
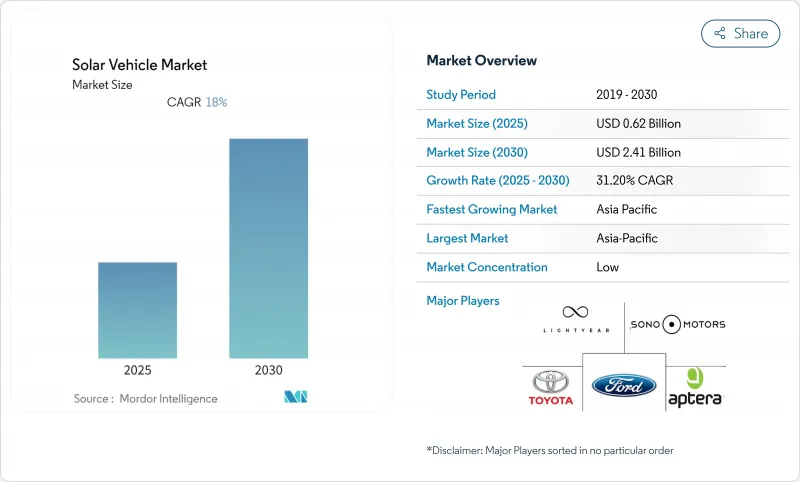
세계의 솔라카 시장은 2025년 6억 2,000만 달러를 창출하고, 2030년까지 24억 1,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예상됩니다.

태양광 발전(PV)의 비용은 하락하고 현재는 전기자동차의 주요 지역에서 일반적인 그리드 전력 가격을 밑돌고 있어 신흥 솔리드 스테이트 배터리와 함께 차량 일체형 태양열 시스템을 경제적으로 실행 가능하게 하고 있습니다. EU의 Fit-For-55 패키지와 캘리포니아 주 첨단 클린 트럭 규제와 같은 제로 배출 차량 의무화는 조기 채용 기업이 이익을 얻고 OEM의 신뢰할 수 있는 주문 파이프라인을 지원합니다. 기존 자동차 제조업체가 솔라 루프 계획을 가속화하는 한편, 전문 제조업체가 PV 스킨의 표면적을 극대화하는 경량 섀시를 개량하고 있기 때문에 경쟁은 격화하고 있습니다. 또한 전력 수요가 많을 때 자동차와 트럭을 이동할 수 있는 전력 자산으로 변신시키는 양방향 차량 투 그리드 모델에 대한 관심 증가도 수요에 반영됩니다.
태양광 발전의 전력 평준화 비용은 주요 전기자동차 보급 지역에서 그리드 패리티를 달성하고 차량 통합형 태양광 발전 시스템의 경제 계산을 근본적으로 바꾸고 있습니다. Fraunhofer ISE의 2024년 분석에 따르면 캘리포니아, 독일, 중국 동부에서는 태양광 발전+축전지의 구성으로 기존 그리드 요금보다 20-30% 낮은 비용으로 전력을 공급할 수 있게 되었습니다. 이 비용 우위는 운영 경비를 줄이면서 에너지 자립을 달성할 수 있는 솔라카 소유자에게 매력적인 가치 제안을 만들어 냅니다. 유틸리티 규모의 태양광 발전 생산 능력이 2025년까지 세계에서 1.8테라와트에 이르면 이 동향은 가속화되고 규모 경제에 따른 비용 절감이 더욱 진행됩니다. 지붕의 면적이 큰 상용차는 에너지 소비의 대부분을 상쇄하기에 충분한 전력을 발전시킬 수 있기 때문에 플릿 사업자는 이 다이나미즘으로부터 이익을 얻을 수 있습니다. 이 경제적 이점은 전기 요금이 높고 태양광 조사가 풍부한 지역에서 두드러지며 솔라카 채용의 지리적 핫스팟이 형성됩니다.
주요 자동차 시장의 규제 프레임워크에서 상용차에 제로 배출 차량을 도입하는 것이 점차 의무화되고 있으며 태양전지 강화 전기자동차에 대한 예측 가능한 수요가 탄생하고 있습니다. EU의 Fit-For-55 패키지는 2025년까지 신형 도시 버스의 30%를 제로 배출로 의무화하고 2030년까지 65%까지 인상합니다. 캘리포니아의 선진 클린 트럭 규제는 2030년까지 트럭 판매량의 40%를 제로 배출로 의무화하고 있습니다. 이러한 규제는 항속거리의 연장과 충전 인프라에 대한 의존도의 저감이 운영상의 이점이 되는 상용 용도에 있어서 태양광 차량을 특히 우월하게 하고 있습니다. 플릿 오퍼레이터는 태양광 발전의 통합을 통해 최적의 조건 하에서 차량의 항속 거리를 20-30% 연장할 수 있음을 인식하고 있으며, 충전 빈도를 줄이고 경로의 유연성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 항공기 조달주기는 일반적으로 5-7년이며 조기 규정 준수는 장기 계약에 유리하게 작동하기 때문에 규제 기세는 태양 상업용 차량을 개발하는 제조업체에게 선행자 이익을 제공합니다. 정부 인센티브는 제로 배출 상용차에 대한 세액 공제 및 가속 상각 일정을 통해 총 소유 비용을 줄임으로써 채용을 더욱 강화하고 있습니다.
차량 탑재 일체형 태양광 발전 시스템의 제조 비용은 기존 자동차 부품보다 상당히 높게 유지되어 대량 시장 도입을 제한하는 가격 장벽이 되고 있습니다. 차량용으로 설계된 특수 태양전지는 거치형 태양광 발전 설비로 달성되는 규모의 경제성이 부족한 커스텀 제조 공정이 필요하며, 그 결과 비용은 표준 태양전지 모듈보다 와트당 3-4배 높아집니다. 통합의 복잡성은 태양전지에 그치지 않고, 특수한 와이어 하네스, 전력 관리 전자기기, 충돌 안전 기준을 유지하면서 태양광 발전 컴포넌트를 탑재하기 위한 구조 변경 등 다양합니다. 2024년에 생산을 시작한 Opes Solar Mobility의 독일 신공장은 자동차용 태양전지 모듈의 제조 규모를 달성하기 위한 노력입니다. 그러나 생산 비용은 기존 자동차 부품에 비해 멈췄습니다. 비용 프리미엄은 가격에 민감한 제조업체가 추가 부품 비용을 흡수하는 능력에 한계가 있는 대중차에 특히 어려움이 있습니다. 그러나, 광전지의 재료 비용이 낮고 제조량이 증가하면 시장이 성숙하고 규모가 커짐에 따라 비용 장벽이 감소한다는 것을 시사합니다.
2024년 태양광 시장 점유율은 승용차가 98.78%를 차지했으며 상용차는 CAGR 55.39%(2025-2030년)로 가장 빠른 성장 궤도를 나타냅니다. 트럭, 버스, 배송 차량의 지붕면이 크기 때문에 대규모 태양광 발전 설비를 설치할 수 있어 의미 있는 에너지 공헌을 기대할 수 있습니다. 동시에 예측 가능한 루트 패턴을 사용하면 함대 운영자가 태양열 충전 전략을 최적화할 수 있습니다. 승용차는 특히 소비자가 순수한 경제적 수익보다 환경 면에서 차별화를 중시하는 고급 차량 부문에서 프리미엄 포지셔닝과 에너지 자율 브랜딩에서 혜택을 누릴 수 있습니다.
상용차의 기세는 플릿 오퍼레이터가 총소유비용의 최적화와 제로 배출 의무화 규제 준수에 중점을 두고 있는 것을 기반으로 하고 있습니다. Flixbus가 도시간 버스에 태양전지판을 도입한 것은 민간 사업자가 태양 기술을 활용하여 연료 비용을 절감하고 장거리 노선에서 전기 항속 거리를 늘리는 것을 보여줍니다. 플릿 용도는 중앙 집중식 유지 보수 기능과 경로 계획 및 주차 전략을 통해 태양전지 충전을 최적화 할 수있는 전문 드라이버에서도 이익을 얻습니다. 상용 부문의 성장 궤도는 함대 채택이 제조 규모의 확대와 비용 절감을 촉진하고 궁극적으로 승용차 용도에 이익을 줄 수 있음을 시사합니다.
하이브리드 전기자동차는 2024년 태양광 시장 점유율에서 99.38%를 차지했는데, 이는 제조업체가 개발 복잡성과 규제 위험을 최소화하기 때문에 태양열 시스템을 기존 하이브리드 플랫폼에 통합했기 때문입니다. 그러나 배터리 전기자동차는 고체 배터리 기술을 통해 보다 효율적인 태양에너지 저장 및 이용이 가능하므로 CAGR 60.83%(2025-2030년)로 가속합니다. 4년 이내에 출시될 예정인 Toyota의 솔리드 스테이트 배터리 로드맵은 비용을 20-40% 절감하면서 전기 항속 거리를 2배로할 것을 약속하고 있으며, 태양광 통합에 매력적인 플랫폼을 만들어 냅니다. 플러그인 하이브리드 전기자동차는 기존의 파워트레인에서 전환하는 소비자에게 유연성을 제공하면서 태양전지 충전 기능을 통합 한 중간 위치를 차지합니다.
배터리 전기자동차로의 이동은 에너지 저장 효율의 향상과 배터리 비용의 감소로 인해 순수한 전기 파워트레인이 태양광 용도에 더 현실적이라는 것을 반영합니다. 차세대 배터리 셀 기술에 대한 Stellantis와 CEA의 파트너십은 제조업체가 태양에너지 이용을 최적화하는 첨단 화학 솔루션을 추구하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이 전환은 항속거리 불안을 줄이고 태양열차가 계통 충전을 대체하는 것이 아니라 보완할 수 있게 하는 충전 인프라의 확대로부터도 혜택을 받습니다. 배터리의 에너지 밀도가 향상되고 비용이 낮아짐에 따라 파워트레인이 간소화되고 에너지 관리 시스템이 최적화되어 순수한 전기자동차 플랫폼이 태양전지와의 통합에 더욱 매력적이 되고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 솔라카 시장에서 가장 큰 점유율을 차지하며 2024년에는 56.79%에 달했습니다. 이는 중국의 PV모듈 생산량이 세계의 90%를 차지하고 있는 것과, 일본의 고효율 셀의 연구개발 체제가 충실하고 있는 것이 배경에 있습니다. 중국의 'Made in China 2025'와 일본의 NEDO 보조금 등 정부 프로그램은 현지에서 부품 조달의 우위를 촉진하고 재료비를 압축합니다. BYD의 일본 진출은 제조 규모의 이점을 프리미엄 수출 시장으로 확대하려는 중국의 의향을 보여줍니다. Toyota와 Sharp는 국내 경쟁력을 유지하는 탠덤 셀을 공동 개발하고 있습니다.
북미는 캘리포니아 주 제로 배출 의무화와 인플레이션 억제법의 국산 태양전지에 대한 생산세 공제로 두 번째로 빠른 성장 경로를 따랐습니다. 이 지역에서는 픽업 트럭과 SUV가 주류이며 PV 어레이용 광대 한 지붕 면적을 확보하고 있습니다. Rivian은 잉여 전력을 일리노이 공장 충전기에 공급하는 커뮤니티 태양광 프로그램을 시험적으로 도입하여 공장에서 플릿으로의 순환 가능성을 보여줍니다.
유럽에서는 EU 전체의 Fit-For-55 목표에 뒷받침되는 각국의 인센티브가 모자이크 형태로 존재합니다. EU권 수준에서는 규제의 확실성이 있지만, 상이한 부가가치세의 감면조치나 인프라의 밀도는 곧바로 엉망인 수요 프로파일을 만듭니다. 2024년 1,000만 유로를 확보한 후, Lightyear가 임베디드 PV 키트 공급에 축족을 옮긴 것은 전차량 생산의 자본 집약도와 모듈식 공급망의 역할에 대한 유럽의 개방성을 보여줍니다. 독일의 Opes Solar Mobility 시설은 EU의 아시아계 모듈 제조업체에 대한 노출을 부분적으로 줄이고 지정학적 수입 의존도를 줄이기 위해 OEM의 현지화 전략을 지원합니다.
The solar vehicle market generated USD 0.62 billion in 2025 and is on track to reach USD 2.41 billion by 2030, advancing at a 31.20% CAGR and underscoring the rapid transition from experimental prototypes to early-stage commercial fleets.
Declining photovoltaic (PV) costs, now below prevailing grid electricity prices in major electric-vehicle regions, combine with emerging solid-state batteries to make vehicle-integrated solar systems economically viable. Early adopters gain from zero-emission fleet mandates such as the EU Fit-For-55 package and California's Advanced Clean Trucks regulation, underpinning reliable order pipelines for OEMs. Competitive intensity rises as legacy automakers accelerate solar-roof programs while specialists refine lightweight chassis that maximize surface area for PV skins. Demand also reflects rising interest in bidirectional vehicle-to-grid models that transform cars and trucks into mobile power assets during peak electricity demand.
Solar photovoltaic levelized cost of electricity has achieved grid parity across key electric vehicle adoption regions, fundamentally altering the economic calculus for vehicle-integrated solar systems. Fraunhofer ISE's 2024 analysis demonstrates that solar-plus-battery storage configurations now deliver electricity at costs 20-30% below conventional grid rates in California, Germany, and eastern China. This cost advantage creates a compelling value proposition for solar vehicle owners who can achieve energy independence while reducing operational expenses. The trend accelerates as utility-scale solar manufacturing capacity reaches 1.8 terawatts globally by 2025, driving further cost reductions through economies of scale. Fleet operators benefit from this dynamic, as commercial vehicles with larger roof surfaces can generate sufficient electricity to offset significant portions of their energy consumption. The economic advantage becomes more pronounced in regions with high electricity tariffs and abundant solar irradiation, creating geographic hotspots for solar vehicle adoption.
Regulatory frameworks across major automotive markets increasingly mandate zero-emission vehicle adoption in commercial fleets, creating predictable demand for solar-enhanced electric vehicles. The EU's Fit-For-55 package requires 30% of new urban buses to be zero-emission by 2025, rising to 65% by 2030. California's Advanced Clean Trucks regulation mandates that 40% of truck sales be zero-emission by 2030. These mandates particularly favor solar vehicles in commercial applications where extended range and reduced charging infrastructure dependence provide operational advantages. Fleet operators recognize that solar integration can extend vehicle range by 20-30% under optimal conditions, reducing charging frequency and improving route flexibility. The regulatory momentum creates a first-mover advantage for manufacturers developing solar commercial vehicles, as fleet procurement cycles typically span 5-7 years and early compliance positions companies favorably for long-term contracts. Government incentives further amplify adoption by reducing total cost of ownership through tax credits and accelerated depreciation schedules for zero-emission commercial vehicles.
Manufacturing costs for vehicle-integrated photovoltaic systems remain substantially higher than those of conventional automotive components, creating price barriers that limit mass market adoption. Specialized solar cells designed for automotive applications require custom manufacturing processes that lack the economies of scale achieved in stationary solar installations, resulting in costs 3-4 times higher per watt than standard photovoltaic modules. The integration complexity extends beyond solar cells, including specialized wiring harnesses, power management electronics, and structural modifications that accommodate photovoltaic components while maintaining crash safety standards. Opes Solar Mobility's new factory in Germany, which began production in 2024, represents efforts to achieve manufacturing scale for vehicle-specific photovoltaic modules. However, production costs remain elevated compared to conventional automotive components. The cost premium becomes particularly challenging for mass market vehicles where price sensitivity limits manufacturers' ability to absorb additional component expenses. However, declining photovoltaic material costs and increasing manufacturing volumes suggest that cost barriers will diminish as the market matures and achieves greater scale.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Passenger cars commanded 98.78% of the solar vehicle market share in 2024, while commercial vehicles demonstrate the fastest growth trajectory at 55.39% CAGR (2025-2030), reflecting the superior economics of solar integration in fleet applications. Large roof surfaces on trucks, buses, and delivery vehicles enable more extensive photovoltaic installations that generate meaningful energy contributions. At the same time, predictable route patterns allow fleet operators to optimize solar charging strategies. Passenger cars benefit from premium positioning and energy-autonomous branding, particularly in luxury segments where consumers value environmental differentiation over pure economic returns.
The commercial vehicle momentum builds on fleet operators' focus on total cost of ownership optimization and regulatory compliance with zero-emission mandates. Flixbus's deployment of solar panels on intercity coaches demonstrates how commercial operators leverage solar technology to reduce fuel costs and extend electric range on long-distance routes. Fleet applications also benefit from centralized maintenance capabilities and professional drivers who can optimize solar charging through route planning and parking strategies. The commercial segment's growth trajectory suggests that fleet adoption will drive manufacturing scale and cost reductions that eventually benefit passenger car applications.
Hybrid electric vehicles captured 99.38% of the solar vehicle market share in 2024 as manufacturers initially integrated solar systems into existing hybrid platforms to minimize development complexity and regulatory risk. However, battery electric vehicles accelerate at 60.83% CAGR (2025-2030) as solid-state battery technology enables more efficient solar energy storage and utilization. Toyota's roadmap for solid-state batteries, expected to launch within four years, promises to double electric range while reducing costs by 20-40%, creating compelling platforms for solar integration. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles occupy a middle position, offering flexibility for consumers transitioning from conventional powertrains while incorporating solar charging capabilities.
The shift toward battery electric vehicles reflects improving energy storage efficiency and declining battery costs that make pure electric powertrains more viable for solar applications. Stellantis's partnership with CEA on next-generation battery cell technology demonstrates how manufacturers pursue advanced chemistry solutions that optimize solar energy utilization. The transition also benefits from expanding charging infrastructure that reduces range anxiety and enables solar vehicles to supplement rather than replace grid charging. As battery energy density improves and costs decline, pure electric platforms become increasingly attractive for solar integration due to their simplified powertrains and optimized energy management systems.
The Solar Vehicle Market Report is Segmented by Vehicle Type (Passenger Cars and Commercial Vehicles), Electric-Drivetrain Type (BEV, HEV, and More), Battery Chemistry (Lithium-Ion, Solid-State Lithium-Metal, and More), Solar-Panel Technology (Monocrystalline Silicon, Thin-Film, and More), Charging Architecture (On-Board Solar-Only, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest regional slice of the solar vehicle market, reaching 56.79% of the solar vehicle market in 2024 on the back of China's 90% global PV module output and Japan's deep R&D bench in high-efficiency cells. Government programs such as China's "Made in China 2025" and Japan's NEDO grants fuel local component sourcing advantages that compress bill-of-materials costs. BYD's cross-border push into Japan illustrates China's intent to extend manufacturing scale benefits into premium export markets. Toyota and Sharp co-develop tandem cells that maintain domestic competitive parity.
North America traced the second-fastest growth path due to California's zero-emission mandates and the Inflation Reduction Act's production tax credits for domestically manufactured solar cells. Pickup trucks and SUVs dominate the region's vehicle mix, presenting expansive roof real estate for PV arrays. Rivian is piloting community solar programs that feed excess electricity into chargers at its Illinois plant, illustrating potential factory-to-fleet circularity.
Europe offers a mosaic of national incentives underpinned by the EU-wide Fit-For-55 targets. While regulatory certainty exists at the bloc level, divergent VAT breaks and infrastructure density create a patchwork demand profile. Lightyear's pivot to supplying embedded PV kits after securing EUR 10 million in 2024 demonstrates the capital intensity of full-vehicle production and Europe's openness to modular supply-chain roles. Germany's Opes Solar Mobility facility partially derisks EU exposure to Asian module suppliers and supports OEM localization strategies to reduce geopolitical import dependencies.