
자율주행 트랙터 시장은 2025년에 22억 달러에 이르고 CAGR 18.6%를 유지하면서 2030년에는 52억 달러에 이를 것으로 예측됩니다.

이 상승의 주요 요인은 심각한 농업 노동 위기, 정밀 농업의 급속한 보급 및 저탄소 접속 기계의 투자 회수 기간을 단축하는 정부 인센티브의 확대에 있습니다. 대규모 상업 재배농가들은 이미 20% 노동력을 감소하여 이익률을 높이고 있으며 24시간 연속 농장 작업으로 계절별 생산량을 높이고 있습니다. 소프트웨어 중심의 수익 모델, 개조 키트, 전동 파워트레인은 대응 가능한 수요를 더욱 확대하고 자율주행 트랙터 시장이 틈새 채용을 초월한 주류 성장 단계에 진입하고 있음을 보여줍니다.
농촌의 노동력 감소가 농가의 평균 연령 상승과 충돌하여 농업의 노동력 절반 가량이 채워지지 않은 채로 남아 있습니다. 임금 인플레이션은 현장의 피크 시 부담을 증대시킵니다. 수확기에는 자율주행식 곡물 운반차가 오퍼레이터 없이 24시간 가동하게 됩니다. 생산자는 중요한 작업 시간대에 30-40%의 생산성 향상을 보고하고 있으며, 자율주행 트랙터 시장이 재량적인 편리성을 부가하는 것이 아니라 구조적인 갭을 메우고 있음을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 이 긴급성은 자율성을 장기적인 농장 생존에 필요한 핵심 인프라로 재정의했습니다.
클라우드 농장 관리 플랫폼은 이미 100만 대 이상의 기계를 연결하여 트랙터를 토양, 수확량 및 자산 정보를 실시간 의사결정 시스템에 공급하는 로밍 데이터 허브로 바꾸고 있습니다. 고급 센서 퓨전, GPS, 머신 비전 및 레이더를 사용하면 센티미터 수준의 지침, 가변 속도 입력 배치 및 풀필드 장애물 회피가 가능합니다.
전동 자율주행 트랙터 1대는 8만 8,000달러를 초과할 수 있으며, 100헥타르 미만의 농장에 있어서는 고액의 지출이 됩니다. 접속성 업그레이드, On-Premise 데이터 인프라 및 서비스 가입이 더욱 부담을 높입니다. 모델에 따라 차이가 있지만 외부 보조금으로 자본 비용을 상쇄하지 않는 한, 채산이 가능한 전개는 500헥타르 이상으로 시작되는 경우가 많으며, 많은 가족 경영의 농장은 가격이 떨어질 때까지 공동 소유 또는 렌탈 서비스에 의지하게 됩니다.
현재 수요의 중심은 31-100마력 이상의 트랙터로 2024년 자율주행 트랙터 시장 점유율의 39.5%를 차지하였습니다. 31-100마력의 중위 레인지는 적당한 경작에 충분한 마력과 관리하기 쉬운 자본 요건이 조화된 매우 중요한 다리 역할을 하고 있습니다. 모듈형 애드온, 비전 키트, 텔레매틱스 및 자동화를 통해 자율성을 점진적으로 업그레이드할 수 있습니다. 대리점 보고서에 따르면 생산자는 200마력의 더 큰 플래그십 기계를 구입하기 전에 기존의 75마력 트랙터에서 반자율적 레벨로 개조를 시도했으며 점진적인 채용 곡선을 보여줍니다.
그러나 스포트라이트는 CAGR 24.0%로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 100마력 이상으로 옮겨가고 있습니다. 이 기계는 광대한 농지에서 경작, 파종, 대규모 농가에서 중/경운기 등에 적합합니다. 30마력까지의 컴팩트한 유닛은 원예, 낙농, 혼작 농가에서 잔디 깎기나 살포 등 반복 작업을 자동화하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 하나의 무거운 트랙터 대신 여러 경량 로봇을 배치하는 플릿 컨셉은 토양 압축을 줄이고 농장 진입 장벽을 줄이고 소규모 농부의 정밀 기술을 민주화합니다.
운영자가 운전석에 탑승하거나 원격 조작으로 기계를 감시하는 반자율형 구성은 2024년 시장 점유율 68.2%를 차지하였습니다. 농부들은 즉각적인 노동력 감소를 중시하면서도 수동 폴백을 유지하고 있습니다. 예측 기간 동안, 완전 자율 솔루션은 다른 부문을 능가하고 CAGR 23.1%로 확대될 전망입니다. 원격 조타 보조, 작업별 자율성 및 완전한 플릿 오케스트레이션이라는 단계적인 경로는 자동차 부문의 진화를 반영합니다. 리얼타임 키네마틱 GPS, 멀티 카메라 인식, 중복 안전 계층이 현재 상업 분야에 도입되고 있는 레벨 4의 기능을 지원하고 있습니다.
생산자는 콤바인이 개입 없이 12시간 연속으로 자율주행함을 홍보하며 자신감을 보이고 있습니다. 규제 당국은 기술을 규정하는 것이 아니라 성능을 기반으로 하는 지침을 수립하여 도입을 용이하게 합니다. 보험 회사는 사고 위험을 줄이는 효과적인 자율주행 시스템에 대한 보험료 할인을 제공하기 시작했습니다.
아시아태평양의 2024년 점유율은 46.3%에 달하였고, 선두를 유지하고 있습니다. 농업의 근대화에 대한 중국의 수조 달러 규모의 계약은 설비 보조금, AI 연구 허브, 농촌에서의 5G 전개에 자본을 주입하는 움직임입니다. 일본에서는 급속히 고령화가 진행되는 농가 인구를 위해 스마트 농업이 추진되고, 호주에서는 광대한 건조지에서의 농업 경영에 적합한 자율형 솔루션에 보조금이 지원되고 있습니다. 이러한 일치 정책은 이 지역 전체의 자율주행 트랙터 시장에 깊은 기회 풀을 제공하고 있습니다.
북미는 CAGR 23.2%로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역입니다. 높은 인건비, 풍부한 벤처 자본, 활발한 OEM R&D 파이프라인이 상업화를 가속화합니다. 미국은 정밀 농업의 연결 프로젝트에서 우위를 차지하고 있지만, 아직 27%의 농장만이 채용하고 있어 큰 여지를 남겨두고 있습니다. 농장 당 최저 광대역 속도를 의무화하는 연방 프로그램은 자율적으로 필요한 디지털 기반을 가속시킵니다. 캐나다는 클린 테크놀로지 보조금을 활용하고, 멕시코는 기계화를 추진함으로써 자동화를 확대시킵니다.
유럽은 디지털 농업, 저탄소 농업에 인센티브를 제공하는 공통 농업 정책 개혁에 힘입어 꾸준한 성장 노선을 따르고 있습니다. 독일, 프랑스, 스페인은 유명한 기계 제조업체와 전기 구동에 유리한 엄격한 배출 기준으로 도입을 이끌고 있습니다. 동유럽은 광대한 연속 농지가 플릿 규모의 자율성에 적합하기 때문에 상승 여지가 있습니다. 보조금이 있는 탄소신용제도와 에너지전환기금이 재정적 장애물을 낮추고 자율주행 트랙터 시장의 중요한 부문으로 유럽을 확고하게 하고 있습니다.
The autonomous tractor market touched USD 2.2 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2030, sustaining an 18.6% CAGR.
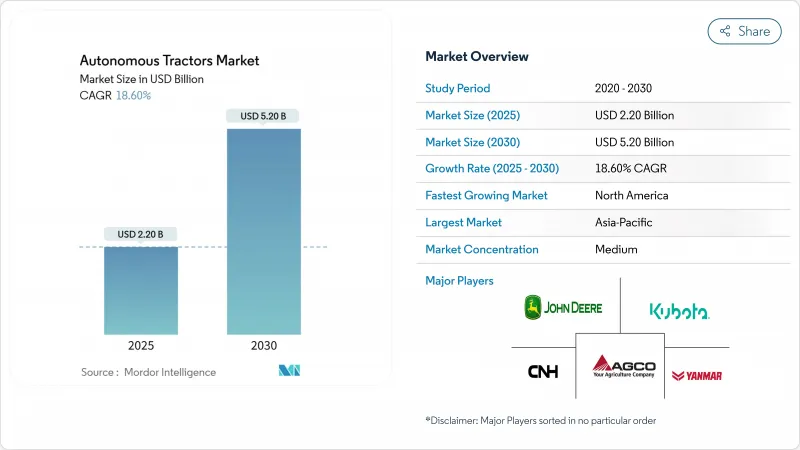
The upswing stems mainly from an acute farm-labor crisis, rapid precision-agriculture uptake, and a widening set of government incentives that shorten payback periods for connected low-carbon machinery. Large commercial growers are already converting labor savings of 20% into higher margins, while continuous 24-hour field operation raises seasonal output. Software-centric revenue models, retrofit kits, and electric powertrains further expand addressable demand, signaling that the autonomous tractor market is entering a mainstream growth phase that transcends niche adoption.
A shrinking rural workforce is colliding with rising average farmer age, leaving half of open agricultural roles unfilled. Wage inflation amplifies the strain during peak field windows, particularly for harvest, where autonomous grain-cart systems now run round-the-clock without operators. Growers report productivity gains of 30-40% during critical windows, confirming that the autonomous tractor market is filling a structural gap rather than adding discretionary convenience. The urgency has reframed autonomy as core infrastructure required for long-term farm viability.
Cloud farm-management platforms already link well over 1 million machines, converting tractors into roaming data hubs that feed soil, yield, and asset information into real-time decision systems. Advanced sensor fusion, GPS, machine vision, and radar enable centimeter-level guidance, variable-rate input placement, and full-field obstacle avoidance.
A single electric autonomous tractor can exceed USD 88,000, a steep outlay for holdings under 100 hectares. Connectivity upgrades, on-premise data infrastructure, and service subscriptions add further load. Models show that profitable deployment often begins above 500 hectares unless external grants offset capital expense, leaving many family farms to rely on co-operative ownership or hire services until prices fall.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Current demand centers on tractors above 31-100, which accounted for 39.5% of the autonomous tractor market share in 2024. The mid-range 31-100 HP bracket serves as a pivotal bridge, blending horsepower sufficient for moderate tillage with manageable capital requirements. Modular add-ons, vision kits, telematics, and implementing automation allow progressive autonomy upgrades. Dealers report that growers trial a semi-autonomous retrofit on an existing 75 HP tractor before purchasing a larger 200 HP flagship machine, illustrating a stepped adoption curve.
Yet the spotlight is shifting to more than 100 HP, the fastest-growing slice at 24.0% CAGR. These machines suit broad-acre tillage, seeding, and heavy draft implements on large farms. Compact units up to 30 HP empower horticulture, dairy, and mixed-crop holdings to automate repetitive tasks such as mowing or spraying. Fleet concepts that deploy multiple lightweight robots instead of one heavy tractor lower soil compaction, reduce field entry barriers, and democratize precision technology for smallholders.
Semi-autonomous configurations, where an operator remains in the cab or oversees the machine remotely, commanded 68.2% market share in 2024. Farmers value immediate labor savings yet retain manual fallback. Over the forecast period, fully autonomous solutions will outpace all others, expanding at 23.1% CAGR. The step-wise path of remote steering aids, task-specific autonomy, and then full fleet orchestration mirrors the automotive sector's evolution. Real-time kinematic GPS, multi-camera perception, and redundant safety layers underpin Level 4 capabilities now entering commercial fields.
Confidence builds as growers witness a combine run autonomously for 12 straight hours without intervention. Regulators are drafting performance-based guidelines rather than prescribing technology, easing deployment. Insurance carriers have started to offer premium discounts for validated autonomous systems that reduce accident risk.
The Autonomous Tractors Market is Segmented by Horsepower (Up To 30HP, and More), by Automation Level (Fully Automated and Semi-Automated), by Drive Type (Diesel, and More), by Application (Tillage, and More), by Component (GPS/GNSS, and More), by Farm Size (Small, Medium, and Large) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Asia-Pacific preserved its leadership with a 46.3% share in 2024, underpinned by sizable land holdings and robust public funding. China's multi-trillion-dollar pledge to modernize farming injects capital into equipment subsidies, AI research hubs, and rural 5G roll-outs. Japan's smart-farming drive counters a rapidly aging farmer demographic, while Australia directs grants toward autonomous solutions suited to vast dryland operations. These aligned policies sustain a deep opportunity pool for the autonomous tractor market across the region.
North America is the fastest-expanding arena at 23.2% CAGR. High labor costs, abundant venture capital, and active OEM R&D pipelines speed commercialization. The United States dominates precision agriculture connectivity projects, yet only 27% of farms have adopted them, implying sizable headroom. Federal programs that require minimum broadband speeds per farm accelerate digital foundations needed for autonomy. Canada leans on clean-tech subsidies, and Mexico's mechanization push spreads automation southward.
Europe follows a steady growth path, supported by Common Agricultural Policy reforms that reward digital, low-carbon farming. Germany, France, and Spain lead deployments through established machinery makers and strict emission standards that favor electric drive. Eastern Europe offers upside as large tracts of contiguous farmland suit fleet-scale autonomy. Subsidized carbon-credit schemes and energy-transition funds lower the financial hurdle, cementing Europe as a vital segment of the autonomous tractor market.