
원격의료 시장 규모는 2025년에 1,963억 7,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간 중 CAGR은 13.88%를 나타내, 2030년에는 3,761억 2,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.

이 두 자릿수의 확장은 팬데믹에 의한 흡수로부터 표준 임상 터치 포인트로서 가상 케어의 영구적인 정착으로의 결정적인 전환을 나타내는 것입니다. 지급자, 의료 제공업체, 정책 입안자는 현재 디지털 헬스 인프라를 탄력적인 케어 제공의 기반으로 취급하고 상호 운용성, 사이버 보안 및 원격 진단에 대한 투자를 촉진하고 있습니다. 따라서 원격의료 산업은 플랫폼의 넓이, 전문가의 커버 범위, 데이터 분석의 깊이가 조달 의사 결정을 좌우하는 스케일 업 단계로 들어가고 있습니다. 관찰 가능한 결과 중 하나로 성숙한 가상 퍼스트 운영 모델을 갖춘 의료 시스템은 지속적으로 높은 환자 참여 지표를 보고했으며, 향후 5년간 원격의료 시장 점유율 증가를 이끌어내는 강력한 위치에 있습니다.
세계적으로 확대되는 의사 부족은 의료 시스템이 환자 수요 증가에 대응하기 위해 어려움을 겪고 있기 때문에 원격의료 시장 채택을 가속화하고 있습니다. 2024년 3월에 발표된 미국 의과대학 협회(Association of American Medical Colleges)의 보고서는 미국 의사 부족이 2036년까지 최대 8만 6,000명에 이르며 현재 의사 중 5명 중 1명이 65세 이상으로 정년을 맞이할 것으로 예측했습니다. 2024년 8월에 발표된 Medicus Healthcare Solutions 기사에 따르면 미국의 46.3% 카운티에는 심장 전문의가 부족하여 주민의 심혈관 위험이 31% 높아졌다고 합니다. 원격의료 플랫폼은 전문의가 여러 시설에 원격으로 대응할 수 있게 함으로써 이러한 갭을 완화하고 물리적인 이동 없이 진료 범위를 확대합니다. 의료 네트워크는 온콜 로테이션을 재구성하고 가상 커버리지를 포함하여 예약 가용성을 미묘하게 개선하고 대기 시간을 단축합니다. 이러한 가상 허브가 초래하는 하류의 효과로는 일상적인 검진시에 다직종이 원격 환자 모니터링 데이터를 도입할 수 있으므로, 케어의 연속성이 향상되는 것을 들 수 있습니다. 이러한 통합 접근법은 품질을 향상시킬뿐만 아니라 장기적인 노동력 계획에서 원격의료가 부족할 수없는 것으로 정착합니다.
건강 관리 지급자는 원격의료를 가치 기반 케어 계약에 통합하여 결과를 향상시키면서 비용을 절감할 수 있다는 것을 알고 있습니다. 2027년까지 기본 추정 9,000만명이 밸류 베이스 케어의 대상이 되어, 피포 서비스로부터 크게 변화할 것으로 예상되고 있습니다. 현재 가상 케어를 활용하여 구급 외래 진찰을 억제하고 회피 가능한 입원을 예방하는 의료 제공업체에게는 재정적인센티브가 주어지고 있습니다. 원격의료 통합은 지속적인 원격 모니터링이 조기 개입과 복용 보험을 지원하는 만성 질환 관리에서 특히 두드러집니다. 가상 퍼스트 모델에 대한 지불자의 신뢰는 적격한 비디오 및 음성 방문에 대한 안정적인 보상의 평준화로 이어지고, 디지털 패스웨이는 표준 급여 설계에 효과적으로 고정되어 있습니다. 결제 인센티브와 플랫폼 사용 편의성의 관계로 인해 의료 시스템은 임상 의사와 환자 모두를 위한 사용자 인터페이스를 개선할 필요가 있습니다.
증가하는 데이터 프라이버시와 사이버 보안 위험은 원격의료 채택의 심각한 장벽으로 떠오르고 있으며 이해 관계자의 신뢰를 저해하고 컴플라이언스 비용을 증가시키고 있습니다. PureDome이 2024년 1월에 발표한 기사에 따르면, 헬스케어 조직은 인터넷 프로토콜의 평판 보안이 77% 저하되어 멀웨어나 피싱 공격에 노출되었습니다. Axios의 2024년 1월 기사에 따르면 연결된 의료기기의 확장으로 추가 취약점이 생겨 감시 당국은 구식 소프트웨어를 다루기 위해 미국 식품의약국(FDA)과 사이버 보안기관의 연계를 강화할 것을 요구했습니다. 의료기관은 현재 디지털 건강 예산의 대부분을 암호화 및 엔드포인트 보안에 할당하여 총 소유 비용을 늘리고 있습니다. 소규모 클리닉에서는 이러한 비용으로 인해 플랫폼 업그레이드를 앞당기게 되는 경우가 많으며, 서비스가 잘 되지 않는 지역에서의 원격의료 시장의 침투가 지연되고 있습니다. 고급 위협 감지 프로토콜을 통합하는 업계 리더는 공급업체 선정 시 차별화를 도모하고 있으며 보안의 강도가 원격의료 업계 전체의 결정적인 구매 기준으로 진화하고 있음을 이야기하고 있습니다.
원격 병원은 2024년에 원격의료 시장 점유율의 41.3%를 차지했지만, m건강은 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 23.5%로 확대돼 기존의 원격 병원과 원격 홈을 웃도는 것으로 예상되고 있습니다. 소비자는 심박수, 수면 패턴 및 혈중 산소 농도를 모니터링하는 웨어러블을 일상적인 건강 루틴에 점점 통합하여 임상 대시보드를 풍부하게 하는 지속적인 데이터 스트림을 생성하고 있습니다. 이 변화는 건강 관리를 단발적인 상호작용에서 지속적인 라이프스타일 관리로 전환시키고, 이러한 추세는 디지털 네이티브 계층과 공명합니다. 의료 제공업체는 m 건강 데이터를 집단 건강 계층화를 위해 활용하여 고위험 집단으로 조기 아웃리치를 가능하게 합니다. 신흥 시장에서는 모바일 퍼스트 전략이 의료 시스템의 인프라 제약을 뛰어넘는데 도움을 주었고, m건강이 원격의료 산업의 확대에 매우 큰 영향력을 가지고 있음을 보여주고 있습니다. 더 많은 장치가 의료용으로 규제 승인을 받으면서 전자 의료 기록과의 상호 운용성이 향상되고 m 건강은 원격의료 시장 점유율에 대한 기여를 강화하고 있습니다.
서비스는 2024년에 원격의료 시장 점유율의 약 66.2%를 차지했고, 원격 정신 의료는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 28.2%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 정신 건강 붐과 가상 배달의 적성은 이 기세를 설명합니다. 2025년 1월에 에이블 e케어가 암웰 정신과 의료를 인수한 것은 전국적인 커버리지를 목표로 한 통합을 강조하고 있습니다. 행동 의료는 이미 외래 진찰의 57%를 차지했으며 이는 환자가 가상 세션을 선호한다는 것을 나타냅니다. 지불자는 원격 정신 의료를 동등하게 다루고 있으며, 공급자에게 경제적 안정을 가져오고 플랫폼에 대한 지속적인 투자를 촉진하고 있습니다. 따라서, 원격 정신과 의료의 확대는 원격의료 시장 전체의 성장 촉진요인이 되고 있습니다.
원격의료 시장은 유형(원격 병원, 원격 홈, m 건강), 구성요소(제품 및 서비스), 배포 모드(On-Premise 배포, 클라우드 기반 배포 등), 배포 모델(실시간, 상점 및 전달 등), 최종 사용자(공급자, 페이어 등), 지역(북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양 등)으로 구분됩니다. 시장 규모와 예측은 금액(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
2024년 세계의 원격의료 시장 점유율은 북미가 37.8%로 톱을 차지했습니다. 견고한 브로드밴드 인프라와 유리한 상환 정책이 뒷받침 전아메리카 의회 회의에 따르면, 2024년 10월 기준 43주와 컬럼비아 특별구가 원격의료 민간 보험법을 제정하고 41주가 보험 적용 범위 평등을 의무화했습니다. 메디케어의 주요 원격의료 유연성은 2025년 3월까지만 연장되지만, 민간 보험 회사는 가상 퍼스트 혜택을 계약에 통합하기를 계속하고 있습니다. 학술의료센터는 원격의료이노베이션을 상업벤처로 스핀오프시켜 기업이의 활력을 높이고 있습니다. 국가를 가로지르는 면허의 컴팩트화는 지역 간 임상의의 가용성을 확대하고 북미의 원격의료 시장 규모의 리더십을 강화합니다.
아시아태평양은 헬스케어 투자 증가, 스마트폰의 보급, 정부의 지원책에 견인되어 CAGR 19.6%로 예측되는 급성장 지역입니다. 2024년 7월 발표된 Center for Global Digital Health Innovation에 따르면 인도의 eSanjeevani 프로그램은 농촌 지역의 접근성을 높이기 위해 공급자에서 제공업체로, 환자에서 의사로 가는 두 가지 모델을 운영하고 확장 가능한 관민 협력을 입증했습니다. 민간 자본은 병원-재택 스타트업 기업과 AI 기반의 트리어지 채팅봇으로 흘러 분산형 케어에 대한 투자자의 신념을 보여줍니다. 다국어 지원 및 저대역폭 비디오 프로토콜은 문화적, 인프라적 다양성을 지원하여 다양한 지역으로 확장 가능한 배포를 보장합니다. 디지털 헬스 서비스의 급속한 보급으로 아시아는 움직임의 둔한 성숙 지역을 희생하여 원격의료 시장 점유율을 획득합니다.
유럽은 국민 모두 보험 제도와 강력한 규제 틀에 힘입어 꾸준한 성장을 보이고 있습니다. 프랑스의 누벨 아키텐 원격의료 이니셔티브는 간병 시설의 78%에 원격의료 기능을 갖추고, 시설 간의 연계를 촉진하고, 이 지역의 혁신적인 배포 모델을 실증하고 있습니다. 일반 데이터 보호 규칙(General Data Protection Regulation)은 엄격한 데이터 취급 규칙을 부과하고 컴플라이언스 비용을 증가시키는 한편 환자의 신뢰를 높입니다. 유럽 의료 데이터 공간은 회원국 간 상호 운용성 프로토콜의 조화를 목표로 원격의료 공급업체의 인증을 간소화합니다. 이러한 규제의 조정은 유럽 대륙에서의 투자를 유치하고 시장 규모의 확대를 안정시키는 예측 가능한 조건이 갖추어집니다.
The Telemedicine market size is estimated at USD 196.37 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 376.12 billion by 2030, reflecting a robust CAGR of 13.88% during the forecast period.
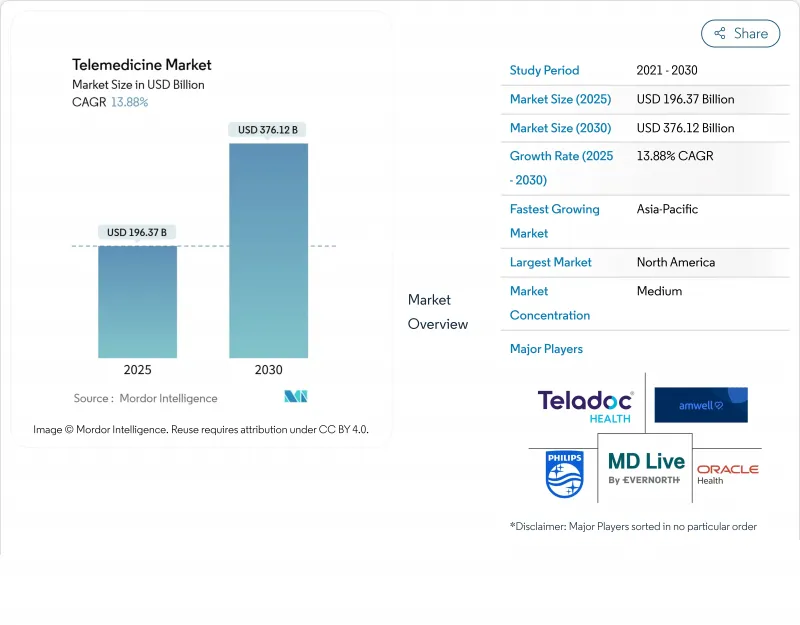
This double-digit expansion signals a decisive transition from pandemic-induced uptake toward the permanent embedding of virtual care as a standard clinical touchpoint. Payers, providers, and policymakers now treat digital health infrastructure as foundational to resilient care delivery, prompting investments in interoperability, cybersecurity, and remote diagnostics. The Telemedicine industry is therefore entering a scale-up phase in which platform breadth, specialist coverage, and data analytics depth determine procurement decisions. One observable outcome is that health systems with mature virtual-first operating models consistently report higher patient-engagement metrics, placing them in a strong position to capture incremental Telemedicine market share over the next five years.
The widening global physician shortage is accelerating telemedicine market adoption as health systems struggle to meet rising patient demand. The Association of American Medical Colleges Report, released in March 2024, projected a United States physician deficit of up to 86,000 by 2036, with one in five current physicians aged 65 or older approaching retirement. Rural areas feel the strain most acutely, where 46.3% of U.S. counties lack a practicing cardiologist, resulting in 31% higher cardiovascular risk for residents, as per an article by Medicus Healthcare Solutions, published in August 2024. Telemedicine platforms mitigate these gaps by enabling specialists to serve multiple facilities remotely, extending reach without physical relocation. Health networks reconfigure on-call rotations to include virtual coverage, subtly improving appointment availability and reducing wait times. A downstream effect of these virtual hubs is improved care continuity because multidisciplinary teams can incorporate remote patient monitoring data during daily rounds. The integrated approach not only elevates quality but also cements telemedicine as an indispensable lever in long-range workforce planning.
Healthcare payers are weaving telemedicine into value-based care contracts, recognizing its potential to lower costs while boosting outcomes. By 2027, an estimated 90 million covered lives are expected to fall under value-based arrangements, marking a pivotal shift away from fee-for-service. Financial incentives now reward providers that leverage virtual care to suppress emergency-department visits and prevent avoidable admissions. Telemedicine's integration is especially pronounced in chronic-disease management, where continuous remote monitoring supports earlier intervention and medication adherence. Payer confidence in virtual-first models has led to stable reimbursement parity for qualified video and audio visits, effectively locking digital pathways into standard benefit designs. The linkage between payment incentives and platform usability is compelling health systems to refine user interfaces for both clinicians and patients, a subtle design focus that reinforces growth in the telemedicine market share.
Heightened data privacy and cybersecurity risks are emerging as a significant barrier to telemedicine adoption, eroding stakeholder trust and increasing compliance costs. Healthcare organizations experienced a 77% decline in Internet Protocol reputation security, exposing them to malware and phishing attacks, as per an article published by PureDome in January 2024. The expansion of connected medical devices introduces additional vulnerabilities, with watchdogs urging better coordination between the United States Food and Drug Administration and cybersecurity agencies to address outdated software, as per an Axios article from January 2024. Providers now allocate larger portions of digital-health budgets to encryption and endpoint security, driving up the total cost of ownership. Smaller clinics often postpone platform upgrades because of these expenses, slowing the telemedicine market penetration in underserved areas. Industry leaders who embed advanced threat-detection protocols differentiate themselves during vendor selection, illustrating how security prowess is evolving into a decisive purchasing criterion across the Telemedicine industry.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Tele-hospitals held 41.3% of the Telemedicine market share in 2024, while mHealth is projected to expand at a 23.5% CAGR through 2030, outpacing traditional tele-hospitals and tele-homes. Consumers increasingly integrate wearables that monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, and blood-oxygen levels into everyday health routines, generating continuous data streams that enrich clinical dashboards. This shift moves healthcare from episodic interaction to ongoing lifestyle management, a trend that resonates with digital-native demographics. Providers leverage mHealth data for population-health stratification, allowing earlier outreach to high-risk cohorts. In emerging markets, mobile-first strategies help health systems leapfrog infrastructure constraints, demonstrating mHealth's outsized influence on the telemedicine industry expansion. As more devices gain regulatory clearance for medical use, interoperability with electronic health records improves, reinforcing mHealth's contribution to the telemedicine market share.
Services control roughly 66.2% of the telemedicine market share in 2024, with telepsychiatry expected to grow at a 28.2% CAGR through 2030. The mental-health boom and virtual delivery's suitability explain the momentum, as physical examinations are less central to psychiatric evaluation. Avel eCare's acquisition of Amwell Psychiatric Care in January 2025 underscores consolidation aimed at nationwide coverage. Behavioral health already accounts for 57% of outpatient visits conducted via telemedicine, illustrating patient preference for virtual sessions. Payers increasingly cover telepsychiatry at parity, providing financial stability to providers and encouraging continued platform investment. The expansion of telepsychiatry, therefore, stands as a major driver of the overall Telemedicine market size growth.
Telemedicine Market is Segmented by Type (Tele Hospitals, Tele Homes, and MHealth), Component (Products and Services), Mode of Delivery (On-Premises Delivery, Cloud-Based Delivery, and More), Deployment Model (Real-Time, Store-And-Forward, More), End User (Providers, Payers, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America leads global Telemedicine market share at 37.8% in 2024, supported by robust broadband infrastructure and favorable reimbursement policies. As of October 2024, forty-three states and the District of Columbia had enacted telehealth private-insurance laws, with forty-one states requiring coverage parity, according to the National Conference of State Legislatures. Although key Medicare telehealth flexibilities are only extended through March 2025, private insurers continue hard-wiring virtual-first benefits into contracts. Academic medical centers spin off telehealth innovations into commercial ventures, adding entrepreneurial vigor. Cross-state licensure compacts expand clinician availability across regions, reinforcing the Telemedicine market size leadership of North America.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with a projected 19.6% CAGR, driven by rising healthcare investment, smartphone penetration, and supportive government initiatives. India's eSanjeevani program demonstrates scalable public-private collaboration, operating two models-provider-to-provider and patient-to-doctor-to broaden rural access, as per the Center for Global Digital Health Innovation, published in July 2024. Private capital flows toward hospital-at-home start-ups and AI-based triage chatbots, signaling investor belief in decentralized care. Multilingual support and low-bandwidth video protocols address cultural and infrastructural diversity, ensuring scalable deployment across diverse geographies. The rapid proliferation of digital health services positions Asia to gain Telemedicine market share at the expense of slower-moving mature regions.
Europe exhibits steady growth, supported by universal healthcare systems and a strong regulatory framework. France's Nouvelle-Aquitaine telemedicine initiative, which equipped 78% of nursing homes with telehealth capabilities, fosters collaboration among establishments and demonstrates the region's innovative deployment models. The General Data Protection Regulation imposes stringent data-handling rules, increasing compliance costs yet enhancing patient trust. The European Health Data Space aims to harmonize interoperability protocols across member states, simplifying certification for telehealth vendors. These regulatory alignments create predictable conditions that attract investment and stabilize Telemedicine market size expansion in the continent.