
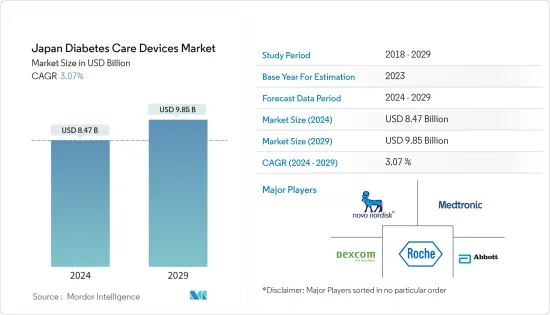
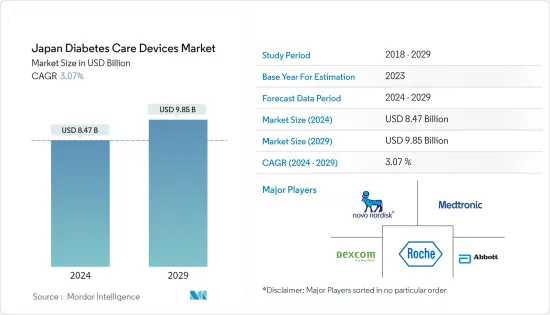
일본의 당뇨병 치료 기기 시장 규모는 2024년 84억 7,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 추정됩니다. 2029년에는 98억 5,000만 달러에 달할 것으로 예상되며, 예측 기간(2024-2029년) 동안 3.07%의 연평균 복합 성장률(CAGR)을 나타낼 전망입니다.
코로나19 팬데믹은 당뇨병 치료 기기 시장에 큰 영향을 미치고 있으며, 코로나19 감염으로 입원한 환자의 당뇨병 유병률과 혈당 조절 개선이 SARS-CoV-2 환자의 예후를 개선하고 입원 기간을 단축시킬 수 있다는 인식 당뇨병 치료 기기의 중요성이 강조되고 있습니다. 제81회 미국당뇨병학회(ADA) 가상 과학 세션에서 후향적 분석이 발표되어 당뇨병이 일본인의 코로나19 환자의 중증도 가속화의 주요 위험 요소임을 보여주었습니다.
당뇨병은 코로나19가 유행하는 동안에도 코로나19의 심각한 위험 요소로 남아있었습니다. 당뇨병과 코로나19를 앓고 있는 입원 환자 10명 중 1명은 입원 후 7일 이내에 사망했습니다.
팬데믹은 또한 의료 제공업체와 당뇨병 환자 간의 가상 상담과 당뇨병 기술 활용을 통해 당뇨병 치료 제공에 있어 혁신을 지속하고 확장할 수 있는 기회를 부각시켰습니다. 위기 관리로 인해 환자와 의료 서비스 제공업체 모두 원격 의료에 대한 전례 없는 관심이 생겨났고, 수년간의 많은 규제 장벽이 제거되었습니다. 이처럼 코로나19 사태는 일본의 당뇨병 치료 기기 시장의 성장을 가속화했습니다.
당뇨병은 세계적인 전염병으로 부상하고 있으며, IDF 2021 데이터에 따르면 일본에는 약 1,100만 명이 당뇨병을 앓고 있습니다. 1형 당뇨병은 면역 체계의 기능 장애로 인해 발생하는 반면, 2형 당뇨병은 앉아서 생활하는 생활 습관과 관련이 있으며, 그 결과 인슐린에 대한 내재적 저항이 발생합니다. 따라서 1형 당뇨병은 인슐린 요구성 당뇨병, 2형 당뇨병은 인슐린 의존성 당뇨병으로 구분할 수 있습니다. 일본은 세계에서 가장 많은 노인인구를 보유하고 있으며, 2형 당뇨병에 걸리기 쉬운 나라입니다. 일본은 고령화가 진행되면서 당뇨병 유병률도 증가하고 있습니다. 심혈관 질환, 신장 질환 및 기타 여러 증상과 같은 부작용을 피하기 위해 혈당 모니터링 및 관리가 증가하고 있습니다.
지속적인 혈당 모니터링 부문은 예측 기간 동안 11% 이상의 CAGR을 기록할 것으로 예상됩니다.
CGM을 사용하려면 피부의 최상층을 관통하는 작은 플라스틱 캐뉼라를 사용하여 작은 센서를 복부 또는 팔에 삽입합니다. 접착 패치가 센서를 제자리에 고정시켜 밤낮으로 간질액 내 포도당을 측정할 수 있도록 합니다. 일반적으로 센서는 7-14일마다 교체해야 합니다. 센서에 연결된 소형 재사용 가능한 송신기를 통해 시스템은 혈당 데이터를 표시하는 모니터 장치에 실시간 측정값을 무선으로 전송할 수 있습니다. 전용 모니터가 장착된 시스템도 있고, 스마트폰 앱을 통해 정보를 표시하는 시스템도 있습니다.
연속 포도당 모니터링 센서는 포도당 산화효소를 사용하여 혈당치를 감지합니다. 포도당 산화 효소는 포도당을 수소 과산화 효소로 변환하여 센서 내부의 백금과 반응하여 송신기로 전달되는 전기 신호를 생성합니다. 센서는 지속적인 혈당 모니터링 장치의 가장 중요한 부분입니다. 연구진은 전기화학 기반 포도당 센서의 대안을 찾고 개발하여 더 저렴하고 침습성이 최소화 된 사용자 친화적 인 CGM 센서를 만들기 위해 노력하고 있습니다. 광학 측정은 포도당 감지를 위한 유망한 플랫폼입니다. 분광법, 형광, 홀로그램 기술 등 지속적인 포도당 감지에 높은 잠재력을 가진 몇 가지 기술이 보고되었으며, Senseonics Company가 개발한 형광 감지 기반 CGM 센서인 Eversense는 전기화학 센서보다 훨씬 더 긴 수명을 보여줍니다. 훨씬 더 긴 수명을 보입니다. 센서의 정확도를 향상시키는 기술의 발전은 예측 기간 동안 부문의 성장을 가속할 것으로 예상됩니다.
혈당 모니터링 빈도는 당뇨병 유형에 따라 다르며 환자마다 다릅니다. 제 1 형 당뇨병 환자는 혈당을 정기적으로 확인하여 혈당을 모니터링하고 그에 따라 인슐린 투여 량을 조정해야합니다. 현재 CGM 장치는 설정된 간격으로 혈당을 일상적으로 확인하는 것과 비교하여 혈당 패턴과 추세를 자세히 표시합니다. 또한 현재의 연속 혈당 모니터링 장치는 데이터를 다운로드하여 혈당 추세를 소급하여 표시하거나 수신기의 디스플레이를 통해 혈당치의 실시간 이미지를 표시 할 수 있습니다. 휴대폰 통합과 같은 새로운 기술로 인해 지속적인 혈당 모니터링 장치가 점점 더 저렴해지고 있습니다. 이는 예측 기간 동안 부문의 성장을 가속할 수 있습니다.
재사용 가능한 펜형 인슐린 카트리지는 올해 관리 장치 부문에서 약 68%로 가장 높은 시장 점유율을 차지했습니다. 이는 인슐린 바이알의 업그레이드 버전입니다. 대부분의 인슐린은 카트리지 형태로 제조되어 쉽게 구할 수 있습니다. 이러한 장치에는 재사용 가능한 펜의 모든 기능적 이점이 포함되어 있으며, 장기적으로 이러한 카트리지는 일회용 인슐린 펜에 비해 저렴하기 때문에 비용 효율성이 높습니다.
인슐린 카트리지에 대한 수요가 증가함에 따라 대부분의 인슐린 장치 제조업체는 다양한 인슐린 제조업체의 카트리지와 호환되는 재사용 가능한 인슐린 펜을 생산했습니다. 이 인슐린 카트리지는 기존의 바이알과 주사기에 비해 작고 눈에 띄지 않기 때문에 소비자 친화적 인 것으로 간주됩니다. 이 장치는 소비자가 휴대하기에도 편리합니다. 개방형 카트리지는 냉장 보관할 필요가 없기 때문에 소비자가 쉽게 보관할 수 있습니다. 따라서 일회용 펜과 달리 재사용 가능한 펜은 한 번만 투자하면 되므로 카트리지는 가장 비용 효율적인 인슐린 사용 방법입니다.
당뇨병은 일본 후생노동성에서 중점 건강관리 대상으로 지정한 질환입니다. 2형 당뇨병의 높은 유병률은 심각한 경제적 부담과 관련이 있습니다. 당뇨병 비용은 고혈압, 고지혈증과 같은 동반 질환이 있거나 합병증을 앓고 있는 환자에서 더 많이 발생합니다. 합병증 수가 증가하면 비용도 증가합니다. 일본에서는 의료보험제도가 잘 정비되어 있어 당뇨병에 대한 의료비를 전액 부담하고, 당뇨병 환자는 자유롭게 진찰을 받을 수 있습니다. 또한 자가주사를 통한 인슐린 요법도 합법화되어 건강 보험이 적용됩니다. 이러한 장점은 이들 제품이 일본 시장에서 채택되는 데 도움이 되었습니다.
The Japan Diabetes Care Devices Market size is estimated at USD 8.47 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 9.85 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 3.07% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a substantial impact on the diabetes care devices market. The prevalence of diabetes in people hospitalized with COVID-19 infection and the recognition that improved glycemic control might improve outcomes and reduce the length of stay in patients with SARS-CoV-2 have underlined the importance of diabetes care devices. A retrospective analysis was presented at the virtual 81st Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association?iR) (ADA) which showed diabetes was the main risk factor for the accelerated advancement to a severe state in Japanese COVID-19 patients.
Throughout the pandemic, diabetes has persisted as a significant risk factor for COVID-19. In hospitalized patients with diabetes and COVID-19, one in 10 people died within seven days of admission.
The pandemic also highlighted opportunities for continuing and expanding innovations in the delivery of diabetes care, through virtual consultations between healthcare providers and people with diabetes, and the use of diabetes technology. Crisis management has created unprecedented interest in remote care from both patients and providers and removed many long-standing regulatory barriers. Thus, the COVID-19 outbreak increased the Japanese diabetes care device market's growth.
Diabetes has emerged as a global epidemic, Japan has around 11 million people with diabetes according to IDF 2021 data. While Type 1 diabetes is caused by an immune system malfunction, Type 2 diabetes is linked to leading a sedentary lifestyle, which results in the development of inherent resistance to insulin. Hence, Type 1 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-requiring, while Type 2 diabetes can be characterized as insulin-dependent diabetes. Japan has one of the largest elderly populations in the world which is more susceptible to the onset of type 2 diabetes. As Japan's population continues to age, the prevalence of diabetes increases as well. The monitoring and management of blood glucose levels are on the rise, to avoid negative consequences, such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney disorders, and many other conditions.
The continuous glucose monitoring segment is expected to register a CAGR of more than 11% over the forecast period.
To use a CGM, a small sensor is inserted into the abdomen or arm with a tiny plastic cannula penetrating the top skin layer. An adhesive patch holds the sensor in place, allowing it to take glucose readings in interstitial fluid throughout the day and night. Generally, the sensors must be replaced every 7 to 14 days. A small, reusable transmitter connected to the sensor allows the system to send real-time readings wirelessly to a monitor device that displays blood glucose data. Some systems contain a dedicated monitor, and some display the information via a smartphone app.
Continuous glucose monitoring sensors use glucose oxidase to detect blood sugar levels. Glucose oxidase converts glucose to hydrogen peroxidase, which reacts with the platinum inside the sensor, producing an electrical signal to be communicated to the transmitter. Sensors are the most important part of continuous glucose monitoring devices. Researchers are trying to find and develop alternatives to electrochemical-based glucose sensors and create more affordable, minimally invasive, and user-friendly CGM sensors. Optical measurement is a promising platform for glucose sensing. Some technologies with high potential in continuous glucose sensing are reported, including spectroscopy, fluorescence, holographic technology, etc. Eversense, a CGM sensor based on fluorescence sensing developed by Senseonics Company, presents a much longer lifespan than electrochemical sensors. Technological advancements to improve the sensor's accuracy are expected to drive segment growth during the forecast period.
The frequency of monitoring glucose levels depends on the diabetes type, which varies from patient to patient. Type-1 diabetic patients need to check their blood glucose levels regularly to monitor their blood glucose levels and adjust the insulin dosing accordingly. The current CGM devices show a detailed representation of blood glucose patterns and tendencies compared to a routine check of glucose levels at set intervals. Furthermore, the current continuous glucose monitoring devices can either retrospectively display the trends in blood glucose levels by downloading the data or give a real-time picture of glucose levels through receiver displays. Continuous glucose monitoring devices are becoming cheaper with new technologies, like cell phone integration. It is likely to drive the segment growth during the forecast period.
Insulin cartridges in reusable pens occupied the highest market share of about 68% in the management devices segment in the current year.
Insulin cartridges in reusable pens are an upgraded version of insulin vials. Most types of insulins are manufactured in the form of cartridges, making them easily accessible. These devices include all the functional benefits of reusable pens and are cost-effective, as these cartridges are less expensive compared to disposable insulin pens in the long run.
Due to the increasing demand for insulin cartridges, most insulin device manufacturers produced reusable insulin pens compatible with various insulin manufacturers' cartridges. These insulin cartridges are considered more consumer-friendly, as they are smaller and less noticeable than the classic vial-and-syringe. These devices are also more portable for consumers. Open cartridges do not need to be refrigerated, making storage easy for consumers. Thus, cartridges are the most cost-effective insulin use, as reusable pens are a one-time investment, unlike disposable pens.
Diabetes is identified as a healthcare priority by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. The high prevalence of type 2 diabetes is associated with a significant economic burden. The costs of diabetes are increased in patients with co-morbidities such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia and in patients who develop complications. Costs increase with an increasing number of complications. Well-organized medical insurance systems cover all medical fees for diabetes mellitus, and people with diabetes can visit doctors freely in Japan. Also, insulin therapy by self-injection became legal and is covered by health insurance. Such advantages helped the adoption of these products in the Japanese market.
The Japanese diabetes care devices market is semi-consolidated, with major manufacturers like Roche, Abbott, Novo Nordisk, Dexcom, Medtronic, etc., and other region-specific manufacturers.