
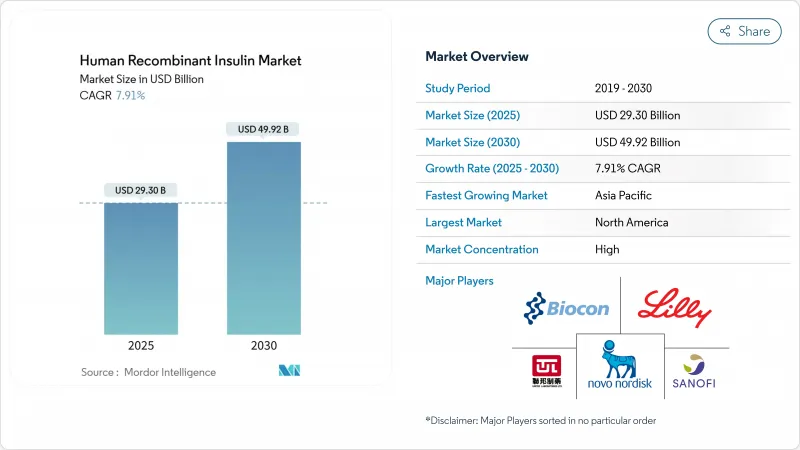
세계의 인간 유전자 재조합 인슐린 시장 규모는 2025년 293억 달러로, 2030년까지 499억 2,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, CAGR은 7.91%로 추이할 것으로 보입니다.

GLP-1 수용체 작용제와 바이오시밀러에 의해 치료법의 선택이 바뀌어도 인슐린이 수억 명의 혈당 조절의 기간제인 것이 변함없기 때문에 수요의 확대는 계속되고 있습니다. 세계보건기구(WHO)의 보고에 따르면 당뇨병 환자수는 세계에서 8억명을 넘어 1990년의 4배가 되고 있습니다. Novo Nordisk와 Eli Lilly는 2030년까지 가동을 시작할 예정인 미국 공장에 합쳐 130억 달러를 넘는 자금을 투자하고 있습니다. 한편, 상환제도 확대, 새로운 바이오시밀러의 등장, 커넥티드 펜이나 자동펌프 등의 디바이스 혁신으로 경쟁은 항상 유동적입니다.
당뇨병 이환율은 8억명 이상으로 급증하고 의료 시스템의 능력을 근본적으로 늘리고 동시에 인슐린에 대한 장기적인 수요를 확고하게 하고 있습니다. 2형 당뇨병의 유병률은 앉기 쉬운 라이프스타일과 식생활 변화가 집중되는 도시화가 진행되는 아시아와 중동의 경제권에서 가장 급속히 증가하고 있습니다. 치료 어드히어런스가 개선됨에 따라, 인슐린 치료는 일반적으로 질병 진행의 초기 단계에서 시작되기 때문에 투여량이 증가합니다. 인슐린의 예측 가능한 평생 사용 특성은 현재 진행중인 수십억 달러 규모의 공장 투자를 지원합니다. 이와 같은 제조의 증강은 공급의 안정성을 강화하고 확대하는 환자 기반에 대응할 수 있도록 리더를 자리매김하게 됩니다.
합리적인 가격의 노력은 대수 증가에 직결합니다. 미국에서는 메디케어 파트 D의 월 금액 상한이 2026년 35달러로 인상되어 수백만 명의 노인에게 장벽이었던 가격이 해소됩니다. 유럽 납부자들은 비용 효과적인 임계값을 강화하면서 바이오시밀러의 우선 처방 프레임을 제공함으로써 접근을 확대하고 있습니다. 2026년에 예정된 인도의 생산 연동 인센티브 제도는 당뇨병 치료제의 현지 생산에 보상함으로써 산업 정책과 환자 접근의 목표를 혼합하고 있습니다. 이러한 조치는 총체적으로 치료 대상자를 확대하고 제제 내에서 브랜드 선택 역학을 변화시킵니다.
합리적 가격 의무화는 금리를 줄이고 연구개발 예산을 돌이킬 수 있습니다. 미국에서는 인플레이션 억제법에 의해 인슐린 제제의 약가에 상한이 설정되어 2026년 1월부터 Tresiba와 Fiasp의 약가가 70% 인하되게 되었습니다. 유럽에서는 현재 모든 당뇨병 치료제가 비용 효과적인 벤치마크에 비추어 평가되고 프리미엄 유사 약물이 예산 보유자의 감시하에 놓여 있습니다. 중국의 수량 기준 조달 방식은 낙찰자에게 상당한 가격 인하를 강요합니다. 이러한 정책을 종합하면 제조업체는 가격 인상보다 생산 효율과 포트폴리오 믹스의 절약을 요구하게 됩니다.
프리믹스형 인간 인슐린은 1일당 주사 횟수가 줄어들 것이라는 기대에서 2025-2030년의 CAGR이 9.45%가 되어 비약적인 성장을 이룰 것입니다. 단시간 작용형 제제는 식사시 혈당 조절에 중요한 역할을 하기 위해 2024년에도 38.45%로 최대 부문을 유지하고 있으며, 인간 유전자 재조합 인슐린 시장을 지원하고 있습니다. 중간작용형 제제는 임상적 가치가 높지만, 1개의 펜으로 기초작용과 볼러스 작용을 겸비한 새로운 배합제에 의한 대체 리스크에 직면하고 있습니다.
인간 유전자 재조합 인슐린 시장은 단순한 요법을 요구하는 환자의 요구에 부응하고 생리적 프로파일을 더 잘 모방한 2상성 비율의 개선을 기업에 촉구하고 있습니다. 생산 능력의 배분도 성장을 형성합니다 : Novo Nordisk가 Levemir 생산 중단을 선택해 더 높은 가치의 유사 약물에 대한 탱크를 비웠으며, 이는 레거시 부문이 수요만으로는 판단 할 수 없을 정도로 급속하게 축소 될 가능성을 시사합니다. 또한 중국의 인슐린 제형 이코덱(icodec)에 대한 승인은 혜택과 위험 허용도의 지역적 편차를 나타냅니다.
Humulin의 2024년 매출은 31.45%이었으며, 수십년에 걸친 처방의 정착이 반영되고 있습니다. 그러나 Sanofi의 Insuman은 신흥 시장에서의 타겟 가격 설정과 바이오시밀러 라인의 확대로 CAGR 9.66%와 더 빠른 궤도를 타고 있습니다. Novolin은 광범위한 소매 유통망을 활용하지만, 지급자의 공감을 얻는 혁신 후크에서는 뒤처져 있습니다.
특허 만료로 바이오시밀러에 대한 압력이 가속됩니다. 오리지네이터는 '우산' 전략을 채택합니다 : Eli Lilly는 브랜드가 없는 lispro를 정가의 반액으로 발매하고, 점유율 저하를 막는 동시에 브랜드 SKU의 리베이트 플로우를 보호했습니다. 유럽에서는 여러 glargine 바이오시밀러가 공존하고, 오리지네이터의 정가는 하락했지만, 리베이트 후의 순가격은 불투명한 채로 있습니다. 따라서 인간 유전자 재조합 인슐린 시장은 목록 가격과 실제 거래 경제가 어떻게 괴리되는지를 보여줍니다.
북미는 2024년 매출의 42.45%를 차지했으며 종합적인 보험 적용과 차세대 전달 시스템의 급속한 도입으로 견인되었습니다. 2026년 발효된 메디케어 35달러 상한은 인간 유전자 재조합 인슐린 시장 수요 연속성을 더욱 확실하게 할 것으로 보입니다. 제조업체는 현지 공급을 강화합니다 : Novo Nordisk의 노스 캐롤라이나 공장과 Eli Lilly의 인디애나 공장은 총 700만 평방 피트 이상의 제형 및 충전 마감 능력을 추가합니다.
아시아태평양은 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 가장 빠른 8.76%로 나타날 것으로 예상됩니다. 중국은 세계 최대의 당뇨병 인구를 보유하고 있으며 최근 우선 의약품의 규제 심사 일정이 앞당겨졌습니다. 국내 제조에 대한 우대조치는 다국적기업과 국내기업 모두에게 공장 건설을 촉구하고 비용경쟁을 격화시킵니다. 인도의 인센티브 프로그램은 마찬가지로 국내 생산을 촉진하고 국가를 지역 수출 허브로 자리매김하고 인간 유전자 재조합 인슐린 시장 도달범위를 확대할 수 있습니다.
유럽은 성숙하면서도 진화하는 환경을 보여줍니다. 의료기술 평가기관이 상대적인 비용효과를 조사함으로써 바이오시밀러에 쫓기는 바람이 불어 가격 인플레이션이 억제됩니다. EMA 지침은 2024년에 업데이트되었으며, 치료법 선택에 경제적 고려 사항이 통합되어 처방자는 임상 효과를 손상시키지 않고 저가 옵션을 선택하게 되었습니다. 가격 수량 계약은 여전히 흔하며 오리지네이터의 할인 전략은 바이오시밀러의 우위를 어느 정도 억제하고 있습니다.
중동 및 아프리카와 남미는 소폭 증가 경향에 있습니다. 아프리카에서는 최근 풀 조달의 시험 운용이 행해져, 공급자의 마진을 압박하고 있지만, 바이알당의 비용은 2 자리수 저하했습니다. 냉장 창고에 대한 인프라 투자는 매우 중요하며, 콜드체인이 오작동에 빠지면 성장 가능성을 막는 간헐적인 품절이 발생합니다. 이러한 지역에서의 성공은 적응 가능한 유통 모델과 안정적인 공급을 보장하는 지역 밀착형 부가가치 서비스에 달려 있습니다.
The human recombinant insulin market size stood at USD 29.30 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 49.92 billion by 2030, advancing at a 7.91% CAGR.
Uptake continues even as GLP-1 receptor agonists and biosimilars alter therapy choices, because insulin remains the backbone of glycemic control for hundreds of millions of people. Demand growth largely traces back to the accelerating diabetes burden: the World Health Organization reports more than 800 million cases worldwide, quadruple the 1990 base. Capacity expansion has therefore eclipsed discovery research as the primary strategic lever; Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly together committed over USD 13 billion to U.S. plants slated to enter service before 2030. Meanwhile, widening reimbursement programs, the arrival of new biosimilars, and device innovations such as connected pens and automated pumps keep the competitive field fluid.
Diabetes incidence has surged to more than 800 million patients, fundamentally stretching health-system capacity and cementing long-duration demand for insulin. Type-2 Diabetes prevalence is rising fastest in urbanizing Asian and Middle-Eastern economies where sedentary lifestyles and dietary shifts converge. As treatment adherence improves, unit volumes climb because insulin therapy typically starts earlier in the disease continuum. The predictable lifetime-use nature of insulin supports the multibillion-dollar factory investments now underway. That manufacturing build-out, in turn, strengthens supply security and positions leaders to meet the expanding patient base.
Affordability initiatives directly translate into higher script volumes. In the United States, the Medicare Part D USD 35 monthly cap takes effect in 2026, neutralizing price as a barrier for millions of seniors. European payers are tightening cost-effectiveness thresholds yet still broaden access by giving biosimilars preferred formulary slots. India's production-linked incentive scheme, scheduled for 2026, mixes industrial policy with patient-access goals by rewarding local output of diabetes medicines. These actions collectively enlarge the treated population and change brand-choice dynamics inside formularies.
Affordability mandates compress margins and can redirect R&D budgets. The Inflation Reduction Act capped U.S. Medicare insulin prices and catalyzed a voluntary 70% list-price cut for Tresiba and Fiasp effective January 2026. Europe now assesses all diabetes therapies against cost-effectiveness benchmarks, putting premium analogues under budget-holder scrutiny. China's volume-based procurement scheme forces deep discounts for tender winners. Collectively, these policies push manufacturers to find savings in production efficiency and portfolio mix rather than price increases.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Premixed Human Insulin is the breakout growth story, tracking a 9.45% CAGR for 2025-2030 on the promise of fewer daily injections. Short-Acting formulations still hold the largest slice at 38.45% in 2024, anchoring the human recombinant insulin market through their critical role in mealtime glucose control. Intermediate-Acting products, although clinically valuable, face substitution risk from newer co-formulations that combine basal and bolus action in a single pen.
The human recombinant insulin market responds to patients' desire for simple regimens, pushing firms to refine biphasic ratios that better mimic physiologic profiles. Capacity allocation also shapes growth: Novo Nordisk's choice to cease Levemir production frees tanks for higher-value analogues, hinting that legacy segments may contract faster than demand alone would dictate. Weekly basal candidates remain in limbo after a U.S. filing setback, yet China's nod to insulin icodec displays regional divergence in benefit-risk tolerance.
Humulin commanded 31.45% revenue in 2024, reflecting decades-deep formulary entrenchment. Still, Sanofi's Insuman is on a faster trajectory with a 9.66% CAGR, buoyed by targeted pricing in emerging markets and expanding biosimilar lines. Novolin leverages wide retail distribution but lags on innovation hooks that resonate with payers.
Biosimilar pressure accelerates as patents sunset. Originators adopt "umbrella" strategies: Eli Lilly released an unbranded lispro at half list price to blunt share erosion while protecting rebate flows on the branded SKU. Europe supplies an early look at end-game dynamics, where multiple glargine biosimilars coexist and originator list prices fell yet net prices, after rebates, remain opaque. The human recombinant insulin market thus illustrates how list-price optics diverge from actual transaction economics.
The Human Recombinant Insulin Market Report is Segmented by Drug Type (Short-Acting Human Insulin, and More), Brand (Humulin, and More), Delivery Device (Vials & Syringes, Insulin Pens (Reusable & Disposable), and More), Diabetes Type (Type-1 Diabetes and Type-2 Diabetes), End User (Hospitals & Clinics, and More), Geography (North America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America led with 42.45% of 2024 revenue, fueled by comprehensive insurance coverage and rapid adoption of next-generation delivery systems. The Medicare USD 35 cap, effective 2026, will further secure demand continuity for the human recombinant insulin market. Manufacturers cement local supply: Novo Nordisk's North Carolina site and Eli Lilly's Indiana complex collectively add more than 7 million square feet of formulation and fill-finish capacity.
Asia-Pacific is set to deliver the fastest 8.76% CAGR through 2030. China holds the world's largest diabetic population and has recently accelerated regulatory review timelines for priority drugs. Domestic manufacturing incentives encourage both multinationals and homegrown firms to build plants, tightening cost competition. India's incentive program will similarly foster local output and could position the country as a regional export hub, deepening the human recombinant insulin market reach.
Europe exhibits a mature yet evolving environment. Health Technology Assessment bodies scrutinize relative cost-effectiveness, giving biosimilars a tailwind and restraining price inflation. EMA guideline updates in 2024 integrated economic considerations into therapy selection, nudging prescribers toward lower-priced options without compromising clinical efficacy. Price-volume contracts remain common, with originator discounting strategies keeping some biosimilar advantages in check.
Middle East & Africa and South America together account for a modest but rising slice. Recent pooled procurement pilots in Africa lowered per-vial costs by double digits, albeit straining supplier margins. Infrastructure investments in refrigerated warehousing are pivotal, as cold-chain lapses currently drive intermittent stock-outs that cap growth potential. Success in these regions will depend on adaptable distribution models and localized value-add services that ensure consistent supply.