
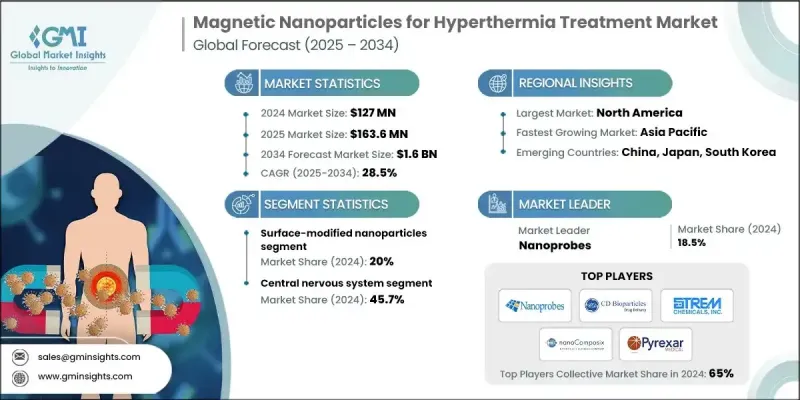
세계의 온열 치료용 자성 나노입자 시장은 2024년에 1억 2,700만 달러로 평가되었고 CAGR 28.5%를 나타내 2034년에는 16억 달러에 이를 것으로 추정되고 있습니다.

자기 온열 요법은 초상자성 산화철 나노입자(SPION)와 교번 자기장에 노출되면 열을 발생시키는 다른 인공 입자를 사용합니다. 이 제어된 열 에너지는 건강한 세포를 보존하면서 종양 조직에 손상을 주는데 사용되며, 이 접근법은 기존의 종양학적 치료의 강력한 대체 요법 또는 보조 요법으로 자리매김하고 있습니다. 내성 암 증가와 표적을 좁힌 비침습적 치료에 대한 수요 증가가 주요 성장 촉진요인이 되고 있습니다. 세계의 의료계가 정밀 기반의 개입을 요구하는 가운데, 특히 난이도가 높은 종양학적 응용에 있어서 조사 노력이 격화하고 있습니다. 자성 나노입자가 생물학적 장벽을 통과하여 종양 깊은 부분에 도달하는 능력은 임상에 큰 관심을 불러일으킵니다. 복잡한 제조 공정과 규제 장벽은 여전히 존재하지만, 표면 기능화, 이중 요법의 조합 및 시험 설계 개발이 이 기술을 보다 광범위한 임상 준비를 향해 뒷받침하고 있습니다.
| 시장 범위 | |
|---|---|
| 시작 연도 | 2024년 |
| 예측 연도 | 2025-2034년 |
| 시작 금액 | 1억 2,700만 달러 |
| 예측 금액 | 16억 달러 |
| CAGR | 28.5% |
2024년 자기 온열 분야의 점유율은 45.7%를 차지했습니다. 이 이점은 신경 종양학에서 비 침습적 접근의 필요성과 관련이 있습니다. 자성 나노입자 기반 시스템은 MR과 호환되는 전달 방법에 의해 고도로 국소화된 가열을 제공하여 뇌종양에서 보다 정확한 치료 계획을 가능하게 합니다. 균질한 가열과 신경보호 전략의 혁신은 현재 진행 중인 연구를 이끌고 있으며 이 분야에서 높은 관심을 유지하고 있습니다. 침공성 종양 및 재발 종양의 치료 프로토콜은 계속 중추 신경계에 특화된 기술에 대한 투자와 채택을 촉진하고 있습니다.
SPIONs 부문은 2024년에 70.1%의 점유율을 차지했습니다. 그 이유는 확립된 안전성, 재현성 있는 자기 성능, 의료 이미징과의 호환성입니다. 이러한 나노입자들은 예측가능한 가열 능력과 안정적인 비흡수율(SAR)로 임상 및 연구 분야에서 널리 사용되고 있습니다. 미세화, 코어의 균일화, 자화 프로파일의 향상 등의 진보에 의해 임상 성적은 현저하게 향상하고 있습니다. SPION은 특히 10-15nm에 최적화된 크기로, 그 생체내 분포와 열제어 효율로 알려져 있으며, 대부분의 초기 단계의 배치에 있어서 우선적인 선택이 되고 있습니다.
유럽의 온열 치료용 자성 나노입자 시장의 2024년 점유율은 35%로 독일, 프랑스, 영국, 스페인, 이탈리아 등 국가들이 채용을 선도했습니다. 이 지역의 성장은 확립 된 정밀 종양학의 틀과 새로운 치료의 원활한 통합을 가능하게하는 유리한 의료 정책에 의해 지원됩니다. 유럽 각지의 종양 센터에서는 카테터 유도 시스템과 MR 대응 하이퍼 서미어 플랫폼의 채용이 시작되고 있습니다. 조정된 테스트 네트워크와 조달 시스템은 임상 검증부터 보급까지의 시간을 단축하는 데 도움이 되며, 병원 시스템 전반에 걸쳐 널리 받아들여지는 단계를 갖추고 있습니다.
세계의 온열 치료용 자성 나노입자 업계에서 사업을 전개하는 주요 기업으로는 nanoComposix, Spherotech, Nanoprobes, Strem Chemicals, BSD Medical Corporation, Pyrexar Medical, CD Bioparticles 등이 있습니다. 온열 치료용 자성 나노입자 시장의 주요 기업은 그 존재감을 높이기 위해 나노입자의 효율, 자기 응답성, 생체적합성을 높이는 연구개발에 많은 투자를 하고 있습니다. 각 회사는 입자 합성법의 개선, 배치의 편차의 저감, 병용 요법을 서포트하기 위한 표면 개질의 개선에 주력하고 있습니다. 학술기관과 임상센터와의 전략적 제휴는 프로토콜 개발과 임상시험 검증의 추진에 도움이 됩니다. 각 회사는 또한 실시간 영상 진단과 환자별 치료 계획의 통합을 위해 노력하고 있습니다. 이와 병행하여, 의료 당국과의 조기 연계에 의해 규제 당국의 승인 프로세스를 합리화하는 대처도 진행되고 있습니다.
The Global Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Treatment Market was valued at USD 127 million in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 28.5% to reach USD 1.6 billion by 2034.
Magnetic hyperthermia therapy uses superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and other engineered particles that generate heat when exposed to alternating magnetic fields. This controlled thermal energy is used to damage tumor tissue while preserving healthy cells, positioning this approach as a powerful alternative or adjunct to conventional oncology treatments. The increasing prevalence of resistant cancer types and the rising demand for targeted, non-invasive therapies are key growth drivers. Research efforts have intensified, particularly in challenging oncologic applications, as the global medical community seeks precision-based interventions. The ability of magnetic nanoparticles to navigate biological barriers and reach deep tumor sites has sparked significant clinical interest. Although complex manufacturing processes and regulatory barriers persist, developments in surface functionalization, dual-therapy combinations, and trial design are pushing the technology toward broader clinical readiness.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $127 Million |
| Forecast Value | $1.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 28.5% |
In 2024, the magnetic hyperthermia segment held a 45.7% share. This dominance is tied to the need for non-invasive approaches in neuro-oncology. Magnetic nanoparticle-based systems offer highly localized heating through MR-compatible delivery methods, allowing for more accurate therapeutic planning in brain tumors. Innovations in homogeneous heating and neuroprotection strategies are guiding ongoing research and maintaining high interest in this segment. Treatment protocols for aggressive and recurrent tumors continue to drive investment and adoption in CNS-focused technologies.
The SPIONs segment held 70.1% share in 2024, owing to their well-established safety, repeatable magnetic performance, and compatibility with medical imaging. These nanoparticles are widely used in clinical and research settings due to their predictable heating capabilities and stable specific absorption rates (SAR). Progress in smaller engineering, uniform cores and enhancing magnetization profiles has significantly improved clinical outcomes. SPIONs, particularly with optimized sizes between 10 and 15 nm, are known for their biodistribution and thermal control efficiency, which has made them the preferred choice in most early-stage deployments.
Europe Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Treatment Market held 35% share in 2024, with countries such as Germany, France, the UK, Spain, and Italy leading in adoption. This regional growth is supported by established precision oncology frameworks and favorable health policies that enable smoother integration of emerging treatments. Oncology centers across Europe have begun adopting catheter-guided systems and MR-compatible hyperthermia platforms. Coordinated trial networks and procurement systems help shorten the time between clinical validation and widespread availability, setting the stage for broader acceptance across hospital systems.
Key companies operating in the Global Magnetic Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Treatment Industry include nanoComposix, Spherotech, Nanoprobes, Strem Chemicals, BSD Medical Corporation, Pyrexar Medical, and CD Bioparticles. To strengthen their presence, key players in the magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia treatment market are investing heavily in R&D to enhance nanoparticle efficiency, magnetic responsiveness, and biocompatibility. Companies are focused on refining particle synthesis methods, reducing batch variability, and improving surface modification to support combination therapies. Strategic collaborations with academic institutions and clinical centers are helping drive protocol development and trial validation. Firms are also working to integrate real-time imaging compatibility and patient-specific treatment planning. In parallel, efforts to streamline regulatory approval processes are underway through early engagement with health authorities.