
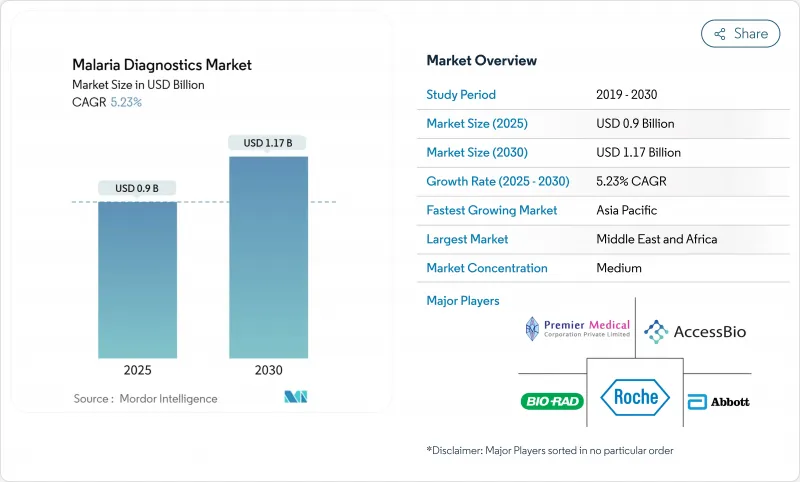
말라리아 진단 시장의 2025년 시장 규모는 9억 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년에는 11억 6,000만 달러에 이를것으로 예측되며, CAGR은 5.23%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

성장은 지속적인 글로벌 질병 부담, 약제 내성 기생충 균주의 출현, 그리고 내성 표지자와 저밀도 감염을 더 정확하게 식별하는 분자 검출 플랫폼으로의 전환에 기반을 두고 있습니다. 다자간 기관의 자금 지원 안정성, 혁신적인 검사 형식에 대한 규제 승인, 국가적 근절 로드맵은 공중보건 조달 채널 전반에 걸쳐 수요를 강화합니다. 동시에 pfhrp2/3 유전자 결손으로 인한 기존 신속진단검사(RDT)의 정확도 격차는 의료 시스템이 루프매개 등온 증폭(LAMP), 중합효소연쇄반응(PCR), 신흥 비침습적 검사법을 채택하도록 촉진하고 있으며, 이는 말라리아 진단 시장의 장기적 성장 동력을 뒷받침하는 기술 갱신 주기를 예고합니다. 경쟁은 여전히 완만하지만, 기존 기업들은 인수 및 제품 승인을 통해 포트폴리오를 지속적으로 갱신하는 한편, 민첩한 스타트업들은 기존 시설 밖에서도 실험실 수준의 민감도를 약속하는 현장진단용 분자 장치 및 AI 강화 영상 분석 기술을 상용화하고 있습니다. 풍토병 지역 전반에 걸쳐 검사가 지역 보건소 및 진단 센터로 분산되면서 처리량이 증가하고 치료까지의 시간이 단축되며 감시 품질이 향상되고 있습니다. 이는 기후 변화로 전파 시기가 확대됨에 따라 필수적인 역량입니다.
말라리아는 2023년 2억 6,300만 건의 발병과 59만 7,000명의 사망을 기록하며 공중보건 시스템에 여전히 막대한 부담을 주고 있으며, 이 중 94%가 사하라 이남 아프리카에서 발생했습니다. 말라리아 유행국은 경제 생산성 저하를 경험하며, 보건부는 당일 치료 결정을 촉발할 수 있는 진단 전달 네트워크 구축을 최우선 과제로 삼고 있습니다. 나이지리아, 우간다, 콩고 민주 공화국 정부는 감시 품질을 강화하는 대량 검사 키트, 이동형 진료팀, 디지털 사례 보고 도구 조달에 기부금을 점점 더 많이 투입하고 있습니다. 지속적인 전파로 인해 광업, 농업, 건설업 고용주들은 근로자 결근을 최소화하기 위해 현장 진단 역량을 확보해야 합니다. 기후 변동성은 모기 번식 가능 기간을 더욱 확대하여 말라리아 진단 시장의 지리적 범위를 사헬 지역, 동아프리카 고원 지대, 남아시아 일부 등 기존 저위험 지역으로 확장시키고 있습니다.
현장 적응형 분자 시스템은 이제 정교한 실험실 없이도 PCR 수준의 민감도를 제공합니다. LAMP 검사는 0.5 기생충/μL의 극소량까지 검출 가능하며 40분 이내에 결과를 판독해 외딴 지역의 대규모 검진 및 치료 캠페인을 지원합니다. AI 기반 중적외선 분광 플랫폼은 클라우드 기반 알고리즘을 통해 건조 혈액 스팟을 분석하여 다양한 기생충 밀도에서 말라리아 원충 종을 구분합니다. 이 기능은 오분류를 줄이고 약물 선택에 정보를 제공합니다. 사이토폰(Cytophone)과 같은 광음향 유세포 분석 장치는 생체 내에서 감염된 적혈구를 90% 이상의 민감도로 식별하여 손가락 채혈 절차를 없애고 환자 수용도를 높입니다. 스마트폰 연동 마이크로플루이딕 면역분석법은 이제 15분 만에 히스티딘 풍부 단백질-2(HRP-2)를 정량화하여 지역사회 환경에서 즉각적인 치료를 가능하게 합니다. 광학 부품, 배터리, 시약 저장 장치의 지속적인 소형화는 냉장 유통망이나 전력망이 부족한 시설까지 말라리아 진단 시장의 접근성을 확대합니다.
저소득 및 중간 소득 국가 중 현대적 진단을 도입한 비율은 고작 26%에 불과해 검사 접근성이 도시 중심부에만 제한되고 농촌 인구는 임상 증상에 의존해 확진을 받아야 합니다. 정전, 불안정한 인터넷, 신뢰할 수 없는 냉장 시설은 시약의 무결성과 데이터 보고를 위협합니다. 부르키나파소와 세네갈의 공급망 연구에 따르면, RDT(현장진단검사) 물품이 운송 중 30°C를 초과하는 경우가 빈번하여 유통기한이 단축되고 재고 부족 위험이 높아집니다. 외딴 지역 진료소에는 PCR 오염 통제에 필요한 생물안전 캐비닛이 거의 없어 분자진단 도입에 더 큰 자본 장벽이 발생합니다. 이러한 결함은 진단을 지연시키고, 사례 사망률을 높이며, 가장 부담이 큰 지역에서 말라리아 진단 시장의 성장 궤적을 제한합니다.
신속 진단 키트(RDT)는 2024년 말라리아 진단 시장 점유율의 45.65%를 차지했으며, 이는 경제성, 최소한의 교육 필요성, 그리고 외곽 지역에서도 20분 이내에 감염 확인이 가능하다는 점을 반영합니다. 그러나 분자 진단은 RDT 및 현미경 검사가 놓치는 미세 기생충 혈증 및 내성 표지자를 탐지할 수 있는 능력 덕분에 6.84%의 연평균 성장률(CAGR)로 가장 빠르게 성장하고 있습니다. 분자 플랫폼 기반 말라리아 진단 시장 규모는 2030년까지 3억 8,100만 달러에 달할 것으로 전망되며, 루프 매개 등온 증폭 카트리지, 일회용 PCR 칩, 휴대용 유전자 시퀀서가 기부자 지원 프로그램에 도입되면서 2024년 기준의 거의 두 배로 성장할 것입니다. RDT 공급업체들은 45°C 보관에 견디는 복합 항원 검사 및 내열성 형식을 출시하며 대응하고 있으나, pfhrp2 결손률이 높은 지역에서는 여전히 성능이 저하되어 분자 진단 도입의 여지를 제공하고 있습니다. 스마트폰 현미경에 적용된 AI 기반 영상 인식 기술은 이제 전문가 현미경 검사자와 95%의 일치율로 기생충을 계수하며, 기존 현미경 검사에 점진적인 가치 향상을 시사합니다.
분자 검사 개발사들은 일회용 카트리지, 동결건조 시약, 오프그리드 운영이 가능한 태양광 분석기를 강조하며, 역사적으로 PCR을 참조 실험실로 제한했던 인프라 격차를 좁히고 있습니다. 카메룬에서 검증된 bCUBE 장치는 모세혈액과 모기 군집에서 플라스모디움을 동일 플랫폼으로 식별하는 기능을 통해 이러한 변화를 부각시키며, 이는 곤충학적 감시팀에게 매력적인 특징입니다. 호흡 기반 휘발성 유기 화합물 센서를 포함한 비침습적 진단 방식에 대한 벤처 캐피털 투자는 2030년 이후 RDT(현장진단검사)의 지배력을 약화시킬 수 있는 혁신 경로를 추가로 제공합니다. 결과적으로 말라리아 진단 시장은 RDT 물량이 광범위한 접근성을 유지하는 한편, 분자 진단은 높은 평균 판매 가격과 확장된 검사 메뉴 유연성으로 매출이 가속화되는 이중 구조를 보입니다.
중동 및 아프리카 지역은 2024년 말라리아 진단 시장 점유율 38.82%를 유지했으며, 이는 해당 지역의 2억 4,600만 건의 사례와 지속적인 기부자 자금 지원을 반영합니다. 나이지리아만 해도 글로벌 펀드 채널을 통해 1억 개 이상의 신속진단키트(RDT)를 조달하여 중앙 창고에서 마을 보건소까지 이어지는 강력한 상품 공급망을 구축했습니다. 20개 아프리카 국가에서 강화된 백신 배포는 돌파 감염 감지 및 균주 다양성 평가가 가능한 고분해능 감시를 요구하여, 보건부들이 일상적인 HRP-2 검사 외에 종 특이적 PCR 시약을 구매하도록 촉진하고 있습니다. 그러나 물류 장애는 지속되고 있습니다. 우기 동안의 도로 접근성 부족과 제한된 콜드체인 용량은 적시 배송을 방해하여, 열안정성 형식과 원격 참조 실험실을 우회하는 현장 분자 장치의 필요성을 강조합니다.
아시아태평양 지역은 2030년까지 연평균 6.26% 성장률로 가장 빠르게 성장하는 지역으로 자리매김하고 있습니다. 인도는 동남아시아 사례의 82.5%를 차지하며, 지역 단위 데이터 세분화를 요구하는 공식적 박멸 목표를 수립해 LAMP 키트와 최근 WHO 사전승인된 G6PD 현장진단 키트 조달을 촉진하여 안전한 P. vivax 근절 치료를 지원하고 있습니다. 메콩강 유역 국가 간 감시 체계는 Kelch13 돌연변이를 추적하며, 국가 프로그램에 일상적 진단 알고리즘에 내성 유전자형 분석을 추가하도록 압박하고 있습니다. 인도네시아의 군도 지형은 드론 배송 검사 키트와 클라우드 기반 결과 집계 시스템에 대한 투자를 촉진하며, 말라리아 진단 시장에서 디지털 인프라가 물리적 상품 유통을 보완하는 방식을 보여줍니다.
북미와 유럽은 수입 사례 관리 및 헌혈자 검사에 집중된 틈새 시장이지만 고부가가치 부문를 형성합니다. 2024년 로슈의 코바스 말라리아 분자 검사가 FDA 승인을 받으면서 핵산 검사가 수혈 안전의 새로운 표준으로 자리매김하며, 혈액은행과 군 검진 시설 전반에 걸쳐 장비 설치가 확대되고 있습니다. 남미는 여전히 시장 점유율이 낮지만 표적 근절 전략을 채택하고 있습니다. 브라질의 아마존 감시 네트워크는 위성 매핑과 PCR 확인을 통합해 발병을 사전에 차단합니다. 이러한 지역별 현황은 근절 또는 예방 목표를 지원하는 민감한 진단 기술로의 수렴을 보여주며, 말라리아 진단 시장의 글로벌 중요성을 강화합니다.
The malaria diagnostics market is valued at USD 0.90 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 1.16 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.23% CAGR.
Growth is anchored in the persistent global disease burden, the emergence of drug-resistant parasite strains, and the transition toward molecular detection platforms that identify resistance markers and low-density infections with greater accuracy. Funding security from multilateral agencies, regulatory approvals for innovative test formats, and national elimination roadmaps collectively strengthen demand across public-health procurement channels. At the same time, accuracy gaps in legacy rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) caused by pfhrp2/3 gene deletions are pushing healthcare systems to adopt loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and emerging non-invasive modalities, signaling a technology refresh cycle that supports the long-term momentum of the malaria diagnostics market. Competitive rivalry remains moderate, yet established firms continue to refresh portfolios through acquisitions and product approvals, while nimble start-ups commercialize point-of-care molecular devices and AI-enhanced image analytics that promise near-laboratory sensitivity outside traditional facilities. Across endemic regions, decentralization of testing to community health posts and diagnostic centres increases throughput, shortens time to treatment, and raises surveillance quality-an essential capability as climate change expands transmission seasons.
Malaria continues to place a heavy toll on public health systems, with 263 million cases and 597,000 deaths recorded in 2023, 94% of which occurred in Sub-Saharan Africa. Endemic countries experience slowed economic productivity that motivates ministries of health to prioritize diagnostic delivery networks that can trigger same-day treatment decisions. Governments in Nigeria, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo increasingly channel donor funds toward procurement of high-volume test kits, mobile outreach units, and digital case-reporting tools that reinforce surveillance quality. Persistent transmission also forces employers in mining, agriculture, and construction to procure on-site diagnostic capacity to minimize worker absenteeism. Climate variability further widens seasonal windows for mosquito breeding, expanding the geographic footprint of the malaria diagnostics market into previously low-risk zones across the Sahel, East African highlands, and parts of South Asia.
Field-adapted molecular systems now deliver PCR-level sensitivity without sophisticated laboratories. LAMP assays can detect as few as 0.5 parasites/μL and read results within 40 minutes, supporting mass screening-and-treat campaigns in remote areas. AI-enabled mid-infrared spectroscopy platforms analyze dried blood spots through cloud-based algorithms, differentiating Plasmodium species at varying parasite densities, a capability that reduces misclassification and informs drug selection. Photoacoustic flow cytometry devices such as the Cytophone identify infected red blood cells in vivo with >= 90% sensitivity, eliminating finger-stick procedures and improving patient acceptance. Smartphone-linked microfluidic immunoassays now quantify histidine-rich protein-2 in 15 minutes, enabling immediate therapy in community settings. Continuous miniaturization of optics, batteries, and reagent storage broadens the reach of the malaria diagnostics market to facilities lacking cold chains or grid electricity.
Just 26% of low- and lower-middle-income nations deploy modern diagnostics, restricting test availability to urban centers and leaving rural populations dependent on clinical symptoms for case confirmation. Power outages, erratic internet, and unreliable refrigeration compromise reagent integrity and data reporting. In Burkina Faso and Senegal, supply-chain studies show RDT consignments frequently exceed 30 °C during transit, shortening shelf life and raising stock-out risks. Remote clinics seldom have biosafety cabinets required for PCR contamination control, translating into higher capital hurdles for molecular adoption. These deficits delay diagnosis, inflate case fatality rates, and cap the growth trajectory of the malaria diagnostics market in the most burdened geographies.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Rapid diagnostic tests held 45.65% of malaria diagnostics market share in 2024, reflecting their affordability, minimal training needs, and ability to confirm infection within 20 minutes in peripheral settings. However, molecular diagnostics are growing fastest at a 6.84% CAGR, propelled by their capacity to detect sub-microscopic parasitemia and resistance markers that RDTs and microscopy miss. The malaria diagnostics market size for molecular platforms is projected to reach USD 381 million by 2030, nearly doubling its 2024 base as loop-mediated isothermal amplification carts, disposable PCR chips, and portable genetic sequencers penetrate donor-funded programs. RDT vendors respond by launching combination antigen tests and heat-stable formats that tolerate 45 °C storage, yet their performance still declines in areas with high pfhrp2 deletions, providing a wedge for molecular adoption. AI-assisted image recognition layered onto smartphone microscopes now counts parasites with 95% concordance to expert microscopists, signaling incremental value upgrades to legacy microscopy.
Molecular test developers emphasize single-use cartridges, lyophilized reagents, and solar-powered analyzers that operate off-grid, narrowing the infrastructure gap that historically confined PCR to reference laboratories. The bCUBE device validated in Cameroon highlights this shift, identifying Plasmodium in capillary blood and mosquito pools on the same platform, a feature attractive to entomological surveillance teams. Venture-capital investment into non-invasive modalities, including breath-based volatile organic compound sensors, further supplies innovation pathways that may erode RDT dominance post-2030. Consequently, the malaria diagnostics market exhibits a dual-track profile where RDT volumes sustain broad access while molecular dollar revenues accelerate on higher average selling prices and expanding menu versatility.
The Malaria Diagnostics Market Report is Segmented by Technology (Clinical Diagnostics, Microscopic Diagnostics, Rapid Diagnostic Tests, Molecular Diagnostics, and Other Technologies) End-User (Hospitals, Clinics, Diagnostic Centres, and Community Health Posts), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
The Middle East & Africa retained 38.82% of malaria diagnostics market share in 2024, reflecting the region's 246 million cases and sustained donor funding. Nigeria alone procured over 100 million RDTs through Global Fund channels, anchoring a robust commodity pipeline that stretches from central warehouses to village health posts. Intensified vaccine deployment in 20 African countries demands high-granularity surveillance capable of detecting breakthrough infections and assessing strain diversity, prompting ministries to purchase species-specific PCR reagents alongside routine HRP-2 tests. Yet logistics hurdles persist; road inaccessibility during rainy seasons and limited cold-chain capacity hamper timely delivery, underscoring the need for heat-stable formats and on-site molecular devices that bypass distant reference labs.
Asia-Pacific stands as the fastest-growing geography, advancing at a 6.26% CAGR to 2030. India contributes 82.5% of Southeast Asian cases and has formalized elimination targets that require district-level data granularity, stimulating procurement of LAMP kits and the recently WHO-prequalified G6PD point-of-care test to support safe P. vivax radical cure. Cross-border surveillance along the Greater Mekong tracks Kelch13 mutations, pressuring national programs to layer resistance genotyping onto routine diagnostic algorithms. Indonesia's archipelagic geography drives investment in drone-delivered test consignments and cloud-based result aggregation, exemplifying how digital infrastructure complements physical commodity distribution in the malaria diagnostics market.
North America and Europe form niche but high-value segments focused on imported case management and blood-donor screening. FDA approval of Roche's cobas Malaria molecular test in 2024 positions nucleic-acid screening as the new standard for transfusion safety, expanding instrument placements across blood banks and military screening facilities. South America remains a smaller share contributor yet adopts targeted elimination strategies; Brazil's Amazon surveillance network integrates satellite mapping with PCR confirmation to pre-empt outbreaks. Collectively, these regional profiles illustrate a convergence toward sensitive diagnostics that support elimination or prevention goals, reinforcing the global relevance of the malaria diagnostics market.