
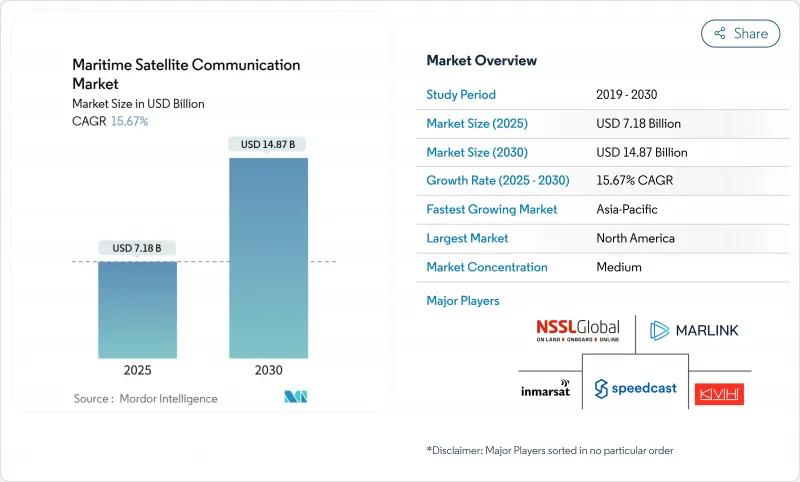
해사 위성 통신 시장 규모는 2025년에 71억 8,000만 달러로 평가되었고, 예측기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 15.67%를 나타낼 것으로 예측되며, 2030년에 148억 7,000만 달러에 달할 전망입니다.

규제 강화, 저궤도(LEO) 위성군 등장, 선원 복지 기대치 상승이 이러한 확장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 국제해사기구(IMO)의 2024년 글로벌 해양 조난 및 안전 시스템(GMDSS) 현대화로 다수 위성 서비스 제공업체의 인증이 가능해지면서 경쟁 압력이 고조되고 사용자 비용이 하락했습니다. 크루즈 선사, 해양 운영사, 국방 기관들은 이제 연결성을 선택적 서비스가 아닌 핵심 인프라로 간주하고 있습니다. 평판 안테나 기술 발전과 함께 하이브리드 정지궤도-저궤도(GEO-LEO) 네트워크의 급속한 보급은 대역폭 비용을 절감하면서도 처리량을 향상시켜 선박에서 클라우드 애플리케이션과 실시간 영상 서비스를 가능하게 합니다. 특히 유럽과 아시아태평양 지역에서 추진되는 디지털화 정책은 지속적인 광대역 연결에 의존하는 배출량 보고 및 예측 유지보수 플랫폼을 운영사가 통합함에 따라 잠재 수요를 더욱 확대하고 있습니다.
2024년 발효된 해사노동협약 개정안은 운영자에게 최소 인터넷 대역폭 제공을 의무화하여 연결성을 선택적 혜택에서 법적 요건으로 전환시켰습니다. 선박 관리자들은 숙련된 선원 확보에 연결성이 핵심적이라고 지적하며, 이는 글로벌 선원 이직 압박이 가중되는 상황에서 최우선 과제입니다. 향상된 연결성은 원격의료, 디지털 교육, 실시간 진단도 가능하게 하여 대역폭 업그레이드의 사업적 타당성을 강화합니다. 저궤도(LEO) 위성군 제공업체가 가장 큰 혜택을 보는데, 그들의 아키텍처가 해상에서 광섬유 수준의 속도를 제공하기 때문입니다. 사례 연구에 따르면 고용량 링크를 장착한 선박은 자발적 선원 이탈률이 두 자릿수 감소했으며, 이는 측정 가능한 운영 비용 절감으로 이어졌습니다.
IMO의 2024년 수명주기 온실가스(GHG) 강도 지침은 연료 소비 및 배출 데이터의 지속적인 전송을 의무화합니다. 2025년에는 탄소 집약도 지표(CII)가 완전히 시행되어 선박들은 실시간에 가까운 운영 데이터를 공유하거나 시정 조치 계획을 수립해야 합니다. 이러한 규제 환경은 대역폭과 통합 규정 준수 모니터링을 결합한 관리형 서비스 제공업체에 유리합니다. 주요 네트워크 통합업체들은 성능 지표를 자동으로 캡처하고 암호화된 데이터를 육상 해양 대시보드로 전송하는 ‘스마트 하이브리드’ 패키지 공급을 시작했습니다. FuelEU Maritime 하의 병행 EU 법안은 유럽 해역 전반에 걸쳐 신뢰할 수 있는 위성 채널 수요를 증폭시킵니다.
차세대 전자식 조향 안테나는 저궤도(LEO) 서비스에 필수적이며 선박당 5만-15만달러의 비용이 발생해 단일 선박 소유주에게는 장벽입니다. 설치에는 종종 드라이독 작업이 필요해 프로젝트 총비용이 2만-4만 달러 추가로 증가하고 투자 회수 기간이 연장됩니다. 제조사들은 가격 경직성을 2024년부터 지속된 반도체 부족 현상 탓으로 돌립니다. 대형 크루즈선 및 에너지 선단은 다년 계약을 통해 비용을 분산할 수 있지만, 소규모 운영사들은 업그레이드를 미루며 해상 디지털 격차를 확대하고 있습니다. 노르웨이와 일본에서 검토 중인 보조금 프로그램은 어업 협동조합의 하드웨어 비용을 상쇄하기 위한 것이나, 아직 글로벌 차원의 메커니즘은 존재하지 않습니다.
해상 위성 통신 시장의 커넥티비티 서비스 규모는 여전히 정지궤도 VSAT(GEO VSAT)에 집중되어 있으며, 2024년 기준 58%의 점유율을 기록했습니다. 그러나 해운사들이 기존 신뢰성 지표보다 처리량과 지연 시간을 우선시함에 따라 비-GEO 광대역 솔루션은 2030년까지 연평균 17.6%의 성장률(CAGR)로 확대될 전망입니다. 초기 도입사들은 클라우드 ERP, 예측 유지보수 대시보드, 선원용 고화질 스트리밍을 동시에 호스팅할 수 있는 능력을 강조합니다. 통합업체들이 전 해양 커버리지를 위한 정지궤도(GEO) 빔과 데이터 집약적 운영을 위한 저궤도(LEO) 버스트를 결합하는 하이브리드 구현 방식이 신규 계약을 주도하고 있습니다. 이중 단말기를 장착한 중형 벌크선 함대는 기가바이트당 비용을 55% 이상 절감하면서 선원 데이터 허용량을 두 배로 늘렸다고 보고했습니다. 규제 기관들도 다중 궤도 설계에 내재된 중복성을 선호하는데, 이는 비상 통신이 네트워크 간 자동 전환이 가능하기 때문입니다. 대역폭의 대체성이 높아짐에 따라 가격 경쟁이 심화될 것으로 예상되며, 이로 인해 기존 GEO 사업자들은 24/7 SOC 모니터링 및 규제 보고와 같은 부가가치 서비스를 번들로 제공하여 고객을 방어해야 할 것입니다.
한때 서비스가 부족했던 상업 어업이 저궤도 위성(LEO)의 이점을 입증하는 사례로 부상했습니다. 실시간 영상 채팅을 통해 육상 구매자와 가격 협상을 진행하는 운영사들은 어획 후 지연을 줄이고 마진을 개선했습니다. 그러나 한계는 여전히 존재합니다. 극지 항로와 남태평양 심해 통로는 안전 통신을 위해 주로 정지궤도(GEO) L-대역을 의존하고 있어, 전면적인 대체보다는 점진적 전환이 보장됩니다. 모바일 위성 서비스(MSS) 라이선스와 기국 운송 규정은 성장세가 저궤도 위성군으로 전환되더라도 기존 시스템에 대한 기본 수요를 계속 보장할 것입니다. 결과적으로 해양 위성 통신 시장은 지구정지궤도(GEO)가 글로벌 복원력을 제공하고 저궤도(LEO)가 커버리지 구역에서 비용 효율적인 용량을 공급하는 이중 구조 동향을 보일 전망입니다.
Ku-대역는 성숙한 지상 장비와 글로벌 빔 패턴 덕분에 2024년 해상 위성 통신 시장 점유율 41%를 차지했습니다. 그러나 Ka-대역 수익은 운영사들이 트랜스폰더당 용량을 높이는 고차 변조 및 주파수 재사용을 추구함에 따라 2030년까지 연평균 18.03% 성장률(CAGR)로 증가할 것으로 전망됩니다. 크루즈 및 해양 에너지 분야에서 Ka 대역의 진전이 두드러지며, 승객용 Wi-Fi, 원격 운영 센터, 실시간 센서 분석을 위한 멀티 기가비트(Gbps) 트렁크가 구축되고 있습니다. 듀얼 대역 피드를 갖춘 평판 안테나는 이제 Ku 대역와 Ka 대역 간 자동 전환을 가능하게 하여, 비로 인한 신호 감쇠(rain-fade)를 우려하는 소유주의 도입 위험을 완화합니다. 국제전기통신연합(ITU)은 지상 이동통신 스펙트럼과 증가하는 Ka 대역 사용 간의 균형을 모색하는 연구를 시작했으며, 이는 장기적인 할당 안정성에 대한 제도적 지원을 시사합니다.
말라카 해협 및 미국 동부 해안과 같은 Ku 대역 회랑의 스펙트럼 혼잡은 사업자들을 고주파 대역으로 밀어붙이고 있습니다. 다중 스팟빔 위성에서 Ka 대역을 사용하는 화물선들은 유사한 Ku 패키지 대비 30% 낮은 지연 시간과 40% 높은 평균 처리량을 보고합니다. 그럼에도 고위도 커버리지와 하드웨어 비용 우위 측면에서 Ku 대역의 중요성은 지속될 전망입니다. L-대역 대역은 GMDSS(해상안전통신시스템) 및 긴급 메시징에 필수적이며, 안정적인 다중 대역 생태계의 기반을 형성합니다. 향후 전망으로, 시제 위성에 탑재된 Q/V-대역 실험은 용량 확장 가능성을 시사하나, 해당 대역의 해상용 단말기는 2028년 이전 상용화 준비가 어려울 것으로 보입니다. 따라서 Ka 대역 도입이 단기 성장을 주도하는 한편, Ku 대역은 기본 서비스 지속성을 뒷받침할 것입니다.
해사 위성 통신 시장 보고서는 접속 유형(모바일 위성 서비스(MSS), 정지 VSAT, 비GEO 광대역(LEO/MEO)), 주파수대역(L-대역, S-대역, C-대역, 기타), 제공서비스(하드웨어와 단말, 접속서비스 등), 최종 사용자 업종(상선(화물선과 유조선, 해외에너지 및 지원선, 여객, 기타)
유럽은 2024년 전 세계 매출의 30%를 유지했으며, 이는 대용량·탄력적 연결을 의무화하는 엄격한 배출 및 사이버 보안 규제로 인해 촉진되었습니다. 노르웨이, 독일, 프랑스에 본사를 둔 선단 관리자들은 FuelEU Maritime 및 NIS2 지침 준수를 보장하기 위해 하이브리드 다중 궤도 패키지를 정기적으로 지정합니다. 노르웨이의 Arctic Way Cable System과 같은 정부 투자는 지역 인프라를 더욱 강화하여 극지 항로의 위성 백홀 중복성을 높입니다.
아시아태평양 지역은 무역량 증가와 선단 현대화로 2030년까지 연평균 12.5% 성장률(CAGR)을 기록하며 가장 빠르게 성장할 것으로 전망됩니다. 일본과 한국 선주들은 지속적인 광대역이 필요한 AI 지원 항해 플랫폼을 시범 운영 중이며, 호주 LNG 운반선들은 용선자 요구사항 충족을 위해 위성 기반 배출 모니터링을 도입하고 있습니다. 중국의 계획 중인 ‘천판(Qianfan)’ 위성군 구축은 국내 우주 자산 확보와 해양 데이터 주권 확보를 위한 전략적 추진을 시사합니다. 5G-NTN(위성 기반 5G 통신) 역량 제공을 위한 지역 통신-위성 파트너십도 형성 중이며, 이는 아시아태평양 지역이 하이브리드 연결 솔루션 분야에서 도약할 수 있는 발판을 마련하고 있습니다.
북미는 저궤도(LEO) 위성 조기 도입과 명확한 규제 체계, 특히 미국 해안경비대의 사이버 보안 규정 하에서 혜택을 누리고 있습니다. 멕시코만 에너지 운영사들은 무인 플랫폼 운영을 위한 안정적인 통신 링크를 요구하며 프리미엄 ARPU를 창출하고 있습니다. 중동과 아프리카는 신흥 수요를 보이고 있으며, 홍해 게이트웨이 같은 에너지 회랑 프로젝트가 위성 게이트웨이 및 광섬유 백본 투자 촉진에 기여하고 있습니다. 라틴아메리카는 다소 뒤처져 있지만, 실시간 선박 데이터 전송이 필수적인 파나마 운하 디지털 트윈 프로젝트로 추진력을 얻고 있습니다. 종합적으로, 상이한 규제 속도와 인프라 준비도는 해양 위성 통신 시장 전반에 걸쳐 지역별 성장 곡선을 만들어 냅니다.
The Maritime Satellite Communication Market size is estimated at USD 7.18 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 14.87 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 15.67% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Intensifying regulatory mandates, the advent of low-earth-orbit (LEO) constellations, and rising crew-welfare expectations underpin this expansion. The International Maritime Organization's 2024 modernization of the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System opened certification to multiple satellite service providers, heightening competitive pressure and lowering user costs. Cruise lines, offshore operators, and defense agencies are now treating connectivity as core infrastructure rather than a discretionary service. Rapid uptake of hybrid GEO-LEO networks, coupled with flat-panel antenna improvements, is compressing bandwidth costs while lifting throughput, enabling vessels to run cloud applications and real-time video. Digitalization initiatives, particularly in Europe and Asia Pacific, are further enlarging addressable demand as operators integrate emissions-reporting and predictive-maintenance platforms that depend on continuous broadband links.
Maritime Labour Convention amendments that took effect in 2024 obligate operators to provide minimum internet bandwidth, transforming connectivity from a discretionary perk into a statutory requirement. Ship managers cite connectivity as critical to retaining skilled seafarers, a priority as global crew turnover pressures mount. Enhanced links also enable telemedicine, digital training, and real-time diagnostics, strengthening the business case for bandwidth upgrades. Providers of LEO constellations benefit most because their architectures deliver fibre-like speeds at sea. Case studies show vessels equipped with high-capacity links reporting double-digit declines in voluntary crew exits, translating into measurable operating-cost savings.
The IMO's 2024 guidelines on life-cycle GHG intensity mandate continuous transmission of fuel-consumption and emissions data. In 2025, the Carbon Intensity Indicator enters full effect, compelling vessels to share near-real-time operating data or face corrective-action plans. This regulatory environment favours managed-service providers that marry bandwidth with integrated compliance monitoring. Leading network integrators have begun shipping "smart hybrid" packages that auto-capture performance metrics and forward encrypted data to on-shore maritime dashboards. Parallel EU legislation under FuelEU Maritime magnifies demand for reliable satellite channels across European waters.
Next-generation electronically steered antennas are essential for LEO services and cost USD 50,000-150,000 per vessel, a barrier for single-ship owners. Installation often requires dry-docking, inflating project totals by another USD 20,000 - 40,000, and extending payback periods. Manufacturers attribute price stickiness to semiconductor shortages that have persisted since 2024. While large cruise and energy fleets can amortise expenses across multi-year contracts, small operators delay upgrades, widening the digital divide at sea. Subsidy programmes under consideration in Norway and Japan aim to offset hardware costs for fishing cooperatives, but no global mechanism yet exists.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
The maritime satellite communication market size for connectivity services remains weighted toward Geostationary VSAT, which secured a 58% share in 2024. However, non-GEO broadband solutions are predicted to expand at a 17.6% CAGR to 2030 as shipping lines prioritise throughput and latency over historical reliability metrics. Early adopters highlight the ability to host cloud ERPs, predictive-maintenance dashboards, and high-definition crew streaming concurrently. Hybrid implementations dominate new contracts, with integrators blending GEO beams for all-ocean coverage with LEO bursts for data-intensive operations. A mid-size bulker fleet that fitted dual terminals reported cutting per-gigabyte costs by over 55% while doubling data allowances to crews. Regulators also favour redundancy inherent in multi-orbit designs because distress traffic can auto-fail over between networks. As bandwidth becomes more fungible, price competition is expected to intensify, compelling GEO incumbents to bundle value-added services such as 24/7 SOC monitoring and regulatory reporting to defend accounts.
Commercial fishing, once underserved, has emerged as a proof point for LEO gain. Operators using real-time video chat to negotiate prices with on-shore buyers have reduced post-harvest delays and improved margins. Yet limitations remain, polar routes and deep-South Pacific corridors still rely primarily on GEO L-band for safety traffic, ensuring a measured transition rather than wholesale displacement. Mobile-satellite-service licences and flag-state carriage rules will continue to guarantee baseline demand for legacy systems even as growth swings to LEO constellations. Consequently, the maritime satellite communication market will likely exhibit a dual-track dynamic where GEO delivers global resiliency and LEO supplies cost-efficient capacity in covered zones.
Ku-Band secured 41% of the maritime satellite communication market share in 2024 thanks to mature ground equipment and global beam patterns. However, Ka-Band revenues are forecast to climb at an 18.03% CAGR through 2030 as operators seek higher-order modulation and frequency re-use that lift capacity per transponder. Ka's progression is visible in the cruise and offshore energy verticals, deploying multi-Gbps trunks to run passenger Wi-Fi, remote operations centres, and real-time sensor analytics. Flat-panel antennas with dual-band feeds now enable automated switching between Ku and Ka, easing adoption risks for owners concerned about rain-fade. The International Telecommunication Union has launched studies to balance growing Ka use with terrestrial mobile spectrum, signalling institutional support for long-term allocation stability.
Spectrum congestion on Ku corridors such as the Strait of Malacca and the US East Coast is pushing operators toward higher frequencies. Cargo lines using Ka on multi-spot-beam satellites report 30% lower latency and 40% higher average throughput than comparable Ku packages. Nonetheless, Ku will stay relevant for high-latitude coverage and hardware cost advantages. L-Band remains indispensable for GMDSS and emergency messaging, anchoring a stable multi-band ecosystem. Looking ahead, Q/V-Band experimentation aboard prototype satellites indicates capacity scaling paths, but maritime terminals for those bands are unlikely to hit commercial readiness before 2028. Thus, Ka adoption will drive near-term growth while Ku underpins baseline service continuity.
The Maritime Satellite Communication Market Report is Segmented by Connectivity Type (Mobile Satellite Services [MSS], Geostationary VSAT, and Non-GEO Broadband [LEO/MEO]), Frequency Band (L-Band, S-Band, C-Band, and More), Offering (Hardware and Terminals, Connectivity Services, and More), End-User Vertical (Merchant (Merchant Cargo and Tanker, Offshore Energy & Support Vessels, Passenger, and More), and Geography.
Europe retained 30% of global revenue in 2024, propelled by strict emissions and cybersecurity regulations that oblige high-capacity, resilient links. Fleet managers domiciled in Norway, Germany, and France routinely specify hybrid multi-orbit packages to ensure compliance with FuelEU Maritime and NIS2 directives. Government investment, such as Norway's Arctic Way Cable System, further strengthens regional infrastructure, increasing satellite backhaul redundancy for polar routes.
Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region, advancing at a 12.5% CAGR through 2030 as trade volumes rise and fleets modernise. Japanese and South Korean owners are piloting AI-assisted navigation platforms that require persistent broadband, while Australian LNG carriers adopt satellite-enabled emissions monitoring to satisfy charterer stipulations. China's planned Qianfan constellation indicates a strategic push to secure domestic space assets and maritime data sovereignty. Regional telecom-satellite partnerships are also forming to deliver 5G-NTN capability, positioning Asia Pacific for a leap-frog in hybrid connectivity solutions.
North America benefits from early LEO adoption and clear regulatory frameworks, particularly under U.S. Coast Guard cybersecurity rules. Gulf of Mexico energy operators demand resilient links to operate unmanned platforms, driving premium ARPU. The Middle East and Africa show emerging demand; energy corridor projects such as the Red Sea Gateway spur investments in satellite gateways and fibre backbones. Latin America lags slightly but gains impetus from Panama Canal digital twin projects that necessitate real-time vessel data feeds. Collectively, divergent regulatory tempos and infrastructure readiness produce region-specific growth curves across the maritime satellite communication market.