
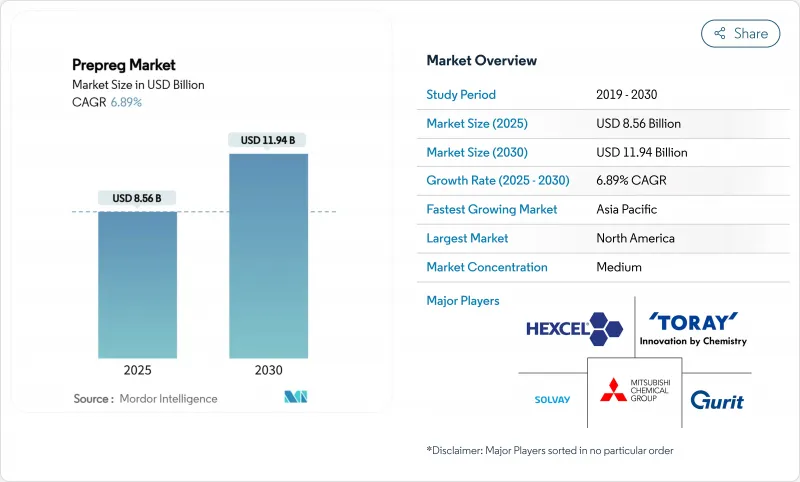
프리프레그 시장 규모는 2025년에 85억 6,000만 달러로 추정되고, 2030년에는 119억 4,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 6.89%를 나타낼 전망입니다.

복합재를 다용한 주익과 동체에 의존하는 민간 항공기 프로그램, 블레이드 길이가 100m를 넘는 해상 풍력 발전 설비, 열가소성 플라스틱 구조를 선호하는 신흥의 eVTOL 플랫폼 등이 이 확대를 총체적으로 지원하고 있습니다. 오토클레이브의 에너지 비용과 재활용 갭이 단기적인 기세를 약화하더라도 항공우주 분야에서의 강력한 연료 소비 경제성, 정책 주도의 재생에너지 건설, 자동차의 경량화 정책이 구조용 복합재 수요를 강화하고 있습니다. 경쟁 차별화는 수직 통합, 자동 레이업 기술 및 비용을 억제하면서 품질을 보호하는 인증 재료 데이터베이스에 달려 있습니다. 공급 환경은 완만하지만 긴축되고 있으며 기존 공급업체는 특히 표준 탄성률 탄소섬유 등급에서 중국의 급속한 생산 능력 증대에 대항하여 가격 포인트를 사수하고 있습니다.
보잉의 777X형기와 에어버스의 A350형기는 각각 중량비 50% 이상의 탄소섬유 강화 폴리머를 사용하고 있어 복합재를 다용한 제조 스케줄을 계속하고 있기 때문에 민간 항공기의 생산이 증가하고 있습니다. 고양력 구조 부품, 기체 동체, 날개 표피는 엄격한 피로 및 손상 저항 요건을 충족하는 인증 에폭시 기반 프리프레그에 의존합니다. NATO 회원국 전체의 방어 근대화는 이러한 동향을 반영하고 레거시 플릿은 항속 거리와 페이로드를 확장하는 경량 미션 시스템으로 개수되고 있습니다. 도레이와 헥셀과 같은 공급업체는 장기 계약으로 안정적인 납품을 보장하면서 인증 비용을 상각할 수 있습니다. 항공기 1대당 복합재 사용량이 증가함에 따라 프리프레그 시장은 자체 재료 데이터베이스에 지원되는 수량 성장과 평균 판매 가격 상승 모두에서 이익을 얻고 있습니다.
오프 쇼어 로터의 평균 직경은 현재 200m를 초과하고 블레이드의 길이는 100m를 초과 할 수 없으며 스파 캡의 강성 요구가 증가하고 있습니다. 탄소섬유 프리프레그의 스파퍼 캡은 구조적 무결성을 유지하면서 블레이드 무게를 25% 줄이고 기존 재킷 기초에 대형 터빈을 설치할 수 있습니다. 베스타스사와 같은 유럽의 OEM은 유리섬유제에서 탄소와 유리의 하이브리드 구조로 이동하고 있으며, 중국 제조업체도 능력 증강 목표를 달성하기 위해 추종하고 있습니다. 진공 보조 수지 전송 성형 및 자동 섬유 배치는 사이클 시간을 단축하고, 인건비를 줄이고, 비용 경쟁력을 강화합니다. 북해와 남중국해에서 가속하는 해상풍력발전의 약속으로 탄소섬유의 지속적인 수요는 프리프레그 시장의 견고한 장기 파이프라인을 확보합니다.
대형 항공우주용 오토클레이브의 자본 비용은 200만 달러를 넘어 상당한 에너지를 소비하는 6-8시간의 열압 사이클을 가동시킵니다. 소규모 Tier 2 공급업체는 자금 조달 장벽이 높고 세계 확장이 제한되고 수요가 급증할 때 공급 병목 위험을 초래합니다. 아웃 오브 오토 클레이브 프로세스 - 진공 가방 전용 경화, 수지 주입 및 오븐 기반 사이클 -은 에너지를 최대 50% 줄이지만 1차 구조용 오토 클레이브 유래의 다공성 제어는 아직 재현할 수 없습니다. 보조 항공우주 부품에 대한 채택이 증가하면 비용 봉투가 감소합니다. 그러나 동체나 주익의 인증에 지연이 생기면 오토클레이브의 우위성이 유지되어 프리프레그 시장의 보급을 계속 억제하게 됩니다.
열경화성 수지 시스템은 민간 항공기와 탄도 등급의 방어 하드웨어에 있어서 인증의 심화에 힘입어 2024년에 73.45%의 매출을 유지했습니다. 에폭시 수지는 고온 경화가 항공기의 수명주기에 걸쳐 안정적인 기계적 특성을 발휘하는 주요 날개와 몸통 부분에 필수적인 것은 아닙니다. 이와는 대조적으로 열가소성 등급은 eVTOL, 자동차, 수소 저장에 대한 요구가 증가함에 따라 CAGR 8.88%를 나타낼 것으로 예측됩니다. 이 확대는 2025-2030년 프리프레그 시장 규모에 13억 5,000만 달러 기여합니다. 폴리에테르 에테르 케톤과 폴리페닐렌 설파이드 제품군은 최대 220℃의 내열성을 제공하여 유도 용접을 가능하게 합니다.
폐쇄 루프의 재료 흐름을 추진하면 열가소성 플라스틱의 매력이 향상됩니다. 높은 토니지 압축 프레스를 가동하고 있는 자동차 OEM은 기존의 180℃ 에폭시 사이클에서 3분 이하의 열가소성 수지 캠페인으로 전환했을 때 사이클 타임이 40% 개선되었다고 보고했습니다. 한편, 비스말레이미드계와 페놀계는 고온 제트 엔진의 덕트나, 난연성·발연성·독성에의 적합이 요구되는 내장 패널로 틈새를 유지하고 있습니다. 전반적으로, 수지 화학 간의 대조적인 성장 궤도는 프리프레그 시장에서 경쟁력의 다양성을 보장합니다.
탄소섬유는 비교할 수 없는 강성 대 중량비가 민간 여객기, 우주 발사, 포뮬러 1의 요건을 지원하기 때문에 2024년에는 금액 기준으로 81.22%를 지배했습니다. 항공기의 공허 중량을 1kg 줄일 때마다 서비스 수명 동안 최대 75t의 연료를 절약할 수 있습니다. 그러나 유리 섬유는 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 7.99%의 성장이 예측되고 있으며, 5G 일렉트로닉스, LED 기판, 저탄성률을 허용하는 비용 중시의 모빌리티 용도 등이 그 요인이 되고 있습니다. 특수 유리 섬유 프리프레그를 배합한 고주파 프린트 기판용 적층판은 24GHz 레이더 이후의 유전 벤치마크에 적합합니다.
풍력 터빈의 스파 캡에서는 탄소 스킨과 유리 코어 패브릭을 결합한 하이브리드 라미네이트가 원료 비용을 낮추면서 무게를 최적화하고 대응 가능한 볼륨을 확대합니다. 아라미드 섬유는 탄도 보호 및 충격 에너지 흡수 분야에서 제한적인 시장 존재를 유지하지만, 각 보강재가 수행하는 재료 고유의 역할을 강조하고 있습니다. 중국 제조업체가 생산량을 확대함에 따라 저급 탄소섬유 가격이 저하되고 상대 비용 델타가 확대되고 성능 마진이 좁은 지역에서의 대체 논쟁에 박차가 걸립니다.
북미는 2024년 프리프레그 시장에서 최대 37.88%의 점유율을 유지하고 보잉 복합재를 많이 사용하는 787, 777X, 독자적인 우주 발사 구조에 의해 지원되었습니다. 국방부의 근대화 계획은 회전익기, 무인 시스템, 극초음속기에도 재료 수요를 확대하여 안정된 다년 수주를 확보합니다. 이 지역의 인증 생태계는 헥셀 및 도레이 어드밴스드 컴포지트와 같은 국내 공급업체에게 유리하며, 두 회사는 탄화에서 프리 그레이드까지 수직 통합 라인을 운영하고 있습니다. 하지만 2025년 민간항공우주사업의 매출은 주요 협폭동체의 납품조정 후에 떨어지고, 그 이외는 견조한 방위사업의 수주 잔 속에서 단기 사이클에서의 변동이 부각되었습니다.
아시아태평양은 2030년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)이 8.12%로 예측되어 가장 급성장하고 있는 지역으로 부상했습니다. 중국의 국영 탄소섬유 제조업체는 2030년까지 세계 생산 능력의 50% 가까이를 장악하는 기세로 가격대를 낮추고 보다 광범위한 산업으로의 섭취를 촉진합니다. COMAC의 C919와 CR929와 같은 국내 항공우주 프로그램과 국내 eVTOL 프로토타입은 고품질 프리프레그 수요를 받아들이고 있습니다. 일본 도레이와 테이진은 고탄성 섬유와 자동차용 열가소성 수지 적층판을 통해 기술적 리더십을 유지하고 한국의 수소저장탱크 구상은 토우 프리프레그의 성장에 박차를 가하고 있습니다.
유럽은 에어버스의 날개조립, 영국의 선진추진기술의 연구개발, 북해에서의 적극적인 해상풍력발전의 목표에 힘입어 1자리대 중반의 성장을 유지합니다. 정책 입안자가 사용한 복합재 폐기물의 정사를 강화해, 가치가 높은 섬유를 재생할 수 있는 열분해와 솔보리시스의 파일럿 플랜트에 대한 투자를 가속. Gurit사가 독일 항공우주용 프리프레그 생산 능력을 확대하는 반면, 스위스 생산 라인을 폐쇄하기로 결정한 것은 유럽의 에너지 가격이 급박한 가운데 비용 합리화를 보여줍니다. 한편, 자동차용 복합재의 채용은 재생가능에너지 및 민간항공기 분야에서는 경량소재가 면제되고 있는 것, 잠재적인 탄소섬유의 사용제한에 관한 규제의 불확실성에 직면하고 있습니다.
The Prepreg Market size is estimated at USD 8.56 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 11.94 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.89% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Commercial aircraft programs that rely on composite-rich wings and fuselages, offshore wind installations that push blade lengths past 100 m, and emerging eVTOL platforms that favor thermoplastic structures collectively underpin this expansion. Strong fuel-burn economics in aerospace, policy-driven renewable-energy build-outs, and vehicle lightweighting regulations reinforce structural-composite demand even as autoclave energy costs and recycling gaps temper near-term momentum. Competitive differentiation hinges on vertical integration, automated lay-up technologies, and certified material databases that safeguard quality while controlling cost. A moderate but tightening supply landscape leaves incumbent suppliers defending price points against rapid Chinese capacity additions, particularly in standard-modulus carbon fiber grades.
Commercial aircraft production is rising as Boeing's 777X and Airbus's A350 continue composite-heavy build schedules, each incorporating more than 50% carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer by weight. High-lift structural components, fuselage barrels, and wing skins rely on certified epoxy-based prepreg that meets stringent fatigue and damage-tolerance requirements. Defense modernization across NATO members mirrors these trends, retrofitting legacy fleets with lighter mission systems that extend range and payload. Long-term contracts allow suppliers such as Toray Industries and Hexcel Corporation to amortize qualification costs while guaranteeing stable deliveries. As composite usage per aircraft climbs, the prepreg market benefits from both volume growth and higher average selling prices anchored by proprietary material databases.
Average offshore rotor diameters now exceed 200 m, forcing blade lengths above 100 m and increasing spar-cap stiffness demands. Carbon-fiber prepreg spar caps reduce blade weight by 25% while maintaining structural integrity, enabling larger turbines to be installed on existing jacket foundations. European OEMs such as Vestas have shifted from fiberglass to hybrid carbon-glass architectures, and Chinese manufacturers are following to meet capacity-addition targets. Vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding and automated fiber placement shorten cycle times and cut labor expenses, bolstering cost competitiveness. With offshore wind commitments accelerating in the North Sea and South China Sea, sustained carbon-fiber demand secures a robust long-term pipeline for the prepreg market.
Large-format aerospace autoclaves exceed USD 2 million in capital cost and operate 6-8-hour heat-pressure cycles that consume substantial energy. Smaller Tier-2 suppliers face steep financing barriers, limiting global expansion and introducing supply-bottleneck risk when demand surges. Out-of-autoclave processes-vacuum-bag-only curing, resin-infusion, and oven-based cycles-reduce energy by up to 50% but cannot yet replicate autoclave-derived porosity control for primary structures. Incremental adoption in secondary aerospace parts lowers cost envelopes; however, any delay in fuselage or wing certification sustains the autoclave's dominance and continues to restrain wider prepreg market penetration.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Thermoset systems retained 73.45% revenue in 2024, underpinned by certification depth in commercial aviation and ballistic-grade defense hardware. Epoxies remain indispensable for primary wings and fuselage sections where high-temperature cures translate to consistent mechanical properties over the aircraft life cycle. In contrast, thermoplastic grades are projected to advance at an 8.88% CAGR on rising eVTOL, automotive, and hydrogen-storage requirements. That expansion contributes USD 1.35 billion to the prepreg market size between 2025 and 2030. Polyetheretherketone and polyphenylene sulfide families deliver heat resistance up to 220 °C and allow induction welding, thereby reducing assembly fastener counts and maintenance downtime.
The push for closed-loop material flows strengthens thermoplastic appeal, as scrap off-cuts can be re-melted into secondary mouldings without degrading performance. Automotive OEMs running high-tonnage compression presses report cycle-time improvements of 40% when switching from classic 180 °C epoxy cycles to sub-3-minute thermoplastic campaigns. Meanwhile, bismaleimide and phenolic systems hold their niche in high-temperature jet-engine ducts and interior panels that demand flame-smoke-toxicity compliance. Overall, contrasting growth trajectories between resin chemistries ensure competitive diversity within the prepreg market.
Carbon fiber controlled 81.22% by value in 2024 as its unmatched stiffness-to-weight ratio underpins commercial airliner, space-launch, and Formula 1 requirements. Each additional kilogram trimmed from an aircraft's operating empty weight saves up to 75 t of fuel over its service life, a direct economic lever that keeps carbon pricing resilient even during downturns. Glass fiber, however, is projected for 7.99% CAGR growth through 2030, riding 5G electronics, LED substrates, and cost-sensitive mobility applications that tolerate lower modulus values. High-frequency printed-circuit-board laminates formulated with specialized glass-fiber prepreg meet dielectric benchmarks for 24 GHz radar and beyond.
Hybrid laminates combining carbon skins with glass core fabrics in wind-turbine spar caps optimize weight while lowering raw-material cost, widening addressable volume. Aramid fibers retain limited market presence in ballistic protection and impact-energy absorption but underscore the material-specific role each reinforcement plays. As Chinese producers scale output, lower-grade carbon fiber pricing compresses, widening the relative cost delta and spurring substitution debates where performance margins are narrower.
The Prepreg Market Report is Segmented by Resin Type (Thermoset, Thermoplastic), Fiber Type (Carbon, Glass, Aramid), Form (Unidirectional Tapes, Tow Prepreg, Fabric/Woven, Organosheets), End-User Industry (Aerospace and Defense, Wind Turbine, Automotive, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America retained the largest 37.88% share of the prepreg market in 2024, buoyed by Boeing's composite-intensive 787, 777X, and proprietary space-launch structures. Pentagon modernization programs extend material demand into rotorcraft, unmanned systems, and hypersonic vehicles, ensuring stable multi-year order books. The region's certification ecosystem favors domestic suppliers such as Hexcel and Toray Advanced Composites, both of which operate vertically integrated lines from carbonization to prepregging. Nevertheless, 2025 commercial-aerospace revenues slipped after a major narrow-body delivery adjustment, highlighting short-cycle variability amid otherwise strong defense backlogs.
Asia-Pacific emerges as the quickest-growing geography with an 8.12% CAGR forecast to 2030. Chinese state-backed carbon fiber producers are on pace to command nearly 50% of global capacity by 2030, lowering price points and catalyzing broader industrial uptake. Indigenous aerospace programs such as COMAC's C919 and CR929, along with domestic eVTOL prototypes, provide captive demand for high-grade prepreg. Japan's Toray and Teijin maintain technology leadership through high-modulus fibers and automotive-qualified thermoplastic laminates, while South Korea's hydrogen-storage tank initiatives fuel tow-prepreg growth.
Europe sustains mid-single-digit growth anchored by Airbus wing-assembly, UK advanced-propulsion R&D, and aggressive offshore-wind targets in the North Sea. Policymakers intensify scrutiny of end-of-life composite waste, accelerating investment into pyrolysis and solvolysis pilot plants that can reclaim high-value fiber. Gurit's decision to expand German aerospace-prepreg capacity while shuttering a Swiss line illustrates cost-rationalization amid tight European energy pricing. Meanwhile, automotive composite adoption faces regulatory uncertainty over potential carbon-fiber usage limits, though lighter materials remain exempt in renewable-energy and commercial-aviation contexts.