
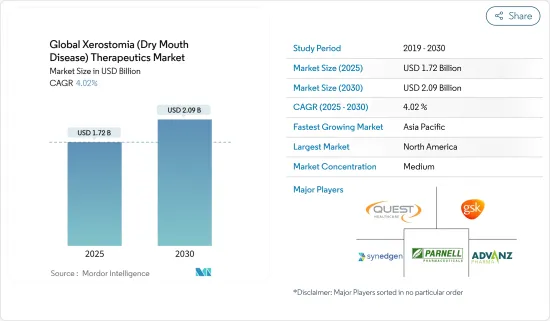
세계의 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 시장 규모는 2025년에 17억 2,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 추정됩니다. 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 4.02%를 나타내 2030년에는 20억 9,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.

구강건조증은 일반적으로 드라이 마우스라고 불리며 타액의 분비량이 감소하는 질병입니다. 어려움, 치과 문제의 위험 증가, 전반적인 불쾌감으로 이어질 수 있습니다 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 시장은 타액 분비 촉진제, 대용 타액 및 기타 증상 완화를 목적으로 한 약물 등 여러 제품 카테고리가 있습니다.
시장의 성장은 주로 당뇨병, 자가면역질환(셰그렌 증후군 등) 등의 구강건조증의 원인이 되는 질환의 유병률 증가, 특정 약제(특히 항우울제, 항히스타민제, 암 치료)의 부작용에 의해 효과적 치료 솔루션에 대한 수요가 높아지고 있다는 점이 배경입니다. for Health Metrics and Evaluation이 2023년 6월에 발표한 데이터에 의하면, 세계에서는 5억명 이상이 당뇨병과 함께 생활하고 있어, 모든 나라의 모든 연령의 남녀, 유아에 영향을 미치고 있어, 그 수는 2043년까지 2배 이상의 13억명이 될 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 혈당은 삼투압 이뇨에 의한 탈수 및 타액 분비량의 감소를 일으킵니다.이 합병증은 당뇨병 환자의 구강건조증의 관리를 목적으로 한 치료에 대한 큰 수요의 원인이 되고 있습니다. 따라서 세계의 당뇨병 유병률 증가가 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 수요를 견인해, 시장 성장
게다가 제약 연구의 진보로 타액 대체품이나 자극제 등의 신제품이 개발되어 효능과 환자의 규정 준수가 개선됨으로써 예측 기간 중 시장 성장이 기대되고 있습니다. Beier가 2023년 12월에 발표한 기사에 따르면, 영국 리즈 대학의 연구 개발자는 드라이 마우스에 고민하는 환자의 불쾌감을 경감하는 타액 대체품을 개발했습니다. 때의 윤활유로서 기능합니다.유제품과 비건용의 제제가 있어, 검사관내 실험에서는 다른 시판 제품보다 효과가 높은 것이 판명되고 있습니다. 이러한 제품의 진보는 약제성 구내염의 치료에의 채용을 촉진해, 시장 성장에 영향을 줍니다.
또한 신흥 시장의 의료 인프라 투자 증가와 가처분 소득 증가는 이러한 치료에 대한 접근성을 높이고 시장 성장을 더욱 촉진하고 있습니다.
따라서 당뇨병 등 구강건조증의 원인이 되는 질환의 유병률 증가, 의약품 연구의 신흥국 시장의 개척에 의한 신규 제품의 개발 등, 상기의 요인에 의해 예측 기간 중에 시장 조사는 성장하면 예 하지만 인지도가 낮고 효과적인 치료법의 미발매 등의 요인은 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료제품의 사용을 방해할 가능성이 높아 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 시장 성장 억제요인으로 작용할 가능성이 있습니다.
타액 분비량의 감소는 충치, 구내 감염, 미각과 후각의 변화, 삼키기 어려움, 통증, 기타 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다., 최대 2시간의 효과를 구가하고 있지만, 사용자는 보다 빈번한 사용을 필요로 하는 경우가 많아, 수면이나 일상생활에 영향을 미칩니다. 또한, 일부 타액 스프레이나 젤에는 강하고 불쾌한 풍미가 있습니다.
드라이 마우스 질환의 부담 증가와 조사 연구 증가와 같은 요인이 이 부문의 성장을 뒷받침하고 있습니다. 2023년 남성의 10%-26%, 여성의 10%-33%에 영향을 미쳤습니다.
수많은 연구가 구강건조증을 앓고있는 사람들을 치료하기 위한 몇 가지 인공 타액 제제의 효능을 보여줍니다. Radiology에 게재된 2024년 3월의 연구에서는 카르복시메틸셀룰로오스나트륨(SCMC) 스프레이와 B글루칸으로 강화한 SCMC 스프레이의 2개의 인공 타액 제제의 효능을 평가·비교했습니다. 카르복시메틸셀룰로오스나트륨(SCMC) 스프레이와 B글루칸을 강화한 SCMC스프레이입니다.컨트롤과 B글루칸을 강화한 인공 타액 모두에서 구강건조의 임상징후와 증상의 개선이 인정되었습니다.
또한 2024년 5월 BMC Oral Health에 게재된 종이제에서는 인공 타액 스프레이가, 비침습적 인공 호흡을 받고 있는 COVID-19 환자의 구강 증상을 유의하게 완화하는 것을 강조했습니다. 무결성과 효능에 대한 귀중한 통찰력을 제공하고 의료 제공업체와 환자의 신뢰를 높이고 시장 성장을 가속합니다.
북미는 셰그렌 증후군, 당뇨병, 암 치료 등 구강건조증의 원인이 되는 질환의 유병률 증가에 의해 시장을 선도하는 전망입니다. 의식 증가, 혁신적인 대용 타액, 자극제, 보습제를 포함한 치료 옵션의 진보, 제약 회사의 연구 개발에 대한 많은 투자가 예측 기간 동안 동일한 부문의 성장을 더욱 촉진할 것으로 예상됩니다.
당뇨병을 앓고있는 환자의 삶의 질을 향상시키는 효과적인 관리 솔루션의 필요성을 반영하고 당뇨병의 유병률 증가가 북미 시장 성장을 밀어 올릴 것으로 예상됩니다. 2023이 발표한 데이터에 따르면 캐나다에서는 2023년에 410만명의 당뇨병 환자(1형과 2형으로 진단)이 기록되어 2033년에 약 520만명으로 증가할 것으로 예측되고 있습니다. 따라서 치주병의 위험이 증가합니다. 따라서 캐나다에서 당뇨병의 유병률이 증가하고 이에 따른 구강 건강 합병증은 구강건조증 관리를 목표로 하는 치료에 대한 수요 증가를 초래하여 이 지역 시장 성장에 영향을 미칩니다.
게다가 제약회사, 연구기관, 벤처캐피탈 등 다양한 기관에 의한 투자 증가가 북미의 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 시장을 크게 견인하고 있습니다. 2024년 10월, 미국 버팔로 대학 치과부의 구강 생물학 준 교수가 미국 국립 위생 실험실의 일부인 국립 치과 두개 안면 실험실(NIDCR)에서 220만 달러에 해당하는 5년간의 보조금을 갱신받았습니다. 이 보조금은 신체의 다양한 땀샘에서 수분을 빼앗는 셰글렌병 등 환자의 고통을 경감하는 것을 목적으로 하고 있습니다.
또한, 구강건조증(건조 마우스 질환)에 대한 제품 승인 및 혁신적인 치료법의 도입과 같은 주요 기업의 전략적 이니셔티브는 치료 옵션을 강화하고, 충족되지 않은 환자의 요구에 대응하고 삶의 질을 개선함으로써 시장의 성장을 가속합니다. Therapeutics는 2024년 10월 RXRG001의 임상신약(IND) 신청에 대한 식품의약국(FDA)의 인가를 취득하고 방사선유발성 구강건조증과 타액감소증을 치료했습니다. 하기 위해 설계된 최초의 원형 RNA 요법을 도입했습니다. 이러한 제품 승인은 환자의 임상 결과를 향상시킬뿐만 아니라 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료에 대한 추가 조사 및 투자를 촉진하고 시장 성장을 뒷받침합니다.
요약하면, 당뇨병의 유병률 증가, 다양한 기관의 투자 증가, 제품 승인은 북미의 구강건조증(건조 마우스 질환) 치료에 대한 수요를 증가시키고 예측 기간 동안 시장 성장을 가속할 것으로 예상됩니다.
구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 시장은 중등도의 경쟁상태에 있습니다. 구강건조증(드라이 마우스) 치료 시장의 주요 진입기업은 제품 포트폴리오 개발, 신흥 진입기업 인수, 지리적 존재를 높이기 위한 판매계약에 주력하고 있습니다. Inc., ADVANZ PHARMA, Lupin, Parnell Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Synedgen, Inc. 등이 있습니다.
The Global Xerostomia Therapeutics Market size is estimated at USD 1.72 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.09 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.02% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Xerostomia, commonly referred to as dry mouth, is a condition characterized by the reduced production of saliva. It can be caused by various factors, including medications, certain medical conditions, and radiation therapy. The dry mouth condition can lead to difficulties in speaking, swallowing, increased risk of dental problems, and overall discomfort. The therapeutics market for xerostomia includes several product categories such as salivary stimulants, saliva substitutes, and other agents designed to alleviate symptoms.
The growth of the market is mainly driven by the increasing prevalence of conditions that contribute to xerostomia, such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases (like Sjogren's syndrome), and the side effects of certain medications (particularly antidepressants, antihistamines, and cancer therapies) has heightened the demand for effective treatment solutions. Additionally, an aging population is contributing to a rise in xerostomia cases, as older adults are more likely to experience related health issues. For instance, according to the data published by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation in June 2023, more than half a billion people are living with diabetes worldwide, affecting men, women, and children of all ages in every country, and that number is projected to more than double to 1.3 billion people by 2043. Hyperglycemia, a common condition in diabetes, can result in dehydration and reduced saliva production due to osmotic diuresis. These complications contribute to a significant demand for therapeutics aimed at managing xerostomia in diabetic patients. Thus, the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide drives the demand for xerostomia therapeutics, thereby influencing market growth.
Additionally, increasing advancements in pharmaceutical research have led to the development of novel products, including saliva substitutes and stimulants, that offer improved efficacy and patient compliance which in turn is anticipated to boost market growth over the forecast period. For instance, according to an article published by Franziska Beier, Dental Tribune International in December 2023, researchers at the University of Leeds United Kingdom developed a saliva substitute to alleviate the discomfort of patients suffering from dry mouth. The novel solution mimics natural saliva in its ability to moisten the mouth and serve as a lubricant during food intake. It comes in a dairy and a vegan formulation, and in vitro experiments have found it to be more effective than other commercially available products. Such advancements in products lead to drive its adoption to treat drug mouth, thereby influencing market growth.
Furthermore, increasing investment in healthcare infrastructure and rising disposable incomes in emerging markets are enhancing access to these therapeutics, further fueling market growth.
Therefore, owing to the above-mentioned factors, such as increasing prevalence of conditions that contribute to xerostomia, such as diabetes and increasing advancements in pharmaceutical research have led to the development of novel products, the market studied is expected to grow over the forecast period. However, factors such as lack of awareness and unavailability of effective treatment will likely hinder the usage of xerostomia therapeutics products and can act as a restraining factor for the xerostomia therapeutics market.
Reduced saliva production can cause tooth decay, mouth infections, changes in taste or smell, difficulty swallowing, pain, and other problems. Artificial saliva, available as a liquid or spray, is used to moisten the mouth and ease the discomfort of chronic dry mouth, especially with regular use. Many artificial saliva sprays and gels claim to work for up to two hours, but users often need more frequent applications, affecting sleep and daily activities. Additionally, several saliva sprays and gels have strong and unpleasant flavours. However, the recent use of naturally sweet xylitol has led to better-tasting alternatives.
Factors such as the growing burden of dry mouth disease and increasing research studies propel the segment's growth. For instance, according to the data published by the American Dental Association in April 2023, xerostomia affected 10% to 26% of men and 10% to 33% of women in 2023. Given the significant prevalence of xerostomia, there's a heightened demand for therapeutic treatments, propelling the growth of the market.
Numerous studies have shown the efficacy of several artificial saliva formulations for treating people affected by xerostomia. For instance, a March 2024 study in the Journal of Oral Medicine, Oral Surgery, Oral Pathology, and Oral Radiology assessed and compared the efficacy of two artificial saliva formulations: the sodium carboxymethylcellulose (SCMC) spray and the SCMC spray enhanced with B-glucan. Both the control and the B-glucan enriched artificial saliva showed improvement in the clinical signs and symptoms of xerostomia.
Additionally, a May 2024 article in BMC Oral Health highlighted that an artificial saliva spray could significantly alleviate dry mouth symptoms in COVID-19 patients undergoing non-invasive mechanical ventilation. Such clinical trials provide valuable insights into the safety and effectiveness of artificial saliva products, leading to greater confidence among healthcare providers and patients, thereby driving market growth. Hence, the segment is expected to register steady growth during the forecast period due to the factors above.
North America is poised to lead the market, driven by increasing prevalence of conditions that contribute to xerostomia, such as Sjogren's syndrome, diabetes, and cancer treatments. Additionally, aging population, heightened awareness of xerostomia among healthcare professionals and patients, advancements in therapeutic options, including innovative saliva substitutes, stimulants, and moisture-retaining agents, and significant investment in research and development by pharmaceutical companies are further anticipated to drive segmental growth over the forecast period.
The increasing prevalence of diabetes is anticipated to boost market growth in North America, reflecting the need for effective management solutions to improve quality of life for those affected by diabetes. For instance, according to the data published by the Canadian Diabetes Association 2023, 4.1 million diabetic (type 1 and type 2 diagnosed) patients were recorded in 2023 in Canada and is projected to grow to around 5.2 million by 2033. Diabetes can cause damage to the salivary glands, leading to reduced saliva production and an increased risk of infections, cavities, and gum disease. Thus, the increasing prevalence of diabetes in Canada, along with its associated oral health complications, has created a growing demand for therapeutics aimed at managing xerostomia, thereby influencing market growth in the region.
Furthermore, the growing number of investments by various institutes, including pharmaceutical companies, research organizations, and venture capitalists, is significantly driving the xerostomia (dry mouth disease) therapeutics market in North America. For instance, in October 2024, an associate professor of oral biology at the University at Buffalo's School of Dental Medicine, United States secured a five-year grant renewal worth USD 2.2 million from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR), part of the National Institutes of Health. This funding aims to alleviate the suffering of patients with conditions like Sjogren's disease, which depletes moisture from various body glands. Such funding enables the development and commercialization of innovative treatment solutions aimed at alleviating symptoms associated with xerostomia, thereby expanding the market's potential and improving patient outcomes in this often-overlooked condition.
Moreover, strategic initiatives by key players such as product approvals and the introduction of innovative therapies for xerostomia (dry mouth disease), enhance treatment options and drive market growth by addressing unmet patient needs and improving quality of life. For instance, in October 2024, RiboX Therapeutics, United States received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance for the investigational new drug (IND) application of RXRG001, introducing the first circular RNA therapy designed to treat radiation-induced xerostomia and hyposalivation. Such product approvals not only enhances clinical outcomes for patients but also stimulates market growth by encouraging further research and investment in xerostomia therapeutics, thereby boosting market growth,
In summary, the increasing prevalence of diabetes, the growing number of investments by various institutions, and product approvals are likely to increase the demand for xerostomia (dry mouth disease) therapeutics in North America and drive the market's growth during the forecast period.
The xerostomia (dry mouth disease) therapeutics market is moderately competitive. Key players in the xerostomia therapeutics market are focusing on developing their product portfolio, acquiring emerging players, and distributing agreements to increase their geographical presence. Some of the key players dominating the xerostomia therapeutics market are Quest Healthcare, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Pharmascience Inc., ADVANZ PHARMA, Lupin, Parnell Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., and Synedgen, Inc., among others.