
선박용 추진 엔진 시장 규모는 2025년에 387억 1,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 439억 3,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) CAGR 2.54%로 성장할 전망입니다.

수요는 상업 화물선대의 능력 갱신 사이클에 지지되고 있지만, IMO의 넷 제로 프레임워크가 2050년까지 온실가스 강도를 80% 삭감하도록 선주를 밀어주고 있기 때문에 그 기세는 대체 연료로 점점 시프트하고 있습니다. LNG와 메탄올의 듀얼 연료 엔진의 조기 채용은 아시아태평양의 견조한 주문과 유럽의 정책 인센티브를 뒷받침하고며 기술 전환을 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
해운회사는 2025년 5월부터 지중해에 적용되는 배출 규제 구역 내 질소산화물 75% 감축의 의무화에 직면하고 있습니다. 새로운 규칙은 EEXI의 에너지 효율 기준치와 교차하며, 세계 톤수의 약 35%를 커버하는 레트로핏의 기회를 유도합니다. SCR과 EGR의 패키지는 2026년의 전개가 예정되어 있는 MAN의 메탄올 개조 키트에 대표되는 바와 같이 가까운 미래 조달의 대부분을 차지합니다. 적합 엔진이 없는 선주는 항구 입항이 제한될 위험이 있으므로 개조 스케줄이 이사회의 우선사항이 되고 있습니다. 따라서 자본 배분은 순수한 유지 보수 예산보다는 업그레이드 프로그램으로 점점 더 쉬워지고 있으며 애프터마켓의 수익 구성을 재구성하고 있습니다.
중국, 한국, 일본의 조선소가 컨테이너선과 LNG선의 계약을 대량으로 획득해, 이 지역 조선소의 가동률을 수년만에 고수준으로 밀어 올렸습니다. 에버그린은 LNG를 연료로 하는 2만 4,000TEU형 선박 11척을 30억 달러로 수주했지만, 이는 양의 급증을 상징하고 있습니다. 2024년 1분기 데이터에서 78건의 LNG 신조선 발주가 기록되어 전년 동기 대비 129% 증가했습니다. 따라서 엔진 제조업체는 듀얼 연료 플랫폼에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 생산 능력 제약을 극복하고 있습니다. 이러한 파이프라인은 아시아태평양 야드가 2028년까지 설계 프레임을 인도로 전환함에 따라 선박용 추진 엔진 시장의 장기 전망을 지원합니다.
2024년 VLSFO는 톤당 평균 630달러였지만 EU-ETS 수수료로 인해 2025년까지 유럽의 항해 비용은 톤당 실질 795달러까지 상승할 수 있습니다. 바이오블렌드의 의무화는 연료 예산을 더욱 부풀리고, e메탄올은 톤당 1,300달러 이상으로 거래되어 화석 대체 연료와의 단기적인 동등성을 손상시킵니다. 선주는 연료의 이중화를 통해 위험을 헤지하고 운영 유연성을 보장하기 위해 더 높은 초기 투자를 받아들입니다. 그러나 변동성의 높이는 소규모 사업자의 장기적인 설비 투자 의욕을 깎아 선대의 근대화가 규모 클래스 간에 불균일해지는 원인이 되고 있습니다. 분석가들은 지역 규제 불일치가 2031년까지 연료비보다 컴플라이언스 비용을 끌어올려 노후 배의 경쟁력을 떨어뜨릴 수 있다고 경고합니다.
디젤 엔진은 2024년 선박용 추진 엔진 시장 점유율의 66.12%를 유지했으며, 정착된 지원망과 비용 경쟁력을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. LNG, 메탄올, 암모니아를 수용하는 듀얼 연료 설계가 기술 갭을 메우고 있으며, 선주는 디젤 기준선을 포기하지 않고 새로운 배출 기준을 준수할 수 있습니다. 연료전지 시스템은 현재 틈새 시장이지만 CAGR은 가장 높은 2.76%를 기록했으며 페리, 크루즈 요트 및 보조 동력 모듈의 조종사를 끌고 있습니다. 듀얼 연료 단위 시장 규모는 특히 북유럽과 동아시아에서 벙커 인프라 정비와 연계하여 확대될 것으로 예측됩니다.
급속한 혁신은 이 부문의 프리미엄 엔드를 정의합니다. TECO 2030의 고속 수소 페리 프로토타입은 연안 여객 서비스의 벤치마크인 160 해리 항해 거리를 지원하면서 연료전지가 35 노트에 도달할 수 있음을 입증합니다. 고급 요트 제조업체는 제로 카본 크루징을 확대하기 위해 극저온 저장과 메탄올 개질기를 실험하고 있습니다. 그러나 수소 취급 규칙은 여전히 유동적이며 기체 연료화물의 보험료는 여전히 높습니다. 이러한 장벽은 전 세계적인 가용성, 간편성 및 수십년에 걸친 운항 데이터가 환경 처벌을 뛰어넘는 심해 항로에서 디젤의 대부분의 점유율을 지키고 있습니다.
2024년 선박용 추진 엔진 시장 규모의 57.37%를 상업 화물선이 차지했고, 팬데믹에 의한 혼란 후 컨테이너 및 벌크 수요의 급증에 밀어붙였습니다. 선대 소유자는 아시아 유럽 루프에서 CII에 준거한 운항을 확보하기 위해 듀얼 연료 엔진을 우선했습니다. 크루즈선과 페리를 커버하는 여객 카테고리는 각국 정부가 피요르드나 항만의 배기가스 규제를 부과하고, 전기 또는 하이브리드 패키지가 선호되기 때문에 CAGR 2.41%로 전체의 성장을 상회합니다. 선박용 추진 엔진 업계는 조용한 주행과 다연료 대응이 운용상의 필수 조건인 방위 분야에서의 파급 주문으로부터도 이익을 얻고 있습니다.
크루즈 라인은 기업의 ESG 목표를 달성하기 위해 새로운 조선에 배터리 모듈과 메탄올 기능을 표준 장비하고 있습니다. 노르웨이의 피요르드 룰은 전기 피요르드 페리의 수주에 박차를 가했고, 캘리포니아의 앳 버스 확장은 북미 운항사를 쇼어 파워 대응으로 향하게 했습니다. 이러한 개발은 선체 당 엔진 수가 감소하더라도 보조 동력 요건을 높이고 시장 가치를 높입니다. 이와는 대조적으로, 화물선주는 가격과 가동률 모두 위험을 헤지하기 위해 연료 유연성에 투자하고, 효율성을 중시하는 화물선과 규제를 중시하는 여객선에 시장을 이분하는 2개 투자 패턴을 굳히고 있습니다.
아시아태평양은 2024년 매출의 43.36%를 차지했으며, 중국의 대량 상업 조선의 거의 독점과 한국의 LNG선 특화에 의해 지원되고 있습니다. 이 지역의 지원은 중국의 수출 톤수에 대한 부가가치 세금 환불과 같은 정책적 우대 조치부터 주조소, 크랭크샤프트 단조소, 밀집된 공급업체 생태계를 포함한 두꺼운 공급망에 이르기까지 다양합니다. 선주는 납품 전에 저비용 선체 제조와 최신 추진 패키지를 결합하여 투자 회수 기간을 단축할 수 있기 때문에 듀얼 연료 기능의 채용이 가속화됩니다. 일본의 첨단 연구개발 클러스터는 즉시 벙커링 네트워크를 새롭게 하지 않고 단계적인 배출 감소를 약속하는 암모니아 대응 설계를 추진하고 있습니다.
유럽은 여전히 규제 혁신의 도가니이며, FuelEU Maritime, EU 배출권 거래 제도, 배출 규제 지역 확대 등의 수단을 통해 기술 수요를 형성하고 있습니다. 노르웨이 피요르드의 제로 방출 의무화는 전기 및 수소 솔루션을 위한 즉각적인 개조와 신규 파이프라인을 만들어 내고, 지중해의 ECA 지정은 지금까지 북부의 규칙을 피해 온 벌크와 유조선의 수송으로 컴플라이언스 압력을 확대합니다. 엔진 공급업체는 유럽 야드의 전문성을 활용하여 연료전지 및 탄소 포획 프로토타입을 상업 항해 조건 하에서 테스트하고 그 결과를 아시아태평양의 대량 배치에 반영합니다.
중동 및 아프리카는 2024년 수익 공헌의 10분의 1 정도에 불과하지만 카타르 가스와 ADNOC가 LNG와 메탄올 인프라에 투자하여 수출 체인을 지원하기 때문에 CAGR 3.37%로 가장 빠른 성장이 전망됩니다. 한화필리조선소의 연산 10척으로의 스케일업 등, 소블린이 지원하는 조선확장은 세계 베스트 프랙티스 노하우를 이 지역으로 끌어들입니다. 북미의 성장의 중심은 국방조달이며, 존스법의 선원 수송 규제가 강화되고, 비용이 높아도 국내 조선소의 수주 잔량이 증가합니다. 남미와 아프리카는 항만의 현대화와 해외 에너지에 대한 투자로 급성장하고 있지만 자금 조달 장애물과 제한된 기술 클러스터가 기술 도입을 늦추고 있습니다.
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market size is estimated at USD 38.71 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 43.93 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 2.54% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
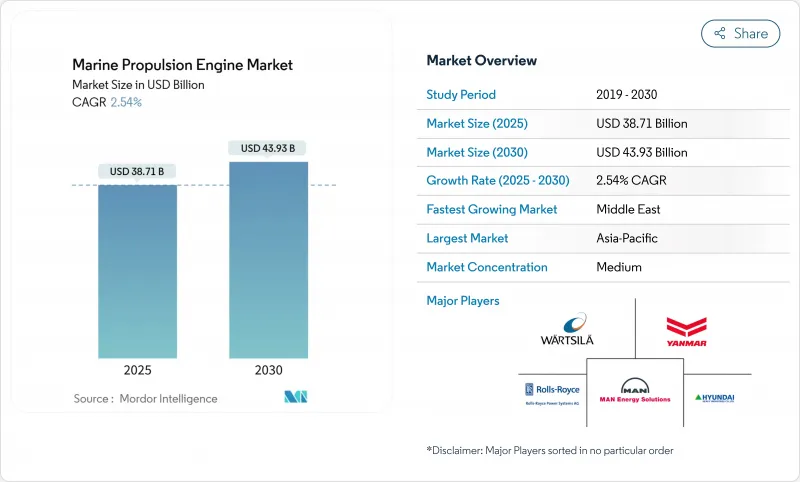
Demand is anchored in the commercial cargo fleet's capacity renewal cycle, yet momentum increasingly shifts toward alternative fuels as the IMO Net-Zero Framework pushes owners to cut greenhouse-gas intensity by 80% before 2050. Early adoption of LNG and methanol dual-fuel engines, fueled by robust Asia-Pacific orderbooks and European policy incentives, is reinforcing the technology transition.
Shipping companies face mandatory 75% nitrogen-oxide cuts inside Emission Control Areas, a requirement that now applies to the Mediterranean as of May 2025. The new rules intersect with EEXI energy-efficiency thresholds, triggering a retrofit opportunity that covers roughly 35% of global tonnage. SCR and EGR packages dominate near-term procurement, illustrated by MAN's methanol retrofit kits slated for 2026 roll-out. Owners without compliant engines risk restricted port access, making retrofit timelines a boardroom priority. Capital allocation, therefore, increasingly shifts toward upgrade programs rather than pure maintenance budgets, reshaping the aftermarket revenue mix.
Chinese, South Korean and Japanese shipyards secured a torrent of container and LNG carrier contracts, pushing regional yard utilization to multi-year highs. Evergreen's USD 3 billion order for eleven LNG-fueled 24,000 TEU vessels typifies the volume surge. First-quarter 2024 data recorded 78 LNG new-building orders, up 129% year on year. Engine makers are therefore juggling capacity constraints alongside heightened demand for dual-fuel platforms. This pipeline supports long-run visibility for the marine propulsion engine market as Asia-Pacific yards convert design slots into deliveries through 2028.
VLSFO averaged USD 630 per ton in 2024 but EU-ETS fees can lift European voyage costs to an effective USD 795 per ton by 2025. Bio-blend mandates inflate fuel budgets further, while e-methanol trades above USD 1,300 per ton, undermining near-term parity with fossil alternatives. Owners hedge risk through dual-fuel installations, accepting higher upfront expenditure for operational flexibility. Yet volatility discourages smaller operators from long-horizon capex, causing uneven fleet modernization across size classes. Analysts warn that misaligned regional regulations could push compliance costs above fuel spend by 2031, eroding competitiveness for aging tonnage.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Diesel engines retained 66.12% of the marine propulsion engine market share in 2024, underscoring their entrenched support network and cost competitiveness. Dual-fuel designs that accept LNG, methanol and ammonia are bridging technology gaps, allowing shipowners to comply with new emission standards without abandoning diesel baselines. Fuel-cell systems, although a niche at present, record the highest 2.76% CAGR and attract pilots in ferries, cruise yachts and auxiliary power modules. The marine propulsion engine market size for dual-fuel units is forecast to rise in tandem with bunker infrastructure roll-outs, especially in Northern Europe and East Asia.
Rapid innovation defines the premium end of the segment. TECO 2030's high-speed hydrogen ferry prototype proves that fuel cells can reach 35 knots while supporting 160 nautical-mile range, a benchmark for coastal passenger services. Luxury yacht builders are experimenting with cryogenic storage and methanol reformers to extend zero-carbon cruising. Yet hydrogen handling rules remain in flux, and insurance premiums for gaseous fuel cargoes are still elevated. These barriers protect diesel's majority share in deep-sea trades where global availability, simplicity and decades of operating data continue to outweigh environmental penalties.
Commercial cargo vessels accounted for 57.37% of the marine propulsion engine market size in 2024, buoyed by a surge in container and bulk demand after pandemic disruptions. Fleet owners prioritized dual-fuel engines to secure CII-compliant operations on Asia-Europe loops. Passenger categories, covering cruise ships and ferries, outpace overall growth at 2.41% CAGR as governments impose fjord and port emission caps that favor electric or hybrid packages. The marine propulsion engine industry also benefits from spill-over orders in the defense segment where silent running and multi-fuel readiness are operational must-haves.
Cruise lines now embed battery modules and methanol capability as standard on newbuilds to meet corporate ESG targets. Norway's fjord rule alone spurred orders for electric fjord ferries, while California's At-Berth extension pushes North American operators toward shore-power compliance. These developments raise auxiliary power requirements, inflating market value even as engine counts per hull decline. Cargo owners, by contrast, invest in fuel flexibility to hedge both price and availability risk, cementing a two-track investment pattern that splits the market between efficiency-driven freighters and regulation-driven passenger craft.
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report is Segmented by Engine Type (Diesel, Dual-Fuel, Gas Turbine, and More), Application (Passenger, Commercial Cargo, and Defense), Ship Type (Container Ship, Tanker, Bulk Carrier, and More), Fuel Type (Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO), Marine Diesel/Gas Oil, and More), Power Range (Up To 1 000 KW, 1 001 KW To 5 000 KW, and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Asia-Pacific commanded 43.36% of 2024 revenue, anchored by China's near-monopoly on high-volume commercial shipbuilding and South Korea's LNG carrier specialization. Regional support extends from policy incentives, such as China's VAT rebates on export tonnage, to supply-chain depth that includes foundries, crankshaft forges and a dense vendor ecosystem. Dual-fuel capability adoption accelerates here because owners can marry low-cost hull production with the latest propulsion packages before delivery, shortening payback periods. Advanced R&D clusters in Japan propel ammonia-ready designs that promise gradual emission abatement without immediate bunkering network overhauls.
Europe remains the crucible for regulatory innovation, shaping technology demand through instruments like FuelEU Maritime, the EU Emissions Trading System and expanding Emission Control Areas. Norwegian fjord zero-emission mandates create an immediate retrofit and new-build pipeline for electric and hydrogen solutions, while Mediterranean ECA designation extends compliance pressures to bulk and tanker traffic that historically skirted Northern rules. Engine suppliers leverage European yards' specialist focus to test fuel-cell and carbon-capture prototypes under commercial voyage conditions, learning that subsequently informs Asia-Pacific volume deployments.
The Middle East and Africa, though only around one tenth of the revenue contributor in 2024, charts the fastest 3.37% CAGR as QatarGas and ADNOC invest in LNG and methanol infrastructure to anchor export chains. Sovereign-backed shipbuilding expansions, such as Hanwha Philly Shipyard's scale-up to ten vessels per year, pull global best-practice know-how into the region. North America's growth centers on defense procurement, reinforced by the Jones Act cabotage shield that drives domestic yard backlog even at higher cost. South America and Africa progress in spurts linked to port modernization and offshore energy investment, but financing hurdles and limited technical clusters slow technology uptake.