
무선 네트워크 보안 시장 규모는 2025년에 228억 4,000만 달러로 추정되며, 예측 기간(2025-2030년)의 CAGR은 11.62%로, 2030년에는 395억 8,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.
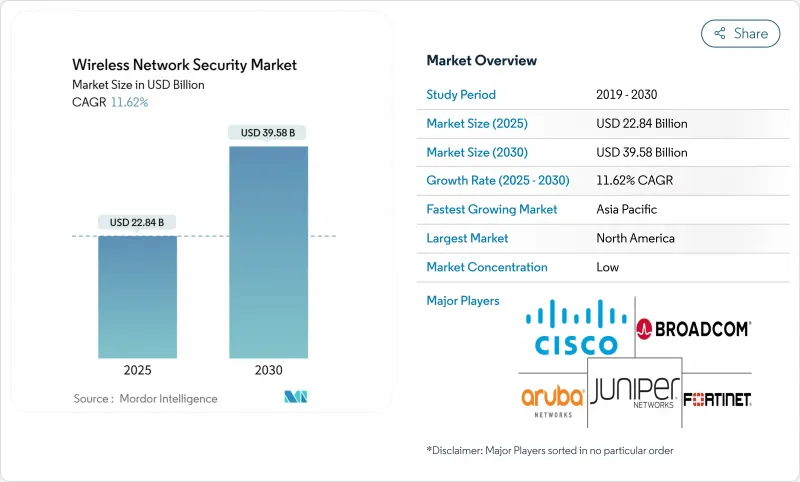
견고한 수요의 배경에는 Wi-Fi 6E 및 Wi-Fi 7의 급속한 보급, 클라우드 퍼스트 전략, 프라이빗 5G의 배치가 있어 공격 대상이 확대되고 차세대 제로 트러스트 보호가 필요합니다. 기업은 보안 액세스 서비스 에지 프레임워크와 원활하게 융합되는 통합 보안 스택으로 경계 중심의 방위를 대체하고 있으며, 미국에서는 다중 요소 인증의 의무화로 통합 무선 안전 가드의 도입이 가속화되고 있습니다. 기존의 딥 패킷 검사 엔진은 대기 시간 페널티 없이 몇 기가비트의 처리량을 유지할 수 없기 때문에 공급업체는 6GHz 동작에 특화된 실리콘 재설계를 강요하고 있으며 하드웨어 리프레시 사이클이 진행 중입니다. 북미는 30억 달러의 Rip-and-Replace 프로그램을 배경으로 선도하고 있지만, 아시아태평양은 모바일 퍼스트 경제권이 5G 주도 디지털화에 자본을 투입하고 있기 때문에 가장 빠른 확대를 기록하고 있습니다. 경쟁이 치열해지면서 공급업체는 마진과 관련성을 유지하기 위해 AI를 활용한 이상 감지, 내양자암호화, 클라우드 네이티브 딜리버리 모델에 대한 노력을 추진하고 있습니다.
WPA3 암호화, 320MHz 채널, Wi-Fi 7의 멀티링크 동작의 의무화로 총 처리량이 30Gbps를 넘어 기존의 검사 어플라이언스가 압도되어 기업은 6GHz에서 실시간 분석이 가능한 보안 하드웨어의 쇄신을 강요하고 있습니다. 현장 평가판에서는 Wi-Fi 6E의 2배인 40피트에서 1Gbps를 유지하는 것으로 확인되었으며 공급업체는 고속 TLS 오프로드와 하드웨어 가속 패턴 매칭을 통합해야 합니다. 자동화된 주파수 조정은 2.4, 5, 6GHz 대역에서 일관된 위협 제어를 유지해야 하므로 정책 복잡성에 박차를 가합니다. 따라서 기업은 사용자 경험을 유지하면서 계산 집약적인 작업을 오프로드하는 확장 가능한 클라우드 관리 방화벽에 자본을 나눌 것입니다. 엔지니어는 결정적인 스케줄링, 멀티링크 스택 구성, 보다 세밀한 서비스 품질 구현에 적응하기 때문에 직원의 재교육이 필수적입니다.
외부 어플라이언스 없이 인라인 방화벽을 구현하는 HPE의 CX 10040 스위치로 대표되는 경계 붕괴로 인해 기업은 액세스 포인트 내에 상태 저장 검사 및 암호화를 직접 통합해야 합니다. 에지 기반 보안은 백홀 비용과 대기 시간을 줄이고 위치를 선택하지 않는 액세스를 요구하는 직원의 요구에 부응합니다. SD-WAN과 WLAN 보안의 융합은 하이브리드 클라우드를 가로지르는 정책 오케스트레이션이 내부 팀의 과제이기 때문에 관리 서비스의 성장을 가속합니다. 그러나 관리자가 On-Premise 라디오, 공용 IaaS 및 엣지 컴퓨팅 노드에 걸쳐 있는 규칙 세트를 동기화하므로 변경 관리 오버헤드가 증가하고 AI를 통한 구성 검증이 필요합니다.
기업은 컴플라이언스를 유지하면서 액세스 포인트 펌웨어, NAC 서버 및 SIEM 애널리틱스를 조정해야 하므로 대규모 무선 보안 프로젝트는 초기 비용으로 1,000만 달러를 초과할 수 있습니다. 어드밴텍의 FWA-6183과 같은 하이 엔드 어플라이언스는 192 코어를 탑재하고 있으며 멀티 기가비트 검사에 필요한 프리미엄 하드웨어임을 명확하게 보여줍니다. 전문 서비스, 연간 유지보수 및 직원 기술 향상이 추가되면 총소유량이 늘어나므로 중소기업은 구독 기반 관리 서비스를 선호합니다.
방화벽 제품은 2024년 무선 네트워크 보안 시장 점유율의 35%를 차지하여 기본 제어 역할을 재확인했습니다. 그러나 SASE 제품은 CAGR 16.21%로 확대되어 게이트웨이, CASB, ZTNA의 기능을 통합한 싱글 패스 아키텍처로 축 발을 옮기고 있어 무선 네트워크 보안 시장을 재구축할 것으로 예측됩니다. 포티넷의 FortiGate 700G는 7배의 처리량 향상과 포스트 양자에 대한 대응으로 이 변화를 명확하게 보여줍니다. 통합 위협 관리는 모놀리식 설계에서 클라우드 네이티브 스택의 탄력성이 부족하기 때문에 부진합니다. 암호화 제품군은 규제적 의무화에 의해 계속 관련이 있지만, ID 중심의 세분화은 제로 트러스트 프로그램 하에서 지지를 모으고 있습니다. SASE의 도입이 가속되는 가운데, 공급자는 AI를 탑재한 상관 엔진이나 체류 시간을 삭감하는 엔드 투 엔드의 정책 가시화로 차별화를 도모합니다.
SASE 플랫폼의 무선 네트워크 보안 시장 규모는 기업이 노후화된 VPN 집중기를 클라우드 제공 에지 노드로 대체함에 따라 급증할 것으로 예측됩니다. 2030년까지 SASE는 절대적인 매출로 방화벽에 필적할 것이며, SIM 기반 아이덴티티를 정책 트리에 주입하는 Palo Alto Networks의 Prisma SASE 5G와 같은 서비스 제공업체의 변종에 의해 뒷받침됩니다. 반면 '기타 솔루션' 버킷에는 내량자 암호화와 블록체인 인증을 통한 온보딩이 포함되어 있으며 초기 단계의 수익 스트림을 제공하지만 예측 기간 후반에 성숙할 수 있습니다.
On-Premise는 2024년 무선 네트워크 보안 시장 규모의 58%를 차지했습니다. 그러나 미국 FCC와 같은 공공기관이 2억 달러의 파일럿 프로그램으로 SaaS 보안을 추진한 후 클라우드 기반은 15.91%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)로 성장을 지속하여 있습니다. 탄력적인 용량, 시그니처 자동 업데이트, 소비 기반 가격 설정은 설비 투자 감소를 요구하는 IT 관리자에게 강력하게 지지를 받고 있습니다.
하이브리드 배포 모델은 복잡한 기업에 지배적인 설계가 되고 있습니다. 핵심 데이터센터는 고보증 검사를 로컬로 유지하고 지점과 모바일 워크포스는 클라우드 게이트웨이를 통해 규모를 확장합니다. 공급망 위험으로 인해 특정 워크로드가 On-Premise로 되돌아가지만 검사가 컨텐츠 소스에 가까워짐에 따라 전반적인 성장 궤도가 클라우드에 유리하게 됩니다. 클라우드 콘솔의 라우팅된 원격 측정은 벤더 전체의 머신러닝 모델을 촉진하고 사일로화된 어플라이언스 데이터와 비교하여 감지의 충실도를 향상시킵니다.
북미는 연방 정부 시스템 전체에 다 요소 인증과 제로 트러스트의 구현을 의무화하는 대통령령 14028호에 밀려 2024년 세계 매출의 38%를 유지했습니다. 이 지역의 무선 네트워크 보안 시장 규모는 30억 달러를 투자한 Rip-and-Replace 프로그램이 전국적으로 취약한 하드웨어를 제거함에 따라 계속 확대될 것으로 보입니다. 캐나다와 멕시코는 미국 표준에 편승하고 FIPS 인증 암호 및 NIST 포스트 양자 알고리즘을 중심으로 조달을 표준화합니다.
아시아태평양의 CAGR은 15.50%로 세계 최고를 기록할 것으로 예측되며 이는 모바일 가입자 수 증가와 대규모 민간 5G 제조 코리도를 배경으로 한 것입니다. 중국, 일본, 인도는 안전한 캠퍼스 네트워크에 재정적인센티브를 할당하고 한국은 스마트 시티 분석을 지원하는 Wi-Fi 7의 전국 배포를 보여줍니다. 지역 정부는 지역 데이터 주권 규칙에 맞는 사이버 규범을 성문화하여 여러 관할권에 대응하는 컴플라이언스 모듈 수요를 촉진하고 있습니다.
유럽에서는 GDPR(EU 개인정보보호규정)의 시행과 정보 유출 보고의 의무화를 확대하는 NIS2 지령에 힘입어 꾸준한 기세를 보이고 있습니다. 공급업체는 금융 기관을 위한 EU DORA와 같은 분야별 규칙에 특화된 정책 템플릿을 패키징합니다. 한편 중동 및 아프리카와 남미는 통신사업자가 오픈 RAN으로 근대화를 진행하고 정부가 중요 인프라 방위에 경기 자극책을 투입하고 있기 때문에 신흥하면서 유망한 지역이 되고 있습니다.
The Wireless Network Security Market size is estimated at USD 22.84 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 39.58 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.62% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
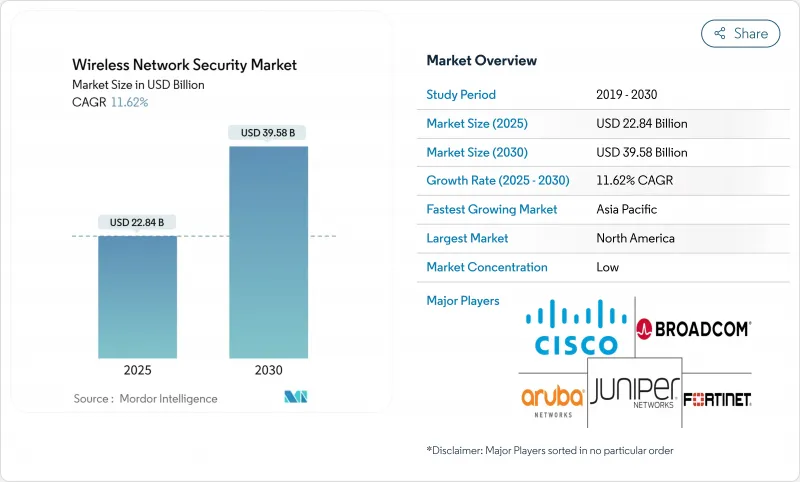
Robust demand stems from rapid Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 adoption, cloud-first strategies and private-5G rollouts that collectively enlarge the attack surface and necessitate next-generation zero-trust protection. Enterprises are replacing perimeter-centric defenses with integrated security stacks that blend seamlessly with Secure Access Service Edge frameworks, while multifactor authentication mandates in the United States accelerate uptake of unified wireless safeguards. Hardware refresh cycles are underway because legacy deep-packet inspection engines cannot sustain multi-gigabit throughput without latency penalties, compelling vendors to redesign silicon specifically for 6 GHz operations. North America leads on the back of the USD 3 billion Rip-and-Replace program, whereas Asia-Pacific registers the fastest expansion as mobile-first economies pour capital into 5G-driven digitalization. Intensifying competitive dynamics push suppliers toward AI-enabled anomaly detection, quantum-resistant encryption and cloud-native delivery models to preserve margin and relevance.
Mandatory WPA3 encryption, 320 MHz channels and multi-link operation in Wi-Fi 7 lift aggregate throughput beyond 30 Gbps, overwhelming legacy inspection appliances and prompting enterprises to refresh security hardware capable of real-time analytics at 6 GHz. Field trials confirmed sustained 1 Gbps at 40 feet-double Wi-Fi 6E-forcing vendors to embed high-speed TLS off-load and hardware-accelerated pattern matching. Automated Frequency Coordination adds policy complexity because threat controls must remain consistent across 2.4, 5 and 6 GHz bands. Organizations therefore allocate capital toward scalable, cloud-managed firewalls that off-load compute-intensive tasks while preserving user experience. Staff retraining becomes essential as engineers adapt to deterministic scheduling, multi-link stack configuration and more granular quality-of-service enforcement.
Collapsing perimeters oblige enterprises to embed stateful inspection and encryption directly inside access points, exemplified by HPE's CX 10040 switch that furnishes inline firewalling without external appliances. Edge-based security reduces backhaul costs and latency, aligning with employee demand for location-agnostic access. The fusion of SD-WAN and WLAN security fuels managed-service growth because policy orchestration across hybrid clouds challenges internal teams. However, change-control overhead rises as administrators synchronize rulesets spanning on-premises radios, public IaaS and edge compute nodes, elevating the need for AI-driven configuration validation.
Large-scale wireless security undertakings can exceed USD 10 million upfront because enterprises must align access-point firmware, NAC servers and SIEM analytics while maintaining compliance. High-end appliances such as Advantech's FWA-6183 wield 192 cores, underscoring the premium hardware required for multi-gigabit inspection. Total ownership balloons once professional services, annual maintenance and workforce upskilling are added, prompting SMEs to prefer subscription-based managed offerings.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Firewall products captured 35% of the wireless network security market share in 2024, reaffirming their role as foundational controls. However, SASE offerings are slated to expand at a 16.21% CAGR, reshaping the wireless network security market as organizations pivot toward single-pass architectures that consolidate gateway, CASB and ZTNA features. Fortinet's FortiGate 700G underscores the shift with 7-fold throughput gains and post-quantum readiness. Unified Threat Management is slipping because monolithic designs lack the elasticity of cloud-native stacks. Encryption suites remain relevant due to regulatory mandates, whereas identity-driven segmentation gains traction under zero-trust programs. As SASE adoption accelerates, suppliers differentiate on AI-powered correlation engines and end-to-end policy visualizations that cut dwell time.
The wireless network security market size for SASE platforms is forecast to climb steeply as enterprises replace aging VPN concentrators with cloud-delivered edge nodes. By 2030, SASE is positioned to rival firewalls in absolute revenue, buoyed by service-provider variants such as Palo Alto Networks' Prisma SASE 5G that inject SIM-based identity into policy trees. Meanwhile, quantum-resistant encryption and blockchain-authenticated onboarding sit in the "Other Solutions" bucket, offering early-stage revenue streams that may mature late in the forecast horizon.
On-premises implementations represented 58% of the wireless network security market size in 2024 because financial-services and public-sector operators favour direct control over sensitive data. Yet cloud variants are pacing at a 15.91% CAGR after public agencies such as the U.S. FCC promoted SaaS security in a USD 200 million pilot program. Elastic capacity, automatic signature updates and consumption-based pricing resonate strongly with IT managers seeking lower capex.
Hybrid deployment models crystallize as the dominant design for complex enterprises: core data centers keep high-assurance inspection local, while branch sites and mobile workforces traverse cloud gateways for scale. Supply-chain risks push certain workloads back on-premises, but overall growth trajectory favours cloud as inspection moves closer to content sources. Routed telemetry from cloud consoles fuels vendor-wide machine-learning models, lifting detection fidelity compared with siloed appliance data.
Wireless Network Security Market Report is Segmented by Solution (Firewall, Encryption, and More), Deployment, End-User Industry (BFSI, Healthcare, and More), Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Smes), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America maintained a 38% slice of global revenue in 2024, catalysed by Executive Order 14028 mandating multifactor authentication and zero-trust implementation across federal systems. The wireless network security market size in the region will keep expanding as the USD 3 billion Rip-and-Replace program removes vulnerable hardware nation-wide. Canada and Mexico piggyback on U.S. standards, standardizing procurement around FIPS-validated cryptography and NIST post-quantum algorithms.
Asia-Pacific is projected to clock a 15.50% CAGR, the highest globally, on the back of swelling mobile-subscriber counts and large-scale private-5G manufacturing corridors. China, Japan and India allocate fiscal incentives for secure campus networks, while South Korea showcases nationwide Wi-Fi 7 rollouts supporting smart-city analytics. Regional governments codify cyber norms tailored to local data-sovereignty rules, driving demand for multi-jurisdictional compliance modules.
Europe shows steady momentum anchored by GDPR enforcement and the NIS2 directive that broadens mandatory breach-reporting. Vendors package policy templates specific to sectoral rules like EU DORA for financial institutions. Meanwhile, Middle East & Africa and South America remain emerging yet promising pockets as telcos modernize with open-RAN and governments channel stimulus into critical infrastructure defense.