
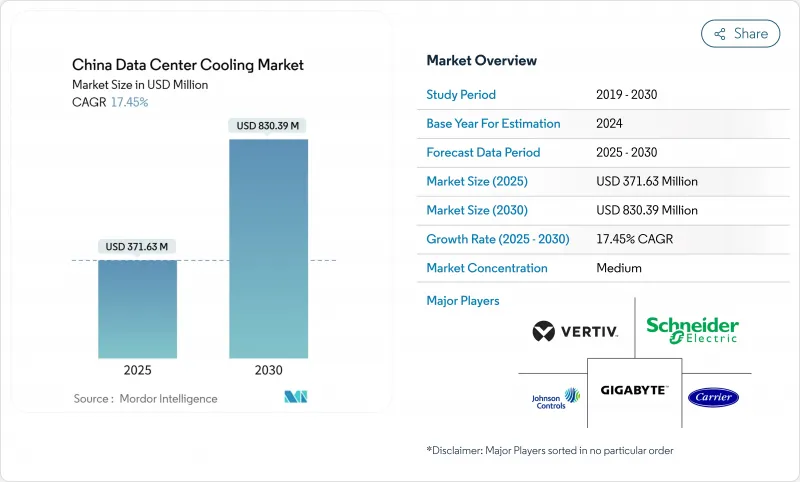
중국 데이터센터 냉각 시장의 2025년 시장 규모는 3억 7,163만 달러로 평가되었고, 2030년에 8억 3,039만 달러에 이를 것으로 예측되며, 2025-2030년의 CAGR은 17.45%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

의무적 전력사용효율(PUE) 상한선, 기존 워크로드 대비 6-8배 더 많은 열을 방출하는 AI 서버 랙 밀도 급증, 정부의 동부 데이터·서부 컴퓨팅 프로그램이 맞물려 액체 기반 냉각에 대한 자본 지출을 가속화하고 있습니다. 운영사들은 1급 도시에서 PUE를 1.3 미만으로 유지하는 기술을 우선시하며, 기존 공기 냉각 시스템에서 직접 칩 냉각, 침지 냉각, 후면 도어 액체 솔루션으로의 전환을 주도하고 있습니다. 동시에 물 부족 규제로 인해 소비를 최소화하면서 열 효율을 극대화하는 폐쇄형 루프 설계가 추진되고 있습니다. 장비 판매가 여전히 지출의 대부분을 차지하지만, 시설 소유주들이 액체 냉각 시스템의 개조 또는 신규 구축을 위한 전문성을 추구함에 따라 특수 서비스 수요가 급증하고 있습니다.
현대식 AI 캐비닛은 기존 서버의 5-10kW 대비 20-130kW를 소비하여 공기 냉각으로는 부족함을 드러내며 액체 기술의 대량 채택을 촉진하고 있습니다. 화웨이의 폐쇄형 액체 냉각 캐비닛은 냉각 전력 96% 절감 및 시설 PUE 1.1 달성으로 하이퍼스케일 수준의 실용성을 입증했습니다. 귀안, 울란차부, 우후의 국가급 AI 컴퓨팅 클러스터는 구축 단계부터 액체 솔루션을 지정하며, 데이터센터 계획에서 칩 성능과 동등한 수준으로 열 설계를 고려하는 구조적 전환을 강조하고 있습니다.
베이징의 제14차 5개년 계획은 2025년까지 모든 신규 데이터센터의 PUE를 1.5 미만으로 운영할 것을 요구하며, 상하이는 기준을 1.3으로 더욱 강화했습니다. 2023년 그린 데이터센터 표준은 준수 범위를 물 소비 비율 및 재생에너지 조달로 확대하여, 대규모 효율 목표 달성을 위한 유일한 실용적 경로로서 액체 냉각의 위상을 공고히 했습니다.
데이터센터 전력 소비량은 2025년 200TWh에서 2030년 400-600TWh로 증가할 전망이며, 장쑤성과 저장성의 전기 요금 인상으로 기존 장비 감가상각으로 인한 절감 효과를 상쇄할 만큼 운영 비용이 상승할 것입니다. 동부 데이터·서부 컴퓨팅 정책은 부하를 재생에너지 풍부 지역으로 이전해 부담을 상쇄하지만, 운영사는 지연 시간과 광섬유 백홀 제약 조건을 조율해야 합니다.
하이퍼스케일러는 2024년 매출의 46.5%를 차지했으며, 중국 데이터센터 냉각 시장 규모에 대한 기여도는 2030년까지 연평균 17.9% 성장할 것으로 전망됩니다. 이들 기업은 랙당 100kW를 초과하는 AI 클러스터를 구축하여 열 여유 공간 확보와 PUE 규정 준수를 위해 액체 기술이 필수적입니다. 이들의 규모는 랙당 냉각 비용을 낮추는 동력이 되어 기업 및 엣지 운영사들이 현재 모방하는 기준을 제시합니다. 그러나 엣지 사이트는 공간 및 유지보수 제약으로 인해 컴팩트한 후면 열교환기를 선호합니다. 하이퍼스케일러의 확산은 공기 시스템이 개조용 틈새 시장을 유지하더라도 신규 증설 용량에서 액체 기반 인프라가 주류를 이룰 것임을 보장합니다.
코로케이션 사업자는 전용 액체 냉각 구역을 프리미엄 서비스로 묶어 밀집도를 마진과 차별화된 고객 경험으로 전환함으로써 이 같은 추세를 반영합니다. 기업 시설은 완전 침수 방식 도입에서 뒤처지지만 기존 냉각 설비를 확장하기 위해 칩 직결 루프를 시범 운영 중입니다. 이러한 움직임들이 결합되어 모든 운영자 부문이 AI 대비 열 설계로 진화함에 따라 중국 데이터센터 냉각 시장은 고성장 궤도를 유지합니다.
2024년 티어 3 사이트는 성숙한 설계 프레임워크와 가동 시간 대 자본 지출의 경쟁적 균형 덕분에 지출의 67.1%를 차지했습니다. 그러나 AI 훈련 워크로드는 계획되지 않은 다운타임조차 몇 분도 감당할 수 없기 때문에 티어 4 시설 건설은 연평균 19.2% 성장률을 보이고 있습니다. 따라서 투자자들이 유지보수 중에도 랙 온도를 30°C 이내로 유지하는 내결함성 및 동시 유지보수 가능한 액체 시스템을 우선시함에 따라 중국 데이터센터 냉각 시장의 티어 4 시설 규모는 급속히 확대될 것입니다.
티어 1 및 티어 2 시설의 점유율은 랙당 전력 및 냉각 용량이 15kW 미만으로 제한되면서 꾸준히 잠식되고 있습니다. 한편, 티어 3 사양은 이중 루프 액체 인프라로 개조되어 운영사가 신규 티어 4 예산 없이도 고객의 새로운 밀도 요구사항을 충족할 수 있게 되었습니다. 이러한 티어 진화는 중국 데이터센터 냉각 시장에서 AI 중심 구축의 기본으로 액체 기술을 확고히 합니다.
중국의 데이터센터 냉각 시장은 데이터센터 유형(하이퍼스케일러(소유 및 임대), 기업 및 엣지, 코로케이션), 티어 유형(티어 1 및 2, 티어 3, 티어 4), 냉각 기술(공기 기반 냉각, 액체 기반 냉각), 컴포넌트(서비스, 장비)로 구분됩니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
The China data center cooling market is valued at USD 371.63 million in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 830.39 million by 2030, advancing at a 17.45% CAGR during 2025-2030.
Mandatory Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) caps, surging AI server rack densities that dissipate 6-8 times more heat than legacy workloads, and the government's Eastern Data and Western Compute program are converging to accelerate capital outlays for liquid-based cooling. Operators are prioritizing technology that keeps PUE below 1.3 in Tier 1 cities, driving a pivot away from conventional air systems toward direct-to-chip, immersion, and rear-door liquid solutions. At the same time, water-stress regulations are pushing closed-loop designs that minimise consumption while maximising thermal efficiency. Although equipment sales still dominate spending, demand for specialised services is climbing fast as facility owners seek expertise to retrofit or green-field liquid deployments.
Modern AI cabinets consume 20-130 kW versus 5-10 kW for legacy servers, rendering air cooling insufficient and propelling mass adoption of liquid technologies. Huawei's closed liquid-cooled cabinet cuts cooling power by 96% and lowers facility PUE to 1.1, proving viability at the hyperscale level. National flagship AI compute clusters in Gui'an, Ulanqab, and Wuhu now specify liquid solutions at the build-out stage, underscoring a structural shift that places thermal design on par with chip performance in data-center planning.
Beijing's 14th Five-Year plan requires all new data centers to operate below 1.5 PUE by 2025, while Shanghai tightens the threshold to 1.3. The 2023 Green Data Center standard expands compliance to water-consumption ratios and renewable-energy sourcing, cementing liquid cooling as the only practical route to meet efficiency targets at scale.
Data center power draw is expected to climb from 200 TWh in 2025 toward 400-600 TWh by 2030, with tariffs in Jiangsu and Zhejiang raising operating costs enough to negate savings from legacy equipment depreciation. The Eastern Data and Western Compute initiative counterbalances the burden by relocating load to renewable-rich provinces but requires operators to reconcile latency and fibre-backhaul constraints.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Hyperscalers accounted for 46.5% of 2024 revenue, and their contribution to the China data center cooling market size is forecast to expand at 17.9% CAGR through 2030. These firms build AI clusters that exceed 100 kW per rack, making liquid technology non-negotiable for thermal headroom and PUE compliance. Their scale also drives down per-rack cooling cost, creating a benchmark that enterprise and edge operators now emulate. Edge sites, however, favour compact rear-door heat exchangers due to space and maintenance limits. The hyperscaler wave ensures that liquid infrastructure will dominate new capacity additions, even though air systems retain a retrofit niche.
Colocation operators mirror this trajectory by bundling dedicated liquid zones as premium services, converting density into both margin and differentiated customer experience. Enterprise facilities lag on full immersion adoption but are piloting direct-to-chip loops to stretch existing chiller plants. Combined, these moves keep the China data center cooling market on a high-growth path as every operator segment advances toward AI-ready thermal architectures.
Tier 3 sites captured 67.1% of spending in 2024 thanks to their mature design frameworks and competitive balance of uptime vs. capex. Yet Tier 4 builds are growing at 19.2% CAGR because AI training workloads cannot afford even minutes of unplanned downtime. The China data center cooling market size for Tier 4 facilities will therefore rise swiftly as investors prioritise fault-tolerant, concurrently maintainable liquid systems that keep racks within 30 °C even during maintenance.
Tier 1 and Tier 2 footprints are steadily cannibalised as their power and cooling envelopes top out below 15 kW per rack. Meanwhile, Tier 3 specifications are being retrofitted with dual-loop liquid infrastructure so operators can satisfy new customer density requirements without a green-field Tier 4 budget. This tier evolution reinforces liquid technology as the baseline for any AI-centric build in China's data center cooling market.
China Data Center Cooling Market is Segmented by Data Center Type (Hyperscalers (Owned and Leased), Enterprise and Edge, Colocation), Tier Type (Tier 1 and 2, Tier 3, Tier 4), Cooling Technology (Air Based Cooling, Liquid Based Cooling), Component (Service, Equipment). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).