
세계의 로봇 센서 시장은 2025년 7억 3,000만 달러에서 2026년에는 7억 9,000만 달러로 성장하고, 2026년부터 2031년까지 CAGR 8.57%로 성장을 지속하여 11억 9,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다.

이 성장은 산업용 로봇의 도입 대수가 과거 최고를 기록하고 있는 것, 협동 로봇 및 휴머노이드 플랫폼의 급속한 보급, 지각 정밀도와 응답 시간을 향상시키는 엣지 AI 모듈의 꾸준한 도입에 기인하고 있습니다. 힘 및 토크 디바이스는 정밀 조립 라인을 지원하는 반면, 비전 시스템은 심층 학습 모델이 클라우드에서 로봇 암으로 이동함에 따라 가속화되고 있습니다. 반도체 제조업체는 현재 단일 칩에 센싱, 프로세싱 및 안전 로직을 통합하여 공장이 저지연화와 뛰어난 사이버 물리 탄력성을 제공합니다. 자동차, 전기자동차, 의료 분야의 최종 사용자는 수율, 추적성, 사람과 기계의 협동을 개선하기 위해 멀티모달 감지에 대한 투자를 강화하고 있습니다. 지역별로는 아시아태평양의 밀집한 제조 거점과 정책 인센티브가 규모의 경제를 지원하는 한편, 남미의 자동화 추구 수요가 고성장의 기반을 제공합니다.
2024년에 세계 가동 대수가 400만대를 돌파한 것으로, 제조업체는 엔코더를 넘어, 비전, 힘, 촉각 모달리티까지를 포함한 고도의 센싱 스위트의 채용을 강요받고 있습니다. FANUC의 500i-A CNC 제어 장치(CPU 처리량 2.7배)는 고속 온보드 컴퓨팅이 복잡한 센서 스트림을 실시간으로 처리하는 예를 보여줍니다. 협동 셀은 중복 안전 센싱 수요를 확대하고 있으며, Delta의 D-Bot 코봇은 적재량에 특화된 플러그 앤 플레이식 센서 패키지로 통합을 간소화하고 있습니다. 설치 대수 증가는 첨단 지각 기술의 투자 회수 기간을 단축하고 로봇 센서 시장 전체에서 수주를 확보하고 있습니다.
견고한 온라인 소매로 인해 2024년 세계 이동 로봇 시장 규모는 45억 달러에 달하여 동적 창고 내에서 광각 지각, 매핑 및 패키지 품질 평가의 필요성을 촉진하고 있습니다. Sonair와 같은 저비용 3D 초음파 어레이는 180x180도의 커버리지를 제공하며 LiDAR보다 최대 80% 미만의 가격으로 중형 풀필먼트 센터의 자본 장벽을 줄입니다. AI 강화 비전은 팔레트 랙, 지게차 및 직원 복장을 식별할 수 있어 가동 시간과 처리량을 향상시킵니다. 터치 대응 그리퍼에 의해 AMR(자율 이동 로봇)이 손상되기 쉬운 SKU(재고 관리 단위)를 취급할 수 있게 되어, 이용 사례가 확대되어, 센서 수요량이 증가하고 있습니다.
갈륨과 안티몬의 무역 제한 외에도 아시아 파운드리의 자연 재해 위험이 리드 타임을 압박하여 다이 레벨 비용을 밀어 올리고 있습니다. Sourceability는 2026년까지 웨이퍼 스타트의 병목이 계속될 것으로 예측하고 있으며, 고핀수 센서 ASIC 공급이 압박될 전망입니다. 노동력 부족도 불확실성을 증대시키고 있으며, 일부 OEM 제조업체는 듀얼 소싱이나 백엔드 패키징의 이전을 검토하고 있지만, 이러한 움직임은 자본 집약도와 운용상의 복잡성을 높이는 결과가 되고 있습니다.
비전 센서는 2026년부터 2031년까지 13.27%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 기록했으며, 다른 모든 카테고리를 초과할 전망입니다. 한편 포스 토크 디바이스는 2025년 시점에서 로봇 센서 시장의 27.62% 점유율을 유지했습니다. 고속 시각 검사 및 픽 앤 플레이스 작업의 보급으로 추론 지연을 30밀리초 미만으로 압축하는 온보드 GPU 및 ASIC에 대한 투자가 정당화되고 있습니다. 카메라 가격의 저하에 따라 중견 OEM 제조업체에서도 심도 추정에 대응하기 위해 듀얼 센서 스테레오 장치를 채용하는 움직임을 볼 수 있습니다. 힘 감지는 프레스 핏, 버링 및 전자 커넥터 조립에 여전히 필수적이며 서브뉴턴 단위의 정확도가 수율을 보장합니다. Cognex의 2023년 매출액 8억 3,750만 달러는 장비 투자가 회복될 때 기계 시각 하드웨어에 대한 주기적인 수요가 여전히 견조하다는 것을 보여줍니다.
센서의 소형화에 의해 근접, 온도 및 비전 모듈을 로봇의 좁은 손목부에 집약할 수 있어 배선과 전자기 노이즈를 삭감할 수 있습니다. XELA Robotics의 uSkin과 같은 0.1그램 힘 감도를 가진 햅틱 어레이는 그리퍼의 편의성을 향상시키지만 로봇 센서 시장에서는 여전히 '기타' 카테고리에 위치하고 있습니다. 스테레오 비전, IMU 및 힘 벡터의 융합은 불규칙한 부품 조립 공정에서 컴플라이언스 제어를 강화합니다. 이 기능은 웨어러블 디바이스 생산 라인 및 맞춤형 정형외과 장비에서 높은 평가를 받았습니다. 표준화된 M12 커넥터와 Power-over-Ethernet(PoE)은 설치를 간소화하고 중소기업 진입 장벽을 줄입니다. 예측기간 동안 모듈형 AI 지원 비전 제품군을 제공하는 공급업체는 이 부문에서 로봇 센서 시장이 증가함에 따라 상대적으로 큰 점유율을 획득할 것으로 예측됩니다.
산업용 로봇은 종래부터 수요의 기반이 되어 2025년 로봇 센서 시장 규모의 54.62%를 차지합니다. 용접, 페인트 및 전자 장비 조립에서 확고한 역할은 안정적인 업데이트 사이클을 보장합니다. 그러나 휴머노이드 플랫폼은 지속적인 벤처 캐피탈 유입과 부품 비용의 저하에 힘입어 2031년까지 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR) 36.7%로 성장을 견인할 것으로 예측됩니다. Tacta Systems의 자금 조달은 안전과 민첩성이 인간 수준에 이르렀을 때 휴머노이드가 물류, 소매, 노인 간호 문제를 해결할 수 있다는 확신을 뒷받침합니다.
협동 로봇은 유연한 라인 변경을 필요로 하고 대규모의 방호 설비를 도입할 수 없는 중규모 공장에서의 채용을 계속 확대하고 있습니다. 에지 AI 서브시스템은 "제로 프로그래밍" 티치 모드를 실현하여 기술적 장애물이 저하되어 대상 사용자층이 확대되고 있습니다. 병원이나 공항에서는 감염 관리나 여객 서비스 업무에 신뢰성 높은 지각 능력과 섬세한 조작이 요구되기 때문에 업무용 서비스 로봇의 도입이 급증하고 있습니다. Yaskawa의 MOTOMAN NEXT 시리즈가 실증하는 자기 최적화 동작 계획은 상황 인식 능력의 향상을 목표로 하는 플랫폼에 있어서 센서수를 증가시키는 동향을 나타내고 있습니다. 향후 휴머노이드 로봇의 보급 가속은 로봇 센서 시장의 더욱 다양화를 촉진하고 기존의 산업용 오토메이션을 넘어 새로운 공급처 시장을 창출할 것입니다.
2025년에는 아시아태평양이 34.72%의 수익 점유율로 선두를 차지했습니다. 이것은 중국의 산업 고도화 보조금, 일본의 Society 5.0 구상, 한국의 메모리 칩 투자 붐에 지지된 것입니다. OMRON의 순매출 8,761억엔은 센서 구동형 자동화에 대한 이 지역의 견조한 수요를 뒷받침하고 있습니다. MEMS 팹에 대한 근접성은 리드 타임을 단축하고, 현지의 일류 자동차 제조업체나 전자기기 대기업이 기반 수요를 보증하고 있습니다. 그러나 칩 수출 규정을 둘러싼 지정학적 마찰로 인해 공급망 재구축과 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다.
유럽 시장은 독일 Industry 4.0 로드맵과 엄격한 안전 기준을 뒷받침하며 인증된 감지 시스템에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있습니다. SICK의 2024년 매출액 23억 700만 유로는 특히 자동차 및 물류 거점에 있어서의 건전한 성장세를 나타내고 있습니다. 남유럽에서는 FANUC의 이베리아 지역 확대로 대표되는 협동 로봇의 보급이 진행되고 시장 규모가 확대되고 있습니다. 북유럽 기업은 해상 풍력 발전과 광업 분야에서 한계 돌파적인 응용을 추진하고 있으며, 방진 방적 사양으로 내진동성이 뛰어난 센서가 주류가 되고 있습니다.
북미는 혁신 중심지이며 미국 연구소에서는 엣지 AI 지각 기술의 정밀화가 진행되고 캐나다 광산에서는 자율 반송용 견고 센서가 채용되고 있습니다. 멕시코의 니어 쇼어링 동향으로 생산 라인이 바히오 회랑에 집적되어 비용 효율적인 센싱 수요를 견인하고 있습니다. 남미는 설치 기반은 작지만, 브라질 자동차 제조업체, 아르헨티나 곡물 취급업자, 칠레 리튬 정제업자가 노동력 부족 해소와 ESG 감사 대응을 위해 자동화를 진행함으로써 10.45%라는 가장 빠른 CAGR을 달성할 전망입니다. 지역 개발 은행과 다국적 기업이 공동으로 파일럿 프로젝트를 자금 지원하고 로봇 센서 시장 전체에 장기적인 센서 수요의 씨앗을 뿌리고 있습니다.
The robotic sensors market is expected to grow from USD 0.73 billion in 2025 to USD 0.79 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 1.19 billion by 2031 at 8.57% CAGR over 2026-2031.
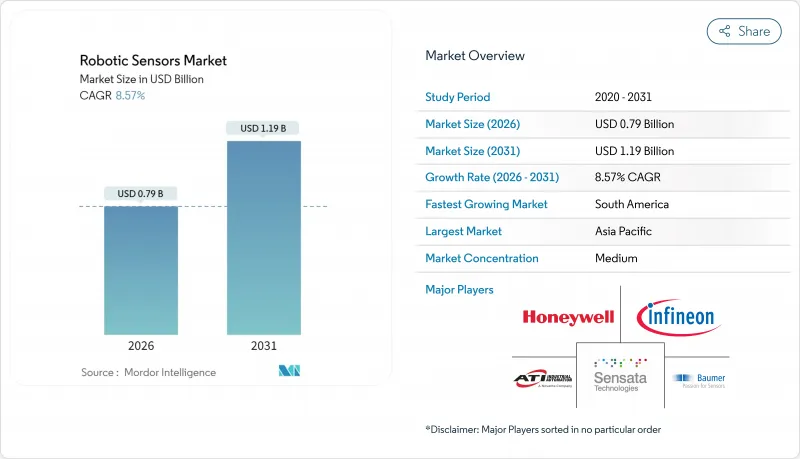
Growth stems from record-high industrial-robot deployments, rapid gains in collaborative and humanoid platforms, and the steady infusion of edge-AI modules that elevate perception accuracy and response times. Force-torque devices underpin precision assembly lines, while vision systems accelerate as deep-learning models migrate from the cloud to the robot arm. Semiconductor makers now bundle sensing, processing, and safety logic on a single chip, giving factories lower latency and better cyber-physical resilience. End-users in automotive, electric-vehicle, and healthcare domains intensify spending on multimodal sensing to improve yield, traceability, and human-machine cooperation. Regionally, Asia-Pacific's dense manufacturing base and policy incentives support scale economics, whereas South America's automation catch-up provides a high-growth runway.
Global operational stock crossed 4 million units in 2024, forcing manufacturers to adopt richer sensing suites that go beyond encoders to vision, force, and tactile modalities. FANUC's 500i-A CNC control, with 2.7X CPU throughput, illustrates how faster on-board computing now digests complex sensor streams in real time. Collaborative cells amplify demand for redundant safety sensing, while Delta's D-Bot cobots demonstrate payload-specific plug-and-play sensor packages that simplify integration. High install volumes shorten the payback period for advanced perception, locking in orders across the robotic sensors market.
Robust online retail lifted the global mobile-robot space to USD 4.5 billion in 2024, propelling need for wide-angle perception, mapping, and package-quality assessment inside dynamic warehouses. Low-cost 3D ultrasonic arrays such as Sonair's deliver 180 X 180 degree coverage while undercutting LiDAR by up to 80%, trimming capital hurdles for mid-tier fulfilment centers. AI-enhanced vision now differentiates between pallet racks, forklifts, and staff apparel, boosting uptime and throughput. Touch-enabled grippers let AMRs handle fragile SKUs, expanding use cases and fuelling sensor volumes.
Trade restrictions on gallium and antimony alongside natural-disaster risks at Asian foundries strain lead times and elevate die-level costs. Sourceability forecasts continued wafer-start bottlenecks through 2026, squeezing availability for high-pin-count sensor ASICs. Labor shortages add uncertainty, prompting some OEMs to dual-source or relocate backend packaging, yet such moves raise capital intensity and operational complexity.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Vision sensors are forecast to post a 13.27% CAGR from 2026-2031, outpacing all other categories. At the same time, force-torque devices retained 27.62% share of the robotic sensors market in 2025. The mass adoption of high-speed visual inspection and pick-and-place tasks legitimises investment in on-board GPUs and ASICs that compress inference latency below 30 ms. As camera prices slide, even mid-tier OEMs adopt dual-sensor stereo rigs to tackle depth estimation. Force sensing stays indispensable for press-fit, deburring, and electronic-connector assembly, where sub-newton accuracy safeguards yield. Cognex's 2023 revenue of USD 837.5 million signals cyclical yet resilient appetite for machine vision hardware when capex rebounds.
Sensor miniaturization lets builders co-locate proximity, temperature, and vision modules within tight robot wrists, reducing cabling and electromagnetic noise. Tactile arrays such as XELA Robotics' uSkin, with 0.1 gram-force sensitivity, deepen dexterity on grippers, but they still sit in the "others" bucket of the robotic sensors market. The fusion of stereo vision, IMU, and force vectors bolsters compliance control during assembly of irregular parts, a capability prized in wearable-device lines and customised orthopedics. Standardised M12 connectors and Power-over-Ethernet streamline installation, widening accessibility for SMEs. Over the forecast window, suppliers that offer modular, AI-ready vision suites are expected to capture a disproportionate slice of incremental robotic sensors market size in this segment.
Industrial robots have historically anchored demand, accounting for 54.62% of the robotic sensors market size in 2025. Their entrenched role in welding, painting, and electronics assembly ensures a stable replacement cycle. However, humanoid platforms are projected to lead growth with a 36.7% CAGR through 2031, energised by sustained venture capital inflows and component cost deflation. Tacta Systems' capital raise underscores confidence that humanoids can address logistics, retail, and eldercare gaps once safety and dexterity reach human parity.
Collaborative robots continue to win midsize factories that need flexible line changeovers and cannot afford extensive guarding. Edge-AI subsystems now allow 'zero-programming' teach modes, lowering skill thresholds and expanding the addressable user base. Professional service robots surge across hospitals and airports, where infection-control or passenger-service tasks require reliable perception and gentle interaction. Yaskawa's MOTOMAN NEXT family demonstrates self-optimising motion planning, a trend that multiplies sensor count per unit as platforms aim for situational awareness. Over the horizon, accelerated adoption in humanoids will further diversify the robotic sensors market, giving suppliers a potent new volume pool beyond classical industrial automation.
The Robotic Sensors Market Report is Segmented by Sensor Type (Force & Torque Sensors, Vision Sensors, and More), Robot Type (Industrial Robots, Collaborative Robots, Service Robots - Professional, and More), End-User Industry (Automotive & EV, Electronics & Semiconductor, and More), Sensing Technology (Strain-Gauge, Capacitive, Optical, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Asia-Pacific led with 34.72% revenue share in 2025, buoyed by China's industrial-upgrade subsidies, Japan's Society 5.0 blueprint, and South Korea's memory-chip investment wave. OMRON's JPY 876.1 billion net sales validate robust regional appetite for sensor-driven automation. Close proximity to MEMS fabs compresses lead times, while local tier-one automakers and electronics giants guarantee baseline demand. Geopolitical frictions around chip export controls, however, may force supply-chain re-routing and incremental costs.
Europe follows, anchored by Germany's Industry 4.0 roadmap and rigorous safety statutes that elevate certified sensing systems. SICK's EUR 2.307 billion turnover in 2024 underscores healthy momentum, especially in automotive and logistics hubs. Southern Europe's growing cobot footprint, exemplified by FANUC's Iberia expansion, widens market breadth. Nordic firms push envelope applications in offshore wind and mining, where IP-rated, vibration-hardy sensors prevail.
North America remains innovation-centric, with US labs refining AI-on-edge perception and Canadian mines adopting rugged sensors for autonomous hauling. Mexico's near-shoring trend channels production lines into Bajio corridors, pulling demand for cost-effective sensing. South America, despite lower installed base, is on track for the fastest CAGR at 10.45% as Brazilian automakers, Argentinian grain handlers, and Chilean lithium refiners automate to offset labor shortages and meet ESG audits. Regional development banks and multinationals co-finance pilot projects, seeding long-run sensor demand across the robotic sensors market.