
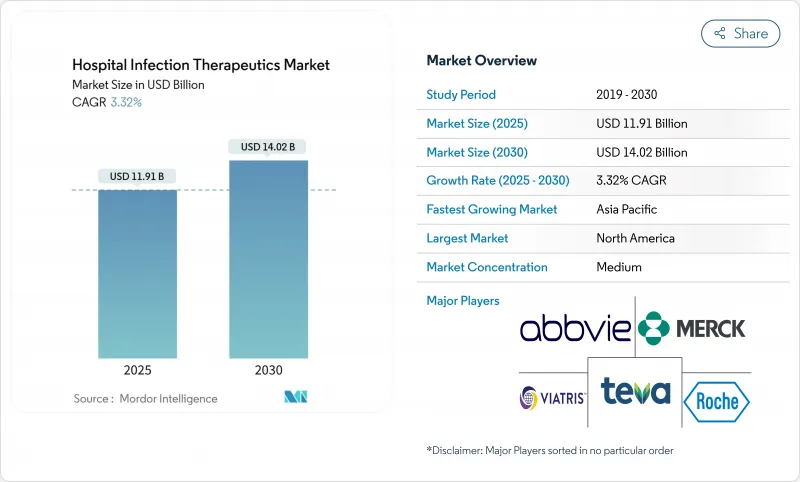
병원 감염 치료제 시장 규모는 2025년에 119억 1,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) CAGR 3.32%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 140억 2,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

수요는 지속적으로 헬스케어 관련 감염(HAI) 발생률의 상승에 추종하고 있지만, 감염 예방 기술의 채용 확대가 성장 가능성을 약화시키고 있습니다. 집중 치료 환경에서 카바페넴 내성 아시네토박터 바우만니와 관련된 사망률은 현재 40%를 넘고 있으며 효과적인 약물에 대한 임상적 긴급성이 높아지고 있습니다. 각국 정부는 항균제 파이프라인에 새로운 자금을 투입하고 있으며 BARDA만으로도 2024년에 5억 달러 이상을 내성 대책에 투입할 예정입니다. 인공지능(AI)을 활용한 창약의 병행적인 진보로 에셋의 동정이 가속되는 한편, 파스툴법(PASTEUR Act)과 같은 구독 형식의 상환안은 혁신자에게 보다 안정된 수익 전망을 약속하는 것입니다.
미국 입원 환자의 약 31명 중 1명이 매일 HAI를 발병하고 있으며, 혈류 감염만으로는 매년 7만 1,000명 이상이 사망하고 있습니다. 고병원성 카르바페넴 내성 Klebsiella pneumoniae 균주는 현재 면역결핍 환자와 건강한 사람 모두에 감염되어 전통적인 항균 요법을 어렵게 만듭니다. 개발도상의 뇌신경외과 센터에서는 척추 수술의 감염률이 11.7%에 달하고 입원 기간 중앙값이 비감염 환자의 23일에서 36.5일로 연장되어 치료 수요가 직접적으로 높아지고 있습니다. 중국 남서부의 3차 병원에서는 혈액 병동, 순환기 병동, 신경 병동에서의 HAI 발생률이 가장 높고, 크렙시에라 폐렴균과 대장균이 우세하다고 보고하고 있습니다. 이러한 패턴을 종합하면 병원 감염 치료제 시장에서 강력하고 폭넓은 스펙트럼을 갖는 약제에 대한 세계적인 요구가 일관되게 높아지고 있는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
외래수술센터(ASC)는 수술 부위 감염(SSI)의 조기 발견을 강화하는 CDC 모니터링 프로토콜 하에서 수백만 건의 외래 수술을 다룹니다. 아시아태평양은 인프라의 확장 및 복잡한 수술을 받는 고령화로 수술 건수의 급격한 성장을 기록하고 있습니다. 요추와 가슴 요추의 수술은 특히 수술 전 48시간 이내에 입원할 경우 SSI 위험이 증가한다는 증거가 있습니다. 사하라 이남의 아프리카에서는 다양한 개입으로 SSI율이 95%나 저하하고 있으며, 예방적 프로토콜이 성숙하면 하류 약량을 억제할 여지가 있음을 강조하고 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 절대적인 절차의 확대는 병원 감염 치료제 시장에서 꾸준한 판매 수를 지원합니다.
반코마이신 내성 장구균 및 메티실린 내성 황색 포도상 구균은 집중 치료실에서 뿌리깊은 위협으로 남아 있습니다. 많은 파이프라인 후보들은 WHO 우선 병원체에 대응하지 않고 치료 갭을 남깁니다. 최근 출시된 세프타지지무아비박탐 배합제 등은 출시 후 수년에 내성이 출현하고 있습니다. 실패율 증가는 독성과 조달 비용을 증가시키는 병용 요법을 촉진합니다. 이 침식은 병원 감염 치료제 시장의 지속적인 성장을 압박하고 있습니다.
항균제가 세계 매출의 72.21%를 차지했습니다. 세프토비프롤과 같은 점적정주제는 79.1%의 복합주 효율로 황색포도상구균균증을 대처하고 B-락탐 클래스의 임상적 우위성을 강화하고 있습니다. 중국 스폰서는 현재 임상 평가 중 20개의 항균제 프로그램을 관리하고 있으며 공급의 탄력성과 경쟁의 심각성을 높이고 있습니다. 카바페넴 내성 아시네토박터와 슈도모나스를 대상으로 한 NIAID의 보조금은 항균제 혁신을 더욱 자극합니다.
항바이러스제는 병원용 항바이러스제와 면역조절제의 채용 확대를 반영하여 현재 규모는 작은 반면, CAGR 3.83%로 성장할 것으로 예측됩니다. Precision Medicin의 워크플로우는 현재 바이러스 내성 유전자형에 맞는 맞춤형 치료를 실시하고 결과를 개선하고 가격 프리미엄을 정당화하고 있습니다. 반면에, 항진균제는 칸디다증에 대한 레자판긴의 승인을 통해 치명적인 치료에서 주 1회 투여의 오랜 갭을 메울 수 있습니다. 기타 '클러스터'에 속하는 박테리오파지 및 단일클론항체 요법은 차별화된 수익원을 추가할 수 있지만, 병원 감염 치료제 시장에 크게 기여하기 위해서는 제조 및 규제의 복잡성을 해결해야 합니다.
북미는 2024년 병원 감염 치료제 시장에서 세계 매출의 37.83%를 차지했습니다. CDC의 National Healthcare Safety Network(미국 의료 안전 네트워크)는 높은 치료에 대한 경계를 유지하는 HAI 보고서 의무 정책을 수립했습니다. BARDA의 자금 지원은 세프토비프롤과 세페피무엔 메타조박탐과 같은 최근 FDA 승인에 결실한 파이프라인 자산의 신속한 실용화를 지원합니다. 화이자는 1억 5,000만 달러를 들여 호주 공장을 현대화하고 60개 이상의 수출 시장에 공급할 예정입니다. 신청 중인 PASTEUR법은 현금 흐름을 더욱 안정시키고 병원 전체의 조달 전략을 형성할 수 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 2030년까지 CAGR 4.53%로 성장이 예측되며, 이는 주요 지역 중 가장 빠릅니다. 중국의 규제개혁 및 혁신적 신약국가 메가 프로젝트를 통해 17개사가 20건의 항균제 임상시험을 실시하여 파이프라인 충실과 국내 가격 경쟁에 기여하고 있습니다. 인도에서는 감염 관리 기준을 강화하는 의료기기 판매 행동 규범이 시행되고 있지만, 산업 폐수에서 고농도의 항생제가 검출되는 등 의약품 폐수 관리는 여전히 긴급한 과제가 되고 있습니다. ASEAN과 남아시아에서는 인프라의 성숙도가 제각각이며 수요도 제각각입니다.
유럽에서는 GSK의 4,500만 파운드 플레밍 센터와의 제휴 등 AMR 대책이 협조되고 있습니다. aztreonam-avibactam에 대한 유럽 의약청(EMA)의 긍정적인 견해는 메탈로-B-락타마제 생산균을 표적으로 한 최초의 B-락탐 및 B-락타마제 억제제의 조합이며, 치료상의 공백을 메우는 것입니다. 베링거 잉겔하임, 에보텍, 바이오메루에 의한 오로백 합작 사업은 진단과 치료의 통합 기능을 추가하여 효과적인 치료까지 시간을 단축할 수 있습니다. 엄격한 환경 배출 규제 및 공동 조달 이니셔티브는 공급망의 품질 조화에 도움이 되지만 병원 감염 치료제 시장 진출기업에게는 컴플라이언스 비용을 높일 수 있습니다.
The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market size is estimated at USD 11.91 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 14.02 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.32% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Demand continues to track rising healthcare-associated infection (HAI) incidence, although wider adoption of infection-prevention technologies tempers growth potential. Mortality linked to carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii now exceeds 40% in intensive-care settings, intensifying clinical urgency for effective agents. Governments are injecting fresh capital into antimicrobial pipelines; BARDA alone committed more than USD 500 million to resistance countermeasures in 2024. Parallel advances in artificial-intelligence (AI) drug discovery accelerate asset identification, while subscription-style reimbursement proposals such as the PASTEUR Act promise steadier revenue visibility for innovators.
Roughly 1 in 31 hospitalized U.S. patients acquires an HAI daily, and bloodstream infections alone account for more than 71,000 deaths each year. Hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains now infect both immunocompromised and healthy individuals, challenging conventional antibacterial regimens. In developing neurosurgical centers, spine-surgery infection rates reach 11.7%, lengthening median hospital stay to 36.5 days from 23 days for uninfected patients and directly raising therapeutic demand. Tertiary hospitals in Southwest China report the highest HAI incidence in hematology, cardiology, and neurology wards, where Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli predominate. Collectively, these patterns reinforce consistent global need for potent, broad-spectrum agents within the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Ambulatory surgery centers handle millions of outpatient operations under CDC-mandated surveillance protocols that heighten early detection of surgical site infections (SSIs). Asia-Pacific records the sharpest procedure growth, buoyed by infrastructure expansion and ageing populations pursuing complex interventions. Evidence links lumbar and thoracolumbar surgeries to elevated SSI risk, particularly when patients are admitted within 48 hours pre-operatively. Multimodal interventions across Sub-Saharan Africa have lowered SSI rates by as much as 95%, highlighting scope to curb downstream drug volumes when preventive protocols mature. Nonetheless, absolute procedure expansion still underpins steady unit sales in the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus remain entrenched threats in intensive-care units. Many pipeline candidates do not address WHO priority pathogens, leaving treatment gaps. Resistance to recently launched combinations such as ceftazidime-avibactam has already emerged within a few years of market entry. Rising failure rates prompt combination regimens that raise toxicity and procurement costs. This erosion pressures sustainable growth in the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Antibacterials held 72.21% of global revenue. Intravenous agents such as ceftobiprole address Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia with 79.1% composite response rates, reinforcing the clinical dominance of B-lactam classes. Chinese sponsors now control 20 antibacterial programs in clinical evaluation, deepening supply resilience and competitive intensity. Generous NIAID grants targeting carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas further stimulate antibacterial innovation.
Antivirals, though smaller today, are projected to grow at a 3.83% CAGR, reflecting broadened adoption of hospital-focused antivirals and immunomodulators. Precision-medicine workflows now match viral resistance genotypes with tailored therapy, improving outcomes and justifying price premiums. Antifungals meanwhile benefit from rezafungin approval for candidemia, filling a longstanding gap for once-weekly dosing in critical care. Bacteriophage and monoclonal-antibody therapies in the "others" cluster could add differentiated revenue streams, though manufacturing and regulatory complexities must be resolved before significant contributions accrue to the hospital infection therapeutics market.
The Hospital Infection Therapeutics Market Report is Segmented by Drug Class (Antibacterial Drugs, Antifungal Drugs, Antiviral Drugs, Others), Infection Type (Blood Stream Infections, Urinary Tract Infections, Surgical Site Infections, Pneumonia (HAP/VAP), Others), Route of Administration (Oral, Intravenous, Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America held 37.83% of global revenue of hospital infection therapeutics market in 2024. The CDC's National Healthcare Safety Network entrenches mandatory HAI-reporting policies that sustain high therapeutic vigilance. BARDA funding underpins rapid translation of pipeline assets, culminating in recent FDA approvals such as ceftobiprole and cefepime-enmetazobactam. Pfizer is investing USD 150 million to modernize an Australian plant intended to supply more than 60 export markets, illustrating regional leadership in responsible manufacturing upgrades. The pending PASTEUR Act may further stabilize cashflows, shaping procurement strategies across hospitals.
Asia-Pacific is forecasted to post a 4.53% CAGR to 2030, the fastest among major regions. China's regulatory reforms and the National Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs have propelled 17 companies with 20 antibacterial trials, contributing pipeline breadth and domestic pricing competition. India is enforcing a code of conduct for medical device marketing that strengthens infection-control standards, yet pharmaceutical effluent management remains a pressing challenge, with high antibiotic residues detected in industrial wastewater. Varied infrastructure maturity across ASEAN and South Asia yields heterogeneous demand, though rising procedure volumes create broad upward momentum within the hospital infection therapeutics market.
Europe benefits from coordinated AMR initiatives such as GSK's £45 million Fleming Centre partnership. The European Medicines Agency's positive opinion on aztreonam-avibactam marks the first B-lactam/B-lactamase inhibitor combination targeting metallo-B-lactamase producers, filling a therapeutic void. The Aurobac joint venture among Boehringer Ingelheim, Evotec, and bioMerieux adds diagnostic-therapeutic integration capabilities that may shorten time-to-effective therapy. Stringent environmental discharge rules and joint procurement initiatives help harmonize supply chain quality, though they also elevate compliance costs for entrants into the hospital infection therapeutics market.