
농기구 렌탈 시장 규모는 2025년에 548억 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년) CAGR 5.70%로 성장할 전망이며, 2030년에는 685억 달러에 달할 것으로 예측됩니다.

트랙터에 대한 안정적인 수요, 디지털 렌탈 플랫폼의 급성장, 정부의 기계화 프로그램 목표는 이러한 꾸준한 확장을 지원합니다. 아시아태평양의 소규모 농부, 북미의 짧지만 격렬한 수확기, 유럽의 지속가능성 규제는 지역마다 다른 비즈니스 기회를 형성합니다. AI를 활용한 플릿 관리와 온디맨드 예약을 융합시킨 디지털 마켓플레이스가 이용 기회를 확대하는 한편 ESG 연동형 금융이 공급자를 전기자동차나 저배출 가스 플릿으로 유도하고 있습니다. 경쟁은 현재 이용 분석, 자율주행기능, 라스트원마일 서비스에 달려 있으며, OEM에 지원된 딜러와 기술에 앞서 진입한 기업 모두 수익성 높은 성장을 위해 자본 부담이 적고 데이터가 풍부한 모델을 정교하게 해야 합니다.
GPS 대응 트랙터와 센서가 있는 수확기의 구입 가격이 상승하고 아시아태평양의 소규모 농가에게 구입하기 쉬운 가격 차이가 넓어지고 있습니다. 기계의 평균 가격이 25-30% 상승했기 때문에 대여 수요가 35% 급증했습니다. 인도의 농업 기계화에 관한 제출은 2014-2024년 8억 7,200만 달러의 보조금을 교부하고, 자본 집약적인 자산을 마을 수준에서 이용할 수 있도록 풀링하는 74,144개의 커스텀 고용 센터를 촉진했습니다. 이러한 허브는 현재 IoT 차량 모니터링 및 스마트폰 예약의 조합으로, 농부는 감가상각하는 장비를 소유하지 않고 정밀 농업을 이용할 수 있습니다.
OECD 경제권에서의 노동력 부족은 이용 가능한 현장 노동력을 5분의 1 가까이까지 삭감하고 있으며, 생산자를 유연한 계약으로 이용 가능한 자율주행 트랙터로 밀고 있습니다. 로봇공학, LiDAR, 루트플래닝 소프트웨어를 갖춘 렌탈 차량은 피크시 반복적인 경작이나 살포 작업을 커버하여 가동률을 높이고 임금 인플레이션을 완화합니다. 머신만의 작업을 둘러싼 윤리적, 책임적인 논의는 뿌리 깊지만, 실시간 진단 및 지오펜싱은 다운타임을 줄이고 안전 의무 준수를 지원합니다.
많은 아프리카 국가에서는 모바일 퍼스트 매칭 앱에도 불구하고 기계화율은 여전히 6% 미만으로 남아 있습니다. 정보의 비대칭과 위험 회피의 의식은 기계가 가까이 있더라도 그 사용을 방해합니다. 이 갭을 메우기 위해 특주품과 농작물 보험료를 연결하는 시험적인 보급 프로그램이 시작되고 있지만, 규모 확대에는 지속적인 아웃리치 및 마이크로 트레이닝이 필수적입니다.
트랙터는 경작, 운반, 동력 취출 용도 분야에서 일정한 수요에 힘입어 2024년 수익의 대부분을 창출했습니다. 38.10%의 농기구 렌탈 시장 점유율은 모든 함대에서 핵심 역할을 반영하며, 전체 시즌의 가동률을 지원합니다. 수확기는 농기구 렌탈 시장에서 작은 슬라이스이지만 높은 스티커 가격으로 많은 생산자에게 단창 렌탈이 유일한 실현 가능한 옵션이기 때문에 CAGR은 가장 빠른 7.40%에 달하는 기세입니다. 수확기의 신형 모델에 내장된 정밀 수율 매핑과 오토스티어 제어는 시간당 가치를 높이고 공급자가 성과 기반 가격 설정을 도입하도록 촉구합니다. 스프레더, 베일러 및 파종기는 작물의 친환경과 관련된 좁은 임대 창을 차지하고 디지털 플랫폼이 수요 예측 알고리즘에 의해 평준화되는 스케줄링의 피크를 생성합니다. 특수 장비는 멀티 장비 패키지에 번들되어 바구니 크기를 높이고 전체 생산 사이클 고객을 고정시킵니다.
두 번째 동향은 연속 트랙터에서 수확기로의 자동화 전환입니다. 북미의 초기 도입 기업은 현재 짧은 수확 기간 동안 인건비를 줄이는 자동 운전 콤바인을 찾고 있습니다. 이 시프트는 감가상각 곡선을 변화시키고 대여 회사는 잔존 가치의 전제를 재조정하고 임대 기간을 급속한 기술 갱신 주기에 맞추어야 합니다. 기기의 접속성이 깊어짐에 따라, 수량 맵, 토양 압축의 인사이트, 기계 건강 상태의 원격 측정 등 데이터의 수익화가, 종래의 렌탈 수입과 나란한 부차적인 수입 라인으로서 부상해 옵니다.
71-130마력의 중형 트랙터는 소규모 농장에서의 작업에 최적인 연비 효율과 능력을 겸비하고 있기 때문에 2024년 농기구 렌탈 시장 규모의 27.40%를 차지했습니다. 250마력이 넘는 대형 유닛은 현재 틈새 시장이지만 농지 통합 및 노동 시간 규제는 보다 대형 스마트 기기를 선호하므로 CAGR 8.50%에서 다른 모든 브래킷을 초과할 것으로 예측됩니다. 이러한 고마력 차량은 엄청난 날씨를 요구하며 풀 서비스 제공업체만 지원할 수 있는 엄격한 운송 및 유지보수 요구 사항을 부과합니다. 30마력 이하의 트랙터는 여전히 원예나 가축이 좁은 작물에는 불가결하며, 131-250마력의 모델은 범용성이 높은 중거리 작업과 특수한 중작과의 갭을 메웁니다. 파워 믹스의 진화는 임대 회사에게 함대의 다양화, 가동 위험 헤지, 연료비 및 텔레매틱스로 검증된 부하율에 링크한 역동적인 가격 설정의 구축을 촉구하고 있습니다.
이와 병행하여 OEM은 유럽 및 캘리포니아의 배기 가스 규제 강화를 지원하기 위해 전체 전력 클래스에 Tier4-Final 엔진과 하이브리드 드라이브 트레인을 통합합니다. ESG와 연계된 대출을 활용하는 공급자는 자본 비용을 절감하고 경쟁력 있는 시간에 반영됩니다. 또, 텔레매틱스를 활용한 부하 추적에 의해 사용량 베이스의 청구에 대한 시프트가 가능하게 되어, 달력이 아니라, 납품된 마력 시간에 코스트를 맞출 수 있게 되어 있습니다.
농기구 렌탈 시장은 장비 유형별(트랙터, 기타), 출력별(30HP 미만, 기타), 구동 유형별(이륜 구동, 기타), 비즈니스 모델별(오프라인 딜러 및 코프야드, 기타), 최종 사용자 농장 규모별(소규모(5헥타르 미만), 기타), 임대 기간별(단기(3M 미만), 기타), 지역별로 구분됩니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)과 수량(단위)으로 제공됩니다.
아시아태평양은 소규모 농가를 위한 보조금 제도에 힘입어 농기구 대여 시장의 2024년 수익의 44.25%를 창출했습니다. 인도의 74,144개의 맞춤 고용 센터와 중국의 보조금 연동형 토지 입찰 규칙은 농부의 부채를 부풀리지 않고 기계화를 확대하고 있습니다. 스마트폰과 현지어 앱은 투명한 예약과 디지털 결제를 가능하게 하고, 쌀, 밀, 원예의 밸류체인 전반에 걸쳐 이용률을 높이고 있습니다. 정밀 장비의 비용은 여전히 높기 때문에 공급자는 공유 소유 구조를 활용하여 기술을 광범위한 사용자 계층에 감가 상각하고 헥타르 당 대여료를 저렴한 수준으로 유지합니다.
북미에서는 성숙하면서도 진화하는 상황을 볼 수 있습니다. 옥수수 벨트의 수확량은 250 마력 이상의 트랙터와 결합에 대한 단기적인 왕성한 수요를 견인하며 9월에서 10월까지 가격 프리미엄이 확대됩니다. 콜로라도 및 기타 주에서는 수리권에 관한 법률이 제정되며 OEM은 진단 도구를 제공해야 하며 가동 중지 시간 및 임대료가 인하될 수 있습니다. 자율적인 리노베이션과 전기 드라이브 트레인은 기후 변화와 관련된 인센티브를 받을 자격이 있으며 대여 대기업과 지역 독립 기업 간에 플리트 업데이트를 촉구합니다.
유럽에서는 이질성이 두드러집니다. 서유럽의 생산자들은 지가 상승과 엄격한 배출량 규제를 극복하기 위해 앱 기반 대여를 채택하고 있습니다. ESG 연동 대출은 전기 트랙터, 바이오연료 수확기 및 저경기 기구를 통합한 함대의 차입 비용을 절감합니다. 유럽 그린 거래의 지속가능성 목표는 임대를 매력적인 컴플라이언스 경로로 만들고 자산 소유에서 성과 기반 서비스로 중점을 둡니다. 중·동유럽에서는 여전히 중간 규모의 가족 경영이 주류이며, 소유하는 핵심 트랙터와 렌탈하는 특수 기계를 조합함으로써 비용과 기술의 균형을 맞추고 있습니다.
The Farm Equipment Rental Market size is estimated at USD 54.8 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 68.5 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.70% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
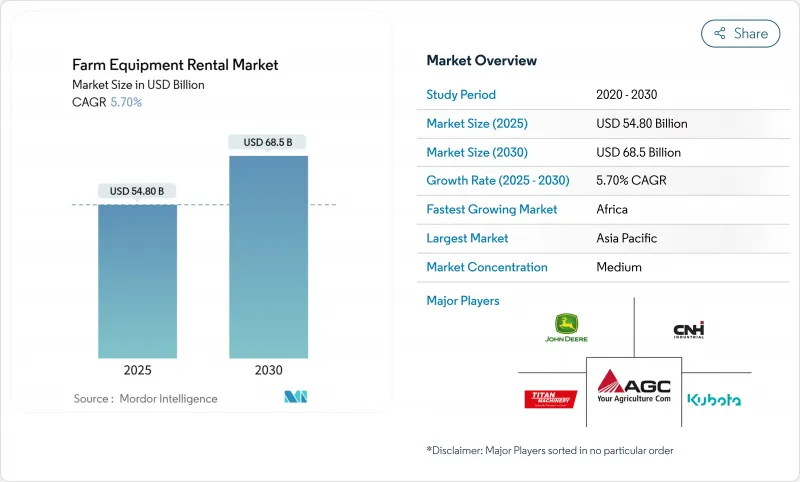
Consistent demand for tractors, rapid growth in digital rental platforms, and targeted government mechanization programs underpin this steady expansion. Asia Pacific prevailing smallholder structure, North America's short but intense harvest windows, and Europe's sustainability regulations shape distinctly regional opportunities. Digital marketplaces that marry AI-driven fleet management with on-demand booking are widening access, while ESG-linked finance is nudging providers toward electric and low-emission fleets. Competition now hinges on utilization analytics, autonomous capabilities, and last-mile service, forcing both OEM-backed dealers and technology-first entrants to refine capital-light, data-rich models for profitable growth.
Rising acquisition prices for GPS-enabled tractors and sensor-rich harvesters are widening the affordability gap for Asia Pacific smallholders. Rental demand surged by 35% as average machinery prices climbed 25-30%. India's Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization issued USD 872 million in subsidies between 2014-2024, catalyzing 74,144 Custom Hiring Centers that pool capital-intensive assets for village-level access. These hubs, now pairing IoT fleet monitoring with smartphone booking, let farmers tap precision agriculture without owning depreciating equipment.
Labor shortages in OECD economies have trimmed the available field workforce by nearly one-fifth, pushing growers toward autonomous tractors available on flexible contracts. Rental fleets outfitted with robotics, LiDAR, and route-planning software cover repetitive tillage and spraying tasks during peak periods, lifting utilization and mitigating wage inflation. Ethical and liability debates around machine-only operations persist, yet real-time diagnostics and geofencing reduce downtime and support compliance with safety mandates.
Mechanization rates in many African nations remain below 6% despite mobile-first matching apps. Information asymmetries and risk aversion dampen uptake even when equipment is nearby. Pilot extension programs linking custom hire to crop-insurance premiums are beginning to bridge this gap, but sustained outreach and micro-training remain essential for scale.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Tractors generated the bulk of revenue in 2024, aided by constant demand across tillage, hauling, and power-take-off applications. Their 38.10% farm equipment rental market share reflects a core role in every fleet and underpins whole-season utilization rates. Harvesters, though representing a smaller slice of the farm equipment rental market, are on track for the fastest 7.40% CAGR as their high sticker prices make short-window rental the only feasible option for many growers. Precision yield mapping and auto-steer controls embedded in newer harvester models raise per-hour value, encouraging providers to introduce outcome-based pricing. Sprayers, balers, and seeders occupy narrower rental windows tied to crop phenology, creating scheduling peaks that digital platforms smooth through predictive demand algorithms. Specialty implements are bundled into multiequipment packages, enhancing basket size and locking in customers for full production cycles.
A second trend is the migration of autonomy from row-crop tractors to harvest machines. Early adopters in North America now seek self-driving combines that cut labor bills during short harvest windows. This shift reshapes depreciation curves, compelling rental firms to recalibrate residual value assumptions and match lease terms to rapid technology refresh cycles. As equipment connectivity deepens, data monetization-yield maps, soil compaction insights, and machine health telemetry-emerges as a secondary revenue line alongside traditional rental income.
Mid-range 71-130 HP tractors anchored 27.40% of the 2024 farm equipment rental market size thanks to an optimal mix of fuel efficiency and capability across small-plot operations. Larger units above 250 HP, though currently niche, are forecast to outgrow all other brackets at 8.50% CAGR as farm consolidation and regulated labor hours favor bigger, smarter machinery. These high-horsepower vehicles command premium day rates and impose stringent transport and maintenance requirements that only full-service providers can meet. Sub-30 HP tractors remain vital for horticulture and tight-row crops, while 131-250 HP models bridge the gap between versatile mid-range and specialized heavy-duty tasks. The power-mix evolution pushes rental firms to diversify fleets, hedge utilization risks, and build dynamic pricing linked to fuel costs and telematics-verified load factors.
In parallel, OEMs embed Tier 4-Final engines and hybrid drivetrains across power classes, meeting tightening emission rules in Europe and California. Providers leveraging ESG-linked loans unlock lower capital costs that filter into competitive hourly rates. Telematics-enabled load tracking is also enabling a shift toward usage-based billing, aligning cost with delivered horsepower hours rather than calendar days.
The Farm Equipment Rental Market is Segmented by Equipment Type (tractors, and More), Power Output (Less Than 30 HP, and More), Drive Type (Two-Wheel Drive and More), Business Model (Offline Dealer & Co-Op Yards and More), End-User Farm Size (Small (less Than 5 Ha) and More), Rental Duration (Short-Term (less Than 3 M) and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Asia Pacific generated 44.25% of 2024 revenue for the farm equipment rental market, underpinned by smallholder-oriented subsidy schemes. India's 74,144 Custom Hiring Centers and China's subsidy-linked land tender rules are expanding mechanization without inflating farm debt. Smartphones and vernacular apps embed transparent booking and digital payments, lifting utilization across rice, wheat, and horticulture value chains. Precision hardware costs are still high, so providers use shared ownership structures to amortize technology over broader user bases, keeping per-hectare rental charges affordable.
North America presents a mature yet evolving landscape. Peak harvest in the Corn Belt drives intense, short-term demand for >250 HP tractors and combines, widening price premiums during September-October. Right-to-repair legislation in Colorado and other states now obliges OEMs to furnish diagnostic tools, potentially lowering downtime and rental rates. Autonomous retrofits and electric drivetrains qualify for climate-linked incentives, encouraging fleet renewal among rental giants and regional independents alike.
Europe exhibits pronounced heterogeneity. Western European growers adopt app-based rental to navigate high land prices and strict emission caps. ESG-linked finance reduces borrowing costs for fleets that integrate electric tractors, biofuel harvesters, and low-till implements. The European Green Deal's sustainability targets make rental an attractive compliance pathway, shifting emphasis from asset ownership to outcome-based service. Central and Eastern Europe, still dominated by mid-sized family holdings, balance cost and technology by mixing owned core tractors with rented specialty machines.