
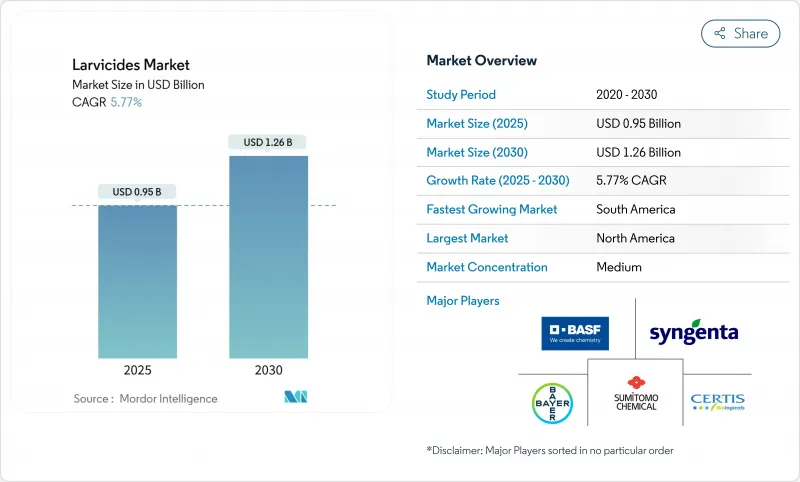
살유충제 시장 규모는 2025년에 9억 5,000만 달러로 추정되고, 예측 기간 중 CAGR은 5.77%를 나타낼 전망이며, 2030년에는 12억 6,000만 달러에 이를 것으로 예상됩니다.
시장 성장의 원동력은 성충 구제법의 효과가 저하되었기 때문에 유충기 모기를 타겟으로 할 필요성이 높아지고 있는 것, 아메리카에서의 헬스케어 예산의 확대, 환경에 적합한 생물 합리적 제제의 지속적인 개발 등입니다. 또한 온대지역에서 모기의 번식기간 연장, 열대도시 지역의 뎅기열의 지속적인 유행, 양식에 적합한 안전한 살유충제를 필요로 하는 쌀과 생선의 통합 양식 시스템의 채용 증가 등도 성장의 원동력이 되고 있습니다. 이 시장은 생물학적 제제의 생산 비용 상승, 농촌 지역의 일관성 없는 살포 방법, 처리 효율성을 높이기 위한 GIS 기반 모니터링 시스템의 필요성 등의 과제에 직면하고 있습니다.
모기는 표적 부위 불감수성과 대사적 해독에 의해 살충제에 대한 내성을 발달시킵니다. 아노페레스와 아에데스 모기는 유전 적응, 행동 변화, 대사 저항성에 의한 화학 치료를 피합니다. 현재, 벡터 컨트롤 프로그램에서는 정체된 수역이나 도시의 저수지 등, 번식 장소에 있는 유충을 타겟으로 하는 것으로, 초기 단계의 개체수를 컨트롤 하는 것에 중점을 두고 있습니다. 이 접근법은 모기가 성충이되는 것을 방지하고 질병의 전파주기를 차단할 수 있습니다. 또한 해충 방제 프로그램은 개별 약제에 대한 선택 압력을 줄이기 위해 다양한 유효 성분을 회전시키는 통합 전략을 실시하는 것이 증가하고 있습니다. 이 변화는 피레스로이드의 실패로 인해 긴급 살포 예산이 위험해진 지역에서 두드러지며, 시정촌은 성충의 무리가 출현하기 전에 홍수 풀과 빗물 배수구를 보호하는 시즌 중 살유충제 그리드에 투자하게 되었습니다.
라틴아메리카의 대도시에서는 감염률 증가와 도시의 모기 개체수 증가에 따라 뎅기열과 치쿤그니아의 예방 프로그램을 강화하고 있습니다. 세계보건기구(WHO)는 특히 볼리비아와 파라과이에서 감염자가 크게 증가하고 있다고 보고합니다. 예방전략에는 아카이에카의 제거, 일반 시민에 대한 계발활동, 위생, 도시계획, 교육을 조합한 통합적 접근 등이 있습니다. 범미 보건기구(PAHO)는 질병의 감염을 줄이기 위한 지역사회에 뿌리를 둔 대책의 실시에 대해, 지역 정부를 지도하고 있습니다. 2024년 브라질에서 뎅기열이 유행함에 따라 세계 모기 프로그램(WMP)은 피오클루스와 제휴하여 브라질 전역에서 모기가 매개하는 질병에 임했습니다. WMP는 뎅기열, 지카열, 치쿤그니야열의 감염을 막기 위해 예고양이 모기에 천연세균을 도입하는 월바키아법을 확대하고 있습니다.
2026년 농약 일반 허가에서는 지표수를 처리할 때 시용량, 장소, 비표적종의 모니터링을 기록할 것을 시용자에게 의무화하고 있습니다. 테메포스를 포함한 유기 인제의 규제 감독은 범람수 습지 및 도시 유역에서 사용할 수 있는 제형의 선택을 감소시켰습니다. 컴플라이언스 비용이 증가함에 따라 카운티는 가격이 비싸지 만 위험이 높은 화학 물질에서 생물학적 대체 물질로 전환했습니다. 종합적인 독물학적 데이터와 디지털 살포 기록을 제공하는 공급업체는 시장 우위를 유지하고 있지만 진입 장벽은 소규모 사업자에게 영향을 주며 지역의 화학 살유충제의 유통을 제한하고 있습니다.
2024년 살유충제 시장 점유율의 45%는 합성 살유충제가 차지했습니다. 시장에서의 리더십은 비용 우위와 확립된 조달 계약에 기인합니다. 생물학적 제품은 CAGR 8.4%라는 높은 성장률로 성장하고 있으며, 통합적인 벡터 관리 접근을 추진하는 정부의 이니셔티브에 의해 지원되고 있습니다. 바실러스 튤링겐시스 이스라엘렌시스(Bti)는 모기 유충, 클로버, 카비부요에 특이적인 독성을 나타냅니다. 2023년, 카트만두 메트로폴리탄시(KMC)는 모기 유충을 대상으로 하는 바이오 살충 프로그램을 실시하여 뎅기열의 발생을 방지했습니다. 이 유기 용액은 모기 유충의 소화 기관을 파괴하여 모기 유충을 제거하고 다른 유기체는 따뜻합니다.
후기 시험 단계에 있는 RNAi 효모 살유충제 시장 개척은 비표적 종에 영향을 주지 않고 유전자 특이적인 조절을 제공하는 잠재적인 시장 변화를 보여줍니다. 제조업체는 제품의 수명과 사용 편의성을 향상시키기 위해 마이크로 캡슐화 기술을 개선했습니다. 2024년 조사는 작물 보호에서 식물성 살유충제의 효능, 특히 메리골드 추출물의 효능을 입증했습니다. 방갈로르의 PES 대학이 실시한 연구에 의해 Tagetes erecta와 Tagetes patula에는 티오펜류가 포함되어 작물의 해충 Spodoptera litura와 Corcyra cephalonica에 대해 현저한 살유충 효과를 나타내는 것이 밝혀졌습니다. 이러한 기술적 개선은 환경적으로 지속가능한 제품에 대한 정부의 인센티브와 함께 생물학적 살유충제가 더 많은 지자체와의 계약을 확보할 수 있게 합니다.
곤충 성장 조절제(IGR)는 특히 기존의 살충제에 대한 저항성 증가에 대응하여 효과적인 유충 제거 방법으로 등장했습니다. IGR은 탈피, 번식, 변태를 저해함으로써 모기의 발육을 저해하고, 유충이 성충이 되는 것을 막는다. 화학접촉 살충제는 2024년 매출의 55%를 차지했지만, 현장 조사에서는 내성발달에 의한 효과의 저하가 지적되었습니다. 주요 IGR 화합물인 메토프렌은 10 ppb 미만의 농도에서 효능을 나타내며, 물에서의 모빌리티은 최소입니다.
해충 방제 프로그램은 피레스로이드와 유기 인산염에 대한 대사 저항성과 행동 저항성이 널리 퍼져 있기 때문에 피리프록시펜과 메토프렌을 포함한 IGR 기반 솔루션의 채용이 증가하고 있습니다. IGR은 잔효성이 길고 환경에 미치는 영향이 적고 내성균 발생 위험이 낮기 때문에 지속 가능한 모기 제거 프로그램에 필수적인 요소입니다.
북미는 2024년에 가장 큰 매출을 기록한 지역으로, 구조화된 벡터 매니지먼트의 틀과 서일 나일과 동부 말 뇌염에 대한 관심이 높아졌습니다. 미국은 북미에서 모기와 살유충제를위한 살유충제의 주요 사용자입니다. 미국 질병 예방 관리 센터(CDC)와 지역 모기 방제 지구는 전국에서 매개 모기 방제 프로그램을 실시했습니다. 이 프로그램은 모기 관리(IMM) 전략 안에 살유충제가 통합되어 서쪽 나일 바이러스와 지카 열과 같은 모기가 매개하는 질병을 예방합니다.
환경보호청(EPA)은 초기의 미성숙 모기를 대상으로 한 여러 살유충제법을 권장합니다. 유충의 소화를 억제하는 세균성 살충제(Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis 및 Bacillus sphaericus) - 발육을 방해하는 메토프렌 등의 곤충 성장 억제제 - 유충을 익사시키는 표면유나 필름. 환경 문제에 대한 우려로 인해 특정 방제 방법, 특히 유기 인계 살충제의 사용이 중단되었습니다. 모든 방제 방법은 취약한 개체군을 보호하기 위한 규정을 따라야 합니다. EPA의 2026년 농약 일반 허가(Pesticide General Permit)는 지표수에 대한 농약 살포에 대한 엄격한 요건을 정하고 있으며, 이것이 북미 전체의 제품 개발을 형성하고 있습니다.
아시아에서는 중국과 인도가 농약 살포에 의한 생산량을 확보하는 한편 동남아시아 시장에서는 쌀과 생선 시스템에 생물학적 살유충제를 의무화하는 보조금을 활용하고 있습니다. 동시에, 인도네시아 의회는 유기 고양이와 피레스로이드제에 저항성을 나타내기 때문에 인도네시아 의회는 IGR과 Bti 조합의 회전을 강요하고 있으며, 이는 판매량 증가를 지원합니다. 아시아에 속하는 살유충제 시장 점유율은 매년 확대되지만 일부 국가에서는 가격에 민감하기 때문에 마진은 압축된 상태로 남아 있을 수 있습니다.
남미는 뎅기열과 치쿤구니아의 유행과 관련된 공중보건 위기가 원동력이 되어 가장 높은 성장률을 보이고 있습니다. 브라질에서는 2024년 뎅기열 환자가 725만 명에 달했고 2023년 기록된 수의 2배에 달했습니다. 도시위생부문은 발생원 삭감 이니셔티브와 주 1회의 살유충제 살포를 조합하여 유통업체의 재고 수준을 유지하는 안정적인 제품 수요를 확보하고 있습니다.
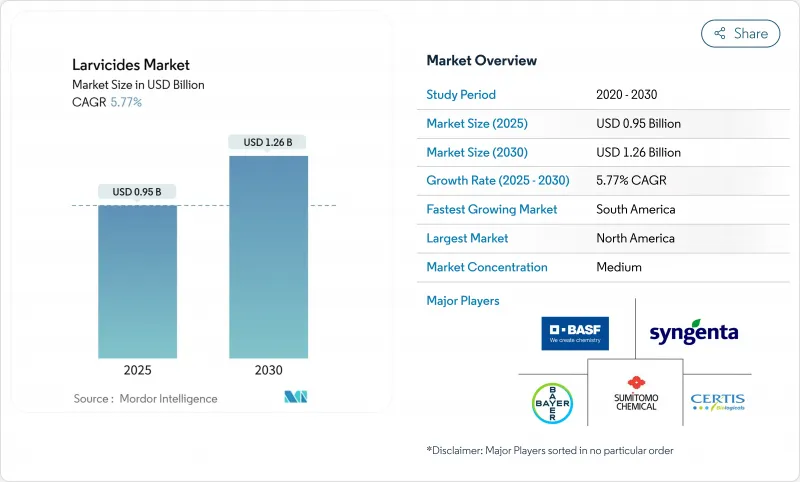
The Larvicides Market size is estimated at USD 0.95 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach USD 1.26 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.77% during the forecast period.
The market growth is driven by several factors, like the increasing necessity to target mosquitoes in their larval stage due to reduced effectiveness of adult mosquito control methods, expanded healthcare budgets in the Americas, and continuous development of environmentally compatible bio-rational formulations. Additional growth drivers include extended mosquito breeding periods in temperate regions, persistent dengue outbreaks in tropical urban areas, and increased adoption of integrated rice-fish farming systems requiring aquaculture-safe larvicides. The market faces challenges including higher production costs for biological products, inconsistent application methods in rural areas, and requirements for GIS-based monitoring systems to enhance treatment efficiency.
Mosquitoes develop resistance to insecticides through target-site insensitivity and metabolic detoxification. Anopheles and Aedes mosquitoes avoid chemical treatments through genetic adaptations, behavioral changes, and metabolic resistance. Vector control programs now focus on early-stage population control by targeting larvae in breeding sites, including stagnant water bodies and urban reservoirs. This approach prevents mosquitoes from reaching adulthood and interrupts disease transmission cycles. Vector control programs increasingly implement integrated strategies that rotate different active ingredients to reduce selective pressure on individual chemical classes. This shift is most visible where pyrethroid failure jeopardized emergency spraying budgets, encouraging municipalities to invest in season-long larvicide grids that protect floodwater pools and storm drains before adult swarms emerge.
Latin American megacities are strengthening their dengue and chikungunya prevention programs in response to increased infection rates and urban mosquito populations. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports a significant increase in cases, particularly in Bolivia and Paraguay. Prevention strategies include Aedes aegypti mosquito control, public awareness initiatives, and integrated approaches combining sanitation, urban planning, and education. The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) guides regional governments on implementing community-based measures to reduce disease transmission. In response to the 2024 dengue outbreak in Brazil, the World Mosquito Program (WMP) has partnered with Fiocruz to address mosquito-borne diseases across the country. The WMP is expanding its Wolbachia method, which introduces a natural bacterium into Aedes aegypti mosquitoes to prevent the transmission of dengue, Zika, and chikungunya.
The 2026 Pesticide General Permit requires applicators to document the dosage, location, and non-target species monitoring when treating surface waters. Regulatory oversight of organophosphates, including temephos, has reduced available formulation options for floodwater marshes and urban catch basins. The increased compliance costs have led counties to shift from high-risk chemicals to biorational alternatives, despite their higher prices. While suppliers providing comprehensive toxicological data and digital application records maintain market advantages, the entry barriers affect small operators and limit local chemical larvicide distribution.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Synthetic larvicides account for 45% of the larvicides market share in 2024. Their market leadership stems from cost advantages and established procurement contracts. Biological products are growing at a higher rate of 8.4% CAGR, supported by government initiatives promoting integrated vector management approaches. Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) demonstrates specific toxicity to mosquito larvae, blackflies, and fungus gnats. In 2023, the Kathmandu Metropolitan City (KMC) implemented bio-larvicide programs to control dengue outbreaks by targeting mosquito larvae. This organic solution eliminates mosquito larvae by disrupting their digestive systems while preserving other organisms.
The development of RNAi yeast larvicides in late-stage testing indicates potential market shifts, offering gene-specific control without affecting non-target species. Manufacturers are improving microencapsulation techniques to enhance product longevity and ease of use. Research in 2024 demonstrated the efficacy of botanical larvicides in crop protection, specifically marigold extracts. A study conducted by PES University in Bangalore revealed that Tagetes erecta and Tagetes patula contain thiophenes, which demonstrate significant larvicidal effects against crop pests Spodoptera litura and Corcyra cephalonica. These technological improvements, coupled with government incentives for environmentally sustainable products, enable biological larvicides to secure more municipal contracts.
Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs) have emerged as an effective larvicide control method, particularly in response to increasing resistance against conventional insecticides. IGRs disrupt mosquito development by inhibiting molting, reproduction, and metamorphosis, preventing larvae from reaching adulthood. While chemical contact poisons generated 55% of revenue in 2024, field studies indicate reduced effectiveness due to resistance development. Methoprene, a primary IGR compound, demonstrates effectiveness at concentrations of <= 10 ppb with minimal aquatic mobility.
Vector control programs are increasingly adopting IGR-based solutions, including pyriproxyfen and methoprene, due to widespread metabolic and behavioral resistance to pyrethroids and organophosphates. IGRs provide extended residual activity, reduced environmental impact, and lower resistance development risk, positioning them as integral components of sustainable mosquito control programs.
The Larvicides Market Report is Segmented by Control Method (Biocontrol Agents, Chemical Agents, and More), by Product Type (Synthetic Larvicides, and Biological Larvicides), by Application (Agricultural and Non-Agricultural), by Target Insects (Mosquitoes and More), by Formulation (Granules, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
North America generated the largest regional revenue in 2024, supported by structured vector-management frameworks and rising concern over West Nile and Eastern equine encephalitis. The United States is the primary user of larvicides for mosquito and larva control in North America. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and local mosquito control districts implement vector control programs across the country. These programs incorporate larvicides within integrated mosquito management (IMM) strategies to prevent diseases such as West Nile virus, Zika, and other mosquito-borne illnesses.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) endorses multiple larval mosquito control methods that target immature mosquitoes in their early stages. These methods include:- Bacterial insecticides (Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus) that disrupt larval digestion - Insect growth inhibitors like methoprene that prevent development - Surface oils and films that cause larvae to drown. Environmental concerns have resulted in the discontinuation of certain control methods, particularly organophosphate insecticides. All control methods must comply with regulations to protect vulnerable populations. The EPA's 2026 Pesticide General Permit has established strict requirements for pesticide applications to surface waters, which shape product development throughout North America.
Asia presents a diverse mix; China and India anchor volume through agricultural applications, while Southeast Asian markets leverage subsidies that mandate biological larvicides in rice-fish systems. Simultaneously, Aedes aegypti resistance to organophosphates and pyrethroids forces councils in Indonesia to rotate IGRs and Bti combinations, underpinning incremental unit growth. The larvicide market share attributable to Asia will expand each year of the outlook, yet margins may stay compressed given price sensitivity in several economies.
South America demonstrates the highest growth rate, driven by public health crises related to dengue and chikungunya outbreaks. Brazil reported 7.25 million dengue cases in 2024, exceeding twice the number recorded in 2023, prompting increased Bti investments across federal, state, and municipal governments. Urban sanitation departments combine source reduction initiatives with weekly larvicide applications, ensuring consistent product demand that maintains distributor inventory levels.