공급업체와의 합작 투자 및 신규 훈련 기관 설립을 위한 정부 인센티브가 촉진되고 있습니다.
유럽은 에어버스의 툴루즈 신캠퍼스(연간 1만 명 훈련, FFS 12대 보유)에 힘입어 꾸준한 기여를 이어갈 전망입니다. 중동은 세계의 항공사 전략에 부합하는 허브 기반 훈련 센터에 지속적으로 투자 중입니다. 반면 아프리카와 남미는 경제적 변동성이 자본 흐름에 영향을 미치며 더딘 진전을 보이고 있습니다. 그럼에도 현지 규제 기관들은 ICAO 기준과 조화를 이루며 향후 10년간 시뮬레이터 시장 확대를 위한 새로운 교육 협력의 문을 열고 있습니다.
The flight simulator market is expected to grow from USD 7.22 billion in 2025 to USD 7.59 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 9.76 billion by 2031 at 5.15% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Mandatory training regulations, a widening pilot shortage, and the shift toward advanced air-mobility platforms keep demand on a steady, structural growth path even as post-pandemic catch-up spending fades. Airlines and militaries are modernizing curricula around competency-based frameworks, prompting sustained investment in immersive technologies that compress training cycles while protecting safety margins. Service-oriented business models increasingly dominate procurement, insulating operators from upfront capital burdens and allowing suppliers to monetize lifetime support. Regionally, North America maintains scale leadership, yet Asia-Pacific shows the fastest capacity build-out as India and China race to staff their record aircraft backlogs. Consolidation among top vendors is accelerating as companies seek vertical integration that bundles hardware, software, and training analytics into a single outcome-based offering.
Global pilot pipelines remain stressed even after temporary hiring pauses, keeping full-motion device utilization at record levels. Regional carriers in the United States report fewer resignations, yet cannot meet long-run cockpit staffing needs as fleet growth outpaces training capacity. Australia lost 25,000 aviation workers during the pandemic, forcing Boeing Australia to double technician apprenticeship slots to maintain maintenance schedules. India's plan for more than 50 new academies underscores how emerging markets institutionalize simulators to close a projected 30,000-pilot gap within 15-20 years. These structural shortages boost recurring demand for both initial and recurrent training devices, anchoring revenue visibility across the flight simulator market.
Regulators have codified upset-prevention and recovery training, transforming what was once best practice into a legal obligation. The International Civil Aviation Organization's competency-based template now guides FAA and EASA rulemaking, embedding high-fidelity simulation into core syllabi. Multi-Crew Pilot License (MPL) pathways further compress live-flight hour requirements, redirecting training budgets toward full-motion and mixed-reality devices replicating complex scenarios. Airlines adopting CBTA frameworks report measurable gains in flight-path management and crew resource skills, reinforcing simulator demand across recurrent cycles.
High-fidelity Level D devices rely on precision optics built by several suppliers. Delivery of collimated display assemblies is slipping as aerospace primes pull critical components into their programs, delaying acceptance tests and inflating backlogs. An industry survey found 60% of tier-2 avionics vendors citing the B737 MAX production ramp as the single largest bottleneck dragging down deliveries across the training device ecosystem. The shortage inflates unit prices and forces OEMs to prioritize airline contracts over flight-school orders, slowing adoption of mixed-reality trainers that rely on the same projection glass. Some operators resort to interim retrofits that fall short of FAA Level-D fidelity, delaying regulatory approvals and revenue service. Unless new suppliers enter the optics niche, these constraints will cap near-term growth despite strong demand signals.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Full-flight simulators (FFS) retained nearly half of 2025 revenue. Yet mixed/virtual-reality procedural trainers are pacing the flight simulator market with a 10.23% CAGR, signaling operator confidence in immersive technologies for non-maneuver tasks. The cost of a compact VR trainer can be a fraction of a full-motion device, enabling airlines to deploy multiple units at crew bases and cut travel overhead. Alaska Airlines' investment in Loft Dynamics VR B737 platforms exemplifies the shift, with installations planned at several hubs pending FAA sign-off.
Immersive headsets paired with motion-cueing now deliver sufficient fidelity for cockpit familiarization and emergency drills, freeing scarce Level D capacity for final proficiency checks. The FAA's joint program with Vertex Solutions and Varjo to craft XR standards should speed certification pathways, accelerating adoption across regional carriers and flight schools. As device prices fall and software ecosystems mature, mixed-reality trainers will capture larger slices of the flight simulator market share by the early 2030s.
The Flight Simulator Market Report is Segmented by Simulator Type (Full Flight Simulator, Flight Training Device, and More), Aircraft Platform (Fixed-Wing, Rotary-Wing, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, and Advanced Air Mobility/EVTOL), Method (Synthetic and Virtual), End User(Civil, Commercial, and Military Aviation), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America retained 39.45% of 2025 spending thanks to entrenched airline hubs, military budgets, and FAA regulatory sway. Yet Asia-Pacific is slated to post 7.12% CAGR as Indian and Chinese carriers induct thousands of narrowbodies and retirees drive attrition across regional fleets. Domestic training capacity is racing to catch up, prompting joint ventures with global providers and government incentives for greenfield academies.
Europe remains a steady contributor, propelled by Airbus's new Toulouse campus, which will train 10,000 personnel annually and house 12 FFS. The Middle East continues to invest in hub-based training centers aligned with its global airline strategy. At the same time, Africa and South America progress more slowly as economic volatility affects capital flows. Nevertheless, local regulators are harmonizing with ICAO standards, opening the door for new training partnerships that will enlarge the addressable flight simulator market over the next decade.