
외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장 규모는 2025년에 41억 6,000만 달러에 달하고, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 5.82%를 나타내, 2030년에는 55억 1,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 전망됩니다.

입원 병원에서 비용 효율적인 외래 시설로 꾸준히 이행하고 있는 것, 밸류 베이스 케어에 대한 지불자의 인센티브가 강해지고 있는 것, 만성 질환 관리에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있는 것 등이, 확대를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 북미는 성숙한 상환정책을 배경으로 계속해서 세계적인 수익의 기둥이 되고 있지만, 아시아태평양은 각국 정부가 외래 인프라를 확대하는 가운데 가장 급속한 보급을 기록하고 있습니다. 낮은 침습 수술, 실시간 분석 및 원격 모니터링을 지원하는 기술은 외래 센터의 임상 범위를 더욱 확장합니다. 동시에 노동력 부족, 사이버 위협, 도시 부동산 비용 상승으로 운영 리스크와 자본 압력이 높아지고 성장세가 약해지고 있습니다.
외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장 수요는 지역 밀착형 케어를 선호하는 고령자들 사이에서 다질환 합병률이 상승함에 따라 깊어집니다. 지급자는 현재 재택 케어와 지역 케어에 대한 보수의 75%를 정부 프로그램에 연결하고 외래 진료를 국가 보건 전략에 통합하고 있습니다. 지역 클리닉은 만성 질환 패널을 확대하고 영양 서비스를 통합하고 소개의 루프를 단축하는 POC(Point of Care) 진단을 도입하여 대응하고 있습니다. 포퓰레이션 건강 계약에는 외래에서 발생하는 고혈압, 당뇨병 및 COPD 관리에 대한 성과 평가 지표가 포함됩니다. 이러한 패턴은 외래 진료가 재량적 보조가 아니라 의료 시스템의 능력의 구조적 요소가 되고 있음을 뒷받침합니다.
로봇공학, 화상처리, AI의 진보에 의해 절개의 크기, 수술실에서의 시간, 요양기간이 단축되고, 과거에는 병원의 수술실에 한정되어 있던 수술이 외래수술센터로 이행할 수 있게 되었습니다. 광자 계수 CT와 디지털 SPECT 스캐너는 스캔 시퀀싱와 방사선 노출을 줄이고 외래 환자의 처리량 목표에 부합합니다. 죽종 절제술과 말초 스텐트 유치술과 같은 심혈관 인터벤션은 외래 보험 적용이 증가하고 절차 구성이 확대되고 있습니다. 자동 이미지 분석 도구는 스캔을 방어하고 신속한 검토를 위해 비정상적인 플래그를 설정하여 방사선과 의사의 부족을 보완합니다. 이러한 기술을 종합하면 시설은 임상 인력을 늘리지 않고 사례 수를 늘릴 수 있습니다.
2033년까지 최대 13만 9,000명의 의사 부족이 예측되어 노동 공급이 부족해지고 있습니다. 고용이 병원 시스템으로 이동하는 동안 개인 개업의 비율은 아직 42.2%에 불과합니다. 번아웃 비율은 임상의가 많은 진찰 횟수와 전자 문서화를 해내는 것으로 상승해, 조기 퇴직이나 근무 시간의 단축을 촉진합니다. 외래센터에서는 야간이나 주말의 진료소의 스탭 확보에 고민하고 있어 피크시의 처리 능력이 제한되어 있습니다. 원격 의료 면허 요건은 주마다 다르므로, 지방은 심지어 인적 부족에 직면하고 전문의의 배치가 지연됩니다. 노동력의 격차는 급여비를 상승시키고 이미 병원보다 얇은 금리를 압박하고 있습니다.
보고서에서 분석된 기타 성장 촉진요인 및 억제요인
1차 케어클리닉이 최대의 수익원이며 2024년 외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장의 40.32%를 차지했습니다. 1차 케어 클리닉은 질병 예방, 처방전 갱신, 소개의 게이트키퍼 역할을 하며, 집단건강 프로그램의 필수 노드로 자리잡고 있습니다. 지속적인 치료는 환자와의 강한 관계를 키우고, 어드히어런스의 향상과 다운스트림 비용의 절감으로 이어집니다. 고급 치료 도구 및 만성 질환 대시보드에 대한 투자를 통해 클리닉은 의사의 수를 비례하지 않고 증가하는 다질환 합병증을 관리할 수 있습니다. 원격 의료 및 가상 클리닉은 절대적인 규모는 작고, 편리하고 온디맨드인 액세스를 요구하는 소비자의 기호를 반영하여 2030년까지의 CAGR은 7.74%를 나타낼 전망입니다.
가상의 급속한 보급은 새로운 경쟁을 가져오고, 24시간 365일 이용가능성에 대한 기대를 높여 기존의 진료소를 하이브리드 모델의 채용으로 밀어 올립니다. 1만 4,000개가 넘는 급환센터는 생명과 무관한 에피소드를 취급하여 구급 외래의 혼잡을 완화하고 있습니다. 이미징 허브는 지불자가 높은 비용의 스캔을 병원의 방사선과에서 이동시킴으로써 번영합니다. 이와 병행하여, 재택치료기관은 원격 생체 모니터링을 활용하고, 특히 급성기 후 회복과 완화 지원을 위해 임상의의 활동 범위를 확대하고 있습니다. 이 부문 모자이크는 다양한 케어 포인트가 공동으로 외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장의 환자와 수익 흐름을 강화하고 있음을 강조합니다.
외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장 보고서는 서비스 환경별(기본 케어클리닉, 외과전문클리닉, 기타), 전문분야별(안과, 정형외과, 기타), 소유모델별(의사소유, 병원/의료시스템 소유, 기타), 지역별(북미, 유럽, 아시아태평양, 중동 및 아프리카, 남미)으로 분류하고 있습니다. 시장 예측은 금액(달러)으로 제공됩니다.
북미는 2024년에 외래 매출의 43.67%를 차지하며 광범위한 지불자 커버리지, 유리한 서비스 부위 차이, 1만 4,000개 이상의 응급의료센터의 성숙한 공급에 지지되었습니다. 미국은 ASC에 대한 2.9%의 메디케어 지불 증액으로부터 혜택을 받고 즉시 현금흐름이 개선되는 반면 캐나다 주 개혁은 지역 밀착형의 만성 질환 클리닉에 보답합니다. 멕시코의 의료 관광 클러스터는 지역 점유율을 강화하기 위해 수술 건수를 증가 시켰습니다. 텔레헬스의 도입은 현재 진찰의 23%에 달하고 있으며, 디지털 경로가 외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장에 정착하고 있는 것을 나타내고 있습니다.
2030년까지 아시아태평양의 CAGR은 10.36%를 나타낼 것으로 예상되지만, 이는 공립 병원의 혼잡을 완화하기 위해 정부가 외래 진료 시설의 건설을 급피치로 진행하고 있기 때문입니다. 싱가포르의 통합 수술센터는 동급 최고의 처리 능력을 보여주며, 중국은 낮은 침습 장비의 국산화를 우선시하며, 일본은 노인을 위한 원격 재활에 보조금을 냅니다. 인도의 보험 확대 정책과 의료 관광의 유입도 다과목 외래의 허브에 자본을 유입시키고 있습니다. 이 지역에서는 인구동태가 고령화되어 심혈관, 안과, 정형외과의 당일치기 수술에 대한 지속적인 수요가 확보되고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 각국의 의료 제도가 예산을 단축하고 변화 리프트를 장려하고 있기 때문에 꾸준한 성장을 보여줍니다. 독일 부인과 수술은 현재 98%가 민간 독립 단위로 이루어지고 있으며, EU 전체의 가치 기반 틀은 외래 시설이 효율적으로 충족할 수 있는 케어의 질 지표에 상환을 맺고 있습니다. 먼 영상 진단의 채택은 방사선과 의사의 부족을 완화하고 국경을 넘어서는 지시의 완화는 지역 내의 환자의 교류를 완화합니다. 중동, 아프리카, 남미의 신흥 시장은 과도한 경향이 있는 공립 병원을 보완하는 민간 외래 클러스터에 투자하여 외래 헬스케어 서비스 시장의 세계적인 확산을 보이고 있습니다.
The Ambulatory Healthcare Service Market size is estimated at USD 4.16 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 5.51 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.82% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
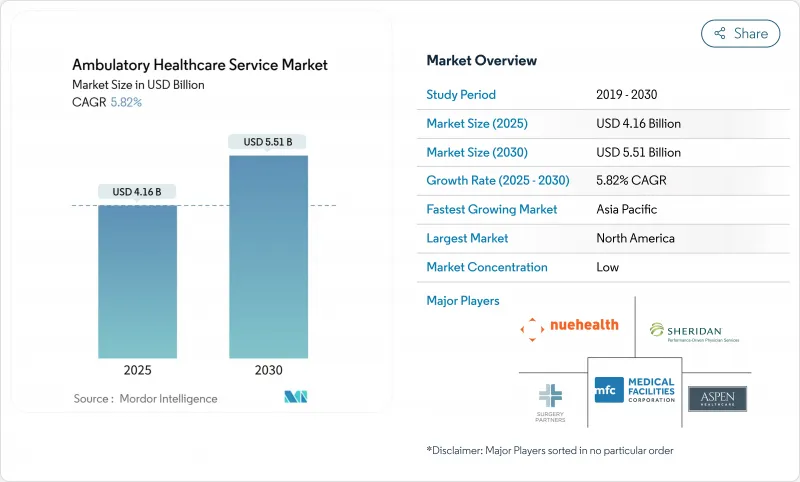
Expansion is propelled by the steady shift of procedures from inpatient hospitals to cost-efficient outpatient facilities, stronger payer incentives for value-based care, and rising demand for chronic-disease management. North America continues to anchor global revenues on the back of mature reimbursement policies, while Asia-Pacific records the most rapid uptake as governments scale outpatient infrastructure. Technology that supports minimally invasive surgeries, real-time analytics, and remote monitoring further widens the clinical scope of ambulatory centers. Concurrently, labor shortages, cyber threats, and rising urban real-estate costs temper growth momentum by adding operational risk and capital pressure.
Demand for the ambulatory healthcare service market deepens as multimorbidity rates climb among seniors who prefer community-based care. Payers now tie 75% of home- and community-care reimbursements to government programs, embedding outpatient delivery in national health strategies. Community clinics respond by enlarging chronic-disease panels, integrating nutrition services, and deploying point-of-care diagnostics that shorten referral loops. Population-health contracts increasingly include performance metrics for hypertension, diabetes, and COPD management conducted in ambulatory settings. These patterns confirm that outpatient care is becoming a structural component of health-system capacity rather than a discretionary adjunct.
Advances in robotics, imaging, and AI reduce incision size, operating-room time, and recuperation periods, allowing procedures once limited to hospital theaters to migrate to ambulatory surgery centers. Photon-counting CT and digital SPECT scanners shrink scan sequences and radiation exposure, aligning with outpatient throughput targets. Cardiovascular interventions such as atherectomy and peripheral stenting are increasingly reimbursed for ambulatory venues, expanding procedure mix. Automated image-analysis tools offset shortages of radiologists by triaging scans and flagging anomalies for rapid review. Collectively, these technologies help facilities boost case volumes without proportional increases in clinical manpower.
A projected deficit of up to 139,000 physicians by 2033 tightens labor supply, with only 42.2% of physicians still in private practice as employment shifts toward hospital systems. Burnout rates climb as clinicians juggle high visit counts and electronic documentation, prompting early retirement and reduced hours. Ambulatory centers struggle to staff evening and weekend clinics, limiting throughput during peak periods. Rural areas face compounded shortages because telehealth licensing requirements vary by state, slowing specialist deployment. Workforce gaps elevate salary expenses, pressuring margins that are already thinner than hospital counterparts.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Primary care clinics generated the largest revenue stream, accounting for 40.32% of the ambulatory healthcare service market in 2024. They serve as gatekeepers for disease prevention, prescription renewals, and referrals, positioning them as indispensable nodes in population-health programs. Continuity of care fosters strong patient relationships, leading to higher adherence and lower downstream costs. Investment in advanced triage tools and chronic-care dashboards enables clinics to manage rising multimorbidity without proportional physician headcount. Telehealth and virtual clinics, though smaller in absolute terms, are on track for a 7.74% CAGR through 2030, reflecting consumer preference for convenient, on-demand access.
Rapid virtual uptake brings fresh competition and raises expectations for 24/7 availability, pushing traditional practices to adopt hybrid models. Urgent care centers, numbering more than 14,000, continue to relieve emergency-room congestion by handling non-life-threatening episodes. Diagnostic imaging hubs prosper as payers shift high-cost scans out of hospital radiology departments. In parallel, home-health agencies leverage remote vitals monitoring to extend the reach of clinicians, particularly for post-acute recovery and palliative support. The segment mosaic underscores how diversified points of care jointly reinforce the ambulatory healthcare service market flow of patients and revenue.
The Ambulatory Healthcare Service Market Report is Segmented by Service Setting (Primary Care Clinics, Surgical Specialty Clinics, and More), Specialty (Ophthalmology, Orthopedics, and More), Ownership Model (Physician-Owned, Hospital / Health-System-Owned, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America controlled 43.67% of global ambulatory revenues in 2024, underpinned by expansive payer coverage, favorable site-of-service differentials, and a mature supply of more than 14,000 urgent care centers. The United States benefits from a 2.9% Medicare payment bump for ASCs, creating immediate cash-flow lift, while Canada's provincial reforms reward community-based chronic-disease clinics. Mexico's medical-tourism clusters generate incremental procedure volume that fortifies regional share. Telehealth adoption now touches 23% of encounters, a signal that digital pathways are firmly embedded in the ambulatory healthcare service market.
Asia-Pacific posts a leading 10.36% CAGR by 2030 as governments fast-track outpatient construction to relieve public-hospital congestion. Singapore's integrated surgery centers demonstrate best-in-class throughput, China prioritizes domestic production of minimally invasive devices, and Japan subsidizes tele-rehabilitation for seniors. India's insurance-expansion policies and medical-tourism inflows also funnel capital into multispecialty ambulatory hubs. Demographic aging in the region ensures sustainable demand for cardiovascular, ophthalmic, and orthopedic day surgeries.
Europe exhibits steady growth as national health systems tighten budgets and encourage shift-left initiatives. Germany's gynecology procedures now occur 98% in private free-standing units, and EU-wide value-based frameworks tie reimbursement to care-quality metrics that outpatient sites can meet efficiently. Adoption of teleradiology mitigates radiologist shortages, while relaxed cross-border directives ease patient flow within the bloc. Emerging markets in the Middle East, Africa, and South America invest in private outpatient clusters that complement often overstretched public hospitals, extending the global footprint of the ambulatory healthcare service market.